Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subjective: The Patient
Subjective: The Patient
Uploaded by
Roscoe Paraan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesThe nursing care plan addresses a patient with impaired physical mobility in their lower extremities. Short term goals include helping the patient understand their diagnosis and willingness to participate in physical therapy. Long term goals involve demonstrating different physical therapy procedures to aid mobility. Interventions include exercises to improve range of motion, balance, and strength. Evaluation will assess progress on mobility and understanding of the condition after periods of nursing care.
Original Description:
Original Title
NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan addresses a patient with impaired physical mobility in their lower extremities. Short term goals include helping the patient understand their diagnosis and willingness to participate in physical therapy. Long term goals involve demonstrating different physical therapy procedures to aid mobility. Interventions include exercises to improve range of motion, balance, and strength. Evaluation will assess progress on mobility and understanding of the condition after periods of nursing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesSubjective: The Patient
Subjective: The Patient
Uploaded by
Roscoe ParaanThe nursing care plan addresses a patient with impaired physical mobility in their lower extremities. Short term goals include helping the patient understand their diagnosis and willingness to participate in physical therapy. Long term goals involve demonstrating different physical therapy procedures to aid mobility. Interventions include exercises to improve range of motion, balance, and strength. Evaluation will assess progress on mobility and understanding of the condition after periods of nursing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
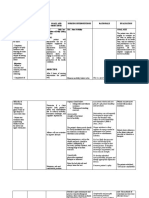
Runez, Roscoe B.
03/--/2023
NCC3
Nursing Care Plan
Assessment Explaination of the Planning Intervention/Rationale Evaluation
Problem
Subjective: The patient A modification in Short Term: Independent: Short term:
“Di ako magalaw yung movement or mobility can After 8 hours of nursing -Execute passive or active After 8 hours of nursing
legs ko. Mejo either be a transient, intervention, the patient assistive ROM exercises to intervention, the patient
nangmamanhid siya.” And recurring, or more will be able to understand all extremities. Exercise understood the longevity
“Pwede po ba ako permanent dilemma. And the longevity of the enhances increased of the diagnosis and
magpatulong ayusin yung when it occurs, it diagnosis present and venous return, prevents demonstrated willingness
higa ko?” becomes a complex demonstrate willingness stiffness, and maintains to participate in physical
Objective: Guarding healthcare problem that to go through physical muscle strength and therapy
behaviour noted. Facial involves many different therapy stamina. It also avoids
grimace noted while members of the contracture deformation,
repositioning. Easily tired healthcare team. In fact, Long Term: which can build up quickly Long Term:
while in physical therapy. some degree of After 4-5 days of nursing and could hinder After 4-5 days of nursing
Functional level of immobility is very intervention, the patient prosthesis usage. intervention, the patient
mobility is at level 4 – common in most will be able to demonstrated different
cannot walk at all and has conditions such as stroke, demonstrate different Dependent: physical therapeutic
no control over lower leg fracture, multiple physical therapeutic -Assist patient with procedures to help in
extremities. Cannot sclerosis, trauma, and procedures to help in muscle exercises as able mobility.
achieve ADL morbid obesity. The mobility or when allowed out of
independently. incidence of the disease bed; execute abdominal-
V/S taken as follows: and disability continues to tightening exercises and
BP 130/80 expand with the longer knee bends; hop on foot;
O2 98 life expectancy for most. stand on toes. Adds to
CR 78 In most cases, even if gaining an enhanced
CR 24 patients are discharged sense of balance and
T 36.7 from the hospital earlier strengthens
than expected, they are compensatory body parts.
Nursing Diagnosis: transferred to -Present a safe
Impaired Physical Mobility rehabilitation facilities or environment: bed rails up,
sent home for physical bed in a down position,
therapy. and important items close
Aging is also considered by. These measures
one of the factors promote a safe, secure
concerning the alteration environment and may
in mobility. A decrease in reduce the risk for falls.
muscle function, loss of Establish measures to
muscle mass, reduction in prevent skin breakdown
muscle strength, gait and thrombophlebitis
changes affecting balance, from prolonged
and stiffer and limited immobility:
mobile joints can Clean, dry, and
significantly jeopardize moisturize skin as
the mobility of aged necessary.
patients. Mobility is Use anti-embolic
needed especially if an stockings or
individual is to maintain sequential
independent living. compression
Limited movement affects devices if
the performance of most appropriate.
ADLs. The human body is Use pressure-
designed for motion; relieving devices
hence, any restriction of as indicated (gel
movement will take its toll mattress).
on every major anatomic Let the patient
system thus resulting in accomplish tasks
impaired physical at his or her own
mobility. pace.
You might also like
- Assisted Stretching 1Document7 pagesAssisted Stretching 1Kostas GhinisNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke NCPDocument11 pagesIschemic Stroke NCPJohannah DaroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalkuroroexileNo ratings yet
- Physician Patient RelationshipDocument25 pagesPhysician Patient RelationshipUser 010897020197100% (1)
- Basic Interventions To Maintain Mobility and Exercise - Nov. 20Document9 pagesBasic Interventions To Maintain Mobility and Exercise - Nov. 20Tom CuencaNo ratings yet
- III. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesIII. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationSTEPHANIE JOSUENo ratings yet
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzDocument7 pagesGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Document4 pagesNCM1023 NursingCarePlan Group2new2Akio OzaragaNo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument5 pagesNCP Case Pressyd19No ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMa Virginia Nathalia CreerNo ratings yet
- NCP (BD)Document5 pagesNCP (BD)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Nag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsDocument4 pagesNag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsNursing LectureNo ratings yet
- NCP of Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesNCP of Impaired MobilityHazel Cabrera0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanCatherine Joy VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Mpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesMpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanTheSweetpea5010% (2)
- Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesComprehensive Nursing Care PlanJustine Joy SolanoNo ratings yet
- Icu NCPDocument8 pagesIcu NCPClaire Nicole ApostolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Surgical, CS)Document5 pagesNursing Care Plan (Surgical, CS)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Independent: 1. Monitor Patient's Vital Signs. 2. Determine Diagnosis That Short Term GoalGeralyn KaeNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobilityDocument1 pageNCP ImmobilityBcoi QuilacioNo ratings yet
- CDC 74349 DS1Document11 pagesCDC 74349 DS1AlinaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentJ. TSNo ratings yet
- NCP For MGDocument2 pagesNCP For MGsalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- 4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs-1 PDFDocument12 pages4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs-1 PDFsaidi MwanamongaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDeanne Carla DalilisNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument6 pagesThoracic Outlet SyndromeCharles MitchellNo ratings yet
- Tos Part 2 B Jam 2017Document6 pagesTos Part 2 B Jam 2017Charles MitchellNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-1idealDocument30 pagesNursing Care Plan-1idealSheila Mae PanisNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired MobilityDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Surgical, Indiv Patient)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan (Surgical, Indiv Patient)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- NCM103A W3 Range of Motion Module - 1774822568Document9 pagesNCM103A W3 Range of Motion Module - 1774822568Esvinch EsvinchNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- CACHO NCP NeuromuscularDocument3 pagesCACHO NCP NeuromuscularJaymee CachoNo ratings yet
- Assess Ment Nursing Diagnos IS Plannin G Nursing Interve Ntion Rationa LE Evaluat IONDocument2 pagesAssess Ment Nursing Diagnos IS Plannin G Nursing Interve Ntion Rationa LE Evaluat IONStephany Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Weebly Questions Week TwoDocument3 pagesWeebly Questions Week Twoapi-459697337No ratings yet
- Mobility and Flexibility TrainingDocument52 pagesMobility and Flexibility TrainingMUGISHA GratienNo ratings yet
- Gedlinske Condition Chart Knee Tka Post OaDocument21 pagesGedlinske Condition Chart Knee Tka Post Oaapi-548295449No ratings yet
- William 2Document15 pagesWilliam 2Jenny VibsNo ratings yet
- On Behalf of Ms. Melendrez, Let's Proceed To: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesOn Behalf of Ms. Melendrez, Let's Proceed To: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMCA OmadtoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: This Is A Good Tool For TheDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: This Is A Good Tool For TheAvery SandsNo ratings yet
- NCP - BedriddenDocument4 pagesNCP - Bedriddenadelaigner_racho589475% (4)
- (NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2Document2 pages(NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2roren100% (1)
- Rio SciDocument17 pagesRio SciPreciousmae Talay JavierNo ratings yet
- CECS ProtocolDocument6 pagesCECS ProtocolTsz Kwan CheungNo ratings yet
- CuesDocument2 pagesCuesKay DiancoNo ratings yet
- TractionDocument2 pagesTractionRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- BalneoDocument9 pagesBalneoVlad ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes Affecting Various Sytem in Older AdultsDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes Affecting Various Sytem in Older AdultsDERRICKKEANNo ratings yet
- Abad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAbad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIzhiel AbadNo ratings yet
- NCP Mics11 MedwardDocument7 pagesNCP Mics11 MedwardAbegail ReyesNo ratings yet
- World Physical Therapy DayDocument18 pagesWorld Physical Therapy DaySu AlexNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument1 pageFractureReechie TeasoonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Length Tension Testing Book 1, Lower Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesFrom EverandLength Tension Testing Book 1, Lower Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Brain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1From EverandBrain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1No ratings yet
- Senior Stretch Revolution: Transforming Lives Through FlexibilityFrom EverandSenior Stretch Revolution: Transforming Lives Through FlexibilityNo ratings yet
- Med SurgDocument2 pagesMed SurgRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- Group 1 PecosyDocument17 pagesGroup 1 PecosyRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- PECOSY Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesPECOSY Reaction PaperRoscoe ParaanNo ratings yet
- CL489F Physiotherapy Reassessment ReportDocument4 pagesCL489F Physiotherapy Reassessment Reportnaeemullah100% (1)
- NIOSH Hazardous DrugsDocument22 pagesNIOSH Hazardous DrugsjimstasonNo ratings yet
- Big Sand Lake Property Owners Association LTR Rev 1 Autosaved 1Document3 pagesBig Sand Lake Property Owners Association LTR Rev 1 Autosaved 1api-267943837No ratings yet
- Pre-Marital QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesPre-Marital Questionnairenajwa husnaNo ratings yet
- Science Heart ProjectDocument6 pagesScience Heart ProjectJerryNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Glands, High Calcium, and HyperparathyroidismDocument2 pagesParathyroid Glands, High Calcium, and HyperparathyroidismsyafeiNo ratings yet
- Mba 1 in PDFDocument41 pagesMba 1 in PDFtheshoeslover1No ratings yet
- Comparison of Endoscopic Cartilage Myringoplasty in Dry and Wet Ears With Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument6 pagesComparison of Endoscopic Cartilage Myringoplasty in Dry and Wet Ears With Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediafatinfatharaniNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Malls and Shopping CentresDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Malls and Shopping CentresVanida SuwannoNo ratings yet
- HRM Final ProjectDocument8 pagesHRM Final ProjectAZAHR ALINo ratings yet
- Medical Ethics For Doctors in EthiopiaDocument41 pagesMedical Ethics For Doctors in EthiopiaBiruk Abebe100% (1)
- Karbohidrat KuliahDocument38 pagesKarbohidrat KuliahMOCHILNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY CollectionDocument12 pagesOBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY CollectionAhmad Syahmi YZNo ratings yet
- The Independent Review of Childrens Social Care Final ReportDocument278 pagesThe Independent Review of Childrens Social Care Final ReportNeil ShellardNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Bahasa Inggris Untuk Kelas 9: I. Choose The Best Answer by Crossing A, B, C or D!Document6 pagesSoal Pat Bahasa Inggris Untuk Kelas 9: I. Choose The Best Answer by Crossing A, B, C or D!Jovan SitinjakNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Mid Term ExamDocument3 pagesLab 3 Mid Term ExamAudrey AndinoNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Instrumentation System:-: Amitshanu - inDocument5 pagesBasic Medical Instrumentation System:-: Amitshanu - inÃmît ShâñúNo ratings yet
- 1 - Class 5 - Healthcare Information Systems - DR - HananDocument35 pages1 - Class 5 - Healthcare Information Systems - DR - HananHanan AlkorashyNo ratings yet
- Holy Basil: Cabangbang, Mathews H. BSHM 2BDocument3 pagesHoly Basil: Cabangbang, Mathews H. BSHM 2BAlexis A. AguilarNo ratings yet
- MJPJAY Procedures 996Document58 pagesMJPJAY Procedures 996bhushan adhariNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Health, Wellness and Well-BeingDocument4 pagesConcepts of Health, Wellness and Well-BeingEthel May AlabastroNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet For Week 1-7 Diass q2Document20 pagesAnswer Sheet For Week 1-7 Diass q2Ben Jacob LarguezaNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid TrainingDocument109 pagesBasic First Aid TrainingFarrukh AhmedNo ratings yet
- TFN Chapter 2Document97 pagesTFN Chapter 2mx odd100% (1)
- Jurnal Transfusi Darah 2Document11 pagesJurnal Transfusi Darah 2widiamNo ratings yet
- Script Assessment of The Head and NeckDocument5 pagesScript Assessment of The Head and NeckKolours KoloursNo ratings yet
- 49 Alcare Website: Permanent No. Referred by Pat. Address: Ms. Sneha Saikia: 486069 Lab No. Age / SexDocument1 page49 Alcare Website: Permanent No. Referred by Pat. Address: Ms. Sneha Saikia: 486069 Lab No. Age / SexTina SaikiaNo ratings yet
- CT Thorax HRCT: TechniqueDocument2 pagesCT Thorax HRCT: TechniqueAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Fire Door Maintenance GuideDocument19 pagesFire Door Maintenance GuideRuslan ZhivkovNo ratings yet