Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 viewsLease Tpa
Lease Tpa
Uploaded by
Reeya PrakashThe document discusses key aspects of leases under the Transfer of Property Act 1882 in India. It defines a lease as the transfer of right to enjoy immovable property for a certain time period in exchange for rent. The lessor transfers possession to the lessee while ownership remains with the lessor. If a lease time period is not specified, the law deems it to be year-to-year for agriculture or manufacturing, and month-to-month otherwise. The document outlines rights and obligations of lessors and lessees, such as the lessor's right to rent and recover damages, and the lessee's right to possession and ability to sublease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Lease - Scope Meaning Creation Rights and Liablities Determination and Holding OverDocument8 pagesLease - Scope Meaning Creation Rights and Liablities Determination and Holding OverAaayushi jainNo ratings yet
- Lease Unit 4Document1 pageLease Unit 4Shahvez RafiNo ratings yet
- Definition of LeaseDocument6 pagesDefinition of LeaseMuhammad ShehzadNo ratings yet
- What Is Lease and What Are Its Elements and Termination?: Prepared by Bindranjan Durvijay Singh, SyllbDocument11 pagesWhat Is Lease and What Are Its Elements and Termination?: Prepared by Bindranjan Durvijay Singh, SyllbRanjanSinghNo ratings yet
- LEASEDocument5 pagesLEASEhaiderbukhari1998No ratings yet
- LEASE AND GIFT Under TOPADocument27 pagesLEASE AND GIFT Under TOPAchickenshavedNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument7 pagesLeaseSeenu SeenuNo ratings yet
- Property Law PDFDocument12 pagesProperty Law PDFAmartya Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument7 pagesLeasetriptisahu1196No ratings yet
- Transfer of Property, LeaseDocument7 pagesTransfer of Property, Leasetriptisahu1196No ratings yet
- Lease (Sections 105 To 117)Document17 pagesLease (Sections 105 To 117)Nitin GoyalNo ratings yet
- LEASEDocument9 pagesLEASEChittothidum ChittothidumNo ratings yet
- Topa Law AssignmentDocument15 pagesTopa Law AssignmentbboydextorNo ratings yet
- Lease: Section 105Document14 pagesLease: Section 105Deepak PanwarNo ratings yet
- TOPA NotesDocument47 pagesTOPA NotesnkNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements: The Essential Elements of A Lease Are As FollowsDocument8 pagesEssential Elements: The Essential Elements of A Lease Are As FollowssssNo ratings yet
- Lease, Under Transfer of Property ActDocument11 pagesLease, Under Transfer of Property ActHimadri TiwariNo ratings yet
- All About Lease and Gift Under Transfer of Property Act 1882 by Ayushi ModiDocument9 pagesAll About Lease and Gift Under Transfer of Property Act 1882 by Ayushi ModiAddya GuptaNo ratings yet
- DPC Semester 8 Study NotesDocument10 pagesDPC Semester 8 Study Notesvritika patelNo ratings yet
- Lease Under Transfer of Property ActDocument11 pagesLease Under Transfer of Property Actdivyavishal75% (4)
- The Transfer of Property Act 1882Document7 pagesThe Transfer of Property Act 1882harshad nickNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument16 pagesLeaseAbir Al Mahmud KhanNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument5 pagesLeaseselvaa kumarNo ratings yet
- TRANSFER OF PROPERTY UNIT4 TpaDocument9 pagesTRANSFER OF PROPERTY UNIT4 Tpaaanya meenaNo ratings yet
- Section 107, 108,111. 1650238. 1650261Document13 pagesSection 107, 108,111. 1650238. 1650261Sakshi AnandNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument10 pagesLeaseHarshvardhan MelantaNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument8 pagesLeaseZukhanyeNo ratings yet
- Formation and Termination of LeaseDocument16 pagesFormation and Termination of LeaseTabeer Yaseen70No ratings yet
- Lease of Immovable PropertyDocument5 pagesLease of Immovable PropertyCharran saNo ratings yet
- PROPEETY LAW AND EASEMENT FINAL (Lease)Document8 pagesPROPEETY LAW AND EASEMENT FINAL (Lease)aopera87No ratings yet
- LeaseDocument6 pagesLeaseKhan farazNo ratings yet
- Lease and It's Types Under TPADocument10 pagesLease and It's Types Under TPAoggamer.2802No ratings yet
- Lease and LicenseDocument9 pagesLease and Licenseejbeth01No ratings yet
- Law of PropertyDocument6 pagesLaw of Propertyraju2007kceaNo ratings yet
- Lease Rights of Lessee - Law NotesDocument7 pagesLease Rights of Lessee - Law NotesAbhishek tiwariNo ratings yet
- Exchange Is A Contract by Which The Parties Give To Each Other One Thing For Another (Art. 410-415 of The Draft Law)Document40 pagesExchange Is A Contract by Which The Parties Give To Each Other One Thing For Another (Art. 410-415 of The Draft Law)uwera sylviaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 19 OvesDocument9 pagesASSIGNMENT 19 OvesfaarehaNo ratings yet
- TPA Notes SebiDocument4 pagesTPA Notes SebiSgt Peppers LonelyNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument13 pagesLeaseamiya bhushanNo ratings yet
- Lease 105-117Document10 pagesLease 105-117Sajad HussainNo ratings yet
- Topa Module 3 and 4Document17 pagesTopa Module 3 and 4Tejas JadhavNo ratings yet
- Property 6th SemDocument12 pagesProperty 6th Sem1994sameerNo ratings yet
- Notes 5Document13 pagesNotes 5Kurukshetra Milk PlantNo ratings yet
- Leasae: Simple MeaningDocument9 pagesLeasae: Simple MeaningSyed Ibrahim HassanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 19: Lease DeedDocument9 pagesAssignment 19: Lease DeedfaarehaNo ratings yet
- Parteek Khera 159 Ba LLB Tpa ProjectDocument22 pagesParteek Khera 159 Ba LLB Tpa Projectaujlaparam10No ratings yet
- 762154Document9 pages762154shreyesh sachanNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document5 pagesModule 7siddhant.balpande120No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Land LawDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Land LawBrajesh BeheraNo ratings yet
- Lease and Determination of LeaseDocument3 pagesLease and Determination of LeaseAdan Hooda100% (1)
- All Q - A Property Law LASTDocument2 pagesAll Q - A Property Law LASTsawan hastaNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument6 pagesLeaseIm NayeonNo ratings yet
- LEASE (Compatibility Mode)Document28 pagesLEASE (Compatibility Mode)Santosh K SinghNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument6 pagesLeases2110917107No ratings yet
- ConveyancingDocument9 pagesConveyancingLuv SuchakNo ratings yet
- Definition of Lease Under Section 105 of Transfer of Property ActDocument5 pagesDefinition of Lease Under Section 105 of Transfer of Property Actshikah sidarNo ratings yet
- (106. Duration of Certain Leases in Absence of Written Contract or LocalDocument2 pages(106. Duration of Certain Leases in Absence of Written Contract or LocalAditi SoniNo ratings yet
- TPA Assignment.. Shashwat Srivastava.. 1020171828 PDFDocument22 pagesTPA Assignment.. Shashwat Srivastava.. 1020171828 PDFKushagra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Landlord And Tenant Relationship: Fast & Easy Solutions To Tenancy Problems; In Simple English, For EveryoneFrom EverandLandlord And Tenant Relationship: Fast & Easy Solutions To Tenancy Problems; In Simple English, For EveryoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Leave and Licenses in India: A Guide with Helpful Notes and TipsFrom EverandLeave and Licenses in India: A Guide with Helpful Notes and TipsNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Thought Record - Lang Eng GB - Format ProfessionalDocument4 pagesDysfunctional Thought Record - Lang Eng GB - Format ProfessionalReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Tentative Date Sheet June 2024Document9 pagesIGNOU Tentative Date Sheet June 2024Reeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 635 - Probono Article 1 Defence of Insanity - Anoushka SinghDocument10 pages635 - Probono Article 1 Defence of Insanity - Anoushka SinghReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Updated Cases List - 11.10.21Document11 pagesUpdated Cases List - 11.10.21Reeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- ASPD Can They CollaborateDocument2 pagesASPD Can They CollaborateReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- S.No. Pg. NoDocument17 pagesS.No. Pg. NoReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- FL PresentationDocument3 pagesFL PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Hans Kelson - 20200425131902Document11 pagesHans Kelson - 20200425131902Reeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Eco PresentationDocument2 pagesEco PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Internship Certificate MatterDocument1 pageInternship Certificate MatterReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- InternshipFeedbackFormDocument1 pageInternshipFeedbackFormReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Waqf-Family Law PsdaDocument11 pagesWaqf-Family Law PsdaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- CRPCDocument6 pagesCRPCReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- CpcpsdaDocument5 pagesCpcpsdaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Reeya EvidenceDocument8 pagesReeya EvidenceReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Shareholder Activism As A New Facet of Corporate Governance in IndiaDocument11 pagesShareholder Activism As A New Facet of Corporate Governance in IndiaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 007 JurisprudenceDocument10 pages007 JurisprudenceReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 007juris ReportDocument2 pages007juris ReportReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 007 ICLpsdaDocument7 pages007 ICLpsdaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- TortDocument16 pagesTortReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- JurisprudenceDocument4 pagesJurisprudenceReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Presentation of HistoryDocument3 pagesPresentation of HistoryReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Check 2 - EcoDocument2 pagesPlagiarism Check 2 - EcoReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Admin PresentationDocument5 pagesAdmin PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Effects of Non-Registration of FirmDocument18 pagesEffects of Non-Registration of FirmReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Pol Sci PresentationDocument3 pagesPol Sci PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- TotalitarianismDocument11 pagesTotalitarianismReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Check 1 - EcoDocument4 pagesPlagiarism Check 1 - EcoReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
Lease Tpa
Lease Tpa
Uploaded by
Reeya Prakash0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesThe document discusses key aspects of leases under the Transfer of Property Act 1882 in India. It defines a lease as the transfer of right to enjoy immovable property for a certain time period in exchange for rent. The lessor transfers possession to the lessee while ownership remains with the lessor. If a lease time period is not specified, the law deems it to be year-to-year for agriculture or manufacturing, and month-to-month otherwise. The document outlines rights and obligations of lessors and lessees, such as the lessor's right to rent and recover damages, and the lessee's right to possession and ability to sublease.
Original Description:
Original Title
lease_tpa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key aspects of leases under the Transfer of Property Act 1882 in India. It defines a lease as the transfer of right to enjoy immovable property for a certain time period in exchange for rent. The lessor transfers possession to the lessee while ownership remains with the lessor. If a lease time period is not specified, the law deems it to be year-to-year for agriculture or manufacturing, and month-to-month otherwise. The document outlines rights and obligations of lessors and lessees, such as the lessor's right to rent and recover damages, and the lessee's right to possession and ability to sublease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesLease Tpa
Lease Tpa
Uploaded by
Reeya PrakashThe document discusses key aspects of leases under the Transfer of Property Act 1882 in India. It defines a lease as the transfer of right to enjoy immovable property for a certain time period in exchange for rent. The lessor transfers possession to the lessee while ownership remains with the lessor. If a lease time period is not specified, the law deems it to be year-to-year for agriculture or manufacturing, and month-to-month otherwise. The document outlines rights and obligations of lessors and lessees, such as the lessor's right to rent and recover damages, and the lessee's right to possession and ability to sublease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
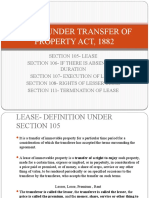
TPA-II
Unit-IV
Lease
Section 105 in The Transfer of Property Act, 1882
105. Lease defined.—A lease of immoveable property is a transfer of a right to enjoy such
property, made for a certain time, express or implied, or in perpetuity, in consideration of a price
paid or promised, or of money, a share of crops, service or any other thing of value, to be
rendered periodically or on specified occasions to the transferor by the transferee, who accepts
the transfer on such terms. Lessor, lessee, premium and rent defined.—The transferor is called
the lessor, the transferee is called the lessee, the price is called the premium, and the money,
share, service or other thing to be so rendered is called the rent.
In India, transfer of property is not possible for every individual because of financial issues. The
permanent or absolute transfer is a luxury for some people, but a temporary transfer is something
that has given every citizen the right of enjoying any property. One of the modes of transferring
property for a particular period of time is Lease. Lease is a transfer of an interest in the property
for a stipulated period of time without transferring the ownership of that property. In a lease,
right of possession is transferred instead of the right of ownership. Transferor here is called the
lessor and the transferee i.e. the one enjoying the property for a period is called lessee. Lease is
governed by the Transfer of Property Act, 1882 and it is given from Sections 105 to 117.
Definition of Lease
Section 105 states the definition of a lease which states that it is a transfer of immovable
property for a particular time period for a consideration of which the transferee has accepted the
terms surrounding the agreement.
What are the essentials of a lease?
•
o Parties must be competent: The parties in a lease agreement should be
competent to enter into a contract. Lesser should be entitled to a property
and have absolute rights over that property.
o Right of possession: Ownership rights are not transferred in a lease, only
the possession of the property is transferred.
o Rent: Consideration for a lease can be taken in the form of a rent or
premium.
o Acceptance: Lessee, who is to get the interest in the property after lease,
has to accept the lease agreement along with the time period and terms &
conditions imposed on the transfer.
o Time Period: Lease always takes place for a particular time period which is
to be specified in the lease agreement. It can be relaxed at the option of the
lessor.
What happens when the lease agreement does not prescribe the time period of the lease?
Section 106 provides for the duration of the lease in the absence of the lease agreement. It
lays down that in the absence of a contract, lease can be ended by both parties to the lease by
issuing a notice to quit. The prescribed time period always commences from the date of receiving
the notice to quit. Following are the circumstances:
Purpose Term (Deemed) Notice Prescribed End
Agricultural or manufacturing purpose. Year to Year 6 month 1 year
Any other purpose. Month to Month 15 days 1 month
In this table, there is a distinction of two purposes in regard to Section 106 i.e. Agricultural or
manufacturing and other purposes. Hence, two things can be derived from this table:
1. When a lease for Agricultural or manufacturing purpose is deemed to be of year to
year, then it will attract a 6-month notice that the lease will end on the expiry of 1 year
from the date of the commencement of the lease.
2. When a lease for any other purpose is deemed to be of the month to month, then it will
attract a 15-day notice that the lease will end on the expiry of 1 month from the
commencement of the lease.
There is proviso to this section which states that the notice to quit in this section should be
written and conveyed to the party who is required to abide by it. If this is not possible then it
should be attached to a conspicuous place in that property.
How is a lease executed?
Section 107 states about lease how made. This section covers three aspects:
1. When there is a lease of Immovable property for a term of 1 year or more – This can
only be made by a registered deed.
2. All other leases of Immovable property – Can be either made by a registered deed or
an oral agreement or settlement along with the transfer of possession of that property.
3. When the lease is of multiple properties that require multiple deeds, it will be made by
both the parties of the lease.
In the case of Punjab National Bank v. Ganga Narain Kapur (1.), Court held that if the lease
is done through an oral agreement, then the provisions of Section 106 will apply.
Rights and liabilities of Lessor and lessee
Rights of the lessor are
1. A lessor has a right to recover the rent from the lease which was mentioned in the
lease agreement.
2. Lessor has a right to take back the possession of his property from the lessee if the
lessee commits any breach of condition.
3. Lessor has a right to recover the amount of damages from the lessee if there is any
damage done to the property.
4. Lessor has a right to take back the possession of his property from the lessee on
the termination of the lease term prescribed in the agreement.
Liabilities of the lessor
1. The lessor has to disclose any material defect relating to the property which the
lessee does not know and cannot with ordinary supervision find out.
2. Lessor is bound by the request of the lessee to give him the right of possession over
his property.
3. Lessor can enter into a contract with the lessee if he agrees to abide by all terms and
conditions prescribed in the agreement, he can enjoy the property for the rest of the
time period without any interference with an obligation to pay the rent later on.
Rights of the lessee
1. During the period lease is in effect if any alteration is made (alluvion for the time
being in force) then that alteration will come under that same lease.
2. If a significant part of the property that has been leased is destroyed wholly or partly
by fire, by flood, by war, by the violent acts of the mob or by any other means
resulting in its inefficiency of being a benefit for the lessee. If this happens, the lease
is voidable at his option.
There is a proviso to this section that states if the damage is done due to any act of the lessee
himself, this remedy will not be available for him.
1. Lessee has the right to deduct any expenses he has made for repairs in the property
from the rent if the lessor has failed to in reasonable time.
2. Lessee has a right to recover any such payment which a lessor is bound to make by
can deducting it from the interest of the rent or directly from the lessor. He has this
right when the lessor has neglected to make that required payment.
3. Lessee has a right to detach all things that he may have attached in the property or
earth. His only obligation is that he has to leave the property in the same condition as
he received it.
4. When a lease is of unspecified duration in the lease agreement, lessee or his legal
representative have a right to collect all the profits or benefits from the crops which
were sown by the lessee at that property. They also have a right of free ingress and
egress from such property even if the lease ends.
5. Lessee has a right to transfer absolutely the property or any part of his interest in that
property by sub-leasing or through mortgaging. Lessee is not independent of the terms
and conditions mentioned in the lease agreement.
Liabilities of the lessee
1. Lessee is under an obligation to disclose all related material facts which are likely to
increase the value of the property for which the lessee has an interest in and the lessor
is not aware of.
2. Lessee is under an obligation to pay the rent or premium which is settled upon in the
agreement to the lessor or his agent within the prescribed time.
3. Lessee is under an obligation to maintain the property in the condition that he initially
got the property on commencement of the lease and he has to return it in the same
condition.
4. If lessee gets to know about any proceedings relating to the property or any
encroachment or any interference, then lessee is under an obligation to give notice to
the lessor.
5. Lessee has a right to use all the assets and goods which are on the property as an
owner would use which is preserving it to the best of its nature. He is although under
obligation to prevent any other person from using that asset or good for any other
purpose from what was prescribed in the lease agreement.
6. The lessee cannot attach any permanent structure without the consent of the lessor
except for the purpose of agriculture.
7. Lessee is under an obligation to give the possession of the property back to the lessor
after the expiry of the prescribed term of the lease.
You might also like
- Lease - Scope Meaning Creation Rights and Liablities Determination and Holding OverDocument8 pagesLease - Scope Meaning Creation Rights and Liablities Determination and Holding OverAaayushi jainNo ratings yet
- Lease Unit 4Document1 pageLease Unit 4Shahvez RafiNo ratings yet
- Definition of LeaseDocument6 pagesDefinition of LeaseMuhammad ShehzadNo ratings yet
- What Is Lease and What Are Its Elements and Termination?: Prepared by Bindranjan Durvijay Singh, SyllbDocument11 pagesWhat Is Lease and What Are Its Elements and Termination?: Prepared by Bindranjan Durvijay Singh, SyllbRanjanSinghNo ratings yet
- LEASEDocument5 pagesLEASEhaiderbukhari1998No ratings yet
- LEASE AND GIFT Under TOPADocument27 pagesLEASE AND GIFT Under TOPAchickenshavedNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument7 pagesLeaseSeenu SeenuNo ratings yet
- Property Law PDFDocument12 pagesProperty Law PDFAmartya Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument7 pagesLeasetriptisahu1196No ratings yet
- Transfer of Property, LeaseDocument7 pagesTransfer of Property, Leasetriptisahu1196No ratings yet
- Lease (Sections 105 To 117)Document17 pagesLease (Sections 105 To 117)Nitin GoyalNo ratings yet
- LEASEDocument9 pagesLEASEChittothidum ChittothidumNo ratings yet
- Topa Law AssignmentDocument15 pagesTopa Law AssignmentbboydextorNo ratings yet
- Lease: Section 105Document14 pagesLease: Section 105Deepak PanwarNo ratings yet
- TOPA NotesDocument47 pagesTOPA NotesnkNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements: The Essential Elements of A Lease Are As FollowsDocument8 pagesEssential Elements: The Essential Elements of A Lease Are As FollowssssNo ratings yet
- Lease, Under Transfer of Property ActDocument11 pagesLease, Under Transfer of Property ActHimadri TiwariNo ratings yet
- All About Lease and Gift Under Transfer of Property Act 1882 by Ayushi ModiDocument9 pagesAll About Lease and Gift Under Transfer of Property Act 1882 by Ayushi ModiAddya GuptaNo ratings yet
- DPC Semester 8 Study NotesDocument10 pagesDPC Semester 8 Study Notesvritika patelNo ratings yet
- Lease Under Transfer of Property ActDocument11 pagesLease Under Transfer of Property Actdivyavishal75% (4)
- The Transfer of Property Act 1882Document7 pagesThe Transfer of Property Act 1882harshad nickNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument16 pagesLeaseAbir Al Mahmud KhanNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument5 pagesLeaseselvaa kumarNo ratings yet
- TRANSFER OF PROPERTY UNIT4 TpaDocument9 pagesTRANSFER OF PROPERTY UNIT4 Tpaaanya meenaNo ratings yet
- Section 107, 108,111. 1650238. 1650261Document13 pagesSection 107, 108,111. 1650238. 1650261Sakshi AnandNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument10 pagesLeaseHarshvardhan MelantaNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument8 pagesLeaseZukhanyeNo ratings yet
- Formation and Termination of LeaseDocument16 pagesFormation and Termination of LeaseTabeer Yaseen70No ratings yet
- Lease of Immovable PropertyDocument5 pagesLease of Immovable PropertyCharran saNo ratings yet
- PROPEETY LAW AND EASEMENT FINAL (Lease)Document8 pagesPROPEETY LAW AND EASEMENT FINAL (Lease)aopera87No ratings yet
- LeaseDocument6 pagesLeaseKhan farazNo ratings yet
- Lease and It's Types Under TPADocument10 pagesLease and It's Types Under TPAoggamer.2802No ratings yet
- Lease and LicenseDocument9 pagesLease and Licenseejbeth01No ratings yet
- Law of PropertyDocument6 pagesLaw of Propertyraju2007kceaNo ratings yet
- Lease Rights of Lessee - Law NotesDocument7 pagesLease Rights of Lessee - Law NotesAbhishek tiwariNo ratings yet
- Exchange Is A Contract by Which The Parties Give To Each Other One Thing For Another (Art. 410-415 of The Draft Law)Document40 pagesExchange Is A Contract by Which The Parties Give To Each Other One Thing For Another (Art. 410-415 of The Draft Law)uwera sylviaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 19 OvesDocument9 pagesASSIGNMENT 19 OvesfaarehaNo ratings yet
- TPA Notes SebiDocument4 pagesTPA Notes SebiSgt Peppers LonelyNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument13 pagesLeaseamiya bhushanNo ratings yet
- Lease 105-117Document10 pagesLease 105-117Sajad HussainNo ratings yet
- Topa Module 3 and 4Document17 pagesTopa Module 3 and 4Tejas JadhavNo ratings yet
- Property 6th SemDocument12 pagesProperty 6th Sem1994sameerNo ratings yet
- Notes 5Document13 pagesNotes 5Kurukshetra Milk PlantNo ratings yet
- Leasae: Simple MeaningDocument9 pagesLeasae: Simple MeaningSyed Ibrahim HassanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 19: Lease DeedDocument9 pagesAssignment 19: Lease DeedfaarehaNo ratings yet
- Parteek Khera 159 Ba LLB Tpa ProjectDocument22 pagesParteek Khera 159 Ba LLB Tpa Projectaujlaparam10No ratings yet
- 762154Document9 pages762154shreyesh sachanNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document5 pagesModule 7siddhant.balpande120No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Land LawDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Land LawBrajesh BeheraNo ratings yet
- Lease and Determination of LeaseDocument3 pagesLease and Determination of LeaseAdan Hooda100% (1)
- All Q - A Property Law LASTDocument2 pagesAll Q - A Property Law LASTsawan hastaNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument6 pagesLeaseIm NayeonNo ratings yet
- LEASE (Compatibility Mode)Document28 pagesLEASE (Compatibility Mode)Santosh K SinghNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument6 pagesLeases2110917107No ratings yet
- ConveyancingDocument9 pagesConveyancingLuv SuchakNo ratings yet
- Definition of Lease Under Section 105 of Transfer of Property ActDocument5 pagesDefinition of Lease Under Section 105 of Transfer of Property Actshikah sidarNo ratings yet
- (106. Duration of Certain Leases in Absence of Written Contract or LocalDocument2 pages(106. Duration of Certain Leases in Absence of Written Contract or LocalAditi SoniNo ratings yet
- TPA Assignment.. Shashwat Srivastava.. 1020171828 PDFDocument22 pagesTPA Assignment.. Shashwat Srivastava.. 1020171828 PDFKushagra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Landlord And Tenant Relationship: Fast & Easy Solutions To Tenancy Problems; In Simple English, For EveryoneFrom EverandLandlord And Tenant Relationship: Fast & Easy Solutions To Tenancy Problems; In Simple English, For EveryoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Leave and Licenses in India: A Guide with Helpful Notes and TipsFrom EverandLeave and Licenses in India: A Guide with Helpful Notes and TipsNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Thought Record - Lang Eng GB - Format ProfessionalDocument4 pagesDysfunctional Thought Record - Lang Eng GB - Format ProfessionalReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Tentative Date Sheet June 2024Document9 pagesIGNOU Tentative Date Sheet June 2024Reeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 635 - Probono Article 1 Defence of Insanity - Anoushka SinghDocument10 pages635 - Probono Article 1 Defence of Insanity - Anoushka SinghReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Updated Cases List - 11.10.21Document11 pagesUpdated Cases List - 11.10.21Reeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- ASPD Can They CollaborateDocument2 pagesASPD Can They CollaborateReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- S.No. Pg. NoDocument17 pagesS.No. Pg. NoReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- FL PresentationDocument3 pagesFL PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Hans Kelson - 20200425131902Document11 pagesHans Kelson - 20200425131902Reeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Eco PresentationDocument2 pagesEco PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Internship Certificate MatterDocument1 pageInternship Certificate MatterReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- InternshipFeedbackFormDocument1 pageInternshipFeedbackFormReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Waqf-Family Law PsdaDocument11 pagesWaqf-Family Law PsdaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- CRPCDocument6 pagesCRPCReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- CpcpsdaDocument5 pagesCpcpsdaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Reeya EvidenceDocument8 pagesReeya EvidenceReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Shareholder Activism As A New Facet of Corporate Governance in IndiaDocument11 pagesShareholder Activism As A New Facet of Corporate Governance in IndiaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 007 JurisprudenceDocument10 pages007 JurisprudenceReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 007juris ReportDocument2 pages007juris ReportReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- 007 ICLpsdaDocument7 pages007 ICLpsdaReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- TortDocument16 pagesTortReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- JurisprudenceDocument4 pagesJurisprudenceReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Presentation of HistoryDocument3 pagesPresentation of HistoryReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Check 2 - EcoDocument2 pagesPlagiarism Check 2 - EcoReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Admin PresentationDocument5 pagesAdmin PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Effects of Non-Registration of FirmDocument18 pagesEffects of Non-Registration of FirmReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Pol Sci PresentationDocument3 pagesPol Sci PresentationReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- TotalitarianismDocument11 pagesTotalitarianismReeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Check 1 - EcoDocument4 pagesPlagiarism Check 1 - EcoReeya PrakashNo ratings yet