Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATH1179 Vectors and Matrices Book Solution
MATH1179 Vectors and Matrices Book Solution
Uploaded by
OviyanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH1179 Vectors and Matrices Book Solution
MATH1179 Vectors and Matrices Book Solution
Uploaded by
OviyanCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH1179 Mathematics for Computer Science
Vectors and Matrices Tutorial Sheet - Answers
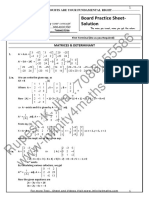
10 − 2 3
1. Let p = q = and r = find p+3q, q-r, p+q-r
3 5 − 2
10 − 2 4
p+3q = +3 =
3 5 18
− 2 3 − 5
q-r = - =
5 − 2 7
10 − 2 3 10 − 5 5
p+q-r = + - = 3 + 7 = 10
3 5 − 2
6 1
1 1
2. Let A = , B = 2 − 3 , C = (2 0 4 )
− 2 5 2 1
3
1 − 5 8 1 0 2 6
D= 1 , E = , F =
− 2 2 1 2 − 2 5 4 3
Evaluate WHERE POSSIBLE the following, if not possible explain why
i) 2A, ii) A+B, iii) BF, iv) CD,
v) DC, vi) B-A, vii) E+F, viii) AE,
ix) ED, x) F2 , xi) A-1
1 1 2 2
i) 2A =2 =
− 2 5 − 4 10
6 1
1 1
ii) A+B = + 2 − 3 not possible - dimensions not the same
− 2 5 2 1
6 1 6 × 2 + 1× 4 6 × 6 + 1 × 3 16 39
2 6
iii) BF = 2 − 3 = 2 × 2 + (−3) × 4 2 × 6 + (−3) × 3 = − 8 3
2 1 4 3 2 × 2 + 1× 4 2 × 6 + 1 × 3 8 15
3
iv) CD = (2 0 4 ) 1 = -2
− 2
3 6 0 12
v) DC = 1 (2 0 4 ) = 2 0 4
− 2 − 4 0 − 8
6 1
1 1
vi) B-A = 2 − 3 - = not possible - dimensions not the same
− 2 5
2 1
Vectors and Matrices Page 1
MATH1179 Mathematics for Computer Science
1 − 5 8 1 0 2 6
vii) E+F = + = not possible - dimensions not the same
2 1 2 − 2 5 4 3
1 1 1 − 5 8 1 0
viii) AE = =
− 2 5 2 1 2 − 2 5
1× 1 + 1× 2 1× (−5) + 1× 1 1× 8 + 1× 2 1× 1 + 1× (−2) 1× 0 + 1× 5
=
( − 2) × 1 + 5 × 2 ( − 2) × ( − 5) + 5 × 1 ( − 2) × 8 + 5 × 2 ( − 2) × 1 + 5 × ( − 2) ( − 2) × 0 + 5 × 5
3 − 4 10 − 1 5
8 15 − 6 − 12 25
3
1 − 5 8 1 0
ix) ED = 1 = not possible –
2 1 2 − 2 5 − 2
rows of D not the same as the number of columns of E.
2 6 2 6 28 30
x) F2 = = =
4 3 4 3 20 33 2 x 2
1 5 − 1 1 5 − 1
xi) A-1 = =
1 × 5 − 1 × (−2) 2 1 7 2 1
3. A rectangle R is given by the coordinates P(1,1) , Q(5,1), R(5,2) and S(1,2)
Draw its position on a graph
Draw its position after transformation with EACH of the following matrices
0 1 0 − 1 − 2 0 − 3
W = V = U = and with the translation vector m =
1 0 1 0 0 − 2 2
You should start each time with R and describe the effect of each of the transformation.
−1 0
Using F = form the product FV and use it to find the position of R after being
0 1
transformed by V and then F.(note the order of composition). Draw FV(R) and comment on
the result.
VR WR FVR =WR
R+m
UR
Vectors and Matrices Page 2
MATH1179 Mathematics for Computer Science
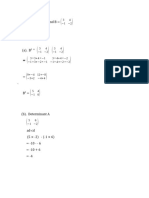
1 5 5 1
R =
1 1 2 2 2 x 4
0 1 1 5 5 1 1 1 2 2
WR = = reflection in the line y = x
1 0 2 x 2 1 1 2 2 2 x 4 1 5 5 1 2 x 4
0 − 1 1 5 5 1 −1 −1 −2 − 2
VR = = rotation 90o a.c.
1 0 2 x 2 1 1 2 2 2x 4 1 5 5 1 2x 4
− 2 0 1 5 5 1 − 2 − 10 − 10 − 2
UR = = enlargement
0 − 2 2 x 2 1 1 2 2 2x 4 − 2 −2 −4 − 4 2 x 4
s.f. -2
− 3
Using w the rectangle is moved back 3 and up 2
2
−1 0 0 − 1 0 1
F × V = =
0 1 2 x 2 1 0 2x2 1 0 2 x 2
0 1 1 5 5 1 1 1 2 2
FVR = =
1 0 2 x 2 1 1 2 2 2 x 4 1 5 5 1 2 x 4
We can see FV = W so the effect is reflection in line y=x
4. Solve the following simultaneous equations using matrices
(i) 2x + 3y = 8 (ii) 4x – y = 21 (iii) 5x +y = 23
x+ 4y = 9 -10x +3y = -53 3x + y = 15
(i) 2x + 3y = 8
2 3 x 8
x+ 4y = 9 =
1 4 2 x 2 y 2 x1 9 2 x1
x 1 4 − 3 8 1 5 1
= = = x=1, y=2
y 2 x1 5 − 1 2 9 5 10 2
(ii) 4x – y = 21
4 − 1 x 21
-10x +3y = -53 =
− 10 3 2 x 2 y 2 x1 − 53 2 x1
x 1 3 1 21 1 10
= = x=5, y=-1
y 2 x1 2 10 4 − 53 2 − 2
(iii) 5x +y = 23
5 1 x 23
3x + y = 15 =
3 1 2 x 2 y 2 x1 15 2 x1
x 1 1 − 1 23 1 8
= = x=4, y=3
y 2 x1 5 − 3 − 3 5 15 2 6
Vectors and Matrices Page 3
MATH1179 Mathematics for Computer Science
5. Why can’t you solve these simultaneous equations ? ( HINT look at them on a graph)
(i) 2x + y = 9 (ii) 2x+3y = 7
6x + 3y = 27 2x + 3y = 8
i) 2x+y=9 Eq.1
6x+3y=27 Eq.2
By dividing Eq.2 by 3 3(2x+y)=3(9) the Eq.2 will became 2x+y=9
So there is only one equation and we cannot solve and obtain two variables (x,y) by one
equation. They represent the same straight line.
ii) There is a conflict on the two equations this can illustrate by subtracting Eq.1 from
Eq.2
2x+3y=7 Eq.1
2x+3y=8 Eq.2
----------------------------------
Result 0 = -1 (?) They represent parallel lines,
In both cases the determinant is 0 alerting you to the problems.
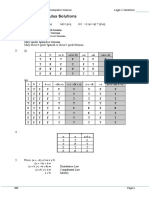
0 − 1
6. Let q be the matrix
1 0
Construct a multiplication table using this as the starting element.
Show that it is closed (eventually no new matrices appear). X
The start of the table is shown 0 − 1 − 1 0
1 0 0 − 1
0 − 1 −1 0 0 1 1 0
X
1 0 0 − 1 −1 0 0 1
0 − 1 −1 0 0 1 1 0 0 − 1
1 0 0 − 1 − 1 0 0 1 1 0
−1 0 0 1 1 0 0 − 1 −1 0
0 − 1 − 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 − 1
0 1 1 0 0 − 1 −1 0 0 1
− 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 − 1 − 1 0
1 0 0 − 1 −1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 − 1 − 1 0 0 1
There are no new matrices appearing in the multiplication table after these as q represents
a quarter turn.
Vectors and Matrices Page 4
You might also like
- Solution Manual of Linear Algebra and Its Application by Gilbert Strang 4th EditionDocument3 pagesSolution Manual of Linear Algebra and Its Application by Gilbert Strang 4th Editionثمر حنیف0% (3)
- 11MM - Chapter 8 Worked SolutionsDocument28 pages11MM - Chapter 8 Worked SolutionsPhuong Ngan Nguyen100% (1)
- Jawapan Revisi Topikal KSSM Matematik Tingkatan 4Document119 pagesJawapan Revisi Topikal KSSM Matematik Tingkatan 4Anuar Bin Che Mi57% (14)
- MATH1179 Text Book Part 1 2021-2022Document78 pagesMATH1179 Text Book Part 1 2021-2022Oviyan100% (1)
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument5 pagesIlovepdf MergedJohn NeperNo ratings yet
- June Practice ExamDocument16 pagesJune Practice ExampritalNo ratings yet
- Cbse Term - Ii Part Test-2: FiitjeeDocument7 pagesCbse Term - Ii Part Test-2: FiitjeeSwastik PandeyNo ratings yet
- Complexnumbers Assmt SolnsDocument3 pagesComplexnumbers Assmt SolnsPran ParakulNo ratings yet
- Complexnumbers Assmt SolnsDocument3 pagesComplexnumbers Assmt SolnsRose WhiteNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full College Algebra 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manual PDFDocument14 pagesDwnload Full College Algebra 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manual PDFreniformcalechexcmp100% (14)
- Business Mathematic CA 1 AssignmentDocument5 pagesBusiness Mathematic CA 1 AssignmentReylend YanataNo ratings yet
- College Algebra 20221940Document9 pagesCollege Algebra 20221940Carl DavisNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Worked-Solutions Year 11 Standard Maths Cambridge NSWDocument33 pagesChapter-3-Worked-Solutions Year 11 Standard Maths Cambridge NSWallthehalls666No ratings yet
- 7 Stepenovanje VezbeDocument2 pages7 Stepenovanje Vezbeapi-358003585No ratings yet
- M-Jawaban Bab 3 MAtriks Kls XI Sukino Ruko 3 Hal 123Document5 pagesM-Jawaban Bab 3 MAtriks Kls XI Sukino Ruko 3 Hal 123Martinus Grady0% (1)
- College Algebra and Trigonometry 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesCollege Algebra and Trigonometry 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manualkavass.quothad29l100% (32)
- Dwnload Full College Algebra and Trigonometry 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full College Algebra and Trigonometry 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manual PDFformyl.luffermto8100% (15)
- Dwnload Full Precalculus A Right Triangle Approach 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Precalculus A Right Triangle Approach 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manual PDFsavidaoicc6100% (10)
- Full Download Precalculus A Right Triangle Approach 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Precalculus A Right Triangle Approach 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions Manualcoosjepurutn100% (28)
- Correção 4ºtesteDocument3 pagesCorreção 4ºtesteCélia NogueiraNo ratings yet
- College Algebra and Trigonometry 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesCollege Algebra and Trigonometry 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualJodyRobinsonawit100% (57)
- College Algebra 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesCollege Algebra 3rd Edition Ratti Solutions ManualMeganPrestonceim100% (52)
- Directed Numbers: SMK Taman Universiti Mathematics Form 2 Teaching & Learning ModuleDocument22 pagesDirected Numbers: SMK Taman Universiti Mathematics Form 2 Teaching & Learning ModuleslpheyNo ratings yet
- Justificaciones CG M Geometria AnaliticaDocument20 pagesJustificaciones CG M Geometria AnaliticaKhris AndrNo ratings yet
- Soalan MCPDocument7 pagesSoalan MCPawangpaker xxNo ratings yet
- Tarea 5 AlgebraDocument6 pagesTarea 5 AlgebraEstefania Rodriguez SanchezNo ratings yet
- Hints & Solutions: Paper-2 Part-I MathematicsDocument6 pagesHints & Solutions: Paper-2 Part-I MathematicsAyushman ParasharNo ratings yet
- (AddMath F4) Ans QB (Add Math F5)Document7 pages(AddMath F4) Ans QB (Add Math F5)Nur SabriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Definite IntegralDocument5 pagesLesson 5 - Definite IntegralEzra M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Fractions RevisionDocument2 pagesAlgebraic Fractions RevisionGangka PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- NM QuadraticDocument4 pagesNM Quadraticvenice wxNo ratings yet
- Chuyên Đề Về Giải Phương Trình Baøi 1.Giaûi caùc phöông trình sauDocument5 pagesChuyên Đề Về Giải Phương Trình Baøi 1.Giaûi caùc phöông trình sauNanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - MatricesDocument77 pagesLesson 3 - MatricesCristine Gersary AguantaNo ratings yet
- 1b. Equations of Straight Lines - AnswersDocument3 pages1b. Equations of Straight Lines - AnswersMacwise IngabireNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper Set 1 Solution 2020 1594823965250Document14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper Set 1 Solution 2020 1594823965250Abhishek thakurNo ratings yet
- Multiplying PolynomialsDocument4 pagesMultiplying PolynomialsFarrah QuiyanNo ratings yet
- Pak 3Document5 pagesPak 3Zahid ButtNo ratings yet
- C1 Coordinate Geometry - AnswersDocument9 pagesC1 Coordinate Geometry - AnswersNazish UsamaNo ratings yet
- Answers QBDocument6 pagesAnswers QBfaeez1979No ratings yet
- MatematikaDocument4 pagesMatematikammusnjakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Tutorial)Document5 pagesChapter 1 (Tutorial)Zikri KiNo ratings yet
- Zadaci Algebarski - IzraziDocument9 pagesZadaci Algebarski - IzraziJelena ZakicNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry: Skills CheckDocument11 pagesCoordinate Geometry: Skills CheckTú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry (Solutions)Document8 pagesAnalytic Geometry (Solutions)Karumon UtsumiNo ratings yet
- 2018 MCR 3UI Exam Review PackageDocument12 pages2018 MCR 3UI Exam Review PackageNHNo ratings yet
- UWA MATHS1721 Workshop 1Document3 pagesUWA MATHS1721 Workshop 1Tai Long HeiNo ratings yet
- Acsbr 2018 Prelim 4exp Am P1 AnsDocument6 pagesAcsbr 2018 Prelim 4exp Am P1 Ansc8ftcky9zwNo ratings yet
- U02 SolucionarioDocument32 pagesU02 SolucionarioÁngel TomásNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12Andrea RojasNo ratings yet
- Soal Matematika Persamaan Kuadrat KelasDocument16 pagesSoal Matematika Persamaan Kuadrat KelasRico YupitaNo ratings yet
- Actividad 4 Unidad 6Document35 pagesActividad 4 Unidad 6Juan David CEBALLOS AGUDELONo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Further Maths Module 1 Assignment AnswersDocument4 pagesAQA A Level Further Maths Module 1 Assignment Answersjlawler69420No ratings yet
- Genmath 5 6Document3 pagesGenmath 5 6Meryl LinesesNo ratings yet
- Solution of Board Practice SheetDocument82 pagesSolution of Board Practice SheetVarnayu AttreeNo ratings yet
- AnsSol JEEMain 2023 PH 2-10-04 2023 Evening PaperDocument23 pagesAnsSol JEEMain 2023 PH 2-10-04 2023 Evening Paperviswanath100% (1)
- Completing The Square Worksheet #01, Algebra Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDocument2 pagesCompleting The Square Worksheet #01, Algebra Revision From GCSE Maths TutorgcsemathstutorNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document1 pageHomework 1Hướng Dương Lê VũNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Soal Try Out 2018 FixDocument20 pagesPembahasan Soal Try Out 2018 Fixwoelancute26ymail.comNo ratings yet
- Soal Matematika Persamaan Kuadrat KelasDocument18 pagesSoal Matematika Persamaan Kuadrat KelasNeta ApriyaniNo ratings yet
- MAT 014 Class PacketDocument83 pagesMAT 014 Class PacketkarpoviguessNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2Document14 pagesAssignment # 2gabriel.charlesNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- MATH1179 Logic Propostional Book Solutions PDFDocument4 pagesMATH1179 Logic Propostional Book Solutions PDFOviyanNo ratings yet
- MATH1179 Graph Theory Book SolutionDocument4 pagesMATH1179 Graph Theory Book SolutionOviyanNo ratings yet
- MATH1179 Probability Book SolutionDocument5 pagesMATH1179 Probability Book SolutionOviyanNo ratings yet
- MATH1179 Calculus Differentiation & Integration Book SolutionDocument5 pagesMATH1179 Calculus Differentiation & Integration Book SolutionOviyanNo ratings yet
- MATH1179 Workbook Part 2 2021-2022Document44 pagesMATH1179 Workbook Part 2 2021-2022OviyanNo ratings yet
- MATH1179 Text Book Part 2 2021-2022Document73 pagesMATH1179 Text Book Part 2 2021-2022OviyanNo ratings yet
- 10.1201 b12471 PreviewpdfDocument600 pages10.1201 b12471 PreviewpdfOviyanNo ratings yet
- U071112WDocument11 pagesU071112WOviyanNo ratings yet
- A Review On User Interface Design PrinciDocument8 pagesA Review On User Interface Design PrinciOviyanNo ratings yet
- Ui DAd 03Document17 pagesUi DAd 03OviyanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Tutorial Activity LifecycleDocument4 pagesWeek 2 Tutorial Activity LifecycleOviyanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Finacial Value of ProjectDocument2 pagesWeek 3 Finacial Value of ProjectOviyanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Tutorial ActivityDocument2 pagesWeek 1 Tutorial ActivityOviyanNo ratings yet
- Development of Smartphone Applications For Nutrition and Physical Activity Behavior ChangeDocument12 pagesDevelopment of Smartphone Applications For Nutrition and Physical Activity Behavior ChangeOviyanNo ratings yet
- User Interface DesginDocument14 pagesUser Interface DesginOviyanNo ratings yet
- Example Heuristic EvaluationDocument21 pagesExample Heuristic EvaluationOviyanNo ratings yet
- Lecture7, Linear TransformationDocument36 pagesLecture7, Linear TransformationHisham MostafaNo ratings yet
- Tajammul HussainDocument2 pagesTajammul HussainMîån ÅbdûllãhNo ratings yet
- SNS Assignment 1-2Document4 pagesSNS Assignment 1-2Farukh AreejNo ratings yet
- 5.6 The Curl of A Vector FieldDocument1 page5.6 The Curl of A Vector FieldRubensVilhenaFonsecaNo ratings yet
- On The Eigenspectrum of The Gram Matrix and Its Relationship To The Operator EigenspectrumDocument18 pagesOn The Eigenspectrum of The Gram Matrix and Its Relationship To The Operator EigenspectrumMartine DumontNo ratings yet
- 15math eDocument7 pages15math eJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Hill CipherDocument3 pagesHill Cipherchime dolkarNo ratings yet
- Vhss Bhawanipatna & Bargarh Bms 3 Quarter Assignment (Set Theory & Matrix)Document2 pagesVhss Bhawanipatna & Bargarh Bms 3 Quarter Assignment (Set Theory & Matrix)Khushi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Theory IMPDocument39 pagesChapter 2 Theory IMPankush ghoshNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - Ii Mathematics - Class Xii Max. Marks: 100Document4 pagesSample Question Paper - Ii Mathematics - Class Xii Max. Marks: 100Nobisuke NobiNo ratings yet
- Viktor T. Toth - A Covariant Form of Maxwell's EquationsDocument3 pagesViktor T. Toth - A Covariant Form of Maxwell's EquationsSenki AlphonsNo ratings yet
- Magic SquaresDocument7 pagesMagic SquaresMassimiliano PatassiniNo ratings yet
- Math 312 Lecture Notes Markov ChainsDocument9 pagesMath 312 Lecture Notes Markov Chainsfakame22No ratings yet
- MATH1310 EngMath1 Sem1!15!16Document7 pagesMATH1310 EngMath1 Sem1!15!16Azrin SaediNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis II HW 2 - Bahran - University of MinnesotaDocument6 pagesReal Analysis II HW 2 - Bahran - University of MinnesotaLinden JavaScriptNo ratings yet
- Cheryl Cleaves, Business Maths, Pearson (Latest Edition) 2. Budnick, Mathematics For Business Economics and Social Science 3. Muhammad AbdullahDocument15 pagesCheryl Cleaves, Business Maths, Pearson (Latest Edition) 2. Budnick, Mathematics For Business Economics and Social Science 3. Muhammad AbdullahRubah Wahla730No ratings yet
- Solution Set 6: To Some Problems Given For TMA4230 Functional AnalysisDocument2 pagesSolution Set 6: To Some Problems Given For TMA4230 Functional AnalysisJoseph Otaku NaruanimangaNo ratings yet
- ME G511 Lect 19 Oct 2018Document44 pagesME G511 Lect 19 Oct 2018Vipul AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics 1 BMFG 1313 Matrices: Slloh@utem - Edu.my Irma@utem - Edu.myDocument32 pagesEngineering Mathematics 1 BMFG 1313 Matrices: Slloh@utem - Edu.my Irma@utem - Edu.myfitriNo ratings yet
- Code: D3 Kcet - 2021 Test Paper With Answer Key (HELD ON SATURDAY 28-08-2021)Document10 pagesCode: D3 Kcet - 2021 Test Paper With Answer Key (HELD ON SATURDAY 28-08-2021)Ryan AahilNo ratings yet
- Can You Hear The Shape of A Manifold?: Andrejs TreibergsDocument44 pagesCan You Hear The Shape of A Manifold?: Andrejs TreibergszazarNo ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument4 pagesVector AlgebraMohammad SajjadNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksDocument3 pagesA Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksAnton Van WykNo ratings yet
- DSP1 - Practice HomeworkDocument3 pagesDSP1 - Practice Homeworkdania alamenNo ratings yet
- TN Board Class 12 Maths-IDocument304 pagesTN Board Class 12 Maths-IVignesh Sdhk Rvs100% (1)
- Palanduz Seperable 2021Document148 pagesPalanduz Seperable 2021Jônatas Oliveira SilvaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gomti Nagar, (Shift-I)Document8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gomti Nagar, (Shift-I)Gg GamerNo ratings yet
- Matthews K.R.-Elementary Linear Algebra - Lecture Notes (1991) PDFDocument146 pagesMatthews K.R.-Elementary Linear Algebra - Lecture Notes (1991) PDFMohammed Demssie MohammedNo ratings yet
- Computational Methods in Power System Analysis - Reijer Idema PDFDocument113 pagesComputational Methods in Power System Analysis - Reijer Idema PDFMichael Parohinog GregasNo ratings yet