Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evaluative 4th Quarter MPPVIIMHS
Evaluative 4th Quarter MPPVIIMHS
Uploaded by
knutcheOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evaluative 4th Quarter MPPVIIMHS
Evaluative 4th Quarter MPPVIIMHS
Uploaded by
knutcheCopyright:
Available Formats
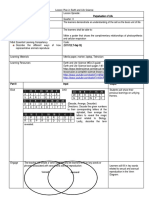
LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8
Section and Time: Grade 8-Cabio Date:05-27-
2021
Learning Predict phenotypic expressions of traits following simple Level 8
Competency patterns of inheritance Quarter 4th
Knowledge: Week
4
No.
Define heredity.
Differentiate between dominant and recessive.
Describe how a Punnett Square is used
Skills:
•
Learning Determine the phenotypes and genotypes of an
Objectives organism.
Predict the outcomes of crosses based on the
principle of probability.
Attitude:
Give a basic explanation of heredity.
• Appreciate the different traits or characteristics of
each organism
Content
Standard 1. how cells divide to produce new cells 2. meiosis as one
of the processes producing genetic variations of the
Mendelian Pattern of Inheritance
Performanc s 2. meiosis as one of the processes producing genetic
e Standard variations of the Mendelian Pattern of Inheritance report
on the importance of variation in plant and animal
breeding
Duration
Topic HEREDITY
1 hr
Learner’s Module
Resources 2 coins
Needed a piece of paper
pencil/pen
1.Heredity- the passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically
from one generation to another.
2.Recessive- relating to or denoting heritable characteristics controlled by
genes that are expressed in offspring only when inherited from both parents
3.Dominant- most important, powerful, or influential
4. Punnet Square- is a square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes
Unlocking of a particular cross or breeding experiment
of terms. 5.Genotype- refers to the genetic makeup of an organism; in other words, it
describes an organism's complete set of genes.
6.Phenotype- the visible or observable expression of the results of genes,
combined with the environmental influence on an organism’s appearance or
behavior.
7.Allele- one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation
and are found at the same place on a chromosome.
8.Gametes- a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell
during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually.
9.Law of Segregation-the pair of genes segregate from each other during
gamete formation.
10. Mutation -is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence, either due to mistakes
when the DNA is copied or as the result of environmental factors such as UV light
and cigarette smoke.
11. Homozygous Dominant -genotype is one in which both alleles are dominant
12. Heterozygous Recessive- alleles only express their phenotype if an organism carries two
identical copies of the recessive allele, meaning it is homozygous for the recessive allele.
13. Heterozygous Dominant -Two different alleles
14. Trait-is a specific characteristic that is unique.
-affect the way we look
-affect how our bodies function
PROCEDURE:
Element of
SUGGESTED ACTIVITIES
the Plan
Awareness
Prayer
Attendance
Review of the past lesson
Showing of a family picture
Activity Tossing of Probability
Intruction
In a group there should be a leader, secretary .Each member should
participate and will give their own idea and opinion. Everyone should
participate in the activity
• Procedure:
On a piece of paper, make a chart similar to the given below.
HEAD TAIL
(H) (h)
Total
Percentage
Ratio of the
combinations
2. Toss a coin. If a head comes up, mark column 1; if a tail, then mark
column 2. Make 50 tosses of the coin.
3. Get the total number of times each face of the coin appears. Calculate
the percentage of the appearance of each face. To compute the percentage:
• (total / 50) x 100 %
4. Let us assume that the coin represents the genotype of a parent, and
each face is an allele, with the head as the dominant allele (H) and the tail
as the recessive allele (h).
On the same piece of paper, make a chart similar to the one given below.
Head -Head Head -Tail Tail-Tail
(HH) (Hh) (hh)
Total
Percentage
Ratio of the
combinations
6. Toss the two coins together. If a head-head combination appears, mark
column 1; if head-tail, mark column 2; and if tail-tail, mark column 3.
Make 50 tosses of the coins.
7. Get the total number of times each combination appears. Calculate the
percentage of the appearance of each combination. To compute the
percentage:
(total / 50) x 100 %
(Math is being integrated in this lesson because students were going
to count the total number of heads, tail and they were going to fine
the percentage of each tail and heads as well as the ratio.)
Criteria
Group Participation 50%
Neatness of output 30%
Display thorough understanding about the activity 20%
100%
In the activity I let students do toss a coin following all the procedures that
is written in their activity sheet. I only facilitated them. This is a learner
centered activity.
Analysis 1.What is the ratio of heads to tails?
2.What is the ratio of the gametes of this parent with heterozygous
genotype?
3.What is the ratio of a head-head, head-tail, and tail-tail combination
when you make 50 tosses.
4. If you toss the same coins in 100,000 times, would you approximately get
the same ratio?
Abstraction
1.What is heredity?
2. What is the use of the Punnett Square?
3. What is the difference between dominant and recessive?
4. What does Law of Segregation states?
Application Solve the following using Punnet square
• 1.Both husband and wife are heterozygous (Aa) for dimples. What are
the chances that their children will have dimples?
• 2.Short hair (L) is dominant over long hair (l) in rabbits. Two
heterozygous rabbits are mated. What phenotypes are expected, and
in what ratios of the bunnies produced?
Assessment Write the letter of the correct answer.
1. One of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation
and are found at the same place on a chromosome.
• A.Heredity C.Allele
• B.Punnet Square D.Phenotype
2. Refers to the genetic makeup of an organism; in other words, it
describes an organism's complete set of genes.
• A.Heredity C.Allele
• B.Genotype D.Phenotype
3. The passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically from one
generation to another.
• A.Heredity C.Allele
• B.Punnet Square D.Phenotype
4. Most important, powerful, or influential trait.
• A.Dominant C.Recessive
• B.Punnet Square D.Phenotype
5. The visible or observable expression of the results of genes, combined
with the environmental influence on an organism’s appearance or behavior.
• A.Heredity C.Allele
• B.Genotype D.Phenotype
Assignment Secure a family picture. Try to observe the characteristics of your (students)
parents, siblings and yourself. Fill in the table below (Add more column if
there are more siblings).
TRAITS FATHER MOTHER YOU
Eye Color
Height
Hair
Hair Color
Facial
features
•
• Research/watch videos about Monohybrid and dihybrid cross. In a ½
sheet of paper write their similarities and differences.Cite atleast
example of each.
(ICT was being integrated in this lesson because students were going
to research/watch videos about monohybrid and dihybrid)
Remarks
Integration Math , ICT are being integrated in the lesson.
You might also like
- Ebook American Corrections 13Th Edition Todd R Clear Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook American Corrections 13Th Edition Todd R Clear Online PDF All Chaptersonya.martinez866100% (11)
- MOHID Matric Result CardDocument1 pageMOHID Matric Result CardAwais Chohan75% (4)
- PF2 S01-15 - The Blooming CatastropheDocument35 pagesPF2 S01-15 - The Blooming CatastropheJared PrestonNo ratings yet
- Biology - The Genetics of Parenthood AnalysisDocument2 pagesBiology - The Genetics of Parenthood Analysislanichung100% (5)
- Rizal's Journey InfographicDocument1 pageRizal's Journey InfographicKrystal shane75% (4)
- Super Hero GeneticsDocument9 pagesSuper Hero GeneticsAnonymous J5sNuoIy100% (2)
- BIOL 1408 Final Exam Review - Chapter 1 - 10 - Concepts and ConnectionsDocument8 pagesBIOL 1408 Final Exam Review - Chapter 1 - 10 - Concepts and ConnectionsTristan ScottNo ratings yet
- The Teacher Will Show Scrambled Words of Recessive, Dominant, Gregor Mendel, Traits, Parents, Offspring, Heredity, Phenotype, Genotype, GenerationDocument3 pagesThe Teacher Will Show Scrambled Words of Recessive, Dominant, Gregor Mendel, Traits, Parents, Offspring, Heredity, Phenotype, Genotype, GenerationDennis Corton Tabinga100% (1)
- Speech Acts: Are The Speaker's Utterances Which Convey Meaning and Make Listeners Do Specific Things (Austin, 1962)Document10 pagesSpeech Acts: Are The Speaker's Utterances Which Convey Meaning and Make Listeners Do Specific Things (Austin, 1962)Ashi Belmonte100% (4)
- Consolidation Worksheets - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesConsolidation Worksheets - Answer KeyAnabela Rodrigues GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Implementing A Curriculum Daily in The ClassroomsDocument3 pagesLesson 2: Implementing A Curriculum Daily in The ClassroomsSherwin Almojera100% (3)
- COT DLL - Science G8 - Food ChainDocument4 pagesCOT DLL - Science G8 - Food ChainRAMIR BECOYNo ratings yet
- K-12 Proposed Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesK-12 Proposed Lesson Plan TemplatePablo Ragay JrNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Inheritance - Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 ScienceDocument7 pagesMendelian Inheritance - Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 SciencebryletumangdayNo ratings yet
- Answers Lab 9 Mendelian GeneticsDocument6 pagesAnswers Lab 9 Mendelian GeneticsIffahRamdzanNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 M4Document16 pagesScience8 Q4 M4Cristy VillamorNo ratings yet
- Honors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Document4 pagesHonors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Irene AntiriNo ratings yet
- Final Edit of Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFinal Edit of Lesson PlanMerjorie BuatisNo ratings yet
- SCI - Learning Packet - Biology Week 3Document9 pagesSCI - Learning Packet - Biology Week 3Pal, Julia HanneNo ratings yet
- 7 Science Week4Document29 pages7 Science Week4NohaNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Learners ModuleDocument23 pagesContextualized Learners ModuleSou MeiNo ratings yet
- Inheritance in Humans 2023Document3 pagesInheritance in Humans 2023Burning PhenomNo ratings yet
- DLL v victoria els-15Document10 pagesDLL v victoria els-15Mark Cristopher NiloNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Document7 pagesInheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Leah HerbertNo ratings yet
- Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Hartwell Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesGenetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Hartwell Solutions ManualNancyWardDDSrods100% (54)
- Cot Lesson Plan GeneticsDocument10 pagesCot Lesson Plan GeneticsPrincess Ronquillo - DuqueNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Teacher Name Date Subject Area Grade Topic TimeDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Teacher Name Date Subject Area Grade Topic Timeapi-534401949No ratings yet
- ME Sci 9 Q1 0201 PSDocument34 pagesME Sci 9 Q1 0201 PSTroy John Rei BautistaNo ratings yet
- Paper Pet ProjectDocument27 pagesPaper Pet Projectapi-406104878No ratings yet
- DLP of 7e (Biology)Document5 pagesDLP of 7e (Biology)Sarah Chua DonascoNo ratings yet
- TAKE HOME TASK GeneticsDocument1 pageTAKE HOME TASK GeneticsjhaghjssNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 3 9Document11 pagesLab Exercise 3 9maria daniela pereyraNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-8 - Q4-Week 3 Mendelian GeneticsDocument20 pagesSCIENCE-8 - Q4-Week 3 Mendelian Geneticsjomarie estibal100% (1)
- Dihybrid Corn Lab: Introduction/BackgroundDocument4 pagesDihybrid Corn Lab: Introduction/BackgroundAnna WilburnNo ratings yet
- Heredity (Incomplete Dominance) DLPDocument7 pagesHeredity (Incomplete Dominance) DLPJasmin CanalesoNo ratings yet
- Week 8.1++Species+&+Phylogenetic+Trees+-+preclass+slidesDocument53 pagesWeek 8.1++Species+&+Phylogenetic+Trees+-+preclass+slidesharleenNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan Nica DemoDocument9 pagesSample Lesson Plan Nica DemoegcajohnpaulNo ratings yet
- And Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceDocument15 pagesAnd Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- GGHHHB CDocument13 pagesGGHHHB CLeyham AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Demonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesDemonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesCherry MaeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Genetics and Heredity 2022Document88 pagesModule 1 Genetics and Heredity 2022Dizzy DeeNo ratings yet
- Genetics Activity BookDocument32 pagesGenetics Activity Bookinamshinte2006No ratings yet
- Taxonomic Concept and PrinciplesDocument14 pagesTaxonomic Concept and Principlespotatoo frieeesNo ratings yet
- SFP Punnet Squares LessonDocument14 pagesSFP Punnet Squares Lessonroni roniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Test Bank BiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Test Bank BiologyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 03.04 Heredity Patterns: Key Questions and Terms Notes ProbabilityDocument5 pagesBiology Notebook: 03.04 Heredity Patterns: Key Questions and Terms Notes ProbabilityKeara RaleighNo ratings yet
- Species Story 2022Document2 pagesSpecies Story 2022Miranda Gowland-WoodNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 4 General ZoologyDocument8 pagesEXERCISE 4 General ZoologyJacob NoraNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Mendelian GeneticsDocument21 pages5.3 Mendelian Genetics25 Mahdi DawoodNo ratings yet
- Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran Genetik Inggris Dan SoalDocument24 pagesRencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran Genetik Inggris Dan SoalAgus Joko SungkonoNo ratings yet
- Altenhoff2019 Protocol InferringOrthologyAndParalogyDocument28 pagesAltenhoff2019 Protocol InferringOrthologyAndParalogyCalvince OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- Cot 2Document4 pagesCot 2Queenie Bonn mae CerlosNo ratings yet
- 03052022024951GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 - Third Quarter-Module 11Document3 pages03052022024951GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 - Third Quarter-Module 11ejNo ratings yet
- Topic Review Guide-Animal Behavior SaranDocument2 pagesTopic Review Guide-Animal Behavior Saranapi-164500293No ratings yet
- Module Learning MaterialDocument18 pagesModule Learning MaterialAngeles, Mark Allen CNo ratings yet
- 302 Biopsychology NotesDocument22 pages302 Biopsychology Notesacz50838No ratings yet
- Genetics W RK SHTDocument123 pagesGenetics W RK SHTChristine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Exemplar Cell Division Canalita&RueloDocument6 pagesExemplar Cell Division Canalita&RueloMICHAEL RUELONo ratings yet
- Melc 3 HeredityDocument37 pagesMelc 3 HeredityJENNIFER DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Exam Review Sbi3u June 2017b2Document7 pagesExam Review Sbi3u June 2017b2BrandonLiNo ratings yet
- D6 Frogs and PhylogenyDocument2 pagesD6 Frogs and Phylogenynshah4No ratings yet
- BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY - Lesson 1, 2 & 3Document5 pagesBIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY - Lesson 1, 2 & 3Jen BadanaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction - Co. CatalyaDocument4 pagesReproduction - Co. CatalyaChristine L. SenoNo ratings yet
- MATATAG-LP DEMO FinalDocument6 pagesMATATAG-LP DEMO Finalmarkmia4334fajardoNo ratings yet
- The Theory and Practice of Breeding to Type and Its Application to the Breeding of Dogs, Farm Animals, Cage Birds and Other Small PetsFrom EverandThe Theory and Practice of Breeding to Type and Its Application to the Breeding of Dogs, Farm Animals, Cage Birds and Other Small PetsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Competencies Taught-UntaughtDocument4 pagesScience 10 Competencies Taught-UntaughtknutcheNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Competencies Taught-UntaughtDocument5 pagesScience 9 Competencies Taught-UntaughtknutcheNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Competencies Taught-UntaughtDocument4 pagesScience 7 Competencies Taught-UntaughtknutcheNo ratings yet
- Grade 9Document3 pagesGrade 9knutcheNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document2 pagesGrade 10knutcheNo ratings yet
- Evaluative 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesEvaluative 3rd QuarterknutcheNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 10 Week 5,3rd QuarterDocument2 pagesDLL Grade 10 Week 5,3rd QuarterknutcheNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 8: ProcedureDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science 8: ProcedureknutcheNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument60 pagesRisk ManagementarunapecNo ratings yet
- Claimant Moot MemoDocument43 pagesClaimant Moot MemoHimanshu Prasad SinghNo ratings yet
- IMRAD FormatDocument3 pagesIMRAD FormatEn Ash100% (1)
- Selene MonologueDocument2 pagesSelene MonologueReign Isabel ValeraNo ratings yet
- GnosticismDocument3 pagesGnosticismGinaPraysNo ratings yet
- Children's WearDocument44 pagesChildren's Wearra s100% (1)
- PW Select October 2016Document22 pagesPW Select October 2016Publishers WeeklyNo ratings yet
- Embodied Yoga Principles Posture Guide Author Embodied Yoga Principles Online Teacher TrainingDocument222 pagesEmbodied Yoga Principles Posture Guide Author Embodied Yoga Principles Online Teacher TrainingKartheek ChandraNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Stories From Dhammapada-P1Document44 pagesBuddhist Stories From Dhammapada-P1Nhuan Tu - TuanNo ratings yet
- Admas University: Faculty of BusinessDocument5 pagesAdmas University: Faculty of Businesseyob negashNo ratings yet
- China Banking Corp vs. CA - GR No.140687Document13 pagesChina Banking Corp vs. CA - GR No.140687Leizl A. VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Arthur Edward Waite - The Pictorial Key To The TarotDocument111 pagesArthur Edward Waite - The Pictorial Key To The TarotFran DossinNo ratings yet
- Rune Name Letter Meaning InterpretationDocument3 pagesRune Name Letter Meaning InterpretationRiley EsaNo ratings yet
- BCG - Upstream M-ADocument18 pagesBCG - Upstream M-AThu NaNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tense PowerPointDocument18 pagesPerfect Tense PowerPointAlejo Chamba100% (1)
- Communication Processes, Principles, and Ethics (Reviewer)Document4 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles, and Ethics (Reviewer)Jessie TindoyNo ratings yet
- 01 Risc MF PDFDocument123 pages01 Risc MF PDFmohmmad omarNo ratings yet
- 4471242v6 1rq National Collective Agreement 2007-2009 Wage Attachment 2016Document15 pages4471242v6 1rq National Collective Agreement 2007-2009 Wage Attachment 2016AdityaNo ratings yet
- THR9 Bro en 3606-8595 12 v0201 PDFDocument16 pagesTHR9 Bro en 3606-8595 12 v0201 PDFJuan Eduardo PFNo ratings yet
- Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000 To 2020Document108 pagesTrends in Maternal Mortality 2000 To 2020shouka.inNo ratings yet
- UCC1Document2 pagesUCC1windykern100% (2)
- He Cordillera Indigenous Peoples ' Right To Land by Arline SantiagoDocument13 pagesHe Cordillera Indigenous Peoples ' Right To Land by Arline SantiagoAallhiex EscartaNo ratings yet
- Petitioners Vs Vs Respondents de Jesus Paguio & Associates Atty. Alberto L. DeslateDocument10 pagesPetitioners Vs Vs Respondents de Jesus Paguio & Associates Atty. Alberto L. DeslateFarrah Stephanie ReyesNo ratings yet