Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MTA Corrlelations With Histologic Grade MEC
MTA Corrlelations With Histologic Grade MEC
Uploaded by
lukman f0028Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Level - 4 - Master Spelling ListsDocument5 pagesLevel - 4 - Master Spelling ListsKarl Lorenze E. Gumsat100% (1)
- SAT Sentence Completion Practice Test 011Document31 pagesSAT Sentence Completion Practice Test 011Tuhin Azad0% (1)
- UreaNitrogen ARC CHEMDocument8 pagesUreaNitrogen ARC CHEMHarika PutraNo ratings yet
- MTA1 Omar AhmedDocument5 pagesMTA1 Omar Ahmedlukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051Document9 pagesMTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051lukman f0028No ratings yet
- Icam 1Document10 pagesIcam 1dusseldorf27No ratings yet
- Ijcep0012 2657Document8 pagesIjcep0012 2657Ethel GeanNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathological Study of Metallothionein Immunohistochemical Expression, in Benign, Borderline and Malignant Ovarian Epithelial TumorsDocument7 pagesClinicopathological Study of Metallothionein Immunohistochemical Expression, in Benign, Borderline and Malignant Ovarian Epithelial TumorsNajmul HasanNo ratings yet
- OncolyticDocument14 pagesOncolytichasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Journal Article 1Document15 pagesJournal Article 1syeda hamnaNo ratings yet
- Immunohistochemical Evaluation of The Tumor Neoangiogenesis As A Prognostic Factor For Gastric CancersDocument12 pagesImmunohistochemical Evaluation of The Tumor Neoangiogenesis As A Prognostic Factor For Gastric Cancerslavinia diaNo ratings yet
- Stelloo Ann Oncol 2017Document7 pagesStelloo Ann Oncol 2017Yachao LiuNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s12022 019 9576 5Document8 pages10.1007@s12022 019 9576 5Kevin AdrianNo ratings yet
- Ijcm 13 4 99210Document7 pagesIjcm 13 4 99210Nurul Ulya RahimNo ratings yet
- Cancers 13 05301Document15 pagesCancers 13 05301Bozner Sanchez EscobarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S102845592300030X MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S102845592300030X Main何燕No ratings yet
- Abstract. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Report-: ONCOLOGY LETTERS 5: 1682-1686, 2013Document5 pagesAbstract. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Report-: ONCOLOGY LETTERS 5: 1682-1686, 2013yuliaNo ratings yet
- M2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon CancerDocument13 pagesM2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon Cancerhup4824No ratings yet
- Ps 28 76Document10 pagesPs 28 76Furando NgNo ratings yet
- Article 5 POCDocument16 pagesArticle 5 POCmariimaria670No ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0267306Document25 pagesJournal Pone 0267306MellysaNo ratings yet
- Prognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Patients With Soft Tissue SarcomaDocument7 pagesPrognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Patients With Soft Tissue SarcomaJemma ArakelyanNo ratings yet
- C Met Is Overexpressed in Type I Ovarian Cancer: Results of An Investigative Analysis in A Cohort of Consecutive Ovarian Cancer PatientsDocument7 pagesC Met Is Overexpressed in Type I Ovarian Cancer: Results of An Investigative Analysis in A Cohort of Consecutive Ovarian Cancer PatientsDavid Isaias Jaimes ReyesNo ratings yet
- Abcr20120200001 55990344Document8 pagesAbcr20120200001 55990344Uum SudrajatNo ratings yet
- AACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 3063-5947From EverandAACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 3063-5947No ratings yet
- AACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 1-3062From EverandAACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 1-3062No ratings yet
- Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Korean Melanoma PatientsDocument9 pagesClinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Korean Melanoma Patientsfebri susantoNo ratings yet
- CX3CR1 Acts As A Protective Biomarker in The Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal CancerDocument16 pagesCX3CR1 Acts As A Protective Biomarker in The Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal CancerIsmaNo ratings yet
- Sustain 2021 10652180Document6 pagesSustain 2021 10652180filonenko0448No ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnosis in Breast Cancer: Mini-Symposium: Breast PathologyDocument12 pagesMolecular Diagnosis in Breast Cancer: Mini-Symposium: Breast PathologyOber Van Gómez LópezNo ratings yet
- Article 2Document5 pagesArticle 2Mahadev HaraniNo ratings yet
- MEJC477911631043000Document10 pagesMEJC477911631043000Riyadh Z. MawloodNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Associated BRCA1 and The Identification of Signaling PathwaysDocument10 pagesMolecular Mechanism of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Associated BRCA1 and The Identification of Signaling PathwaysnagarajharishNo ratings yet
- Neoadjuvant ChemotherapyDocument8 pagesNeoadjuvant ChemotherapyrakaNo ratings yet
- Ankle1 N - Methyladenosine-Related Variant Is Associated With Colorectal Cancer Risk by Maintaining The Genomic StabilityDocument13 pagesAnkle1 N - Methyladenosine-Related Variant Is Associated With Colorectal Cancer Risk by Maintaining The Genomic Stabilitytirasi1214No ratings yet
- Fimmu 14 1000497Document15 pagesFimmu 14 1000497Aswar AnasNo ratings yet
- Metaplastic CA 2 IhkDocument10 pagesMetaplastic CA 2 IhkWinta MayantiNo ratings yet
- PMC CancerDocument2 pagesPMC CancervivekNo ratings yet
- Apicella 2015Document16 pagesApicella 2015bawoji1763No ratings yet
- The Potential of Conditionally Replicating AdenovirusDocument1 pageThe Potential of Conditionally Replicating AdenovirusJairo BermúdezNo ratings yet
- New WHO Classification of Pituitary Adenomas (4th Edition) : Assessment of Pituitary Transcription Factors and The Prognostic Histological FactorsDocument5 pagesNew WHO Classification of Pituitary Adenomas (4th Edition) : Assessment of Pituitary Transcription Factors and The Prognostic Histological FactorscristianescNo ratings yet
- Guyot 2021, MSI Colorectal Discordance Molecular Vs IHKDocument9 pagesGuyot 2021, MSI Colorectal Discordance Molecular Vs IHKmercy marcmarquezNo ratings yet
- Calon2015 2Document13 pagesCalon2015 2Javier Cerda InfanteNo ratings yet
- PIIS1074761313004378Document14 pagesPIIS1074761313004378ZadorxsNo ratings yet
- Alaeddini Et Al 2008 HistopathologyDocument6 pagesAlaeddini Et Al 2008 HistopathologyEdgardo CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Expression of Mirnas and Pten in Endometrial Specimens Ranging From Histologically Normal To Hyperplasia and Endometrial AdenocarcinomaDocument9 pagesExpression of Mirnas and Pten in Endometrial Specimens Ranging From Histologically Normal To Hyperplasia and Endometrial AdenocarcinomaFerdina NidyasariNo ratings yet
- Angiogenic Activities of Interleukin-8, Vascular Endothelial Growth FactorDocument28 pagesAngiogenic Activities of Interleukin-8, Vascular Endothelial Growth FactorReda RamzyNo ratings yet
- Or 26 1 185 PDFDocument7 pagesOr 26 1 185 PDFRoland_IINo ratings yet
- Boll Et Al-2023-Scientific ReportsDocument14 pagesBoll Et Al-2023-Scientific ReportsJoy IsmailNo ratings yet
- Familial Risk-Colorectal Cancer - ESMO Clinical Practice GuidelinesDocument8 pagesFamilial Risk-Colorectal Cancer - ESMO Clinical Practice GuidelinesAnonymous 8KN8IR1GTWNo ratings yet
- Comparison of IHC Expression of EGFR On SGTDocument5 pagesComparison of IHC Expression of EGFR On SGTMehreen MalikNo ratings yet
- PD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Research ArticleDocument14 pagesPD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Research ArticleFebrian Parlangga MuisNo ratings yet
- Signaling Cancer SpecialDocument4 pagesSignaling Cancer SpecialcadimogirlNo ratings yet
- W de WenisimoDocument18 pagesW de WenisimoBJ CarminatorNo ratings yet
- Cho Et Al-2019-International Journal of CancerDocument12 pagesCho Et Al-2019-International Journal of Cancerlouisehip UFCNo ratings yet
- 2015 Molecular KlimstraDocument7 pages2015 Molecular KlimstramaomaochongNo ratings yet
- Apigenin Parsley Melanoma PD-1 PD-L1Document15 pagesApigenin Parsley Melanoma PD-1 PD-L1valgurNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Blood Cancer - 2023 - Abstracts From The 39th Annual Meeting of The Histiocyte SocietyDocument64 pagesPediatric Blood Cancer - 2023 - Abstracts From The 39th Annual Meeting of The Histiocyte SocietySeham GoharNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1470204522007835 Main PDFDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1470204522007835 Main PDFOncología CdsNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathological Significance of Fascin and CD44v6 Expression in Endometrioid CarcinomaDocument7 pagesClinicopathological Significance of Fascin and CD44v6 Expression in Endometrioid CarcinomaelisasusantiNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers in MelanomaDocument6 pagesBiomarkers in MelanomaMatthew NgNo ratings yet
- Azim 2016Document10 pagesAzim 2016Jocilene Dantas Torres NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Jclinpath 2019 206273Document7 pagesJclinpath 2019 206273lukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Omar AhmedDocument5 pagesMTA1 Omar Ahmedlukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051Document9 pagesMTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051lukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Erb PathwayDocument6 pagesMTA1 Erb Pathwaylukman f0028No ratings yet
- Honey Authenticity - 2013Document27 pagesHoney Authenticity - 2013romanciucclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Dickinson and Fa 2000Document11 pagesDickinson and Fa 2000Ze WlyNo ratings yet
- HernioplastyDocument58 pagesHernioplastyFobin VargheseNo ratings yet
- NUTR1R06w PDFDocument110 pagesNUTR1R06w PDFAli Rıza Üreten100% (1)
- Să Nu Omori Niciodată Această Insectă Ciudată! Iată de Ce!Document8 pagesSă Nu Omori Niciodată Această Insectă Ciudată! Iată de Ce!Alexandra CrăciunNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Homeostasis: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell Biology J.carbrey@cellbio - Duke.eduDocument17 pagesAcid-Base Homeostasis: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell Biology J.carbrey@cellbio - Duke.eduMaggieLocke100% (1)
- BioPsy 1 - Intro To BioPsyDocument4 pagesBioPsy 1 - Intro To BioPsyTim AroscoNo ratings yet
- Bacterio Rhodopsin MemoryDocument6 pagesBacterio Rhodopsin Memorydurgalakshmi100100% (2)
- Mindfulness in 10 Easy StepsDocument13 pagesMindfulness in 10 Easy StepsMomina Abid100% (10)
- Bich411 Enzyme Regulation PDFDocument4 pagesBich411 Enzyme Regulation PDFAn TranNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument40 pagesMedulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd Gradetuhin100% (1)
- GTR in Management of Gingival RecessionDocument15 pagesGTR in Management of Gingival RecessionMalavika JaiNo ratings yet
- Biolatest LSR Ver 1.0Document2 pagesBiolatest LSR Ver 1.0Indah Puspita Sari IINo ratings yet
- Sloterdijk - Spheres TheoryDocument8 pagesSloterdijk - Spheres TheoryKatma Vue100% (2)
- Hoover 1961Document14 pagesHoover 1961Azmi FarhadiNo ratings yet
- Activity 13 DNAReplicationPupil Case StudyDocument9 pagesActivity 13 DNAReplicationPupil Case Studyavita rukmanaNo ratings yet
- November 2014 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument16 pagesNovember 2014 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFmanan damaniNo ratings yet
- GLOSARIO de Terminos Agricolas NAL 2018 PDFDocument1,968 pagesGLOSARIO de Terminos Agricolas NAL 2018 PDFLidia NoreseNo ratings yet
- Nata de Coco Poast LabDocument2 pagesNata de Coco Poast LabMae100% (1)
- Cell Adhesion MoleculesDocument90 pagesCell Adhesion MoleculesPooja Bappanna100% (1)
- TNV 321Document202 pagesTNV 321Principal PolytechnicNo ratings yet
- Osteogénesis ImperfectaDocument13 pagesOsteogénesis ImperfectaCheby MorenoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAmino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFKHURT MICHAEL ANGELO TIU100% (1)
- Extracellular Matrix ScafoldDocument16 pagesExtracellular Matrix ScafoldmanishNo ratings yet
- Cancer Is Only Going To Be A Chapter in You Life, Not The Whole StoryDocument3 pagesCancer Is Only Going To Be A Chapter in You Life, Not The Whole StoryDonna AntonetteNo ratings yet
- Periosteal Pocket Flap For Horizontal Bone RegenerDocument10 pagesPeriosteal Pocket Flap For Horizontal Bone RegenerViorel Ion100% (1)
- 2022-Association of iSGLT2 Use With Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With Stabilized AMIDocument8 pages2022-Association of iSGLT2 Use With Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With Stabilized AMIWENDY JOHANA HENRIQUEZ SEGURA ESTUDIANTE ACTIVONo ratings yet
MTA Corrlelations With Histologic Grade MEC
MTA Corrlelations With Histologic Grade MEC
Uploaded by
lukman f0028Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MTA Corrlelations With Histologic Grade MEC
MTA Corrlelations With Histologic Grade MEC
Uploaded by
lukman f0028Copyright:
Available Formats
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic
Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed (BDS)1,Lehadh M Al-Azzawi (PhD)2 and Mustafa G Taher (PhD)3
Abstract
Background: Metastasis associated protein-1 (MTA1) has been a recently identified as a
unique gene playing important role in tumorigenesis and progression of cancer cells.
Objective:To evaluate MTA1 expression and its predictive value in determining histologic
grade of salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC).
Patients and Methods: MTA1 expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in
paraffin-embedded tumor specimens blocks from 22 patients. Assessment of MTA1
immunostaining was achieved by counting the proportion of positively-stained tumor cells in
5 high power microscopic fields; and staining was analyzed in relation to clinicopathological
variables.
Results: MTA1 show nuclear and cytoplasmic expression in varying intensity in 95% of cases.
No significant correlation was found between MTA1expression and age, gender, site of the
tumor (p>0.05). However, statistically significant correlation was found between
MTA1expression and clinical stage, nodal involvement (p=0.009 and 0.007; respectively).
Regarding histologic grade, high MTA1 level was significantly associated with grade of tumors
categorized by Auclair and Brandwein systems (<0.001 and 0.009; respectively).
Conclusion:MTA1 expression significantly correlates with tumor grade and progression, and
has a potential role in diagnosis and prediction of behavior in salivary MEC.
Keywords: Salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma, MTA1, Tumor grade, Metastasis.
Corresponding Author: mostafa.ghany@yahoo.com
Received: 18th January 2018
Accepted: 23th January 2018
https://doi.org/10.26505/DJM
1
Diyala Health Governorate - Diyala – Iraq.
2
Department of Oral Pathology - College of Dentistry - Baghdad University- Baghdad - Iraq.
3
Department of Pathology - College of Medicine - University of Diyala - Diyala - Iraq.
Introduction
Salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma based on the various criteria of grading
(MEC) is clinically and pathologically, a systems; and generally these tumors are
relentless disease with different biologic categorized tumor into low, intermediate, or
behavior.1 MEC is the most common high grade[3].In salivary gland carcinoma,
salivary gland carcinoma, which is the histologic grade ranks highly among the
approximately accounting for 5-15 of all most important prognostic parameters,
salivary neoplasms and 30-35% of salivary although grading systems still have no
gland malignancies[2].The histopathologic consensus concerning its accurate value for
features of MEC are complex and largely predicting outcome and tumor behavior[4,5].
Diyala Journal of Medicine 1 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
Metastasis-associated protein-1 (MTA1), from patients’ medical records for the period
the basic member of the MTA family was extending from 2009 to 2017. For all
originally identified via differential screening specimens, 4µm thick sections were prepared
of the cDNA Library from rat metastatic and stained with hematoxylin and eosin
breast tumors as an up regulated gene[6,7]. (H&E) stain to confirm the diagnosis.
MTA1 overexpression was seen in various Clinicopathologic characteristics of the
human cancers and shown to be involved in overall series are summarized in Table (1).
tumor invasion, and metastasis; regardless its The histological grade of tumors, in this
nuclear and cytoplasmic expression[8,9]. In study, was evaluated according to criteria of
previous study, the investigators observed Auclair 1991), in addition to schemes
that MTA1 was overexpressed during proposed by Brandwein , (2001), which are
neoplastic transformation, and it was approved by The WHO classification of
inversely related to tumor progression[10]. tumors[15,16]. All the cases were staged
Whereas, Dias (2013) found that nuclear according to the 7th edition of the American
overexpression of MTA1 is significantly Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC)[17].
correlated to the aggressive biologic behavior Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and analysis
and metastasis in human prostate cancer[11]. The sections in these series were
Regarding tumor grading, elevated MTA1 deparaffinized in xylene, rehydrated through
expression was found to be closely associated graded alcohols, immersed in 3% H2O2 for
with higher grade in human cancers[12]. 20 min to inhibit endogenous peroxidase
However, some researchers found a negative activity, and antigen retrieval performed
correlation between MTA1expression and using citrate buffer with PH=6. Nonspecific
clinicopathologic features of salivary binding was blocked with 1% serum albumin
MEC[13,14]. The purpose of this study was at room temperature for 10 min, then the
to assess the correlation between MTA1 sections were incubated with anti-MTA1
expression and the histologic grade of rabbit-polyclonal antibody (1:500 dilution;
salivary MEC. Abcam, Cambridge, UK) overnight at 4°C in
Patients and Methods a humidified chamber. Negative controls
This study included 22 pretreatment were achieved by omitting the primary
formalin fixed, paraffin embedded salivary antibody. After washing with PBS, the tissue
MEC that retrieved from the archives of the sections were incubated with biotin-free,
Department of Oral Diagnosis / College of anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated
Dentistry/ Baghdad University, and with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 15
Department of specialized surgery in Al- min, and then stained with 3, 3-
Shaheed Ghazi Hospital in Baghdad. Clinical diaminobenzidine (DAB), counterstained
data concerning the age, gender, site of tumor with Mayer’s hematoxylin, dehydrated and
and lymph node metastasis was obtained mounted.
Diyala Journal of Medicine 2 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
Statistical analysis adjacent non-cancerous ductal epithelial
The degree of IHC staining was separately tissues in the same section Figure(1A).
evaluated by two pathologists who were Correlation between MTA1 expression
blinded to the clinicopathologic information. and the clinicopathological features of
MTA1 immunostaining was scored by salivary MEC
calculating the proportion of positively As shown in Table(2), the relationship
stained tumor cells in 5 microscopic high between MTA1 expression and the
power fields that reveal higher clinicopathological characteristics of all
immunopositivity as follows: Score 0 (0-5% series of salivary MEC. There was no
positive cells); Score 1 (6-25% positive statistically significant correlation between
cells); score 2 (26-50% positive cells); score MTA1 protein expression and
3 (51-75% positive cells) and Score 4 (≥ 76 clinicopathological features, such as age,
positive cells). A Mann-Whitney test, gender and tumor site (P>0.05). However,
Kruskal Wallis test, Chi-Square test, the expression level of MTA1 protein was
Spearman´s correlation coefficient test were found to be significantly associated with
used to compare the result between groups clinical stage, showing a lower expression
and the relation with clinical-pathological pattern in early-stage disease (I and II), and a
parameters such as patient age, gender, tumor stronger expression (median MTA1 score 4),
site, metastasis to lymph nodes, tumor grade in late stages (III and IV; P = 0.009). High
and clinical stage. We used the SPSS version MTA1 expression also was found to be
24 software to statistically analyze the data. significantly associated with positive nodal
P-values <0.05 were considered statistically metastasis (p=0.007). Regarding both Auclair
significant in all cases. and Brandwein grading systems, the median
Results MTA1 score was significantly higher among
Representative images of MTA1 tumors with high grade (score-3) compared
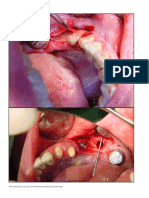
immunohistochemical expression in MEC are to those with low grade (median score=2),
shown in Figure(1A-F).Positive thus a statistically significant correlation was
immunostaining of MTA1 was observed in found between MTA1 overexpression and
both nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments tumor grade categorized by Auclair and
in (95%) of the MEC tissues. While, negative Brandwein systems (p value <0.001 and
or weak MTA1stanining was found in the 0.009; respectively).
Diyala Journal of Medicine 3 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
A B
C D
E F
Figure (1): Immunohistochemical analysis of MTA1 protein in salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
(A) Negative staining in normal salivary ductal tissue (40x); (B) low grade tumor shows cystic
components lined by mucous and intermediate cell: brown stain (40x); (C) MEC, with small islands of
intermediate and epidermoid cell, mainly cytoplasmic expression (20x); (D) High grade MEC with
nuclear MTA1expression (40x); (E) Solid tumor with sheets of anaplastic epidermoid cells with
cytoplasmic expression (40x); (F) lymph node infiltrated with tumor cells expressing nuclear MTA1
protein (20x).
Diyala Journal of Medicine 4 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
Table (1): Clinical-pathological parameters of the overall series.
Parameters Total
No. (%)
Age group (years)
<40 5 22.7 Mean ±SD of (45.6± 13.1)
>40 17 77.3
Gender
Female 12 54.5
Male 10 45.4
Site
Major 11 50
Minor 11 50
Clinical stage
I 9 40.9
II 7 31.8
III 3 13.6
IV 3 13.6
Lymph node status
-ve 16 72.7
+ve 6 27.3
Histologic grade
Auclair system
Low 15 68.1
High 7 31.8
Brandwein system
I 6 27.2
II 6 27.2
III 10 45.4
Diyala Journal of Medicine 5 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
Table (2): Correlation between MTA1 expression and the clinicopathologic features.
Parameters No.of MTA1 scores Median p-value
cases 0 I II III IV MTA
score
Age group (years)
<40 5 0 1 3 1 0 2 0.15
>40 17 1 3 6 5 2 3 [NS]
Gender
Male 10 0 1 4 3 2 3 0.10
Female 12 1 3 5 3 0 2 [NS]
Site
Minor 11 0 1 6 3 1 2 0.45
Major 11 1 3 3 3 1 2 [NS]
Clinical Stage
I-II 16 1 4 8 3 0 2 0.009*
III-IV 6 0 0 1 3 2 4
Lymph node metastasis
N0 16 1 4 8 3 0 2
N1 3 0 0 0 1 2 4 0.007 *
N2 3 0 0 1 2 0 3
Auclair grading system
Low 15 1 4 9 1 0 2 <0.001*
High 7 0 0 0 5 2 3
Brandwein grading system
Low 6 1 2 3 0 0 2 0.009*
Intermediate 6 0 2 3 1 0 2
High 10 0 0 3 5 2 3
*significant relation (p<0.05); [NS] non- significant (p>0.05)
Discussion
Histologic grade of salivary gland find a new biomarkers that specifically
carcinomas is a significant predictor of predict tumor aggressiveness and behavior.
tumor aggressiveness and patient’s outcome. MTA1 gene is a regulating factor that
However, the sheer diversity of tumor mediated cell signaling pathway and
differentiation and the rarity of these tumors chromosomes remodeling, and also has
pose challenges to invent highly predictive transcriptional activity, so it is implicated in
grading schemes. Grading of MEC is not tumor progression and invasion of metastatic
without flaws, one clear deficiency in all epithelial cells[20,21]. In the present study,
systems, particularly the point based we evaluated MTA1 expression in salivary
schemes, was the difficulty in MEC, and there was no statistically
application[18,19]. Thus, it is necessary to significant correlation between MTA1 level
Diyala Journal of Medicine 6 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
and clinical findings, such as patient age, according to both Auclair and Brandwein
gender and tumor site. This finding was in system (p< 0.001 and 0.009, respectively). In
agreement with previous studies[22,23]. In this context, we found a significant strong
this study, also we observed that positive linear correlation between MTA1
MTA1expression was significantly score (r=0.7) and Brandwein tumor grade.
correlated with clinical stage and lymph This result suggests a strong association of
node metastasis. Our finding was in line with MTA1 expression with the progression of
other researches which were indicated, by MEC. In contrast to our findings,
immunohistochemical analysis that MTA1 Andishehtadbir (2016), found no correlation
protein expression is significantly correlated between MTA1 expression and histologic
with aggressive tumor progression, and grade of salivary MEC, although high MTA1
positive nodal status in head and neck expression was seen in cases with advanced
cancer[24,25]. However, our results were not tumor size and clinical stage. The possible
in conformity with findings from cause behind this disagreement is that, in our
Andishehtadbir, (2016) who found that analysis we have approved a standardized
MTA1 protein expression had no significant grading systems in tumor classification, with
statistical relation with clinical stage, lymph focus on more subjective criteria, compared
node status and metastasis of salivary MEC to previous study which was built on a
which may be attributable to an insufficient descriptive morphologic and histologic
number of cases, in which a small size of features[14].
sample was associated with tumor Conclusion
progression and positive lymph node MTA1 expression significantly correlates
metastasis[14].On the other hand, we with histologic grade and progression of
observed that a significant cohort of our salivary MEC and may be a valuable
series showed nuclear MTA1 expression biomarker in diagnosis and predicting tumor
compared to cytoplasmic one, which suggest behavior.
the invasive and metastatic potential of these References
tumors[22].Earlier investigations stated that [1] Pires FR, Almeida OP, de Araújo VC,
MTA1s, a short version of cytoplasmic Kowalski LP. Prognostic factors in head and
MTA1 may bind to estrogen receptor-alpha neck mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Arch
(ER-α) and inhibit its nuclear function by Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2004; 130:
non-genomic activity of (ER-α) that occurs 174-180.
in cytoplasm of cancer cells. Thus, this may [2] Luna MA. Salivary mucoepidermoid
rationalize the aggressive behavior of these carcinoma: revisited. Adv Anat Pathol 2006;
tumors[22,26]. Regarding tumor grading, we 13: 293-307.
found a significant up-regulation of MTA1
expression in higher grade tumors classified
Diyala Journal of Medicine 7 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
[3] Barnes L. Surgical Pathology Of Head inversely related to progression of oral
and Neck: Diseases of the Salivary Glands, squamous cell carcinoma in Taiwan. J Dent
Third Edition.USA:2009; p. 506. Sci 2007; 2:1.
[4] Seethala RR. Histologic Grading and [11]Dias, S.J., et al.. Nuclear MTA1
Prognostic Biomarkers in Salivary Gland overexpression is associated with aggressive
Carcinomas. Adv Anat Pathol. 2011; 18: 29- prostate cancer, recurrence and metastasis in
45. African Americans. Sci. Rep. 2013; 3: 2331.
[5] Ahmed O. and Al-Azzawi L. Salivary [12] Jang k, Paik S, Chung H, Oh Y and
mucoepidermoid carcinoma: Auclair vs Kong G. MTA1 overexpression correlates
Brandwein grading system (histopathological significantly with tumor grade and
comparative study). 2017; 977. angiogenesis in human breast cancers.
[6] Toh Y, Pencil SD, Nicolson GL. A novel Cancer Sci. 2006; 97 (5 ): 375.
candidate metastasis-associated gene, mta1, [13]Andisheh-Tadbir A, Ashraf MJ,
differentially expressed in highly metastatic Khademi B, Ahmadi Sh. Clinical implication
mammary adenocarcinoma cell lines. cDNA of CD166 expression in salivary gland
cloning, expression, and protein analyses. J tumor. Tumor Biology 2015; 36(4): 2793-9.
Biol Chem 1994; 269:22958–63. [14]Andisheh-Tadbir A, Dehghani-Nazhvani
[7] Toh Y and Nicolson GL. The role of the A, Ashraf MJ, Khademi B, Mirhadi H,
MTA family and their encoded proteins in Torabi-Ardekani S. MTA1 Expression in
human cancers: molecular functions and Benign and Malignant Salivary gland
clinical implications. Clin Exp Metastasis Tumors. Iranian Journal of
2009; 26:215-27. Otorhinolaryngology, 2016; 28(1):51-59.
[8] Nicolson GL, Nawa A, Toh Y, Taniguchi [15]Auclair PL, Goode RK. Ellis GL
S, Nishimori K, Moustafa A. Tumor Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of intraoral
metastasis-associated human MTA1 gene salivary glands: evaluation and application of
and its MTA1 protein product: role in grading criteria in 143 cases. Cancer
epithelial cancer cell invasion, proliferation 1992;69:2021-2030.
and nuclear regulation. Clinical & [16]Brandwein MS, Ivanov K, et al.
experimental metastasis 2003;20(1):19-24. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma. A
[9] Sen N, Gui B, and Kumar R. Role of clinicopathological study of 80 patients with
MTA1 in Cancer Progression and special reference to histological grading. Am
Metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014; ; J Pathol 2001;25:835–45.
33(4): 879–89.-9. [17] Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz
[10] Yu, C. H., Chen, H. H.,Wang, J. T., Liu, AG, Greene FL, Trotti A: AJCC Cancer
B. Y., Wang, Y. P., Sun, A. , Kuo, R. C. , Staging Manual. 7th edition. New York:
Chiang, C. P. Nuclear expression of Springer; 2010.
metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) is
Diyala Journal of Medicine 8 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
MTA1 Expression Correlates Significantly with Histologic Grade in Salivary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Omar I Ahmed
[18] Seethala RR. An update on grading of Expression of MTA1 in nasopharyngeal
salivary gland carcinomas. Head Neck carcinoma and its correlation with prognosis.
Pathol. 2009; 3: 69–77. Med Oncol. 2014; 31:330.
[19] Seethala RR HA, Bennett A, Arrosi AA, [26]Kumar R, Wang RA, Mazumdar A,
Dvison JM, Krasinkas AM, Hunt JL. Talukder AH, Mandal M, Yang Z, et al. A
Reproducibility of grading in salivary gland naturally occurring MTA1 variant sequesters
mucoepidermoid carcinoma and correlation oestrogen receptor-alpha in the cytoplasm.
with outcome: does system really matter? Nature. 2002;418(6898):654-7.
Mod. Pathol. 2008; 2; Abstract 1105.
[20]Liu, J., Haijuan Wang , Changzhi Huang
, Haili Qian. Subcellular localization of
MTA proteins in normal and cancer cells.
Cancer Metastasis Rev 2014a ; 33, 843–856.
[21]Liu, J., Haijuan Wang , Changzhi Huang
, Haili Qian. The subcellular distribution and
function of MTA1 in cancer differentiation.
Oncotarget 2014b; 5: 5153- 64.
[22] Li W F, Liu N, Xue R X, He Q M, Chen
M, Jiang N, Sun Y, Zeng J, Liu L Z and Jun
MNuclear overexpression of metastasis-
associated protein 1 correlates significantly
with poor survival in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Journal of Translational
Medicine 2012, 10:78.
[23]Liu T, Yang M, Yang S, Ge T, Gu L,
Lou G. Metastasis-associated protein 1 is a
novel marker predicting survival and lymph
nodes metastasis in cervical cancer. Hum
Pathol. 2013;44(10):2275–81.
[24] Kawasaki, S. Yanamoto, I. Yoshitomi, S
Yamada, A Mizuno: Overexpression of
metastasis-associated MTA1 in oral
squamous cell carcinomas: correlation with
metastasis and invasion. Int. J. Oral
Maxillofac. Surg. 2008; 37: 1039–1046.
[25] Yuan T, Zhang H, Liu B, Zhang Q,
Liang Y, Zheng R, Deng J, Zhang X.
Diyala Journal of Medicine 9 Vol.16.Issue 1,April 2019
You might also like
- Level - 4 - Master Spelling ListsDocument5 pagesLevel - 4 - Master Spelling ListsKarl Lorenze E. Gumsat100% (1)
- SAT Sentence Completion Practice Test 011Document31 pagesSAT Sentence Completion Practice Test 011Tuhin Azad0% (1)
- UreaNitrogen ARC CHEMDocument8 pagesUreaNitrogen ARC CHEMHarika PutraNo ratings yet
- MTA1 Omar AhmedDocument5 pagesMTA1 Omar Ahmedlukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051Document9 pagesMTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051lukman f0028No ratings yet
- Icam 1Document10 pagesIcam 1dusseldorf27No ratings yet
- Ijcep0012 2657Document8 pagesIjcep0012 2657Ethel GeanNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathological Study of Metallothionein Immunohistochemical Expression, in Benign, Borderline and Malignant Ovarian Epithelial TumorsDocument7 pagesClinicopathological Study of Metallothionein Immunohistochemical Expression, in Benign, Borderline and Malignant Ovarian Epithelial TumorsNajmul HasanNo ratings yet
- OncolyticDocument14 pagesOncolytichasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Journal Article 1Document15 pagesJournal Article 1syeda hamnaNo ratings yet
- Immunohistochemical Evaluation of The Tumor Neoangiogenesis As A Prognostic Factor For Gastric CancersDocument12 pagesImmunohistochemical Evaluation of The Tumor Neoangiogenesis As A Prognostic Factor For Gastric Cancerslavinia diaNo ratings yet
- Stelloo Ann Oncol 2017Document7 pagesStelloo Ann Oncol 2017Yachao LiuNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s12022 019 9576 5Document8 pages10.1007@s12022 019 9576 5Kevin AdrianNo ratings yet
- Ijcm 13 4 99210Document7 pagesIjcm 13 4 99210Nurul Ulya RahimNo ratings yet
- Cancers 13 05301Document15 pagesCancers 13 05301Bozner Sanchez EscobarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S102845592300030X MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S102845592300030X Main何燕No ratings yet
- Abstract. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Report-: ONCOLOGY LETTERS 5: 1682-1686, 2013Document5 pagesAbstract. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Report-: ONCOLOGY LETTERS 5: 1682-1686, 2013yuliaNo ratings yet
- M2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon CancerDocument13 pagesM2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon Cancerhup4824No ratings yet
- Ps 28 76Document10 pagesPs 28 76Furando NgNo ratings yet
- Article 5 POCDocument16 pagesArticle 5 POCmariimaria670No ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0267306Document25 pagesJournal Pone 0267306MellysaNo ratings yet
- Prognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Patients With Soft Tissue SarcomaDocument7 pagesPrognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Patients With Soft Tissue SarcomaJemma ArakelyanNo ratings yet
- C Met Is Overexpressed in Type I Ovarian Cancer: Results of An Investigative Analysis in A Cohort of Consecutive Ovarian Cancer PatientsDocument7 pagesC Met Is Overexpressed in Type I Ovarian Cancer: Results of An Investigative Analysis in A Cohort of Consecutive Ovarian Cancer PatientsDavid Isaias Jaimes ReyesNo ratings yet
- Abcr20120200001 55990344Document8 pagesAbcr20120200001 55990344Uum SudrajatNo ratings yet
- AACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 3063-5947From EverandAACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 3063-5947No ratings yet
- AACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 1-3062From EverandAACR 2017 Proceedings: Abstracts 1-3062No ratings yet
- Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Korean Melanoma PatientsDocument9 pagesClinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Korean Melanoma Patientsfebri susantoNo ratings yet
- CX3CR1 Acts As A Protective Biomarker in The Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal CancerDocument16 pagesCX3CR1 Acts As A Protective Biomarker in The Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal CancerIsmaNo ratings yet
- Sustain 2021 10652180Document6 pagesSustain 2021 10652180filonenko0448No ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnosis in Breast Cancer: Mini-Symposium: Breast PathologyDocument12 pagesMolecular Diagnosis in Breast Cancer: Mini-Symposium: Breast PathologyOber Van Gómez LópezNo ratings yet
- Article 2Document5 pagesArticle 2Mahadev HaraniNo ratings yet
- MEJC477911631043000Document10 pagesMEJC477911631043000Riyadh Z. MawloodNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Associated BRCA1 and The Identification of Signaling PathwaysDocument10 pagesMolecular Mechanism of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Associated BRCA1 and The Identification of Signaling PathwaysnagarajharishNo ratings yet
- Neoadjuvant ChemotherapyDocument8 pagesNeoadjuvant ChemotherapyrakaNo ratings yet
- Ankle1 N - Methyladenosine-Related Variant Is Associated With Colorectal Cancer Risk by Maintaining The Genomic StabilityDocument13 pagesAnkle1 N - Methyladenosine-Related Variant Is Associated With Colorectal Cancer Risk by Maintaining The Genomic Stabilitytirasi1214No ratings yet
- Fimmu 14 1000497Document15 pagesFimmu 14 1000497Aswar AnasNo ratings yet
- Metaplastic CA 2 IhkDocument10 pagesMetaplastic CA 2 IhkWinta MayantiNo ratings yet
- PMC CancerDocument2 pagesPMC CancervivekNo ratings yet
- Apicella 2015Document16 pagesApicella 2015bawoji1763No ratings yet
- The Potential of Conditionally Replicating AdenovirusDocument1 pageThe Potential of Conditionally Replicating AdenovirusJairo BermúdezNo ratings yet
- New WHO Classification of Pituitary Adenomas (4th Edition) : Assessment of Pituitary Transcription Factors and The Prognostic Histological FactorsDocument5 pagesNew WHO Classification of Pituitary Adenomas (4th Edition) : Assessment of Pituitary Transcription Factors and The Prognostic Histological FactorscristianescNo ratings yet
- Guyot 2021, MSI Colorectal Discordance Molecular Vs IHKDocument9 pagesGuyot 2021, MSI Colorectal Discordance Molecular Vs IHKmercy marcmarquezNo ratings yet
- Calon2015 2Document13 pagesCalon2015 2Javier Cerda InfanteNo ratings yet
- PIIS1074761313004378Document14 pagesPIIS1074761313004378ZadorxsNo ratings yet
- Alaeddini Et Al 2008 HistopathologyDocument6 pagesAlaeddini Et Al 2008 HistopathologyEdgardo CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Expression of Mirnas and Pten in Endometrial Specimens Ranging From Histologically Normal To Hyperplasia and Endometrial AdenocarcinomaDocument9 pagesExpression of Mirnas and Pten in Endometrial Specimens Ranging From Histologically Normal To Hyperplasia and Endometrial AdenocarcinomaFerdina NidyasariNo ratings yet
- Angiogenic Activities of Interleukin-8, Vascular Endothelial Growth FactorDocument28 pagesAngiogenic Activities of Interleukin-8, Vascular Endothelial Growth FactorReda RamzyNo ratings yet
- Or 26 1 185 PDFDocument7 pagesOr 26 1 185 PDFRoland_IINo ratings yet
- Boll Et Al-2023-Scientific ReportsDocument14 pagesBoll Et Al-2023-Scientific ReportsJoy IsmailNo ratings yet
- Familial Risk-Colorectal Cancer - ESMO Clinical Practice GuidelinesDocument8 pagesFamilial Risk-Colorectal Cancer - ESMO Clinical Practice GuidelinesAnonymous 8KN8IR1GTWNo ratings yet
- Comparison of IHC Expression of EGFR On SGTDocument5 pagesComparison of IHC Expression of EGFR On SGTMehreen MalikNo ratings yet
- PD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Research ArticleDocument14 pagesPD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Research ArticleFebrian Parlangga MuisNo ratings yet
- Signaling Cancer SpecialDocument4 pagesSignaling Cancer SpecialcadimogirlNo ratings yet
- W de WenisimoDocument18 pagesW de WenisimoBJ CarminatorNo ratings yet
- Cho Et Al-2019-International Journal of CancerDocument12 pagesCho Et Al-2019-International Journal of Cancerlouisehip UFCNo ratings yet
- 2015 Molecular KlimstraDocument7 pages2015 Molecular KlimstramaomaochongNo ratings yet
- Apigenin Parsley Melanoma PD-1 PD-L1Document15 pagesApigenin Parsley Melanoma PD-1 PD-L1valgurNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Blood Cancer - 2023 - Abstracts From The 39th Annual Meeting of The Histiocyte SocietyDocument64 pagesPediatric Blood Cancer - 2023 - Abstracts From The 39th Annual Meeting of The Histiocyte SocietySeham GoharNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1470204522007835 Main PDFDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1470204522007835 Main PDFOncología CdsNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathological Significance of Fascin and CD44v6 Expression in Endometrioid CarcinomaDocument7 pagesClinicopathological Significance of Fascin and CD44v6 Expression in Endometrioid CarcinomaelisasusantiNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers in MelanomaDocument6 pagesBiomarkers in MelanomaMatthew NgNo ratings yet
- Azim 2016Document10 pagesAzim 2016Jocilene Dantas Torres NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Jclinpath 2019 206273Document7 pagesJclinpath 2019 206273lukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Omar AhmedDocument5 pagesMTA1 Omar Ahmedlukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051Document9 pagesMTA1 Ekspression in Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Ijo-28-051lukman f0028No ratings yet
- MTA1 Erb PathwayDocument6 pagesMTA1 Erb Pathwaylukman f0028No ratings yet
- Honey Authenticity - 2013Document27 pagesHoney Authenticity - 2013romanciucclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Dickinson and Fa 2000Document11 pagesDickinson and Fa 2000Ze WlyNo ratings yet
- HernioplastyDocument58 pagesHernioplastyFobin VargheseNo ratings yet
- NUTR1R06w PDFDocument110 pagesNUTR1R06w PDFAli Rıza Üreten100% (1)
- Să Nu Omori Niciodată Această Insectă Ciudată! Iată de Ce!Document8 pagesSă Nu Omori Niciodată Această Insectă Ciudată! Iată de Ce!Alexandra CrăciunNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Homeostasis: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell Biology J.carbrey@cellbio - Duke.eduDocument17 pagesAcid-Base Homeostasis: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell Biology J.carbrey@cellbio - Duke.eduMaggieLocke100% (1)
- BioPsy 1 - Intro To BioPsyDocument4 pagesBioPsy 1 - Intro To BioPsyTim AroscoNo ratings yet
- Bacterio Rhodopsin MemoryDocument6 pagesBacterio Rhodopsin Memorydurgalakshmi100100% (2)
- Mindfulness in 10 Easy StepsDocument13 pagesMindfulness in 10 Easy StepsMomina Abid100% (10)
- Bich411 Enzyme Regulation PDFDocument4 pagesBich411 Enzyme Regulation PDFAn TranNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument40 pagesMedulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd Gradetuhin100% (1)
- GTR in Management of Gingival RecessionDocument15 pagesGTR in Management of Gingival RecessionMalavika JaiNo ratings yet
- Biolatest LSR Ver 1.0Document2 pagesBiolatest LSR Ver 1.0Indah Puspita Sari IINo ratings yet
- Sloterdijk - Spheres TheoryDocument8 pagesSloterdijk - Spheres TheoryKatma Vue100% (2)
- Hoover 1961Document14 pagesHoover 1961Azmi FarhadiNo ratings yet
- Activity 13 DNAReplicationPupil Case StudyDocument9 pagesActivity 13 DNAReplicationPupil Case Studyavita rukmanaNo ratings yet
- November 2014 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument16 pagesNovember 2014 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFmanan damaniNo ratings yet
- GLOSARIO de Terminos Agricolas NAL 2018 PDFDocument1,968 pagesGLOSARIO de Terminos Agricolas NAL 2018 PDFLidia NoreseNo ratings yet
- Nata de Coco Poast LabDocument2 pagesNata de Coco Poast LabMae100% (1)
- Cell Adhesion MoleculesDocument90 pagesCell Adhesion MoleculesPooja Bappanna100% (1)
- TNV 321Document202 pagesTNV 321Principal PolytechnicNo ratings yet
- Osteogénesis ImperfectaDocument13 pagesOsteogénesis ImperfectaCheby MorenoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAmino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial PDFKHURT MICHAEL ANGELO TIU100% (1)
- Extracellular Matrix ScafoldDocument16 pagesExtracellular Matrix ScafoldmanishNo ratings yet
- Cancer Is Only Going To Be A Chapter in You Life, Not The Whole StoryDocument3 pagesCancer Is Only Going To Be A Chapter in You Life, Not The Whole StoryDonna AntonetteNo ratings yet
- Periosteal Pocket Flap For Horizontal Bone RegenerDocument10 pagesPeriosteal Pocket Flap For Horizontal Bone RegenerViorel Ion100% (1)
- 2022-Association of iSGLT2 Use With Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With Stabilized AMIDocument8 pages2022-Association of iSGLT2 Use With Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With Stabilized AMIWENDY JOHANA HENRIQUEZ SEGURA ESTUDIANTE ACTIVONo ratings yet