Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Covid 19 Testing Eng
Understanding Covid 19 Testing Eng
Uploaded by
Ty0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pageA COVID-19 test involves taking a sample from the nose or throat which is then tested for the presence of genetic material from the virus. The accuracy of tests depends on when in the infection the sample is taken. Tests are most accurate 5 or more days after exposure when the virus is usually plentiful. Tests taken earlier may show false negatives as the virus levels are still low. A negative test result does not rule out infection as it could be too early in the disease timeline to detect the virus.
Original Description:
COVID
Original Title
understanding-covid-19-testing-eng
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA COVID-19 test involves taking a sample from the nose or throat which is then tested for the presence of genetic material from the virus. The accuracy of tests depends on when in the infection the sample is taken. Tests are most accurate 5 or more days after exposure when the virus is usually plentiful. Tests taken earlier may show false negatives as the virus levels are still low. A negative test result does not rule out infection as it could be too early in the disease timeline to detect the virus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pageUnderstanding Covid 19 Testing Eng
Understanding Covid 19 Testing Eng
Uploaded by
TyA COVID-19 test involves taking a sample from the nose or throat which is then tested for the presence of genetic material from the virus. The accuracy of tests depends on when in the infection the sample is taken. Tests are most accurate 5 or more days after exposure when the virus is usually plentiful. Tests taken earlier may show false negatives as the virus levels are still low. A negative test result does not rule out infection as it could be too early in the disease timeline to detect the virus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
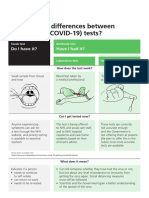
UNDERSTANDING COVID-19 TESTING
TESTING FOR THE VIRUS
SAMPLE COLLECTION POSITIVE TEST RESULT NEGATIVE TEST RESULT
A swab is taken from TRUE POSITIVE TRUE NEGATIVE
the inside of the nose You are currently infected. You are not currently infected.
or back of the throat. Almost all positive results There is no risk of infecting others.
are true positives.
PROCESSING
Molecular tests detect
FALSE POSITIVE FALSE NEGATIVE
whether there is You are not infected, but You are infected, but test negative. Can
genetic material from test positive (very rare). happen when the test is done too early
the virus. to detect the disease or when sample
collection is poor.
FALSE NEGATIVE TEST RESULT
POSITIVE TEST RESULT
UNAWARE OF THEIR INFECTION
INDIVIDUAL ISOLATES
AND COULD INFECT OTHERS
TESTING ACCURACY DEPENDS ON WHEN YOU GET TESTED
Test accuracy based on a 5 day incubation period from exposure to symptoms
INITIAL EXPOSURE INCUBATING SYMPTOMS RECOVERING
WORST (DAYS 0-2) BEST (DAYS 4-8)
Days 0-2 Days 0-5 Days 5+ Days 15+
Very low virus Virus multiplying Virus plentiful Virus decreasing
~98% not detected* ~50% not detected* ~10% not detected* May not be infectious
to others
May take longer to
recover from severe
disease
* Based on preliminary data and
expert opinion. Some do not
develop symptoms. Test accuracy
Those tested too early will be unaware of Up to half of those tested will get a false for asymptomatic cases is unclear
Low false negative rate.
infection and may infect others. as it is not known where they are
negative result and may infect others.
in the disease timeline.
TESTING FOR ANTIBODIES
A blood test detects antibodies to the virus that usually
start to appear when a person is recovering. Research is underway to find out whether
antibodies protect you from future infections.
This blood test is not used to diagnose active COVID-19.
This blood test is not used to diagnose
active COVID-19.
You might also like
- Key Drugs, Mnemonics, Study TipsDocument16 pagesKey Drugs, Mnemonics, Study TipsDrashtibahen Patel100% (3)
- Evaluation of Acute Pharyngitis in Adults - UpToDateDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Acute Pharyngitis in Adults - UpToDateJavier Manuel Escobedo CalderónNo ratings yet
- The Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesDocument1 pageThe Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesqwNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument4 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedJuan PeNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Covid-19 Test Results: Guidance OnDocument1 pageInterpreting Covid-19 Test Results: Guidance OnromalejNo ratings yet
- TTAV Coronavirus - Field - Guide Ty and Charlene BollingerDocument78 pagesTTAV Coronavirus - Field - Guide Ty and Charlene BollingerSakamoto ShintaroNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicDocument1 pageThe Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicChloe WrightNo ratings yet
- INTEGRIS COVID19Interpreting COVID19 Test Results7720Document2 pagesINTEGRIS COVID19Interpreting COVID19 Test Results7720nellyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Covid-19 Test Results: Guidance OnDocument1 pageInterpreting Covid-19 Test Results: Guidance OnAnthony HopkinsNo ratings yet
- HIV Testing Labs FlowchartDocument1 pageHIV Testing Labs Flowcharthamody662002No ratings yet
- Different Types of Coronavirus TestsDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Coronavirus TestsRosano Mario FloresNo ratings yet
- Self Care Guide Pantai 1Document33 pagesSelf Care Guide Pantai 1puterishaliza272No ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedPrincess JanNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument2 pagesFlowAlexander FrostNo ratings yet
- Prevention: CauseDocument2 pagesPrevention: CauseIvan PiñonNo ratings yet
- Marburg BrochureDocument2 pagesMarburg Brochureapi-408890732No ratings yet
- This Test Is For You: No Matter Who You AreDocument2 pagesThis Test Is For You: No Matter Who You AreTee Kok KeongNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls of HIV Infection - Dr. Rizqi Amalia, Sp.ADocument46 pagesPitfalls of HIV Infection - Dr. Rizqi Amalia, Sp.AandreknhNo ratings yet
- Aids FileDocument13 pagesAids Fileayansiddiqui0422No ratings yet
- Torch: Reliable Screening For Early Diagnosis: Loly RD SiagianDocument40 pagesTorch: Reliable Screening For Early Diagnosis: Loly RD SiagianIrawati Amd AKNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test EvaluationDocument95 pagesDiagnostic Test EvaluationADUGNA DEGEFENo ratings yet
- Disease Outbreak InvestigationDocument4 pagesDisease Outbreak Investigationkoass100% (1)
- Influenza: What We Know: Mohammad Nuriman Bin Mohd Zainuddin (Aa0890) Lablink, KPJ Puteri Specialist HospitalDocument24 pagesInfluenza: What We Know: Mohammad Nuriman Bin Mohd Zainuddin (Aa0890) Lablink, KPJ Puteri Specialist Hospitaliman zainuddinNo ratings yet
- Facts About HIV Worksheet 0Document4 pagesFacts About HIV Worksheet 0Maxi RockNo ratings yet
- COVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingDocument5 pagesCOVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingdaam naamNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Document3 pagesCovid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Amy LawsonNo ratings yet
- Nugt1524 Lu 10 Hiv NewDocument27 pagesNugt1524 Lu 10 Hiv NewschroderanzelNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Klamidia: Tulo. Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument45 pagesKlamidia: Tulo. Chlamydia TrachomatisMarjorie Galicia Romano-AndalisNo ratings yet
- Flyer de Sustentabilidad Ilustrado Divertido ColoridoDocument2 pagesFlyer de Sustentabilidad Ilustrado Divertido ColoridoHobi -ahNo ratings yet
- Hiv Testing What You Need To Know - enDocument1 pageHiv Testing What You Need To Know - enDewi Candra KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Diff Betw Cohort N Case ControlDocument1 pageDiff Betw Cohort N Case ControlFirzuan WanNo ratings yet
- Health 8: Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityDocument14 pagesHealth 8: Issues and Problems Related To Human SexualityAizel Mae Consas /Amado HernandezNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedjockoNo ratings yet
- Hiv/Aids: Wagiyo, SKP., M.Kep., SP MatDocument34 pagesHiv/Aids: Wagiyo, SKP., M.Kep., SP MatNettha Bintang DhiafakhriNo ratings yet
- Finals 3Document5 pagesFinals 3Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- ELISA Western BlotDocument5 pagesELISA Western BlotRusthavia AfriliantiNo ratings yet
- Progress in Clinical Research (Linda-Gail Bekker MBCHB, DTMH, DCH, FCP (SA), PHD.)Document171 pagesProgress in Clinical Research (Linda-Gail Bekker MBCHB, DTMH, DCH, FCP (SA), PHD.)National Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- Interim Sars-Cov-2 Self-Testing Guidance: IsolateDocument5 pagesInterim Sars-Cov-2 Self-Testing Guidance: IsolateSariSyahruniNo ratings yet
- LadyporscheDocument2 pagesLadyporscheapi-350694491No ratings yet
- Covid-19: Testing TimesDocument2 pagesCovid-19: Testing TimeshgfksqdnhcuiNo ratings yet
- UF Immunization Cheat Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesUF Immunization Cheat Sheet PDFJag UnathNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Test Covid - Texas ArticleDocument4 pagesPerbandingan Test Covid - Texas ArticlePutri SyawalNo ratings yet
- Crux 01Document8 pagesCrux 01Rajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-05-28 at 3.16.54 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2022-05-28 at 3.16.54 PMMc MomNo ratings yet
- Beware Be AwareDocument5 pagesBeware Be AwareJOY JEAN MARIE RAPADANo ratings yet
- Corona FindingDocument70 pagesCorona Findinggfaya77No ratings yet
- ScreeningDocument40 pagesScreeningDhrubajyoti Sen100% (1)
- Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease (Cird) : Management of Outbreak SituationsDocument16 pagesCanine Infectious Respiratory Disease (Cird) : Management of Outbreak SituationsGustavo MNo ratings yet
- Bioe 211 - Screening and Public Health SurveillanceDocument3 pagesBioe 211 - Screening and Public Health Surveillancebabalegaspi09No ratings yet
- STEP 1 Could It Be HIV? STEP 2 Informed Consent and Testing STEP 3 Conveying Test ResultsDocument2 pagesSTEP 1 Could It Be HIV? STEP 2 Informed Consent and Testing STEP 3 Conveying Test ResultsahjkseflhasefNo ratings yet
- Hiv Notes 2021Document24 pagesHiv Notes 2021Vïñy KïñgzNo ratings yet
- Hiv TesDocument50 pagesHiv Teswilmanurilla17No ratings yet
- Philadelphia VIHDocument27 pagesPhiladelphia VIHAraceli CoriaNo ratings yet
- NSRA Pandemic Influenza Planning Assumptions Compared With WN-CoV SAGE SecretariatDocument3 pagesNSRA Pandemic Influenza Planning Assumptions Compared With WN-CoV SAGE SecretariatRogueNo ratings yet
- Premarital Screening ProgramDocument6 pagesPremarital Screening Programbaashii4No ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument1 pageAction PlanVince BagguatanNo ratings yet
- Epstein-Barr Virus: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Managing EBV Naturally Through Diet, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandEpstein-Barr Virus: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Managing EBV Naturally Through Diet, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- You Are Infected and You Don't Even Know It: The Viruses, Bacteria, and Parasites Already Inside YouFrom EverandYou Are Infected and You Don't Even Know It: The Viruses, Bacteria, and Parasites Already Inside YouRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Sexually Transmitted Infections, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Capucinne Ring Size GuideDocument1 pageCapucinne Ring Size GuideTyNo ratings yet
- Lotto 649 Game ConditionsDocument9 pagesLotto 649 Game ConditionsTyNo ratings yet
- Pupos PDFDocument1 pagePupos PDFTyNo ratings yet
- 7530 B Changing Table - Assembly - InstructionsDocument11 pages7530 B Changing Table - Assembly - InstructionsTyNo ratings yet
- 30 Mai-5 IunieDocument20 pages30 Mai-5 IunieCarina CenusaNo ratings yet
- MDTruth - PathDocument433 pagesMDTruth - Pathabdul88fNo ratings yet
- Section 5193.1 Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument21 pagesSection 5193.1 Sexually Transmitted InfectionsjessremNo ratings yet
- Dealing With The PandemicDocument3 pagesDealing With The PandemicLeaNo ratings yet
- German Lyme GuidelinesDocument37 pagesGerman Lyme GuidelineszzirfNo ratings yet
- Demography Is The: Statistical Study Human PopulationDocument17 pagesDemography Is The: Statistical Study Human PopulationYash SejpalNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance and Persistence-Implications For Human Health and Treatment PerspectivesDocument24 pagesAntibiotic Resistance and Persistence-Implications For Human Health and Treatment PerspectivesserviceNo ratings yet
- DR Cowan On Mask StudyDocument3 pagesDR Cowan On Mask StudyK Mehmet ŞensoyNo ratings yet
- "XXX Provided, Further, That The Vaccine Cards Shall Not Be Considered As Other Similar Government Transaction Purposes." (Emphasis Supplied) XXX"Document1 page"XXX Provided, Further, That The Vaccine Cards Shall Not Be Considered As Other Similar Government Transaction Purposes." (Emphasis Supplied) XXX"Mark Anthony LiparNo ratings yet
- Unity 3Document3 pagesUnity 3Gabigames CarottiNo ratings yet
- ObatDocument1 pageObatLiezna MusyarofaNo ratings yet
- L3 - DermatophytesDocument40 pagesL3 - Dermatophytesdvph2fck6qNo ratings yet
- Risk of Transmission Instrument Playing VsfinalDocument6 pagesRisk of Transmission Instrument Playing VsfinalJohn LinerNo ratings yet
- Bacte Reviewer FinalDocument264 pagesBacte Reviewer FinalRoselle Joyce Arce CalubanNo ratings yet
- How To Escape From Mosquitoes Without Killing Them: by Interrupting Their ScentDocument28 pagesHow To Escape From Mosquitoes Without Killing Them: by Interrupting Their Scentdist2235No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Medical Nursing 1 UpdatedDocument148 pagesMedical Nursing 1 UpdatedcomfortaporoNo ratings yet
- Biosafety Levels Biological Safety Cabinets and Biosafety Laboratory ConstructionDocument64 pagesBiosafety Levels Biological Safety Cabinets and Biosafety Laboratory ConstructionAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Oral Maxillofacial Pathology NotesDocument18 pagesOral Maxillofacial Pathology NotesJose TeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Exam Questions 2023 Part 4Document5 pagesNursing Exam Questions 2023 Part 4Lejo SunnyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7. Antifungal AgentsDocument30 pagesLecture 7. Antifungal AgentsyomifNo ratings yet
- Luna Apple Fungicide - 2012 Product GuideDocument2 pagesLuna Apple Fungicide - 2012 Product GuideLunaFungicidesNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument8 pagesFungis138140No ratings yet
- Fatima's CommissionDocument7 pagesFatima's CommissionSachie Daniela CheungNo ratings yet
- Black DeathDocument2 pagesBlack DeathSnehal JainNo ratings yet
- ChiroRab Press Release Nov 13 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesChiroRab Press Release Nov 13 2019 PDFsr bNo ratings yet
- Components of EpidemiologyDocument13 pagesComponents of EpidemiologyGAURAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Measles Care Study-1Document28 pagesMeasles Care Study-1YourFav RNNo ratings yet