Professional Documents
Culture Documents
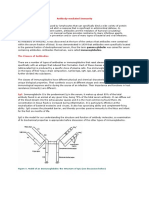
Antibodies
Antibodies
Uploaded by
Cherry AbañoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antibodies
Antibodies
Uploaded by
Cherry AbañoCopyright:
Available Formats
Antibodies Function How is it produced?
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) IgG antibodies are found in blood IgG is found in both fetal and adult
and extracellular fluid, where they livers, and it is thought to be
can neutralize toxins, viruses, and produced locally by B lymphocytes
bacteria, opsonize them for or transported from the blood in the
phagocytosis, and activate the form of immune complexes.
complement system. Furthermore, IgG concentrations in
hepatic and gall bladder bile have
been found to be high in both adult
humans and rats.
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) The most abundant type of antibody The majority of IgA is generated by
in the body, comprising most of the gastrointestinal lymphoid tissue in
immunoglobulin in secretions and a most higher vertebrates, with minor
significant amount of circulating amounts synthesized at other
immunoglobulin. In secretions, it mucosal locations such as the
serves to protect the mucosal respiratory system, salivary glands,
tissues from microbial invasion and and reproductive tract. Mammary
maintain immune homeostasis with tissue includes a large number of
the microbiota. IgA-producing cells during lactation.
Because the bulk of them are
assumed to move from the gut,
protective IgA antibodies produced
by the mother against
gastrointestinal organisms in the
environment may be passed on to
the newborn through breast
feeding.
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) IgM is not only the initial line of IgM is the primary antibody
defense for the host against produced during an initial antigen
infections, but it also plays a vital challenge.
role in immune modulation and
immunological tolerance.
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) IgD is a B cell antigen receptor that IgD is also produced in a secreted
can help in B cell maturation, form, which can be found in trace
maintenance, activation, and amounts in blood serum.
silencing. Although its precise
function is unknown, IgD may play a
role in humoral immune responses
by regulating B cell selection and
homeostasis.
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) IgE is the least common, with a IgE is produced by plasma cells in
serum concentration 10,000 times lymph nodes draining the site of
that of IgG. However, IgE levels rise antigen entry or by plasma cells
dramatically in allergic illnesses derived from germinal centers
including bronchopulmonary growing within inflamed tissue at
aspergillosis and parasitic infections the sites of allergic responses.
like schistosomiasis.
You might also like
- Aoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementDocument49 pagesAoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementJordan67% (3)
- 1358453842.3856hematology Question BankDocument182 pages1358453842.3856hematology Question BankKay Bristol100% (1)
- Immunoglobulin ADocument7 pagesImmunoglobulin AsuperlalacuteNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulin GDocument1 pageImmunoglobulin GJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- G. CHIRICO Immunologic Components of Human Milk PDFDocument4 pagesG. CHIRICO Immunologic Components of Human Milk PDFJose Garcia DeniaNo ratings yet
- Types of ImmunoglobulinDocument14 pagesTypes of ImmunoglobulinZubair AlamNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and Immunity 2Document2 pagesLymphatic System and Immunity 2Joven GloriaNo ratings yet
- AntibodyDocument10 pagesAntibodyRokhmat Bintang DjaisNo ratings yet
- Microbiology II 2 (Antigens &antibodies)Document18 pagesMicrobiology II 2 (Antigens &antibodies)lmar696210No ratings yet
- Bovine IgG Milk Colostrum Dietary Supplement Analysis Review Gapper 2007Document17 pagesBovine IgG Milk Colostrum Dietary Supplement Analysis Review Gapper 2007Don OtterNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins: Submitted byDocument8 pagesImmunoglobulins: Submitted byNoman AnwarNo ratings yet
- Antibody and Its Types: Submitted To: Dr. Zahid Amin Kashoo. Deptt. of Veteriniary MicrobiologyDocument23 pagesAntibody and Its Types: Submitted To: Dr. Zahid Amin Kashoo. Deptt. of Veteriniary Microbiologyjunaid hassanNo ratings yet
- List of ImmunoglobulinsDocument2 pagesList of ImmunoglobulinsYagnik BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins: NotesDocument4 pagesImmunoglobulins: NotesJerald BennyNo ratings yet
- Lahore College For Women University: Biochemistry AssignmentDocument9 pagesLahore College For Women University: Biochemistry AssignmentAzka AsimNo ratings yet
- Preconception Allergen Sensitization Can Induce B10 Cells in Offspring - A Potential Main Role For Maternal IgGDocument11 pagesPreconception Allergen Sensitization Can Induce B10 Cells in Offspring - A Potential Main Role For Maternal IgGDaniel Carvalho de AraújoNo ratings yet
- Immunizing Agents MarieDocument37 pagesImmunizing Agents MarieMaariyah J NainaNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument49 pagesImmunityfaheemakbar8816No ratings yet
- (6P) Basic Concepts in Immunity and InflammationDocument6 pages(6P) Basic Concepts in Immunity and InflammationNegrus Stefan100% (1)
- Structure of ImmunoglobulinDocument4 pagesStructure of ImmunoglobulinCarla Lagar FloresNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Pitch DeckDocument7 pagesHealthcare Pitch DeckDragan LuciaNo ratings yet
- Arsi University: Review On Mucosal Immune ResponseDocument17 pagesArsi University: Review On Mucosal Immune Responsehngdf bfbnNo ratings yet
- 3.feb Seminar - Caries ImmunologyDocument73 pages3.feb Seminar - Caries Immunologysaloni singhNo ratings yet
- Antigens & Antibodies: 3. 1 - Factors Affecting Immune ResponseDocument7 pagesAntigens & Antibodies: 3. 1 - Factors Affecting Immune ResponseAmanda AmiraultNo ratings yet
- Antibody Iggandiga: Presented by Syed - Khaja.Ali Uddin M.S.D (Endodontics)Document39 pagesAntibody Iggandiga: Presented by Syed - Khaja.Ali Uddin M.S.D (Endodontics)Ali SyedNo ratings yet
- L8 - Complement SystemDocument7 pagesL8 - Complement SystemmujahidatinstituteNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument20 pagesUntitledDouaa BenNo ratings yet
- Dynamic of AntibodyDocument34 pagesDynamic of AntibodyututelNo ratings yet
- Humoral Immune ResponseDocument34 pagesHumoral Immune ResponseAnjiNo ratings yet
- Chap 16 Part 2 Major Arms of The Immune System Humoral Immunity (Antibodies)Document5 pagesChap 16 Part 2 Major Arms of The Immune System Humoral Immunity (Antibodies)clrssNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immunity Natural Antibodies Bridge Innate And: References Cites 124 ArticlesDocument9 pagesAdaptive Immunity Natural Antibodies Bridge Innate And: References Cites 124 ArticlesAndikhaNo ratings yet
- Finals (Mga Wala Sa Module)Document9 pagesFinals (Mga Wala Sa Module)Krisha CafongtanNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYLAXIS - MedSurgDocument1 pageANAPHYLAXIS - MedSurgAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BTDocument27 pagesUnit-3 BTDhananjay KhadeNo ratings yet
- Non-IgE Mediated Food AllergyDocument8 pagesNon-IgE Mediated Food AllergyDede NovHyNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulin SDocument22 pagesImmunoglobulin Scessy.manusig9No ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW CDC Govvaccinespubspinkbookdownloadsprinvac PDFDocument8 pagesHTTPSWWW CDC Govvaccinespubspinkbookdownloadsprinvac PDFSubash KhatiwadaNo ratings yet
- Script ImmDocument14 pagesScript ImmVivianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunoglobulins.: Igm Igg Iga Ige IgdDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Immunoglobulins.: Igm Igg Iga Ige IgdHashamNo ratings yet
- Inflammation & Immunity Final Final FinalDocument53 pagesInflammation & Immunity Final Final FinalMyzing OraaNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding, The Immune Response, and Long-Term Health: Review ArticleDocument5 pagesBreastfeeding, The Immune Response, and Long-Term Health: Review ArticleAk GirlNo ratings yet
- Inmunologia Celulas T y BDocument18 pagesInmunologia Celulas T y BLisa MarroquinNo ratings yet
- ImmuneDocument12 pagesImmuneoldpenguinNo ratings yet
- Plasma Proteins-IIDocument25 pagesPlasma Proteins-IIZoraiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2020 Biochem Activity 11 PDFDocument5 pages2020 Biochem Activity 11 PDFGabrielle John HernaezNo ratings yet
- Macpherson 2001Document15 pagesMacpherson 2001carolineNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Imunologi: DR Ruswana Anwar Spog Pembimbing: DR Tita Husnitawati MajidspogDocument42 pagesKonsep Dasar Imunologi: DR Ruswana Anwar Spog Pembimbing: DR Tita Husnitawati Majidspogyuyu tuptupNo ratings yet
- 2020 Biochem Activity 13Document5 pages2020 Biochem Activity 13Gabrielle John HernaezNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulin and Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument43 pagesImmunoglobulin and Monoclonal AntibodiesDr.O.R.GANESAMURTHINo ratings yet
- Analysis of Bovine Immunoglobulin G in Milk, Colostrum and Dietary Supplements: A ReviewDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Bovine Immunoglobulin G in Milk, Colostrum and Dietary Supplements: A ReviewGomatheeswari100% (1)
- Study Stack - Immunology Final Table Review PDFDocument8 pagesStudy Stack - Immunology Final Table Review PDF장주연No ratings yet
- ImmunoserologyDocument3 pagesImmunoserologyanon_686369323No ratings yet
- Siga UsusDocument9 pagesSiga UsusMira MaindraNo ratings yet
- Review of sIgADocument4 pagesReview of sIgALuis Castro Xtrm100% (1)
- Antigen and Antibodies-2021Document37 pagesAntigen and Antibodies-2021مروه عماد عيسىNo ratings yet
- Muscozol Anti BodiesDocument6 pagesMuscozol Anti BodiesAli SyedNo ratings yet
- Immuno 3Document5 pagesImmuno 3diwanakram83No ratings yet
- AntibodiesDocument1 pageAntibodiesgeislernetNo ratings yet
- Defence Mechanism of BodyDocument26 pagesDefence Mechanism of BodyTika GurungNo ratings yet
- Antigens and AntibodiesDocument4 pagesAntigens and AntibodiesSoni VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Cultivating Wellness The Comprehensive Guide to Probiotics and Human HealthFrom EverandCultivating Wellness The Comprehensive Guide to Probiotics and Human HealthNo ratings yet
- Management of Infections in the Immunocompromised HostFrom EverandManagement of Infections in the Immunocompromised HostBrahm H. SegalNo ratings yet
- Blood TypingDocument2 pagesBlood TypingCherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication: Clear Statements Are Important As It Makes Understanding EasierDocument1 pageEffective Communication: Clear Statements Are Important As It Makes Understanding EasierCherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- Psych 100Document1 pagePsych 100Cherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- Hist100 M3Document2 pagesHist100 M3Cherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- HIST100Document2 pagesHIST100Cherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- Florence NifhtingaleDocument1 pageFlorence NifhtingaleCherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- HISTDocument2 pagesHISTCherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- Analysis PDFDocument1 pageAnalysis PDFCherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- CommunciationDocument1 pageCommunciationCherry AbañoNo ratings yet
- Nobel Prize 2018 - Complete Winners ListDocument3 pagesNobel Prize 2018 - Complete Winners Listsudhir roenNo ratings yet
- Protein Microarray Naveed Up MushtaqDocument16 pagesProtein Microarray Naveed Up MushtaqAngumaniNo ratings yet
- Uso de CollpasDocument8 pagesUso de CollpasAna AmableNo ratings yet
- Plant Review Sheet - BiologyDocument2 pagesPlant Review Sheet - Biologywhipporwill13No ratings yet
- Blood and BloodstainsDocument7 pagesBlood and BloodstainsJames Van Arquero NaronNo ratings yet
- The Forced-Choice Paradigm and The Perception of Facial Expressions of EmotionDocument11 pagesThe Forced-Choice Paradigm and The Perception of Facial Expressions of EmotionjnkjnNo ratings yet
- Oase FT WG LM Pricelist 2010 EurDocument12 pagesOase FT WG LM Pricelist 2010 EurAneta AtanasovaNo ratings yet
- Lakshya Classes Mahua: CLASS 10. Biology (Heredity)Document4 pagesLakshya Classes Mahua: CLASS 10. Biology (Heredity)Lakshya Classes, MAHUA LC,MNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument70 pagesProjectRumi BegumNo ratings yet
- Growing Taller ForeverDocument44 pagesGrowing Taller ForeverDr Hector C Sikazwe0% (2)
- Separation and Isolation of Phytochemicals RevDocument90 pagesSeparation and Isolation of Phytochemicals RevWendz BouvierNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Genetics A Conceptual Approach Sixth Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Genetics A Conceptual Approach Sixth Edition PDF Full Chaptermoorpandaddyn2tmh1100% (21)
- M.Sc. (Ag.) Agronomy (F&F) SyllabusDocument25 pagesM.Sc. (Ag.) Agronomy (F&F) SyllabusAbhishek MauryaNo ratings yet
- Thermo Scientific 2020 - PCR Reagents Price ListDocument16 pagesThermo Scientific 2020 - PCR Reagents Price Listpuspita 2002No ratings yet
- LABORATORY EXERCISE Annelida MergedDocument32 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE Annelida MergedFernando Martin BarbaNo ratings yet
- Ped 221 Developmental PsychologyDocument42 pagesPed 221 Developmental PsychologymubarakNo ratings yet
- Crystal DatabaseDocument64 pagesCrystal DatabaseJoe Dorje100% (4)
- Pediatric Nursing 1: Points 100 Questions 100 Time Limit 90 MinutesDocument54 pagesPediatric Nursing 1: Points 100 Questions 100 Time Limit 90 MinutesSean Lloyd RigonNo ratings yet
- Questions of The Introduction: By: DR. Khaled MiladDocument7 pagesQuestions of The Introduction: By: DR. Khaled MiladMahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Jurnal InternasionalDocument4 pagesJurnal Internasionalckcy ahaiNo ratings yet
- Wonderful EarthDocument1 pageWonderful EarthĐỗ Quỳnh TrangNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and ControlDocument25 pagesChapter Seven The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and ControlCalapati, Jhon Rovic R.100% (1)
- Agricultural MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesAgricultural MicrobiologyManjunath RamannaNo ratings yet
- Las-Science 6 Quarter 2 Week 1Document4 pagesLas-Science 6 Quarter 2 Week 1EvelynMartinezNo ratings yet
- General Microbiology Quiz - Franyce ThomasDocument3 pagesGeneral Microbiology Quiz - Franyce Thomasfranyce thomasNo ratings yet
- Transkrip Akademik: SpecimenDocument2 pagesTranskrip Akademik: SpecimenYolaShintaNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL PT - 8Document4 pagesSSC CGL PT - 8Rovin AshbelNo ratings yet
- Russian CurrentDocument10 pagesRussian Currentdrng4867% (3)