Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development of Surfaces
Development of Surfaces
Uploaded by
Unamgri O0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThis document provides instructions for 8 problems involving the parallel line development and radial line development of various 3D shapes. The shapes include prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and frustums. For each problem, the document specifies the dimensions and orientation of the shape, as well as any cutting planes, and instructs the reader to draw the development of the resulting surfaces. The problems cover a range of techniques for creating 2D net representations of 3D objects.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides instructions for 8 problems involving the parallel line development and radial line development of various 3D shapes. The shapes include prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and frustums. For each problem, the document specifies the dimensions and orientation of the shape, as well as any cutting planes, and instructs the reader to draw the development of the resulting surfaces. The problems cover a range of techniques for creating 2D net representations of 3D objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesDevelopment of Surfaces
Development of Surfaces
Uploaded by
Unamgri OThis document provides instructions for 8 problems involving the parallel line development and radial line development of various 3D shapes. The shapes include prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and frustums. For each problem, the document specifies the dimensions and orientation of the shape, as well as any cutting planes, and instructs the reader to draw the development of the resulting surfaces. The problems cover a range of techniques for creating 2D net representations of 3D objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
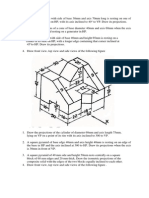
Computer Aided Engineering Drawing
Development of Surfaces
Parallel Line Development:
1. A square prism of base side 30 mm and axis length 60 mm is resting on HP on its
base with all the vertical faces being equally inclined to VP. It is cut by an inclined
plane 600 to HP and perpendicular to VP and is passing through a point on the axis
at a distance 15 mm from the top face. Draw the development of the lower portion
of the prism.
2. Draw the Development of the lateral surfaces of a Pentagonal prism of 30mm base
edges and 60mm height. The prism rests on the HP on its base with one of its
lateral surfaces parallel to the VP. A section plane cuts the solid at its mid-point at
45° to the HP & 90° to the VP.
3. A cube of side 40 mm is resting with its base on HP such that one of its vertical
faces is inclined at 300 to the VP. It is cut by a section plane perpendicular to VP,
inclined to HP at an angle 450 and passes through the midpoint of the axis. Draw
the development of the lower lateral surface of the cube.
4. Draw the development of the truncated portion of the lateral faces of a pentagonal
prism of 20 mm sides of base and 50 mm height standing vertically with one of its
rectangular faces parallel to VP and nearer to it so as to produce a one piece
development. The inclined face of the truncated prism is 300 to its axis and passes
through the right extreme corner of the top face of the prism.
5. A pentagonal prism of 30 mm side of base and height 50 mm lies with its base on
HP such that one of the rectangular faces is inclined at 400 to VP. It is cut to the
shape of a truncated pyramid with the truncated surface inclined at 300 to the axis
so as to pass through a point on it 30 mm above the base. Develop the truncated
portion of the prism so as to produce a one piece development.
6. Draw the Development of the lateral surfaces of a Pentagonal prism of 30mm base
edges and 60mm height. The prism rests on the HP on its base with one of its
lateral surfaces parallel to the VP. A section plane cuts the solid at its mid-point at
45° to the HP & 90° to the VP.
7. A cylinder of base diameter 40 mm and axis length 50 mm is cut by a section plane
which is perpendicular to VP and inclined at 300 to HP and passing through a point
10 mm above the midpoint of the axis. Draw the development of the lateral surface
of the cylinder
Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NIE
Computer Aided Engineering Drawing
8. A vertical cylinder of base diameter 50 mm and axis length 60 mm is cut by two
planes which are perpendicular to VP and inclined at 450 to HP and passing
through either side the centre point of the top face. Draw the development of the
lateral surface of the cylinder
Radial Line Development:
1. A square pyramid of 25 mm base edge and 50 mm height rests with its base on HP
with all of its base edges equally inclined to VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular
to VP and inclined to HP at 600, passing through the extreme right corner of base.
Draw the development of its lateral surfaces.
2. Draw the development of lateral surfaces of a pentagonal pyramid of sides 35mm
and height of 70mm resting on HP. A section plane parallel to slant edge cuts the
axis at 10mm from apex.
3. A frustum of a pentagonal pyramid, smaller base sides 16 mm and bigger top face
sides 32 mm and height 40 mm, is resting on the HP on its smaller base, with one
of its base sides parallel to the VP. Draw the development of its lateral surfaces.
4. A hexagonal pyramid 25 mm side of base and axis 65 mm long is resting on its base
on HP with one of the edges of the base parallel to VP. It is cut by a vertical section
plane at a distance of 8 mm from the axis towards its right. Draw the development
of its lateral surfaces.
5. The inside of a hopper of a flour mill is to be lined with thin sheet. The top and
bottom of the hopper are regular pentagons with each side equal to 30 mm and
22.5 mm respectively. The height of the hopper is 30 mm. Draw the shape of the
sheet to which it is to be cut so as to fit into the hopper.
6. A cone base 50 mm diameter and axis 60 mm long is resting with its base on HP it
is cut by a section plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 60° to the HP and
bisecting axis. Draw the development of the lateral surface.
7. The frustum of a cone of base diameter 60 mm, top diameter 30 mm and height 40
mm rests on the HP. A horizontal hole of diameter 20 mm is drilled through the
midpoint of the axis. Draw the development of the lateral surface.
8. A cone of base diameter 50 mm and height 60 mm is resting with its base on HP.
A section plane cuts the solid at its mid-point at 45° to the HP & 90° to the VP.
Draw the development of its lateral surface.
Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, NIE
You might also like
- ED Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesED Important QuestionsNitin NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- Math5 3rd PeriodicalDocument7 pagesMath5 3rd PeriodicalSteve Maiwat100% (3)
- Department of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-VDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-Vramu vasaNo ratings yet
- EG Module 3 QuestionsDocument1 pageEG Module 3 QuestionsAjithkumar K.TNo ratings yet
- EGDocument4 pagesEGbalajimeieNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Sample Paper, NIT CalicutDocument3 pagesEngineering Graphics Sample Paper, NIT CalicutMATHEW GEORGENo ratings yet
- Question Plate For EgDocument4 pagesQuestion Plate For EgNagaraj Muniyandi0% (1)
- EG Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesEG Practice QuestionsAjithkumar K.TNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)A.R. Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EGDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank EGMohd AbrarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 06 Development of Lateral Surfaces Question BankDocument2 pagesUNIT 06 Development of Lateral Surfaces Question BanksirfentertertainmenthaiNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Questions (Iae III)Document5 pagesUnit IV Questions (Iae III)Anonymous 4p20nXgWDZNo ratings yet
- 5&6 ModuleDocument3 pages5&6 Modulerajee101No ratings yet
- Unit IV Section of SolidsDocument14 pagesUnit IV Section of SolidsPrashant UbarhandeNo ratings yet
- GE 2111: Engineering Graphics:: Unit IV - Development of SolidsDocument1 pageGE 2111: Engineering Graphics:: Unit IV - Development of Solidsmuthupecmec4908No ratings yet
- EG Important QuestionDocument1 pageEG Important QuestionsenthurrNo ratings yet
- Caed NotesDocument46 pagesCaed Notesrohanshetty5512No ratings yet
- Section of Solid and Development of SurfacesDocument2 pagesSection of Solid and Development of SurfacesPrashantNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IV (EG&D)Document1 pageAssignment - IV (EG&D)Sajad HaqueNo ratings yet
- QuestionBank Projection of SolidsDocument4 pagesQuestionBank Projection of SolidsAmritanshu AmritNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 CONCISE Q A Sections of Solids and Development of SolidsDocument9 pagesUNIT 5 CONCISE Q A Sections of Solids and Development of SolidsVathyasamNo ratings yet
- Development of Surfaces 240416Document7 pagesDevelopment of Surfaces 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiNo ratings yet
- Section of SolidsDocument4 pagesSection of Solidsanandandmeena100% (1)
- Qus PaperDocument6 pagesQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 & 8: Sections of Solids & Development of SurfacesDocument1 pageAssignment 7 & 8: Sections of Solids & Development of SurfacesAnanyaMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Projection of SolidsDocument2 pagesProjection of SolidsanandandmeenaNo ratings yet
- Geethanjali Institute of Science & Technology: NelloreDocument2 pagesGeethanjali Institute of Science & Technology: Nelloreramu vasaNo ratings yet
- Model Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantDocument1 pageModel Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantculvertsNo ratings yet
- Solids HWDocument2 pagesSolids HWnavneet patilNo ratings yet
- Section of Solids and Devlopment of SurfaceDocument3 pagesSection of Solids and Devlopment of Surfacewww.venky9876No ratings yet
- EnggqpDocument4 pagesEnggqpRambabuDaraNo ratings yet
- Projection of SolidsDocument1 pageProjection of SolidsKHUSHBOO KHUSHBOONo ratings yet
- 05 - Projections of SolidsDocument2 pages05 - Projections of SolidsSumukh KiniNo ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankflorenceprasadNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsDhanushree DhanuNo ratings yet
- E.G Q.B. Solutions - Part BDocument28 pagesE.G Q.B. Solutions - Part BTeegavarapu Sriram hrithikNo ratings yet
- Caedp PaperDocument3 pagesCaedp PaperKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Projection of SolidDocument2 pagesUnit 3 - Projection of Solidranjith kumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics QB PDFDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics QB PDFKarthi SanNo ratings yet
- Woldia University Technology of Faculty Department of Mechanical Engineering Target Group:-Technical Drawing and Design Summer StudentDocument2 pagesWoldia University Technology of Faculty Department of Mechanical Engineering Target Group:-Technical Drawing and Design Summer StudenttadesseNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDocument6 pagesEngineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- MCP 100 Lab Sheet 5Document1 pageMCP 100 Lab Sheet 5Prakhar AnandNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document1 pageAssignment 8mohimab230105eeNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Engineering Drawing: (2017-18 Odd Semester) Assignment 7 & 8: Sections of Solids & Development of SurfacesDocument2 pagesComputer Aided Engineering Drawing: (2017-18 Odd Semester) Assignment 7 & 8: Sections of Solids & Development of SurfacesdsdNo ratings yet
- Sheets 7 To14Document16 pagesSheets 7 To14myselfnoobcoderNo ratings yet
- Questions of Projection of PlanesDocument2 pagesQuestions of Projection of PlanesSubhajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics Question BankSriram JNo ratings yet
- 22ME160-Engg Graphics Worksheet 6 - 2023-24Document1 page22ME160-Engg Graphics Worksheet 6 - 2023-24ShankarNo ratings yet
- SBM College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul-5 Engineering Graphics-I Year (2012-13) Sectioning of SolidsDocument4 pagesSBM College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul-5 Engineering Graphics-I Year (2012-13) Sectioning of SolidsSahaya RajNo ratings yet
- Projection Solids PrismDocument2 pagesProjection Solids PrismKarthick DavoothNo ratings yet
- Eg 2 TutorialDocument10 pagesEg 2 TutorialGanni GowthamNo ratings yet
- Aux Projection 240416Document2 pagesAux Projection 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiNo ratings yet
- Eg - Unit - 5 Assignment QuestionDocument1 pageEg - Unit - 5 Assignment QuestionsureshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Graphics - Question BankimamuddeenNo ratings yet
- Eg Unit 4Document6 pagesEg Unit 4rajasekaran23230% (1)
- Unit 5Document13 pagesUnit 5gansumaaNo ratings yet
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument11 pagesKings: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrammit2007No ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet No. 5 & 6 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment Sheet No. 5 & 6 PDFArnav Anuj KasarNo ratings yet
- Projection of SolidsDocument4 pagesProjection of SolidsSharon ElijahNo ratings yet
- Development of Solid SectionsDocument1 pageDevelopment of Solid SectionsSaumya SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Visualizing and Describing Solid Figures and Making Models of Different Solid FiguresDocument6 pagesLesson: Visualizing and Describing Solid Figures and Making Models of Different Solid FiguresChikay Ko UiNo ratings yet
- Conic Section - SolutionsDocument12 pagesConic Section - SolutionsFrank MartinezNo ratings yet
- Circles Ad Infinitum - Nrich - MathsDocument1 pageCircles Ad Infinitum - Nrich - MathsgonsalvisNo ratings yet
- Bentuk Dan Ruang: Shapes and SpaceDocument4 pagesBentuk Dan Ruang: Shapes and SpaceMohd Safwan EwanNo ratings yet
- Ellipse-04 - Exercise LevelDocument17 pagesEllipse-04 - Exercise LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Lect-2 Parabolla and Ellipse PropertiesDocument36 pagesLect-2 Parabolla and Ellipse PropertiesSachin SawantNo ratings yet
- Surface Areas and Volumes: Cuboid Whose Length L, Breadth B and Height HDocument8 pagesSurface Areas and Volumes: Cuboid Whose Length L, Breadth B and Height HKrishna Moorti MishraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Constructing Geometrical FiguresDocument40 pagesModule 2 - Constructing Geometrical FiguresHelen AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Brief Elus Cohen Invocations For BeginniDocument1 pageBrief Elus Cohen Invocations For BeginniSebastien McCollin100% (1)
- InvolutesDocument13 pagesInvolutesmbeaelnaaNo ratings yet
- IIT - Notas de Hipérbole PDFDocument27 pagesIIT - Notas de Hipérbole PDFlucasNo ratings yet
- Purple Comet MATH MEET April 2014Document8 pagesPurple Comet MATH MEET April 2014विनय खरेNo ratings yet
- Engineering GrpaphicsDocument283 pagesEngineering GrpaphicsB ruikarNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet - Midterm 2.2023 p1 Exact Math (Main Test)Document2 pagesAnswer Sheet - Midterm 2.2023 p1 Exact Math (Main Test)maw.teacher.nuttyyNo ratings yet
- 1 Conic Sections (Summative)Document2 pages1 Conic Sections (Summative)Field StudyNo ratings yet
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - AllDocument29 pagesSLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - Allwww.bhawesh.com.np75% (8)
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument18 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationRoselle Vallero SalaysayNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 8 Geometry of Shape and SizeDocument25 pagesEASE Module 8 Geometry of Shape and SizeGenalyn Tambiao AchanzarNo ratings yet
- Double Bubble Theorem - WikipediaDocument40 pagesDouble Bubble Theorem - Wikipediasterling goinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Knowledge - Grade 8Document21 pagesUnit 3 - Knowledge - Grade 8RoopaNo ratings yet
- Disentangling A Triangle - Jerzy Kocik and Andrzej SoleckiDocument2 pagesDisentangling A Triangle - Jerzy Kocik and Andrzej SoleckiAltananyNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Points, Lines, and CirclesDocument20 pagesAnalytic Geometry: Points, Lines, and CirclesMark Bethoven Jemio MalaluanNo ratings yet
- IGO2017Document25 pagesIGO2017denisNo ratings yet
- I. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer For The Following Questions On The Blank Before The NumberDocument17 pagesI. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer For The Following Questions On The Blank Before The NumberRhenan WafooNo ratings yet
- List of Sheets - Engineering Drawing LabDocument3 pagesList of Sheets - Engineering Drawing LabprashantattNo ratings yet
- SphereDocument8 pagesSphereDenise Ann CuencaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Area MethodDocument14 pagesChapter 34 Area Methodthorgod941500% (1)
- g8m7 Triangle Congruence WeeblyDocument54 pagesg8m7 Triangle Congruence Weeblyapi-273372560100% (1)
- KG English Preposition Worksheets Sep272018Document7 pagesKG English Preposition Worksheets Sep272018ane lwanNo ratings yet