Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer PDF
2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer PDF
Uploaded by
Antoline Natasha RayappanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pathogenesis of Neoplasm PDFDocument3 pagesPathogenesis of Neoplasm PDFTasya Citra KiranaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Lab Activity)Document3 pagesAnaphy (Lab Activity)Mvl KakashiNo ratings yet
- Oncology 1Document178 pagesOncology 1SUNIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Set 3 SBL100 Introduction To Cancer 10nov2023Document66 pagesSet 3 SBL100 Introduction To Cancer 10nov2023dandotiya.yash73No ratings yet
- 2.3.1 Cancer Biology Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument5 pages2.3.1 Cancer Biology Cheat Sheet: by Viaimk_mithunNo ratings yet
- CanserDocument50 pagesCansertarek ahmed100% (1)
- CancerDocument18 pagesCancerIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsDocument9 pagesModule 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) JayloiseDocument6 pagesMedical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) Jayloisejeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- OncologynotesDocument22 pagesOncologynotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Cancer Cells: How They Start and CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesCancer Cells: How They Start and CharacteristicsARISNo ratings yet
- What Is CancersDocument17 pagesWhat Is Cancersmalaran.deboraheloisaNo ratings yet
- 2011OncologyBasics Tutorial1 0Document12 pages2011OncologyBasics Tutorial1 0Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- L2-Principles of Surgical OncologyDocument25 pagesL2-Principles of Surgical OncologyTofeeq101 WaNo ratings yet
- Cancer BasicsDocument28 pagesCancer BasicsIndranil ModakNo ratings yet
- Rishika Vijayvargiya Class XII ADocument21 pagesRishika Vijayvargiya Class XII ARajat PorwalNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project On CANCERDocument15 pagesInvestigatory Project On CANCERSreeja SwainNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Cancer Is Defined As An Uncontrolled Proliferation ofDocument12 pagesCancer: Cancer Is Defined As An Uncontrolled Proliferation ofnikNo ratings yet
- Cancer ResearchDocument5 pagesCancer ResearchmelanieNo ratings yet
- Cancer The Inimate EnemyDocument2 pagesCancer The Inimate EnemyAlaa EddinNo ratings yet
- Index: DescriptionDocument17 pagesIndex: DescriptionDeepak R SriRamNo ratings yet
- 212F - Oncology L1 - 2104Document25 pages212F - Oncology L1 - 2104Tyler LiuNo ratings yet
- Cancer Info SheetDocument2 pagesCancer Info SheetRenee MehNo ratings yet
- HBC 408 19Document79 pagesHBC 408 19Stanley ChikoveNo ratings yet
- Project - Aids and CancerDocument6 pagesProject - Aids and CancerMihir SagarNo ratings yet
- Research On Cancer by Sahal Xii ADocument14 pagesResearch On Cancer by Sahal Xii AM. Mohamed SahalNo ratings yet
- Essay WritingDocument2 pagesEssay WritingJohn Ray ColmenarNo ratings yet
- Pharma en OncologyDocument14 pagesPharma en Oncologyyaqoob008No ratings yet
- BookDocument11 pagesBookNeeru GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberration Lecture 1Document93 pagesCellular Aberration Lecture 1David Dwane Art SilorioNo ratings yet
- Cancer Ms LecDocument16 pagesCancer Ms LecJulia Rae Delos Santos100% (1)
- The Effects of Uncontrolled Mitosis in Living ThingsDocument3 pagesThe Effects of Uncontrolled Mitosis in Living ThingsDanishNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia S. M Jawwad AliDocument25 pagesNeoplasia S. M Jawwad AliAnt EverafterNo ratings yet
- Healthy You Processed Foods Wk. 4Document49 pagesHealthy You Processed Foods Wk. 4Nathaly DiazNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFDocument7 pagesWhat Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFAlexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- Tumors: Benign and Malignant: Cancer Therapy & OncologyDocument3 pagesTumors: Benign and Malignant: Cancer Therapy & OncologyMaria ArifahNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia (I) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityDocument113 pagesNeoplasia (I) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityleyreaNo ratings yet
- Cancer and Cell Division 14-15Document4 pagesCancer and Cell Division 14-15api-242868690No ratings yet
- q4 Wk4 CancerDocument36 pagesq4 Wk4 CancerRyson De leonNo ratings yet
- Oncolgy UnitDocument12 pagesOncolgy UnitAtia IftikharNo ratings yet
- How Cancer Cells AriseDocument4 pagesHow Cancer Cells AriseLilyNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Cancer Stem CellsDocument13 pages8.1 Cancer Stem CellsClaraNo ratings yet
- Cancer 2022Document16 pagesCancer 2022Nikhil BijuNo ratings yet
- Comparison Malignant BenignDocument2 pagesComparison Malignant BenignChloé Jane HilarioNo ratings yet
- Hello Everyone!Document38 pagesHello Everyone!samsung picturesNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cancer (Class XII)Document2 pagesNotes On Cancer (Class XII)Aryan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument2 pagesCancermikErlhNo ratings yet
- Stem - Cells - and - Cancer - PPT 1Document31 pagesStem - Cells - and - Cancer - PPT 1Muhammad Ikram RabbaniNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument51 pagesNeoplasiaElstella Eguavoen Ehicheoya100% (1)
- Neoplasm ADocument46 pagesNeoplasm ANur FaidahNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyDocument28 pagesCharacteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyRoxie SolisNo ratings yet
- Unco Ntrolled Proliferation: Distinguishing Property of Malignant Cells. Without Intervention, Cancerous Tissues Grow inDocument7 pagesUnco Ntrolled Proliferation: Distinguishing Property of Malignant Cells. Without Intervention, Cancerous Tissues Grow inYukiNo ratings yet
- Healthcare TransDocument9 pagesHealthcare TransKeihla NiebresNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument15 pagesPathologySaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- 6 May 2023 Name Colby JansenDocument1 page6 May 2023 Name Colby JansenJames DboyNo ratings yet
- Thursday, 3 November 2022 10:14 PMDocument5 pagesThursday, 3 November 2022 10:14 PMAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Differences Between Cancer Cells and Normal CellsDocument17 pagesCancer: Differences Between Cancer Cells and Normal CellsAira Anne Tonee VillaminNo ratings yet
- Colorectal (Bowel) Cancer Enlarged Image: Tumours' For Further Details About Cancer in GeneralDocument5 pagesColorectal (Bowel) Cancer Enlarged Image: Tumours' For Further Details About Cancer in GeneralIan AlisonNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument2 pagesCancerTariq AhmedNo ratings yet
- 9233 PhysicsDocument5 pages9233 PhysicsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Mode and MeanDocument1 pageMode and MeanAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- 2.5 The Cell CycleDocument5 pages2.5 The Cell CycleAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- 9233 ChemistryDocument5 pages9233 ChemistryAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base ReactionsDocument4 pagesAcid and Base ReactionsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- 11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsDocument6 pages11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical Waste TheoryDocument14 pagesBio Medical Waste TheoryManish Kumawat100% (1)
- Case Analysis Group 1Document47 pagesCase Analysis Group 1bunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy of Cancer: Submitted by Syama - J.S Roll No:15 2 SEM M Pharm PharmacologyDocument64 pagesChemotherapy of Cancer: Submitted by Syama - J.S Roll No:15 2 SEM M Pharm PharmacologySyama J.S100% (1)
- Skenario Baru 4Document6 pagesSkenario Baru 4Nabila SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Stagehodgkinlymphoma: by Joseph M. Connors, MDDocument5 pagesAdvanced-Stagehodgkinlymphoma: by Joseph M. Connors, MDJOHN LOPERANo ratings yet
- BioSpectrum Asia - November 2016 VK Com StopthepressDocument52 pagesBioSpectrum Asia - November 2016 VK Com StopthepressxibernetixNo ratings yet
- Dandelion Root TreatmentDocument6 pagesDandelion Root Treatmenthubabuba100% (1)
- Fasting and Prayer The Power That Breaks The YokeDocument7 pagesFasting and Prayer The Power That Breaks The YokeRoy C. EstenzoNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument27 pagesBreast Cancerrikshya k c100% (4)
- Pancreatic CancerDocument30 pagesPancreatic CancerHealth Education Library for People75% (4)
- Oncology Conference - HepatoblastomaDocument95 pagesOncology Conference - HepatoblastomaJaysonSoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenNo ratings yet
- Aseptic Dispensing SOPsDocument19 pagesAseptic Dispensing SOPsvickanovriNo ratings yet
- Bun PT Introducere - Removal of Cytostatic Drugs From Aquatic Environment A ReviewDocument18 pagesBun PT Introducere - Removal of Cytostatic Drugs From Aquatic Environment A ReviewsorinamotocNo ratings yet
- Fasting - Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical ApplicationsDocument12 pagesFasting - Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical ApplicationserixsparhawkNo ratings yet
- Aia Health Shield Gold Max English BrochureDocument20 pagesAia Health Shield Gold Max English BrochureRaymond AngNo ratings yet
- Malignant Diseases of The CervixDocument128 pagesMalignant Diseases of The Cervixnicewan0% (1)
- Unedited Trs 2019 Ec22 SeptDocument330 pagesUnedited Trs 2019 Ec22 SeptTeddyNo ratings yet
- Bleomycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageBleomycin Drug StudykyawNo ratings yet
- Insight of Nanomedicine Strategies For A Targeted Del 2021 Journal of Drug DDocument16 pagesInsight of Nanomedicine Strategies For A Targeted Del 2021 Journal of Drug DdianaNo ratings yet
- Tuko BenefitsDocument3 pagesTuko Benefitsalvin_348100% (2)
- Singh 2018Document16 pagesSingh 2018Georgiana BunghiuzNo ratings yet
- Budwig Guide 2020 MinDocument37 pagesBudwig Guide 2020 MinJoão Franco100% (3)
- Pemetrexed As First Line Chemotherapy For NSCLCDocument36 pagesPemetrexed As First Line Chemotherapy For NSCLCAnton HariadiNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy and Nursing ManagementDocument84 pagesChemotherapy and Nursing ManagementAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Ijp - AewqpprovedDocument11 pagesIjp - AewqpprovedIndra HedarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice & Skill: Chemotherapeutic Drugs: Preparing and HandlingDocument6 pagesNursing Practice & Skill: Chemotherapeutic Drugs: Preparing and HandlingAlessandra Dominique MarianoNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs Final PDFDocument8 pagesAnticancer Drugs Final PDFAisha Jamil100% (1)
- HIT LLA Recaida en Pediatria 2020Document34 pagesHIT LLA Recaida en Pediatria 2020Nathalie Soler BarreraNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic Drug ReconstitutionDocument6 pagesCytotoxic Drug Reconstitutioniqhwan riatNo ratings yet
2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer PDF
2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer PDF
Uploaded by
Antoline Natasha RayappanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer PDF
2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer PDF
Uploaded by
Antoline Natasha RayappanCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
7 Cell Division Going Wrong: Cancer
cancer a broad group of diseases that Cancer is a group of diseases in which cells grow and divide out of control
result in uncontrolled cell division It results from a change in the DNA that controls the cell cycle. This change
prevents the cells from staying in interphase for the normal amount of time.
READING Tip One or more of the checkpoints (addressed in Section 2.5) fails, so the cell
Making Connections and all of its subsequent daughter cells continue to divide uncontrollably.
While reading a text, whenever you read Some types of cancer run in families, whereas others are triggered
a part that reminds you of a related
by environmental factors. Some cancers may have both hereditary and
experience that you, your family, or
friends have had, jot it down on a sticky environmental causes. Cancer is not infectious: you cannot catch it from
note and attach it to the text. After someone who has it.
reading, you can review and synthesize Cancer is a serious concern for humans, but many other organisms, such as
your text-to-self connections. cats, dogs, fish, and even plants, can also develop cancer.
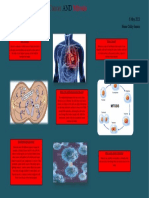
Cell Growth Rates and Cancer
A cancer cell is one that continues to divide despite messages from the
nucleus or the surrounding cells to stop growing and dividing. The
cell’s checkpoints may fail to identify problems or kill off the cell. The
tumour a mass of cells that continue uncontrolled growth and division may create a rapidly growing mass of cells
to grow and divide without any obvious that form a lump or tumour (Figure 1). The cells of the tumour may stay
function in the body
together and have no serious effect on surrounding tissues. This is called
benign tumour a tumour that does not a benign tumour. Cells in a benign tumour are not cancerous. However,
affect surrounding tissues other than by sometimes a benign tumour can grow so large that it physically crowds
physically crowding them nearby cells and tissues. This can affect their normal function.
malignant tumour a tumour that A mass of cells is a malignant tumour if it interferes with the function
interferes with the functioning of of neighbouring cells and tissues, such as the production of enzymes
surrounding cells; a cancerous tumour
or hormones. Malignant tumours may even destroy surrounding tissues.
To watch an animation of cancer The cells in a malignant tumour are considered cancerous.
cell growth over 24 hours, In some cases, cancer cells break away from the original (primary)
GO TO NELSON SCIENCE tumour and move to a different part of the body. If they settle there
and continue growing and dividing uncontrollably, they can start a new
(secondary) tumour (Figure 2 on the next page). This process is known
metastasis the process of cancer as metastasis and is one of the reasons why cancer is such a dangerous
cells breaking away from the original disease.
(primary) tumour and establishing another malignant (cancerous)
(secondary) tumour elsewhere in the body tumour affects
surrounding cells
metastatic (cancerous)
cells leave the tumour
and start a secondary
tumour elsewhere
Figure 1 A tumour is a mass of cells normal potentially
with no function. A tumour can remain cell cancerous
benign, or it can become malignant. cell
Tumour cells can metastasize, spreading benign (non-cancerous)
to other areas of the body. Malignant tumour does not affect
and metastatic tumours are considered normal uncontrolled surrounding cells, unless by
cancerous. cell division cell division physically crowding them
48 Chapter 2 • Cells, Cell Division, and Cell Specialization NEL
blood
vessel
tumour metastatic tumour is
established by these
migrating cells
cells from original
tumour may break
through blood
vessel walls and
travel to other Figure 2 Cancer cells sometimes break
areas of the free from the primary tumour site. These
body metastatic cells can then move through
the blood vessels. Secondary tumours
may develop at other sites.
Causes of Cancer
Every time a cell divides, its DNA is faithfully duplicated. Usually, this process
is error-free and the genetic information in the daughter cells is exactly the
same as that in the parent cell. Sometimes, however, random changes occur
in DNA. These random changes are known as mutations. These changes may mutation a random change in the DNA
either result in the death of the cell or allow the cell to survive and continue to
grow and divide. Very rarely, the change occurs in the DNA that controls cell
division. Once this crucial cell cycle DNA starts behaving abnormally, the cells
may become cancerous and proliferate wildly through repeated, uncontrolled
mitosis and cytokinesis. They multiply until all nutrients are exhausted. carcinogen any environmental factor that
Some mutations are caused by carcinogens: environmental factors that cause causes cancer
cancer. Well-known carcinogens include tobacco smoke; radiation, such as X-rays
and UV rays from tanning beds and sunlight; some viruses, such as human To find out about some of the
myths relating to things that
papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B; certain chemicals in plastics; and many cause, or cure, cancer,
organic solvents. If a group of people is exposed to a carcinogen, some will develop GO TO NELSON SCIENCE
cancer, but others will not. This is a major challenge for cancer researchers because
they cannot predict who will develop cancer. Until this process is completely
understood, it is best to limit your exposure to carcinogens.
nasal cavity
Some cancers appear to be at least partly hereditary. This means that mouth
pharynx
the DNA passed from one generation to the next may contain information larynx (upper throat)
that leads to disease. These cancers include some breast cancers and some esophagus
colon cancers. A genetic link makes it more likely that you will develop a
lung
particular type of cancer, but it does not guarantee that you will get cancer.
Smoking and Cancer
stomach
Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in Canadians over 40. liver
kidney
According to Health Canada, smoking currently causes 9 out of 10 cases of
lung cancer. Carcinogens in tobacco affect more than just the lungs. Smoking
also increases the risk of over a dozen other types of cancer (Figure 3). The
good news is that most of these smoking-related cancers can be prevented bladder
by giving up smoking—or never starting in the first placeand staying away
from second-hand smoke.
Figure 3 The carcinogens in tobacco
smoke can affect all of these parts of
the body.
NEL 2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong: Cancer 49
Cancer Screening
READING Tip Cancer screening means checking for cancer even if there are no symptoms.
Making Connections
Different types of cancer can be screened for in different ways. Cancer
Text-to-world connections involve screening can be done at home, as part of a routine medical checkup, or
facts about the world that you have with a special appointment. Screening is especially important for people
collected during your lifetime. This type who have a family history of certain cancers (such as breast cancer or
of connection can be very useful when
colon cancer). If you have a family history of cancer, you may choose to go
reading a science text because it can
help you take a more critical approach through genetic screening. This will determine if you have inherited DNA
to the ideas and information in the text. that is linked to cancer. Screening can also be valuable for people who are
exposed to carcinogens at work or because of their lifestyle.
Screening does not prevent cancer, but it does increase the chance of
detecting cancer early enough to successfully treat it. This is one important
way to reduce your risk.
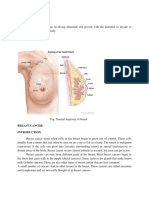
Many women take responsibility for their health by performing regular
breast self-examinations to check for lumps that may indicate breast cancer.
Women can also be screened for early signs of cervical cancer, starting
Pap test a test that involves taking around age 18, by getting a regular Pap test. This is a procedure in which a
a sample of cervical cells to determine doctor takes a sample of cervical cells, which are checked for cancer.
if they are growing abnormally
Men can detect testicular cancer early through testicular self-examination.
There is also a blood test, called the PSA test, that a doctor can prescribe to
To determine what your
checkup checklist looks like, screen for prostate cancer. This is not widely used for men under the age of
GO TO NELSON SCIENCE 50 as the incidence of prostate cancer is lower for that age group.
Other screening tests include a blood test for colon cancer and regular
skin checks by a doctor or dermatologist to look for changes in moles, new
growths, and sores. You can learn to check your own skin regularly for moles.
Table 1 illustrates the “ABCD of moles.” The letters stand for Asymmetry,
Border, Colour, and Diameter. If you see any suspicious-looking moles or
growths, ask your doctor or dermatologist to check them out.
Table 1 The ABCD of Moles
Asymmetry Border Colour Diameter
Benign
Malignant
Reducing Your Cancer Risk
Cancer prevention and early detection are very important. Many factors can
affect your risk of getting cancer. These risks include your personal and family
medical history, carcinogens in your environment, and your lifestyle choices.
Inform yourself about these factors so that you can minimize your exposure
to known cancer risks. You cannot change your family history, and some
aspects of your environment are beyond your control. You can, however, make
lifestyle choices that have a big impact on your likelihood of getting cancer.
50 Chapter 2 • Cells, Cell Division, and Cell Specialization NEL
RESEARCH THIS CANCER SCREENING AND PREVENTION
SKILLS HANDBOOK
SKILLS: Defining the Issue, Researching, Identifying Alternatives, Defending a Decision, Communicating 4.B., 4.C.
Each year, approximately 150 women in Ontario die because A. Analyze the information that you have collected. Decide which
of cervical cancer. There is no single cause of cervical cancer, of the cancer-reduction approaches you support. Write a
but research has shown that the main risk factor is untreated statement of your decision, including your rationale. T/I C A
infection with human papillomavirus (HPV). By preventing B. What questions do you still have regarding screening and
HPV infections, the risk of developing cervical cancer can prevention for this type of cancer? How do you think answers
be reduced. to these questions could be found? T/I
1. Research cervical cancer, or another type of cancer, C. In your class, debate the medical and ethical issues
to discover why it is particularly dangerous. surrounding cancer screening and prevention. C A
2. Research information about ways to reduce the risk from
your chosen type of cancer. Search a number of sources.
GO TO NELSON SCIENCE
Lifestyle Choices
There are many lifestyle choices, besides avoiding tobacco smoke, that can
help reduce your risk of developing cancer. A healthy diet including a lot of
fruits and vegetables and less fatty meat may help. Research has shown that
certain “super foods” contain substances that help your body protect itself
from cancers (Figure 4). Even though vitamin supplements may include To read about a Canadian
some of these substances, the best way to obtain them is by eating the food researcher studying factors
itself. These super foods do not prevent cancer; rather, they lower your that affect prostate cancer,
cancer risk. GO TO NELSON SCIENCE
The risk of some cancers increases with the amount of body fat a person
has. A healthy diet may aid weight loss, which could lower the risk of cancer.
DID YOU KNOW?
Antiperspirants and Breast
Cancer—A Myth?
There is no known link between using
antiperspirants and breast cancer.
This is a myth that has been spread
tomatoes
tomatoes carrots
carrots avocados
avocados grapefruit
grapefruit
tomatoes carrots avocados grapefruit using e-mail and the Internet. A
study in 2002 found no increase in
breast cancer risk for women using
antiperspirants or deodorants, even
right after shaving their underarms.
red grapes
red broccoli garlic raspberries
red grapes
grapes broccoli
broccoli garlic
garlic raspberries
raspberries
Figure 4 These cancer-fighting “super
foods” are rich in many substances that
nuts
nuts cabbage
cabbage figs
figs help keep you healthy.
nuts cabbage figs
NEL 2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong: Cancer 51
CITIZEN ACTION
Cancer Education and Research
SKILLS HANDBOOK
4.C.7.
The Canadian Cancer Society (CCS) works to educate people on the Decide how you would like to get involved. You may make this
lifestyle factors that can lead to cancer, what we can do to prevent decision by doing online research, talking to a cancer agency
cancer, and how to find cancer in its earliest stages. staff member or a researcher, or some other way. Prepare a
Cancer research is expensive and time-consuming. It can take written or verbal message to your fellow students to get them
years of work before a single research study is completed. excited about your cause.
There is only so much money to go around. Every year, many
GO TO NELSON SCIENCE
worthy research projects go unfunded.
What Can You Do to Help?
One person can make a differencejust look at Terry Fox! He was
18 years old when he was diagnosed with bone cancer in his right
leg. The only treatment at that time was to amputate his leg just
above the knee. This remarkable young man brought international
awareness to the importance of cancer research by deciding to run
a cross-country marathon. He ran more than 5 000 km from St.
John’s, Newfoundland, to Thunder Bay, Ontario, before discovering
that the cancer had spread to his lungs. He died on June 28, 1981,
at the age of 22. The efforts of this heroic young Canadian have
inspired others to raise hundreds of millions of dollars in his name
to fund cancer research.
There are many opportunities to volunteer in your local
community to increase cancer awareness or raise funds. Figure 5 Terry Fox on his Marathon of Hope
Diagnosing Cancer
In some cases, a growing tumour creates swelling or causes discomfort.
In other cases, the patient may feel very tired or start losing weight for no
apparent reason. The earlier a cancer is diagnosed, the better the chances
of it being successfully treated. If cancer is suspected, the doctor will order
medical tests to investigate further. These tests can include blood tests and
special imaging techniques.
Figure 6 An endoscope
Imaging Technologies
Imaging techniques may include endoscopy, X-ray, ultrasound,
CT scanning, and MRI.
An endoscope is commonly used to screen for colon cancer. The
endoscope is made up of a fibre-optic cable to deliver light, a tiny camera,
and a cable that sends the images to a screen (Figure 6). Tools, such as
forceps, can also be attached. The patient may be given a sedative before the
endoscope is inserted into the colon through the rectum. The camera allows
the doctor to look for abnormal growths. Forceps can be used to remove
a small sample (biopsy) of any suspicious-looking growth. The sample can
then be studied under a microscope.
You may already be familiar with X-rays. Doctors use X-ray images to
Figure 7 Chest X-ray of a patient with view parts of the body such as bones and lungs (Figure 7). A mammogram
lung cancer (red areas). is a specialized X-ray technique for imaging breast tissue.
52 Chapter 2 • Cells, Cell Division, and Cell Specialization NEL
X-rays can also cause DNA damage. They are particularly harmful to READING Tip
rapidly dividing cells such as those in a growing fetus. For this reason, Recording Connections
women who are pregnant should not undergo X-ray examinations. Make a double-entry diary labelled
Another imaging technique that you may already be familiar with is “Connections” and “Understanding.”
Use the left side to record text-to-
ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound imaging uses ultra–high-frequency sound
self, text-to-text, and text-to-world
waves to create a digital image. The digital image allows doctors to view connections. On the right side, explain
certain soft tissues, such as the heart or the liver (Figure 8). how the connections helped you to
Another commonly used imaging technique is a CT or CAT scan better understand the text by visualizing,
(computerized axial tomography). A CT scan allows the X-ray technician making predictions, inferences, or
judgements, forming opinions, drawing
to take multiple X-rays of the body from many different angles. The images
and supporting conclusions, or
are then assembled by computer to form a series of detailed images. This evaluating.
technology allows doctors to view parts of the body that cannot be seen with
a conventional X-ray scan (Figure 9).
A fourth imaging technique is MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
(Figure 10). In an MRI, radio waves and a strong magnetic field create
images with more detail than a CT scan. Computers can assemble the
information into three-dimensional models.
Figure 8 Ultrasound scan of the liver, Figure 9 CT scan of a cross-section of the
showing increased blood flow (orange areas) body, showing cancer tumours (darker red Figure 10 MRI scan showing brain cancer
due to malignant tumours areas) in a liver (green area)
Examining Cells
If any of the medical tests or images show abnormalities, the next step is to
examine a sample of the suspected cancer cells under a microscope. This is
the only way to confirm a diagnosis of cancer.
Certain cell samples can be obtained easily, such as blood cell samples.
Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood, often resulting in a high ratio of
white blood cells to red blood cells. An experienced technician can identify
this problem when looking at a sample of blood through a microscope.
A sample of tumour cells may have to be removed surgically. This
technique is known as “taking a biopsy.” The sample is then viewed under
a microscope. It may also be tested for genetic abnormalities. If the tumour
cells are determined to be non-malignant (not cancerous), then the tumour
is diagnosed as benign. Cancer cells are often irregularly shaped and may
be smaller or larger than the surrounding cells. Experienced medical
professionals can identify cancer cells just by looking at them (Figure 11).
After diagnosis, the doctors must discover where the cancer originally
Figure 11 Illustration of cancer cells
began. They also need to find out how large the tumour is, how quickly it
(shown in purple) among normal cells
is growing, and whether the cancer has spread. This information helps to (pink). Notice that the cancer cells have
determine suitable treatments and to predict the outcome. irregular shapes.
NEL 2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong: Cancer 53
Treatments for Cancer
The goal of cancer treatment is to slow down the growth of the tumours
or destroy as many cancer cells as possible. Currently, there are three
main conventional methods of treating cancer: surgery, chemotherapy,
and radiation therapy. An emerging technique is biophotonics. A cancer
treatment plan may consist of one or a combination of these methods.
To learn more about working in Cancer treatment involves a team of medical specialists that may include
the field of medical oncology, surgeons, medical oncologists (doctors who specialize in cancer diagnosis
GO TO NELSON SCIENCE and treatment), radiation oncologists, and oncology nurses.
Surgery
To find out the wait times for Surgeryphysically removing the cancerous tissueis sometimes the
cancer surgery in your area, preferred way of treating cancer. If the tumour is easily accessible and fairly
GO TO NELSON SCIENCE well defined, the doctors may recommend this option.
Chemotherapy
DID YOU KNOW?
Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer using drugs. These work by
slowing or stopping the cancer cells from dividing and spreading to other
The Blood-Brain Barrier
It is very difficult to deliver treatment parts of the body, and by killing the cells. The drugs can be injected or taken
drugs to tumours in the brain. This orally (by mouth). Side effects may include hair loss, nausea, and fatigue, but
is because a barrier of dense cells the benefits of the treatment generally outweigh the negative effects.
prevents most chemicals from passing Chemotherapy is often one of the first stages of cancer treatment. Its aim
from the blood into the brain.
is to shrink a tumour for surgical removal or for radiation treatments. A
huge advantage of chemotherapy is that the drugs travel throughout the body
and reach almost all tumours, even if they are much too small to be detected.
Radiation
READING Tip Cancer cells are easily damaged by ionizing radiation because they divide
Cross-Checking Connections rapidly. Radiation therapy takes advantage of this. The DNA of many of the
Use sticky notes while reading to make daughter cells is damaged by the radiation, so the cells cannot divide further.
text-to-text connections with other texts The radiation is directed at the tumour either by using a focused beam
you have read or viewed. After reading
or by implanting a radioactive source into the tumour (Figure 12). This
you can check these connections to see
whether the new information matches
minimizes side effects.
or challenges what you already know.
Figure 12 Radiation therapy is delivered by very technologically advanced machines.
54 Chapter 2 • Cells, Cell Division, and Cell Specialization NEL
Biophotonics
The newest weapon in the fight against cancer, biophotonics, uses beams of biophotonics the technology of using
light to detect and treat cancer. It is a very sensitive diagnostic tool, allowing light energy to diagnose, monitor, and treat
for early detection of cancer. It has fewer side effects than conventional living cells and organisms
radiation treatment as it can more accurately target the cancerous tissue.
Much of this research is being pioneered at the University of Toronto.
To read more about the
Scientific research and technological advancements play an important development of biophotonics at
part in understanding cell biology. Canadian researchers are at the forefront the University of Toronto,
in discovering better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat cancer. GO TO NELSON SCIENCE
UNIT TASK Bookmark
The information about cancer diagnosis and treatment may be useful to you as you work
on the Unit Task described on page 156.
IN SUMMARY
• Cancer is a group of diseases that result from • Various imaging technologies, including
uncontrolled cell growth. endoscopy, X-ray, ultrasound, CT scanning, and
• Tumours can be benign (non-cancerous) or MRI, can be used to identify abnormalities and
malignant (cancerous). diagnose cancer.
• Some cancer cells are able to move to new areas • Biopsy is a method of diagnosis in which
of the body in a process called metastasis. a sample of cells is surgically removed and
examined under a microscope.
• Many early stages of cancers have no noticeable
symptoms. • Many screening tests are available to diagnose
cancer early and improve treatment success rates.
• Cancer risks can be reduced through avoiding
carcinogens and by making healthier lifestyle • The main treatment methods for cancer include
choices. surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. A newer
technology is biophotonics.
CHECK YOUR LEARNING
1. How is the behaviour of cancer cells different from that of 6. Briefly describe the three main conventional methods of
normal cells? K/U treating cancer. K/U
2. (a) Can a person inherit cancer genetically? Explain. 7. Why might a doctor be concerned to find cancer cells in a
(b) Can you catch cancer from a person who has cancer? patient’s blood? K/U
Explain. K/U 8. Identify at least three simple lifestyle changes that could
3. (a) What is a carcinogen? help reduce your risk of developing cancer. K/U
(b) Give some examples of carcinogens that may be 9. What cancer screening tests should young adults include
present in your everyday life. A in their cancer-fighting plan? K/U
4. Why might it be easy to overlook cancer in its early 10. Why might there be a risk of cancer recurring, even when
stages? K/U surgery is performed to remove a malignant tumour? K/U
5. List at least five diagnostic techniques used to detect
cancer. K/U
NEL 2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong: Cancer 55
You might also like
- Pathogenesis of Neoplasm PDFDocument3 pagesPathogenesis of Neoplasm PDFTasya Citra KiranaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Lab Activity)Document3 pagesAnaphy (Lab Activity)Mvl KakashiNo ratings yet
- Oncology 1Document178 pagesOncology 1SUNIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Set 3 SBL100 Introduction To Cancer 10nov2023Document66 pagesSet 3 SBL100 Introduction To Cancer 10nov2023dandotiya.yash73No ratings yet
- 2.3.1 Cancer Biology Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument5 pages2.3.1 Cancer Biology Cheat Sheet: by Viaimk_mithunNo ratings yet
- CanserDocument50 pagesCansertarek ahmed100% (1)
- CancerDocument18 pagesCancerIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsDocument9 pagesModule 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) JayloiseDocument6 pagesMedical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) Jayloisejeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- OncologynotesDocument22 pagesOncologynotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- Cancer Cells: How They Start and CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesCancer Cells: How They Start and CharacteristicsARISNo ratings yet
- What Is CancersDocument17 pagesWhat Is Cancersmalaran.deboraheloisaNo ratings yet
- 2011OncologyBasics Tutorial1 0Document12 pages2011OncologyBasics Tutorial1 0Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- L2-Principles of Surgical OncologyDocument25 pagesL2-Principles of Surgical OncologyTofeeq101 WaNo ratings yet
- Cancer BasicsDocument28 pagesCancer BasicsIndranil ModakNo ratings yet
- Rishika Vijayvargiya Class XII ADocument21 pagesRishika Vijayvargiya Class XII ARajat PorwalNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project On CANCERDocument15 pagesInvestigatory Project On CANCERSreeja SwainNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Cancer Is Defined As An Uncontrolled Proliferation ofDocument12 pagesCancer: Cancer Is Defined As An Uncontrolled Proliferation ofnikNo ratings yet
- Cancer ResearchDocument5 pagesCancer ResearchmelanieNo ratings yet
- Cancer The Inimate EnemyDocument2 pagesCancer The Inimate EnemyAlaa EddinNo ratings yet
- Index: DescriptionDocument17 pagesIndex: DescriptionDeepak R SriRamNo ratings yet
- 212F - Oncology L1 - 2104Document25 pages212F - Oncology L1 - 2104Tyler LiuNo ratings yet
- Cancer Info SheetDocument2 pagesCancer Info SheetRenee MehNo ratings yet
- HBC 408 19Document79 pagesHBC 408 19Stanley ChikoveNo ratings yet
- Project - Aids and CancerDocument6 pagesProject - Aids and CancerMihir SagarNo ratings yet
- Research On Cancer by Sahal Xii ADocument14 pagesResearch On Cancer by Sahal Xii AM. Mohamed SahalNo ratings yet
- Essay WritingDocument2 pagesEssay WritingJohn Ray ColmenarNo ratings yet
- Pharma en OncologyDocument14 pagesPharma en Oncologyyaqoob008No ratings yet
- BookDocument11 pagesBookNeeru GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberration Lecture 1Document93 pagesCellular Aberration Lecture 1David Dwane Art SilorioNo ratings yet
- Cancer Ms LecDocument16 pagesCancer Ms LecJulia Rae Delos Santos100% (1)
- The Effects of Uncontrolled Mitosis in Living ThingsDocument3 pagesThe Effects of Uncontrolled Mitosis in Living ThingsDanishNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia S. M Jawwad AliDocument25 pagesNeoplasia S. M Jawwad AliAnt EverafterNo ratings yet
- Healthy You Processed Foods Wk. 4Document49 pagesHealthy You Processed Foods Wk. 4Nathaly DiazNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFDocument7 pagesWhat Is Cancer - National Cancer Institute PDFAlexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- Tumors: Benign and Malignant: Cancer Therapy & OncologyDocument3 pagesTumors: Benign and Malignant: Cancer Therapy & OncologyMaria ArifahNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia (I) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityDocument113 pagesNeoplasia (I) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityleyreaNo ratings yet
- Cancer and Cell Division 14-15Document4 pagesCancer and Cell Division 14-15api-242868690No ratings yet
- q4 Wk4 CancerDocument36 pagesq4 Wk4 CancerRyson De leonNo ratings yet
- Oncolgy UnitDocument12 pagesOncolgy UnitAtia IftikharNo ratings yet
- How Cancer Cells AriseDocument4 pagesHow Cancer Cells AriseLilyNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Cancer Stem CellsDocument13 pages8.1 Cancer Stem CellsClaraNo ratings yet
- Cancer 2022Document16 pagesCancer 2022Nikhil BijuNo ratings yet
- Comparison Malignant BenignDocument2 pagesComparison Malignant BenignChloé Jane HilarioNo ratings yet
- Hello Everyone!Document38 pagesHello Everyone!samsung picturesNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cancer (Class XII)Document2 pagesNotes On Cancer (Class XII)Aryan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument2 pagesCancermikErlhNo ratings yet
- Stem - Cells - and - Cancer - PPT 1Document31 pagesStem - Cells - and - Cancer - PPT 1Muhammad Ikram RabbaniNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument51 pagesNeoplasiaElstella Eguavoen Ehicheoya100% (1)
- Neoplasm ADocument46 pagesNeoplasm ANur FaidahNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyDocument28 pagesCharacteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyRoxie SolisNo ratings yet
- Unco Ntrolled Proliferation: Distinguishing Property of Malignant Cells. Without Intervention, Cancerous Tissues Grow inDocument7 pagesUnco Ntrolled Proliferation: Distinguishing Property of Malignant Cells. Without Intervention, Cancerous Tissues Grow inYukiNo ratings yet
- Healthcare TransDocument9 pagesHealthcare TransKeihla NiebresNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument15 pagesPathologySaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- 6 May 2023 Name Colby JansenDocument1 page6 May 2023 Name Colby JansenJames DboyNo ratings yet
- Thursday, 3 November 2022 10:14 PMDocument5 pagesThursday, 3 November 2022 10:14 PMAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Differences Between Cancer Cells and Normal CellsDocument17 pagesCancer: Differences Between Cancer Cells and Normal CellsAira Anne Tonee VillaminNo ratings yet
- Colorectal (Bowel) Cancer Enlarged Image: Tumours' For Further Details About Cancer in GeneralDocument5 pagesColorectal (Bowel) Cancer Enlarged Image: Tumours' For Further Details About Cancer in GeneralIan AlisonNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument2 pagesCancerTariq AhmedNo ratings yet
- 9233 PhysicsDocument5 pages9233 PhysicsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Mode and MeanDocument1 pageMode and MeanAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- 2.5 The Cell CycleDocument5 pages2.5 The Cell CycleAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- 9233 ChemistryDocument5 pages9233 ChemistryAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base ReactionsDocument4 pagesAcid and Base ReactionsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- 11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsDocument6 pages11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical Waste TheoryDocument14 pagesBio Medical Waste TheoryManish Kumawat100% (1)
- Case Analysis Group 1Document47 pagesCase Analysis Group 1bunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy of Cancer: Submitted by Syama - J.S Roll No:15 2 SEM M Pharm PharmacologyDocument64 pagesChemotherapy of Cancer: Submitted by Syama - J.S Roll No:15 2 SEM M Pharm PharmacologySyama J.S100% (1)
- Skenario Baru 4Document6 pagesSkenario Baru 4Nabila SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Stagehodgkinlymphoma: by Joseph M. Connors, MDDocument5 pagesAdvanced-Stagehodgkinlymphoma: by Joseph M. Connors, MDJOHN LOPERANo ratings yet
- BioSpectrum Asia - November 2016 VK Com StopthepressDocument52 pagesBioSpectrum Asia - November 2016 VK Com StopthepressxibernetixNo ratings yet
- Dandelion Root TreatmentDocument6 pagesDandelion Root Treatmenthubabuba100% (1)
- Fasting and Prayer The Power That Breaks The YokeDocument7 pagesFasting and Prayer The Power That Breaks The YokeRoy C. EstenzoNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument27 pagesBreast Cancerrikshya k c100% (4)
- Pancreatic CancerDocument30 pagesPancreatic CancerHealth Education Library for People75% (4)
- Oncology Conference - HepatoblastomaDocument95 pagesOncology Conference - HepatoblastomaJaysonSoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenNo ratings yet
- Aseptic Dispensing SOPsDocument19 pagesAseptic Dispensing SOPsvickanovriNo ratings yet
- Bun PT Introducere - Removal of Cytostatic Drugs From Aquatic Environment A ReviewDocument18 pagesBun PT Introducere - Removal of Cytostatic Drugs From Aquatic Environment A ReviewsorinamotocNo ratings yet
- Fasting - Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical ApplicationsDocument12 pagesFasting - Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical ApplicationserixsparhawkNo ratings yet
- Aia Health Shield Gold Max English BrochureDocument20 pagesAia Health Shield Gold Max English BrochureRaymond AngNo ratings yet
- Malignant Diseases of The CervixDocument128 pagesMalignant Diseases of The Cervixnicewan0% (1)
- Unedited Trs 2019 Ec22 SeptDocument330 pagesUnedited Trs 2019 Ec22 SeptTeddyNo ratings yet
- Bleomycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageBleomycin Drug StudykyawNo ratings yet
- Insight of Nanomedicine Strategies For A Targeted Del 2021 Journal of Drug DDocument16 pagesInsight of Nanomedicine Strategies For A Targeted Del 2021 Journal of Drug DdianaNo ratings yet
- Tuko BenefitsDocument3 pagesTuko Benefitsalvin_348100% (2)
- Singh 2018Document16 pagesSingh 2018Georgiana BunghiuzNo ratings yet
- Budwig Guide 2020 MinDocument37 pagesBudwig Guide 2020 MinJoão Franco100% (3)
- Pemetrexed As First Line Chemotherapy For NSCLCDocument36 pagesPemetrexed As First Line Chemotherapy For NSCLCAnton HariadiNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy and Nursing ManagementDocument84 pagesChemotherapy and Nursing ManagementAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Ijp - AewqpprovedDocument11 pagesIjp - AewqpprovedIndra HedarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice & Skill: Chemotherapeutic Drugs: Preparing and HandlingDocument6 pagesNursing Practice & Skill: Chemotherapeutic Drugs: Preparing and HandlingAlessandra Dominique MarianoNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs Final PDFDocument8 pagesAnticancer Drugs Final PDFAisha Jamil100% (1)
- HIT LLA Recaida en Pediatria 2020Document34 pagesHIT LLA Recaida en Pediatria 2020Nathalie Soler BarreraNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic Drug ReconstitutionDocument6 pagesCytotoxic Drug Reconstitutioniqhwan riatNo ratings yet