Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Different Types of Adverbs With Examples
Different Types of Adverbs With Examples
Uploaded by
Rocio FernándezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Different Types of Adverbs With Examples
Different Types of Adverbs With Examples
Uploaded by
Rocio FernándezCopyright:
Available Formats
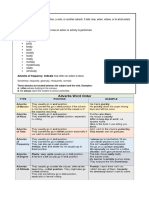
Different Types of Adverbs with Examples
Let us now take a look at each of these adverb types in detail.
Adverbs of Manner: These adverbs are those that describe the manner in which an
action is done. Basically, it can be said that the adverbs of manner answer the question
‘how’.
Examples of adverbs of manner:
Quickly, promptly, clearly, slowly, gradually, eventually, rapidly, seriously, instantly, keenly, etc.
Adverbs of Time: As the name suggests, the adverbs of time are used to tell the
reader when some action is occurring. Adverbs of time include general time periods
and specific times. We can identify an adverb of time by asking the question ‘when’.
Examples of adverbs of time:
Now, soon, today, tomorrow, the day after tomorrow, next month, recently, forever, etc.
Adverbs of Place: These adverbs are used to indicate where the action mentioned in
the sentence is taking place. Adverbs of place can be identified by asking the question
‘where’.
Examples of adverbs of place:
Somewhere, anywhere, nowhere, here, outside, inside, wherever, elsewhere, left, right, north,
east, south, west, etc.
Adverbs of Frequency: These adverbs are used to denote how often an action or
event is happening. The adverbs of frequency can be recognised by asking the
question ‘how often’.
Examples of adverbs of frequency:
Seldom, rarely, never, often, weekly, monthly, yearly, annually, usually, sometimes,
occasionally, constantly, frequently, etc.
Adverbs of Degree: These adverbs are used to indicate how intense an action of
quality is. It is used to describe adjectives and adverbs. For instance, an adverb of
manner expresses how fast or how slow a vehicle is moving, how hot or cold the
weather is, how interesting or boring a movie is and so on.
Examples of adverbs of degree:
Very, too, extremely, much, more, most, little, less, incredibly, totally, greatly, hardly, deeply,
barely, etc.
Conjunctive Adverbs: Conjunctive adverbs perform a little differently from the other
types of adverbs. These adverbs are seen to act like a conjunction to link two
sentences or clauses together and hence the name, ‘conjunctive adverbs’.
Examples of conjunctive adverbs:
However, nevertheless, meanwhile, therefore, instead, likewise, notably, subsequently, rather,
namely, on the other hand, incidentally, in addition to, etc.
You might also like
- Different Types of Adverbs With ExamplesDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Adverbs With ExamplesAustin FerweloNo ratings yet
- English 100Document3 pagesEnglish 100marymarielcatahayNo ratings yet
- CReativeDocument19 pagesCReativeCuddle BunnyNo ratings yet
- Adverb 1 PDFDocument62 pagesAdverb 1 PDFAxel Joy AlonNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Describe VerbsDocument11 pagesAdverbs Describe Verbsjalebie talabangNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument26 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisMelly ShahabNo ratings yet
- Types of Adverbs As Part of Speech: Adverb: It Is A Word Used To Modify A Verb, An Adjective, Another Adverb or AnDocument9 pagesTypes of Adverbs As Part of Speech: Adverb: It Is A Word Used To Modify A Verb, An Adjective, Another Adverb or AnHammad Ali ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Adverb and Its TypesDocument9 pagesAdverb and Its TypesNOELNo ratings yet
- Functional English 2Document21 pagesFunctional English 2Afzala YaseenNo ratings yet
- An AdverbDocument4 pagesAn AdverbBry AnNo ratings yet
- Performance Task No.1 AdverbsDocument11 pagesPerformance Task No.1 Adverbsgemma minaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs FileDocument7 pagesAdverbs FileCzarinah PalmaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Are Words That Modify VerbsDocument12 pagesAdverbs Are Words That Modify VerbsrajuashnaikNo ratings yet
- AdverbDocument9 pagesAdverbPuja NurmalaNo ratings yet
- ADVERBDocument8 pagesADVERBvitozNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Adverbs Adverbs Adverbs: Adverbs Usually Answer The Following QuestionsDocument7 pagesAdverbs Adverbs Adverbs Adverbs: Adverbs Usually Answer The Following QuestionsAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument39 pagesParts of SpeechRida AkramNo ratings yet
- Adverb: Rules of Using AdverbsDocument3 pagesAdverb: Rules of Using AdverbsArsalan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Adver and AdjectivesDocument7 pagesAdver and AdjectivesAmelito GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Blue Doodle Project Presentation 20240219 133719 0000Document17 pagesBlue Doodle Project Presentation 20240219 133719 0000alanNo ratings yet
- The AdverbsDocument7 pagesThe Adverbssergeyka2004No ratings yet
- AdverbDocument11 pagesAdverbV chanelNo ratings yet
- AdverbialsDocument9 pagesAdverbialsPrisha Popat100% (1)
- Week 6: Parts of Speech: AdverbsDocument22 pagesWeek 6: Parts of Speech: AdverbsVivian MwangiNo ratings yet
- Review Lessons - Language 5Document21 pagesReview Lessons - Language 5Mommy Joyee100% (1)
- Adverbs: Mohammad Farhan Abid Eham ID: 171010101001, Department of English Batch 44, Prime UniversityDocument16 pagesAdverbs: Mohammad Farhan Abid Eham ID: 171010101001, Department of English Batch 44, Prime UniversityFarhan AbidNo ratings yet
- Adverbs - Lecture I PermbledhurDocument17 pagesAdverbs - Lecture I PermbledhurFrida QordjaNo ratings yet
- Фонетика емтиханDocument4 pagesФонетика емтиханАйжан СактапбергеноваNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs LessonDocument5 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs LessonRowena LinnumNo ratings yet
- Literacy Fri 12.2.21Document9 pagesLiteracy Fri 12.2.21Ma. Antonette PanchoNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument6 pagesAdverbsAmna KhaliqNo ratings yet
- English PPT ALSDocument28 pagesEnglish PPT ALSKatrina NalanganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document25 pagesLesson 2mari silvioNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument12 pagesParts of SpeechKh adijaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs - Big List of Adverbs and Its Types - Learn What Are AdverbsDocument4 pagesAdverbs - Big List of Adverbs and Its Types - Learn What Are AdverbsSharksNo ratings yet
- Boards English Grammar Parts of Speech Adverb l2 Bhumika Chauhan 647868419Document28 pagesBoards English Grammar Parts of Speech Adverb l2 Bhumika Chauhan 647868419Umang KumarNo ratings yet
- Adverb and Its TypesDocument10 pagesAdverb and Its TypesAlex LodelNo ratings yet
- SSC Hacks - EnglishDocument202 pagesSSC Hacks - EnglishArun Dominic100% (1)
- Adverbs Adverbial PhrasesDocument12 pagesAdverbs Adverbial PhrasesLauGalindo100% (1)
- Adverbs Adverbial PhrasesDocument12 pagesAdverbs Adverbial Phrasespijawfka100% (1)
- Adverbs LessonDocument29 pagesAdverbs LessonYVONIE DEMAISIPNo ratings yet
- Doe Adverbs and AdjectivesDocument22 pagesDoe Adverbs and AdjectivesPavitra GanesanNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument30 pagesPart of SpeechKaren BlanqueraNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument4 pagesAdverbschurrito88No ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument2 pagesAdverbsChinonso KingsleyNo ratings yet
- AdverbDocument6 pagesAdverbFlorencefrom YtNo ratings yet
- AdverbiosDocument19 pagesAdverbiosaldair12No ratings yet
- Reviewing Lexical Categories: (Adjective and Adverb)Document29 pagesReviewing Lexical Categories: (Adjective and Adverb)Marianne GatchoNo ratings yet
- Adverb of Manner: These Adverbs Are Located Between The Subject and The Verb. ExamplesDocument4 pagesAdverb of Manner: These Adverbs Are Located Between The Subject and The Verb. ExamplesJan Arabella LabayNo ratings yet
- ADVERBSDocument9 pagesADVERBSCharyll MaeNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument30 pagesAdverbsVane SolisNo ratings yet
- Learn Adverbs As Part of Speech For Bank 1Document10 pagesLearn Adverbs As Part of Speech For Bank 1waseemNo ratings yet
- Adverbs-Kinds: Adverb AdjectiveDocument4 pagesAdverbs-Kinds: Adverb AdjectiveAngelus ElizabethNo ratings yet
- AdverbDocument22 pagesAdverbHema SengodanNo ratings yet
- Adverbs 7Document12 pagesAdverbs 7Kean Ejay R CelarioNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyDocument18 pagesParts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyKrishan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronouns With ExamplesDocument1 pageTypes of Pronouns With ExamplesBa DraNo ratings yet
- Macabidang - Alhazen - Adverb and Their KindsDocument3 pagesMacabidang - Alhazen - Adverb and Their KindsALLIYAH MACABIDANGNo ratings yet
- ADVERBDocument20 pagesADVERBHan YouNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - AnimalsDocument29 pagesUnit 2 - AnimalsRocio FernándezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Science and ComputersDocument18 pagesUnit 1 - Science and ComputersRocio FernándezNo ratings yet
- BOOKLET CUFBA - Expresion EscritaDocument118 pagesBOOKLET CUFBA - Expresion EscritaRocio FernándezNo ratings yet
- SummarryDocument1 pageSummarryRocio FernándezNo ratings yet
- AnimeDocument2 pagesAnimeRocio FernándezNo ratings yet