Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsDiesel Power Plant
Diesel Power Plant
Uploaded by
kapun kumar nayakA diesel power plant uses a diesel engine as the prime mover to generate electricity. Diesel is burned inside the engine and the combustion products power the engine, which drives an alternator to convert the mechanical energy to electrical energy. Diesel power plants are used for small-scale power generation and as backup power sources due to their high fuel costs. They are installed where demand is low, coal and water availability is limited, and grid infrastructure is inadequate. The key components of a diesel power plant are the fuel, air intake, exhaust, cooling, lubrication and starting systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- SerenaDocument13 pagesSerenamusnmanariffinNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Team C Pricing Strategy Case Draft #1Document5 pagesTeam C Pricing Strategy Case Draft #1kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Waukesha Gas Engines VHP Series Four P9394GSIDocument2 pagesWaukesha Gas Engines VHP Series Four P9394GSIrohizat0% (1)
- Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument44 pagesHydro Electric Power Plantpachucoc300No ratings yet
- Layout Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument6 pagesLayout Diesel Engine Power PlantJyotismoy SarmaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Notes - OrganizedDocument107 pagesPower Plant Engineering Notes - Organizeddeepak kantipudiNo ratings yet
- Diesel Powep Plant: CNSC College of EngineeringDocument26 pagesDiesel Powep Plant: CNSC College of EngineeringMark LimboyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes PDFDocument29 pagesLecture Notes PDFThulasi Ram100% (2)
- Me 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Lecture NotesDocument98 pagesMe 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Lecture NotesBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (2)
- Bcme Unit-IiiDocument22 pagesBcme Unit-IiiJeevabinding xeroxNo ratings yet
- Power Plant AssinmentDocument8 pagesPower Plant Assinmentfawad javadNo ratings yet
- EE2252 PPE Lecture Notes - NPRDocument91 pagesEE2252 PPE Lecture Notes - NPRmaniNo ratings yet
- Essential Components of Diesel Power Plant: The Diesel Power Plants Are Generally Used As FollowsDocument5 pagesEssential Components of Diesel Power Plant: The Diesel Power Plants Are Generally Used As FollowsajayNo ratings yet
- Powerplant EngineeringDocument29 pagesPowerplant Engineeringswechchha adhikariNo ratings yet
- PPE Lecture NotesDocument118 pagesPPE Lecture NotesMITTA NARESH BABU100% (1)
- Power PlantDocument27 pagesPower PlantaloknegiNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii PpeDocument17 pagesUnit-Iii PpeRAJASEKHAR KNo ratings yet
- Lecture-87 Other Power PlantsDocument48 pagesLecture-87 Other Power Plantspandya bhavikNo ratings yet
- PPE NotesDocument30 pagesPPE NotesmeenaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Electric Powerplant Lab ActDocument5 pagesDiesel Electric Powerplant Lab ActAndrei BarbazaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On "Diesel Power Plant": BY Gautam DangiDocument14 pagesSeminar On "Diesel Power Plant": BY Gautam DangiGautam DangiNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant PDFDocument12 pagesDiesel Power Plant PDFZaul tatingNo ratings yet
- DieselPower PlantDocument12 pagesDieselPower PlantJC ElarmoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Document56 pagesBasics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Pushparaj ManickamNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant PresentationDocument13 pagesDiesel Power Plant PresentationAljomar Bas JularbalNo ratings yet
- Applications of Diesel Power PlantDocument3 pagesApplications of Diesel Power PlantAljebeth D. TuraNo ratings yet
- 202005131131260418garurav-G-Diesel Electric Power PlantDocument11 pages202005131131260418garurav-G-Diesel Electric Power PlantJqNo ratings yet
- e Content Electrical Power IDocument185 pagese Content Electrical Power Igkulkarni298No ratings yet
- Diesel Electric Power PlantsDocument16 pagesDiesel Electric Power PlantsCharlo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngDocument93 pagesPower Plant Engsenthilkumarece100% (3)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAnil KandakatlaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 3 BCME FinalDocument26 pagesUNIT - 3 BCME FinalAnith Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BcmeDocument21 pagesUnit-3 BcmeBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VibrationsDocument49 pagesMechanical VibrationsKennedy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Diesel Power PlantDocument5 pagesAdvantages of Diesel Power PlantRuss AñosaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantDocument30 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantmaniNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument46 pagesPower Plant Engineeringmahi90kanNo ratings yet
- Notes CompleteDocument69 pagesNotes Completebernabas100% (2)
- What Is Diesel Power PlantDocument6 pagesWhat Is Diesel Power PlantJomarie PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument93 pagesPower Plant EngineeringMani Vannan Soundarapandiyan100% (1)
- PPE Unit IIDocument114 pagesPPE Unit IIHD Movies DownloadNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering OutlineDocument27 pagesPower Plant Engineering OutlineDexter Baret0% (1)
- Study of Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument17 pagesStudy of Diesel Engine Power Plantbsaid77100% (5)
- Electric Power Generation NotesDocument64 pagesElectric Power Generation NotesnikhilNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power PlantDocument37 pagesDiesel Power PlantAndrewNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power PlantsDocument19 pagesHydroelectric Power PlantsMijanulNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power PlantDocument15 pagesDiesel Power PlantJennsonFernandezNo ratings yet
- Water HarvestingDocument44 pagesWater HarvestingTanmay KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument32 pagesSummer Training ReportKuldeep ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument25 pagesPower Plant EngineeringlitonNo ratings yet
- REPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Document11 pagesREPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Rohit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Generating StationsDocument49 pagesGenerating StationsZafar Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Calingasan Cantara CaringalDocument53 pagesCalingasan Cantara CaringalCliff Joen CarurucanNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument9 pagesSteam Power PlantAnne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedFrom EverandMarine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedNo ratings yet
- Naval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsFrom EverandNaval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsNo ratings yet
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemFrom EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning 3Document36 pagesAir Conditioning 3kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Fire FightingDocument4 pages1.4 Fire Fightingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- L 5 - Chapter 3 2Document13 pagesL 5 - Chapter 3 2kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- IC Engines AutomobilesDocument91 pagesIC Engines Automobileskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- New Me-5Document3 pagesNew Me-5kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- 1.2.2machine SafetyDocument34 pages1.2.2machine Safetykapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- EarthingDocument32 pagesEarthingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Lifting DevicesDocument28 pagesLifting Deviceskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Types of Machine ToolsDocument39 pagesTypes of Machine Toolskapun kumar nayak100% (1)
- FuelsDocument42 pagesFuelskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Presentation SlideDocument56 pagesMaintenance Presentation Slidekapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive TestingDocument38 pagesNon-Destructive Testingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Gears and Gear DrivesDocument44 pagesMaintenance of Gears and Gear Driveskapun kumar nayak100% (2)
- TechnicalDocument20 pagesTechnicalkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- UNO and Saarc PDFDocument18 pagesUNO and Saarc PDFkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Types of PumpDocument32 pagesTypes of Pumpkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance CouplingSprocket FinalDocument38 pagesMaintenance CouplingSprocket Finalkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Losses in FlowDocument30 pagesLosses in Flowkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance BearingDocument26 pagesMaintenance Bearingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- AkesDocument103 pagesAkeskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of Automobile Chassis: ISO 9001:2008 CertifiedDocument10 pagesDesign & Analysis of Automobile Chassis: ISO 9001:2008 Certifiedkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Chap 4Document51 pagesDigital Logic Chap 4kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Ex:-Pitch Circle Drilling: Descriptio N N G M X Y Z I J K F S S P Q R T Abs Cords Metric Units 1st ToolDocument2 pagesEx:-Pitch Circle Drilling: Descriptio N N G M X Y Z I J K F S S P Q R T Abs Cords Metric Units 1st Toolkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Name:Kapun Nayak DATE:12-02-2019 MR - Pratisthit L.Shrestha: Signature TitleDocument1 pageName:Kapun Nayak DATE:12-02-2019 MR - Pratisthit L.Shrestha: Signature Titlekapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- 2.4 FAC I L I TY Locat I ON: 1. Deciding On Domestic or International LocationDocument10 pages2.4 FAC I L I TY Locat I ON: 1. Deciding On Domestic or International Locationkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Compressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockDocument10 pagesCompressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockPalak ShivhareNo ratings yet
- Key Notes: Wall SystemDocument1 pageKey Notes: Wall SystemMyo Min ThuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Alcoholometry. Ethanol Recuperation and Rectification.Document30 pagesLecture 3. Alcoholometry. Ethanol Recuperation and Rectification.salman fard33% (3)
- Gps-Imod: Modular Needlepoint Bipolar Ionization Air Purification SystemDocument1 pageGps-Imod: Modular Needlepoint Bipolar Ionization Air Purification Systemcharadeg100No ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram of Common Rail Diesel Injection (CDI) Control ModuleDocument1 pageWiring Diagram of Common Rail Diesel Injection (CDI) Control ModuleАндрей Олененко100% (1)
- Lecture 0 Appendix Intro Fluid PowerDocument61 pagesLecture 0 Appendix Intro Fluid PowerSAMUEL MAKATANE100% (1)
- TFM - Turbine Flowmeter PDFDocument2 pagesTFM - Turbine Flowmeter PDFAlaaNo ratings yet
- Solid State PharmaceuticalDocument56 pagesSolid State PharmaceuticalAci LusianaNo ratings yet
- Inverter Kstar Iec Certificate Ksg30 - 60kDocument19 pagesInverter Kstar Iec Certificate Ksg30 - 60khussainhasnainNo ratings yet
- KINETICSDocument47 pagesKINETICSMarilia BonorinoNo ratings yet
- Report Belt SlipDocument3 pagesReport Belt Slipjunreylaureto003No ratings yet
- Aerospace Magazine January 2023Document60 pagesAerospace Magazine January 2023GeorgeNo ratings yet
- GOWIN MicrojetDocument6 pagesGOWIN MicrojetPrayaag TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Siprotec 7sj62 PDFDocument704 pagesSiprotec 7sj62 PDFCLAVOTNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Piping SystemDocument5 pagesModule 3 Piping Systembotch belmiNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM 2018 QuestionDocument14 pagesIIT-JAM 2018 Questionrupesh sahuNo ratings yet
- CV Europass 20170222 Memon, Waqar AliDocument2 pagesCV Europass 20170222 Memon, Waqar AliWaqar AliNo ratings yet
- Disconnecting Circuit Breaker - One Device, Two OptionsDocument2 pagesDisconnecting Circuit Breaker - One Device, Two Optionslac1981No ratings yet
- Sunx SerieDocument10 pagesSunx SerieMarcelo LescanoNo ratings yet
- 01 PDFDocument69 pages01 PDFYUNASRIL SYARIEFNo ratings yet
- Energy Medicine PDFDocument14 pagesEnergy Medicine PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- Led Alto Brillo 3-5mm PDFDocument2 pagesLed Alto Brillo 3-5mm PDFAngel HilasacaNo ratings yet
- Turbine WakeDocument19 pagesTurbine Wakeabraham_imam_muttaqinNo ratings yet
- Hess - MCQDocument5 pagesHess - MCQsumeghathunga25No ratings yet
- Azkoyen Vitale - S PDFDocument34 pagesAzkoyen Vitale - S PDFAhmad FauzanNo ratings yet
- r/IBO Group 4 Study Materials - Experimental SciencesDocument66 pagesr/IBO Group 4 Study Materials - Experimental SciencesHumberto RodríguezNo ratings yet
- OMNIPOWER 3-Phase - Installation and User Guide - EnglishDocument8 pagesOMNIPOWER 3-Phase - Installation and User Guide - EnglishSamuel KamauNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Technical University, Kota: DC Transmission TechnologyDocument2 pagesRajasthan Technical University, Kota: DC Transmission TechnologyIQAC ARYANo ratings yet
Diesel Power Plant
Diesel Power Plant
Uploaded by
kapun kumar nayak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views32 pagesA diesel power plant uses a diesel engine as the prime mover to generate electricity. Diesel is burned inside the engine and the combustion products power the engine, which drives an alternator to convert the mechanical energy to electrical energy. Diesel power plants are used for small-scale power generation and as backup power sources due to their high fuel costs. They are installed where demand is low, coal and water availability is limited, and grid infrastructure is inadequate. The key components of a diesel power plant are the fuel, air intake, exhaust, cooling, lubrication and starting systems.
Original Description:
power plant
Original Title
1. Diesel Power Plant.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA diesel power plant uses a diesel engine as the prime mover to generate electricity. Diesel is burned inside the engine and the combustion products power the engine, which drives an alternator to convert the mechanical energy to electrical energy. Diesel power plants are used for small-scale power generation and as backup power sources due to their high fuel costs. They are installed where demand is low, coal and water availability is limited, and grid infrastructure is inadequate. The key components of a diesel power plant are the fuel, air intake, exhaust, cooling, lubrication and starting systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views32 pagesDiesel Power Plant
Diesel Power Plant
Uploaded by
kapun kumar nayakA diesel power plant uses a diesel engine as the prime mover to generate electricity. Diesel is burned inside the engine and the combustion products power the engine, which drives an alternator to convert the mechanical energy to electrical energy. Diesel power plants are used for small-scale power generation and as backup power sources due to their high fuel costs. They are installed where demand is low, coal and water availability is limited, and grid infrastructure is inadequate. The key components of a diesel power plant are the fuel, air intake, exhaust, cooling, lubrication and starting systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 32
Diesel Power Plant
By Er. Kabita Ojha
Diesel Power Plant
⚫ A generating station in which diesel engine is used as
prime mover for generation of electrical energy is
known as diesel power plant.
⚫ In diesel power plant, the diesel burns inside the engine
and the products of this combustion act as the working
fluid to produce mechanical energy.
⚫ The diesel engine drives the alternator which converts
mechanical energy into electrical energy.
⚫ As generation cost is considerable due to a high price of
diesel, therefore such power stations are only used to
produce small power.
⚫ Diesel power plant are installed at places where the
demand for power is less, sufficient quantity of coal
and water is not available and the transformation
facilities are inadequate.
⚫ These plants are also used as standby sets for
continuity of supply to important points such as
hospitals, radio stations, cimena houses etc.
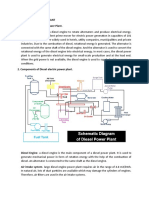
Diesel Power Plant Line Diagram
Schematic Diagram
Parts of Diesel Power Plant
1) Fuel Supply System
⚫ It consists of a storage tank, strainers, fuel transfer pump
and fuel tank.
⚫ The fuel oil is supplied at the plant site by rail or road
and stored in the storage tank.
⚫ Oil is pumped from the storage tank to the all day tank
at short interval.
⚫ From this tank, fuel oil is passed through strainers to
remove suspended impurities.
⚫ Then, the clean oil is injected into the engine by fuel
injection pump.
2)Air Intake System:
⚫ This system supplied necessary air to the engine for
fuel combustion.
⚫ It consists of pipes for the supply of fresh air to the
engine manifold.
⚫ Filters are provided to remove dust particles from the
air which may act as abrasive in the engine cylinder.
3) Exhaust System:
⚫ This system leads the engine exhaust gas outside the
building and discharges it into the atmosphere.
⚫ A silencer is usually incorporated in the system to
reduce the noise level.
4) Cooling System:
⚫ The heat released by burning of the fuel in the engine
cylinder is partially converted into work.
⚫ The remaining part of the heat passes through the cylinder
walls, piston, rings etc. and may cause damage to the system.
⚫ In order to keep the temperature of the engine parts within
the safe operating limits, cooling is necessary.
⚫ The cooling system consists of a water source, pump and
cooling towers.
⚫ The pump circulates water through a cylinder and head
jacket.
⚫ The water takes heat away from the engine and itself
become hot and hot water is cooling by cooling towers and
recirculated for cooling.
5) Lubricating System:
⚫ This system minimizes the wear of rubbing surfaces of
the engine.
⚫ It consists of lubricating oil, pump, filter and oil
cooler.
⚫ The lubricating oil is drawn from the lubricating oil
tank by the pump and is passed through filtres to
remove impurities.
⚫ The clean lubricating oil is delivered to the points
which require lubrication.
⚫ The oil coolers incorporated in the system keep the
temperature of the oil low.
6) Engine Starting System:
⚫ This system is an arrangement to rotate the engine
initially while starting until firing starts and the unit
runs with its own power.
⚫ Small sets are started manually by handles but for
larger units, compressed air is used for starting.
⚫ Air at high pressure is admitted to a few of the
cylinders, making them act as reciprocating air motors
to turn over the engine shaft.
⚫ The fuel is admitted to the remaining cylinders which
make the engine to start under its own power.
Advantages
⚫ The construction of diesel power plant is simple.
⚫ The diesel power plant can be easily installed at any
place where the demand for power is very less.
⚫ Time required to start and stop this power plant is very
minimum as compare to time take by other plants to
start and stop.
⚫ It starts quickly and easily picks up the load variations.
⚫ The maintenance cost is minimal as compared to the
thermal and steam power plants.
⚫ It requires minimum quantity of water which is
essential for cooling purpose.
⚫ For the installation of the power plant, sufficient area
that is required is very less.
⚫ This plant does not require more labours or workers
under operation conditions.
⚫ The diesel power plant has more thermal efficiency as
compared to the steam power plant.
⚫ It is widely used as a standby set in compact areas (like
as hospitals, cinema houses, industrial machineries,
etc.) that can provide a continuous power supply to the
load.
Disadvantages
⚫ The running cost of diesel power plant is high because
diesel fuel is more expensive.
⚫ It is not much comfortable under the overload
condition and long duartion.
⚫ This plant has limited power generation and storages
capacity than thermal and hydroelectric power plants.
⚫ The lubrication cost for this plant is very high
⚫ This diesel power plant produces limited amount of
electricity (approximately 50MW).
⚫ The life span of the diesel energy is relatively short.
Maintenance of Diesel Power Plant
Points to be considered during maintenance:
⚫ To maintain the operating condition of a diesel engine
at every half hour.
⚫ To maintain the correct record of the instrument
reading in the log sheet.
⚫ To maintain the record of instrument temperature,
pressure, electrical load, flow etc.
⚫ Filtered the fuel and remove unwanted impurities.
⚫ Check the level of fuel oil periodically.
⚫ Clean the fuel tank at regular interval.
Applications of Diesel Power Plant
⚫ It is used where small power generation is a
requirement.
⚫ It produces AC as well as DC voltages.
⚫ It is used to restart the boilers.
⚫ In case of any emergency diesel engines are used.
⚫ It is used in remote places.
⚫ It is also used for peak load during a small period of
time.
⚫ It can be used in areas having low load factor.
Hydropower Plant
⚫ Hydropower or hydroelectricity is a renewable source of
energy that utilizes the energy of fast-flowing water to
generate electricity.
⚫ The use of hydropower for various purposes is not a
modern concept; its application can be seen even a
thousand years ago.
⚫ The hydroelectric power plants generate electricity from
the potential and kinetic energy of the water.
⚫ When water flows down, its potential energy is first
converted to kinetic energy and then mechanical energy
with the help of turbines. With the use of a generator, the
mechanical energy is transformed into electrical energy.
Hydropower Plant
Components of Hydroelectric Power
Plant
1) Reservoir:
⚫ A reservoir is the most essential part of the
hydropower plant. It stores the water and supplied it
down to the hydro turbine for electricity generation.
⚫ The reservoir can be natural lakes in the hilly areas, or
it can be made artificially by establishing a dam across
the water bodies.
⚫ The reservoirs of the hydropower plants are also used
for flood control, irrigation purposes, industrial, and
aquaculture.
2) Forebay:
⚫ A Forebay is an area to temporarily store the water
before flowing it down to the turbine.
⚫ It stores the excess water in the case of rainy seasons
and supplies it during the dry seasons, i.e., it
maintains the amount of water to be needed as per the
requirement at the load area.
⚫ The forebay is constructed when the hydroelectric
plants are situated far from the reservoir, else the
reservoir itself acts as the forebay when it is located
near the plant.
3) Dam:
⚫ A dam is the most expensive element of the
hydroelectric power plant.
⚫ It is a barrier constructed across the water bodies to
restrict the flow of the naturally flowing water and to
raise the water level in the reservoirs.
⚫ They are usually made of concrete, rocks, earth, or
stonemasonry.
⚫ The type of material to be used for their construction
depends upon the geography of the area, transportation
availability, and the chances of occurrence of any natural
disasters such as earthquakes or floods in that particular
area.
4) Spillways:
⚫ In case of heavy rainfall or flood situations, the water
level in the reservoir may rise beyond its storage capacity
that may affect the proper functioning of the hydropower
plant.
⚫ To prevent this situation, a hydraulic structure called a
spillway is built at the site of the dam.
⚫ The spillway safely diverts the extra water from the
reservoir to a downstream area.
⚫ Spillways are constructed either as a part of the dam or
just beyond them.
⚫ They are usually made of concrete, and they consist of
metal control gates to stop or discharge the water from
the reservoir.
5) Tailrace:
⚫ The water left at the hydroelectric plant after being
generated electricity by the hydro turbine is carried
away from that area through a channel called
tailrace.
⚫ The tailrace is present behind the dams at a lower
level than that of the reservoir.
⚫ As the potential energy of the water due to the
elevated reservoir is being used up by the hydro
turbine, the water through the tailrace flows at the
natural speed of the water and joins the same or
another water stream.
6) Penstocks
⚫ Penstocks are the channels or large pipes at the hydroelectric
station that carries the water down to the turbines at the
power station from the reservoir.
⚫ The penstocks are generally made of steel or reinforced cement
concrete (RCC).
⚫ The material to be used for constructing penstocks depends
upon the water-head of the dam.
⚫ The steel penstocks can be used for any head or working
pressure of water, whereas the RCC penstocks are used for the
low water heads, usually less than 30 meters.
⚫ As a large amount of water flows through the penstocks, hence
the abrupt opening and closing of the gates at the ends of the
penstock can cause a water hammer effect (pressure surges).
7) Water Intakes:
⚫ The water intake includes the structures that collect the
water stored in the reservoir or forebay and direct it
towards the turbines through the penstocks.
⚫ Water intakes consist of several gates, screens, filters,
booms, sluices, and trash racks that control the amount of
water that reaches the turbines and also block any kind of
debris such as trunks, waste products, or branches from
entering the channel by diverting it to the bypass chute.
⚫ The screens and trash racks are installed at the entrance of
the penstock to forbid the debris from entering inside as
debris can cause damage to the various important
hydraulic parts such as turbine blades, nozzles, and
turbine runners.
8) Sluice:
⚫ Sluices are also part of water intake structures.
⚫ The flow of water through the penstocks is controlled
by the sluice; the sluice is the gate that is installed at the
ends of the penstocks, which can be raised or lowered
according to the requirement of the water at the
turbine.
⚫ The water freely flows through the penstocks when the
sluice is open completely, but less water flows through
the penstock when the sluice is partially closed.
⚫ They are generally kept open in the dry seasons to allow
water to pass through the penstocks, but in rainy
seasons they are slightly kept closed to avoid flooding.
9) Surge Tank:
⚫ The sudden water surges due to the changes in the water
flow may result in variations in the pressure that can damage
the components of the hydropower plant.
⚫ To control the pressure changes, small cylindrical water
storage tanks called surge tanks are used.
⚫ Surge tanks are open from their top to reduce or neutralize
the pressure changes in the reservoir and are used to
regulate the turbines.
⚫ They protect the conduit (channel) from excess internal
pressure and are also capable of storing water to raise the
internal pressure in case of pressure drop.
⚫ Surge tanks are usually located at the centre of the penstock
(steep-sloped) before the water turbine
10) Power House:
⚫ A powerhouse is a separate room or building at the
hydroelectric power stations, which consist of
various electrical and hydraulic components.
⚫ The powerhouse is responsible for controlling the
various inlet and outlet gates and stopping the flow
of water in the equipment areas in case of repairing
or changing various pieces of equipment.
⚫ Hydroelectric power plants also consists of general
auxiliaries like control panels, service area, testing
rooms, generators, and transformers.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is not part of diesel engine
power plant?
a) Cooling Tower
b) Penstock
c) Oil Pump
d) Strainer
b) Penstock
2. The diesel plants are mainly used ________
a) As peak load pants
b) As base load plants
c) As standby power plants
d) Both peak and stand by plants
d) Both peak and stand by plants
3. The speed of the diesel engine may vary from
a) 0-100 rpm
b) 200-1000 rpm
c) 500-5000 rpm
d) 1000-3000 rpm
d) 1000-3000 rpm
4. What is the ranging capacity of the diesel plant?
a) 50-750 kW
b) 100-1175 kW
c) 75-3750 kW
d) 150-4575 kW
c) 75-3750 kW
5. What is requirement of cooling system in diesel
plants?
a) Eliminate hotness of air entering into the filter
b) To act as filter for main fuel tank
c) Eliminate heat coming out of engine
d) To cool down lubrication system
c) Eliminate heat coming out of engine
6. Small service storage tanks in a fuel system of diesel plant
are known as
a) Temporary fuel tank
b) Engine day tank
c) Reserve
d) Main fuel tank
b) Engine day tank
7. Following are the advantages of diesel power engines,
except
a) High operating efficiency
b) Low noise
c) Easier handling of fuel
d) No standby loss
b) Low noise
Thank You !!!
You might also like
- SerenaDocument13 pagesSerenamusnmanariffinNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Team C Pricing Strategy Case Draft #1Document5 pagesTeam C Pricing Strategy Case Draft #1kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Waukesha Gas Engines VHP Series Four P9394GSIDocument2 pagesWaukesha Gas Engines VHP Series Four P9394GSIrohizat0% (1)
- Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument44 pagesHydro Electric Power Plantpachucoc300No ratings yet
- Layout Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument6 pagesLayout Diesel Engine Power PlantJyotismoy SarmaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Notes - OrganizedDocument107 pagesPower Plant Engineering Notes - Organizeddeepak kantipudiNo ratings yet
- Diesel Powep Plant: CNSC College of EngineeringDocument26 pagesDiesel Powep Plant: CNSC College of EngineeringMark LimboyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes PDFDocument29 pagesLecture Notes PDFThulasi Ram100% (2)
- Me 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Lecture NotesDocument98 pagesMe 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Lecture NotesBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (2)
- Bcme Unit-IiiDocument22 pagesBcme Unit-IiiJeevabinding xeroxNo ratings yet
- Power Plant AssinmentDocument8 pagesPower Plant Assinmentfawad javadNo ratings yet
- EE2252 PPE Lecture Notes - NPRDocument91 pagesEE2252 PPE Lecture Notes - NPRmaniNo ratings yet
- Essential Components of Diesel Power Plant: The Diesel Power Plants Are Generally Used As FollowsDocument5 pagesEssential Components of Diesel Power Plant: The Diesel Power Plants Are Generally Used As FollowsajayNo ratings yet
- Powerplant EngineeringDocument29 pagesPowerplant Engineeringswechchha adhikariNo ratings yet
- PPE Lecture NotesDocument118 pagesPPE Lecture NotesMITTA NARESH BABU100% (1)
- Power PlantDocument27 pagesPower PlantaloknegiNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii PpeDocument17 pagesUnit-Iii PpeRAJASEKHAR KNo ratings yet
- Lecture-87 Other Power PlantsDocument48 pagesLecture-87 Other Power Plantspandya bhavikNo ratings yet
- PPE NotesDocument30 pagesPPE NotesmeenaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Electric Powerplant Lab ActDocument5 pagesDiesel Electric Powerplant Lab ActAndrei BarbazaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On "Diesel Power Plant": BY Gautam DangiDocument14 pagesSeminar On "Diesel Power Plant": BY Gautam DangiGautam DangiNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant PDFDocument12 pagesDiesel Power Plant PDFZaul tatingNo ratings yet
- DieselPower PlantDocument12 pagesDieselPower PlantJC ElarmoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Document56 pagesBasics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Pushparaj ManickamNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant PresentationDocument13 pagesDiesel Power Plant PresentationAljomar Bas JularbalNo ratings yet
- Applications of Diesel Power PlantDocument3 pagesApplications of Diesel Power PlantAljebeth D. TuraNo ratings yet
- 202005131131260418garurav-G-Diesel Electric Power PlantDocument11 pages202005131131260418garurav-G-Diesel Electric Power PlantJqNo ratings yet
- e Content Electrical Power IDocument185 pagese Content Electrical Power Igkulkarni298No ratings yet
- Diesel Electric Power PlantsDocument16 pagesDiesel Electric Power PlantsCharlo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngDocument93 pagesPower Plant Engsenthilkumarece100% (3)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAnil KandakatlaNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 3 BCME FinalDocument26 pagesUNIT - 3 BCME FinalAnith Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BcmeDocument21 pagesUnit-3 BcmeBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VibrationsDocument49 pagesMechanical VibrationsKennedy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Diesel Power PlantDocument5 pagesAdvantages of Diesel Power PlantRuss AñosaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantDocument30 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantmaniNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument46 pagesPower Plant Engineeringmahi90kanNo ratings yet
- Notes CompleteDocument69 pagesNotes Completebernabas100% (2)
- What Is Diesel Power PlantDocument6 pagesWhat Is Diesel Power PlantJomarie PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument93 pagesPower Plant EngineeringMani Vannan Soundarapandiyan100% (1)
- PPE Unit IIDocument114 pagesPPE Unit IIHD Movies DownloadNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering OutlineDocument27 pagesPower Plant Engineering OutlineDexter Baret0% (1)
- Study of Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument17 pagesStudy of Diesel Engine Power Plantbsaid77100% (5)
- Electric Power Generation NotesDocument64 pagesElectric Power Generation NotesnikhilNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power PlantDocument37 pagesDiesel Power PlantAndrewNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power PlantsDocument19 pagesHydroelectric Power PlantsMijanulNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power PlantDocument15 pagesDiesel Power PlantJennsonFernandezNo ratings yet
- Water HarvestingDocument44 pagesWater HarvestingTanmay KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument32 pagesSummer Training ReportKuldeep ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument25 pagesPower Plant EngineeringlitonNo ratings yet
- REPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Document11 pagesREPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Rohit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Generating StationsDocument49 pagesGenerating StationsZafar Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Calingasan Cantara CaringalDocument53 pagesCalingasan Cantara CaringalCliff Joen CarurucanNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument9 pagesSteam Power PlantAnne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedFrom EverandMarine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedNo ratings yet
- Naval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsFrom EverandNaval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsNo ratings yet
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemFrom EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning 3Document36 pagesAir Conditioning 3kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Fire FightingDocument4 pages1.4 Fire Fightingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- L 5 - Chapter 3 2Document13 pagesL 5 - Chapter 3 2kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- IC Engines AutomobilesDocument91 pagesIC Engines Automobileskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- New Me-5Document3 pagesNew Me-5kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- 1.2.2machine SafetyDocument34 pages1.2.2machine Safetykapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- EarthingDocument32 pagesEarthingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Lifting DevicesDocument28 pagesLifting Deviceskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Types of Machine ToolsDocument39 pagesTypes of Machine Toolskapun kumar nayak100% (1)
- FuelsDocument42 pagesFuelskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Presentation SlideDocument56 pagesMaintenance Presentation Slidekapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive TestingDocument38 pagesNon-Destructive Testingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Gears and Gear DrivesDocument44 pagesMaintenance of Gears and Gear Driveskapun kumar nayak100% (2)
- TechnicalDocument20 pagesTechnicalkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- UNO and Saarc PDFDocument18 pagesUNO and Saarc PDFkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Types of PumpDocument32 pagesTypes of Pumpkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance CouplingSprocket FinalDocument38 pagesMaintenance CouplingSprocket Finalkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Losses in FlowDocument30 pagesLosses in Flowkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance BearingDocument26 pagesMaintenance Bearingkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- AkesDocument103 pagesAkeskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of Automobile Chassis: ISO 9001:2008 CertifiedDocument10 pagesDesign & Analysis of Automobile Chassis: ISO 9001:2008 Certifiedkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Chap 4Document51 pagesDigital Logic Chap 4kapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
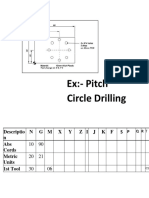
- Ex:-Pitch Circle Drilling: Descriptio N N G M X Y Z I J K F S S P Q R T Abs Cords Metric Units 1st ToolDocument2 pagesEx:-Pitch Circle Drilling: Descriptio N N G M X Y Z I J K F S S P Q R T Abs Cords Metric Units 1st Toolkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Name:Kapun Nayak DATE:12-02-2019 MR - Pratisthit L.Shrestha: Signature TitleDocument1 pageName:Kapun Nayak DATE:12-02-2019 MR - Pratisthit L.Shrestha: Signature Titlekapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- 2.4 FAC I L I TY Locat I ON: 1. Deciding On Domestic or International LocationDocument10 pages2.4 FAC I L I TY Locat I ON: 1. Deciding On Domestic or International Locationkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Compressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockDocument10 pagesCompressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockPalak ShivhareNo ratings yet
- Key Notes: Wall SystemDocument1 pageKey Notes: Wall SystemMyo Min ThuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Alcoholometry. Ethanol Recuperation and Rectification.Document30 pagesLecture 3. Alcoholometry. Ethanol Recuperation and Rectification.salman fard33% (3)
- Gps-Imod: Modular Needlepoint Bipolar Ionization Air Purification SystemDocument1 pageGps-Imod: Modular Needlepoint Bipolar Ionization Air Purification Systemcharadeg100No ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram of Common Rail Diesel Injection (CDI) Control ModuleDocument1 pageWiring Diagram of Common Rail Diesel Injection (CDI) Control ModuleАндрей Олененко100% (1)
- Lecture 0 Appendix Intro Fluid PowerDocument61 pagesLecture 0 Appendix Intro Fluid PowerSAMUEL MAKATANE100% (1)
- TFM - Turbine Flowmeter PDFDocument2 pagesTFM - Turbine Flowmeter PDFAlaaNo ratings yet
- Solid State PharmaceuticalDocument56 pagesSolid State PharmaceuticalAci LusianaNo ratings yet
- Inverter Kstar Iec Certificate Ksg30 - 60kDocument19 pagesInverter Kstar Iec Certificate Ksg30 - 60khussainhasnainNo ratings yet
- KINETICSDocument47 pagesKINETICSMarilia BonorinoNo ratings yet
- Report Belt SlipDocument3 pagesReport Belt Slipjunreylaureto003No ratings yet
- Aerospace Magazine January 2023Document60 pagesAerospace Magazine January 2023GeorgeNo ratings yet
- GOWIN MicrojetDocument6 pagesGOWIN MicrojetPrayaag TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Siprotec 7sj62 PDFDocument704 pagesSiprotec 7sj62 PDFCLAVOTNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Piping SystemDocument5 pagesModule 3 Piping Systembotch belmiNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM 2018 QuestionDocument14 pagesIIT-JAM 2018 Questionrupesh sahuNo ratings yet
- CV Europass 20170222 Memon, Waqar AliDocument2 pagesCV Europass 20170222 Memon, Waqar AliWaqar AliNo ratings yet
- Disconnecting Circuit Breaker - One Device, Two OptionsDocument2 pagesDisconnecting Circuit Breaker - One Device, Two Optionslac1981No ratings yet
- Sunx SerieDocument10 pagesSunx SerieMarcelo LescanoNo ratings yet
- 01 PDFDocument69 pages01 PDFYUNASRIL SYARIEFNo ratings yet
- Energy Medicine PDFDocument14 pagesEnergy Medicine PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- Led Alto Brillo 3-5mm PDFDocument2 pagesLed Alto Brillo 3-5mm PDFAngel HilasacaNo ratings yet
- Turbine WakeDocument19 pagesTurbine Wakeabraham_imam_muttaqinNo ratings yet
- Hess - MCQDocument5 pagesHess - MCQsumeghathunga25No ratings yet
- Azkoyen Vitale - S PDFDocument34 pagesAzkoyen Vitale - S PDFAhmad FauzanNo ratings yet
- r/IBO Group 4 Study Materials - Experimental SciencesDocument66 pagesr/IBO Group 4 Study Materials - Experimental SciencesHumberto RodríguezNo ratings yet
- OMNIPOWER 3-Phase - Installation and User Guide - EnglishDocument8 pagesOMNIPOWER 3-Phase - Installation and User Guide - EnglishSamuel KamauNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Technical University, Kota: DC Transmission TechnologyDocument2 pagesRajasthan Technical University, Kota: DC Transmission TechnologyIQAC ARYANo ratings yet