Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Pressure Student Notes
Air Pressure Student Notes
Uploaded by
Worku Ayele0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesAir has mass and pressure due to its density. Pressure is defined as the force pushing on an area, and air pressure comes from the weight of the atmosphere pushing down. Changes in air pressure can be measured using barometers like mercury or aneroid barometers. Air pressure is typically reported in inches of mercury for the public and millibars on weather maps. Air pressure and density decrease with increasing altitude or elevation above sea level.
Original Description:
Air pressure note
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAir has mass and pressure due to its density. Pressure is defined as the force pushing on an area, and air pressure comes from the weight of the atmosphere pushing down. Changes in air pressure can be measured using barometers like mercury or aneroid barometers. Air pressure is typically reported in inches of mercury for the public and millibars on weather maps. Air pressure and density decrease with increasing altitude or elevation above sea level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesAir Pressure Student Notes
Air Pressure Student Notes
Uploaded by
Worku AyeleAir has mass and pressure due to its density. Pressure is defined as the force pushing on an area, and air pressure comes from the weight of the atmosphere pushing down. Changes in air pressure can be measured using barometers like mercury or aneroid barometers. Air pressure is typically reported in inches of mercury for the public and millibars on weather maps. Air pressure and density decrease with increasing altitude or elevation above sea level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Ch. 1 Sec.
2 –Air Pressure – Notes
Properties of Air
Air consists of atoms and molecules which have mass, therefore air has mass.
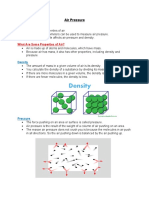
Because air has mass, it also has other properties including density and pressure.
Density is the amount of mass in a given volume.
Density = Mass ,
Volume
Pressure = The amount of force pushing on an area.
Air Pressure = the pressure caused by the weight of a column of air pushing down on an area.
-the atmosphere is heavy so why doesn’t it crush you?
-gas pushes in all directions not just downward like solids
-Air pressure can change from day to day…denser air has more mass so therefore exerts
more pressure
Measuring Air Pressure
A barometer is an instrument used to measure changes in air pressure.
A Mercury Barometer is an instrument that measures changes in air pressure,
consisting of a glass tube partially filled with mercury, with its open end
resting in a dish of mercury.
An Aneroid Barometer has an airtight metal chamber,
Units of Air Pressure
Most weather reports for the general public use inches of mercury.
National Weather Service maps indicate air pressure in millibars.
- One inch of mercury is approximately 33.87 millibars, so 30 inches of
mercury is approximately equal to 1,016 millibars.
Altitude and the Properties of Air
Altitude is elevation above sea level.
Air pressure decreases as altitude increases.
As air pressure decreases, so does density.
You might also like
- CHP 11-13 PDFDocument106 pagesCHP 11-13 PDFLittle-psyco :30% (1)
- Air Pressure - G6 Lesson NotesDocument3 pagesAir Pressure - G6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- محاضرة الاولى كيمياء 2Document13 pagesمحاضرة الاولى كيمياء 2hananshawish40No ratings yet
- What Is PressureDocument3 pagesWhat Is PressureJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure and WindsDocument10 pagesAtmospheric Pressure and Windsavani khannaNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure: Pressure Variations Across The EarthDocument2 pagesAir Pressure: Pressure Variations Across The EarthDeepa Ramiah Deepa RamiahNo ratings yet
- Air Pressue WorksheetDocument2 pagesAir Pressue Worksheetapi-368213959No ratings yet
- Sorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 1 (Las 7)Document4 pagesSorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 1 (Las 7)Jorgia lianne UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Sub Unit 1.2 - Fluid ForceDocument24 pagesSub Unit 1.2 - Fluid ForceAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- atmospheric pressureDocument9 pagesatmospheric pressureFizza FatimaNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument15 pagesPressureapi-260281405100% (1)
- Aneroid BarometerDocument4 pagesAneroid BarometerBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressureDocument15 pagesGRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressuredodoNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional de Cajamarca: Facultad de Ciencias AgrariasDocument14 pagesUniversidad Nacional de Cajamarca: Facultad de Ciencias AgrariasDelmer David RomeroNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure PDF 7d86d04aDocument5 pagesAtmospheric Pressure PDF 7d86d04asumansurin2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chem101 YhDocument161 pagesChapter 5 Chem101 YhmmmNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument19 pagesPressuregrantstuartwNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument12 pagesAtmospheric Pressureanwar9602020No ratings yet
- GP6 PressureDocument5 pagesGP6 Pressuredinakempho3No ratings yet
- Physics NoteDocument8 pagesPhysics NotePoul GonaNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure and Wind: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document11 pagesAtmospheric Pressure and Wind: Study Guide For Module No. 3REGINA MAE JUNIONo ratings yet
- Gases YayaDocument6 pagesGases Yayav26r7jcqk8No ratings yet
- Pressure and Its Measuring InstrumentsDocument12 pagesPressure and Its Measuring InstrumentsVishu RaiNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Its Measuring InstrumentsDocument12 pagesPressure and Its Measuring InstrumentsVishu RaiNo ratings yet
- PHY 111aDocument29 pagesPHY 111aCharisse StevensNo ratings yet
- Pressure As A Property of AirDocument3 pagesPressure As A Property of AirJinky P. RefurzadoNo ratings yet
- Pressure PDFDocument19 pagesPressure PDFAbdul rafay ImranNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture NotesDocument41 pagesModule 1 Lecture Notesrz2853No ratings yet
- Agrometeorology Atmospheric PressureDocument39 pagesAgrometeorology Atmospheric PressureRamos, Keith A.No ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesDocument47 pagesFluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesSin Za DolaNo ratings yet
- What Is Air PressureDocument6 pagesWhat Is Air PressurePriyah JeevarajooNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measuring Devices: Experiment No: 01 Fluid MechanicsDocument12 pagesPressure Measuring Devices: Experiment No: 01 Fluid MechanicsGayantha Induwara RanasinghaNo ratings yet
- Perubahan Iklim B Kuliah # 1: Atmosphere Composition and StructureDocument60 pagesPerubahan Iklim B Kuliah # 1: Atmosphere Composition and StructureKelas Empat DuaaarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Flight 1 of 2Document19 pagesPrinciples of Flight 1 of 2EarlHanzJairossFortuNo ratings yet
- Pressure in FluidsDocument23 pagesPressure in FluidsANDREW BMGONo ratings yet
- Earth Science InfographicDocument3 pagesEarth Science InfographicyanlucNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument47 pagesAtmosphereRocker HuzzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 M3Document3 pagesChemistry 2 M3Rain AlmsNo ratings yet
- CH - 18 - Den - PressureDocument46 pagesCH - 18 - Den - PressureThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Earth Science InfographDocument3 pagesEarth Science InfographyanlucNo ratings yet
- Understanding Gas Pressure and Atmospheric PressureDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Gas Pressure and Atmospheric Pressuretidanni100% (1)
- How Is The Atmosphere Structured?Document6 pagesHow Is The Atmosphere Structured?Rebecca PaceNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityDocument7 pagesPresident Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityTn F'dzNo ratings yet
- Pressure in Fluids and Atmospheric PressureDocument4 pagesPressure in Fluids and Atmospheric PressureAditya VijayNo ratings yet
- Density of Air - Density of Dry and Humid Air, Factors Affecting The Density of Air, Video, and FAQsDocument2 pagesDensity of Air - Density of Dry and Humid Air, Factors Affecting The Density of Air, Video, and FAQsSantosh JayasavalNo ratings yet
- Haven't Already: Please Pick Up Your Midterm If YouDocument27 pagesHaven't Already: Please Pick Up Your Midterm If YousptbalaNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument2 pagesPRESSUREannmarieNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure The AtomsDocument3 pagesAir Pressure The AtomsGowshikaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-11Document3 pagesLecture-11mfaida272No ratings yet
- CH 10Document30 pagesCH 10api-298420434No ratings yet
- GP6 PressureDocument5 pagesGP6 Pressureellenjune632No ratings yet
- Pressure Is The Concentration of A ForceDocument11 pagesPressure Is The Concentration of A ForceNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document7 pagesLesson 5ricapearl.zorillaNo ratings yet
- CHP: 13 PhysicsDocument32 pagesCHP: 13 PhysicsAbdul Rahman Mohammed MoezNo ratings yet
- 5.0 PressureDocument82 pages5.0 PressureKalkien CtNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument14 pagesAtmospheric PressureIsabel Filan100% (1)
- Pressure Measuring DevicesDocument11 pagesPressure Measuring DevicesKevin HiralalNo ratings yet
- G9 Physics - Monday Lesson NoteDocument2 pagesG9 Physics - Monday Lesson NotemicahxNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document10 pagesPhysics Form 4Woody CysNo ratings yet