Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBT Competences - Map Sept 2015
CBT Competences - Map Sept 2015
Uploaded by
Roxana Blejeru0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views1 page1. The document outlines the competencies required to implement cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) using a collaborative approach.
2. It lists generic therapeutic competencies, basic CBT competencies, specific behavioral and cognitive therapy techniques, and problem specific and metacompetencies.
3. The competencies cover knowledge of CBT principles and models, engagement skills, assessment abilities, and techniques like exposure, activity monitoring, and guided discovery.
Original Description:
CBT competences
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document outlines the competencies required to implement cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) using a collaborative approach.
2. It lists generic therapeutic competencies, basic CBT competencies, specific behavioral and cognitive therapy techniques, and problem specific and metacompetencies.
3. The competencies cover knowledge of CBT principles and models, engagement skills, assessment abilities, and techniques like exposure, activity monitoring, and guided discovery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views1 pageCBT Competences - Map Sept 2015
CBT Competences - Map Sept 2015
Uploaded by
Roxana Blejeru1. The document outlines the competencies required to implement cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) using a collaborative approach.
2. It lists generic therapeutic competencies, basic CBT competencies, specific behavioral and cognitive therapy techniques, and problem specific and metacompetencies.
3. The competencies cover knowledge of CBT principles and models, engagement skills, assessment abilities, and techniques like exposure, activity monitoring, and guided discovery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
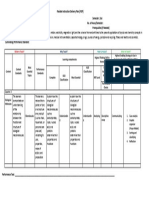
Ability to implement CBT using a collaborative
approach
Generic therapeutic Basic CBT competencies Specific behavioural and Problem specific competencies Metacompetencies
competencies cognitive therapy techniques
Knowledge and Knowledge of basic principles of Exposure techniques Specific phobias
understanding of mental CBT and rationale for treatment Generic
health problems Applied relaxation & applied metacompetencies
tension Social Heimberg model
Knowledge of, and ability to Knowledge of common cognitive Phobia
operate within, professional biases relevant to CBT Activity monitoring & Clark model Capacity to use clinical
and ethical guidelines scheduling judgment when
implementing treatment
Knowledge of the role of safety- Panic Clark model
models
Knowledge of a model of seeking behaviours Guided discovery & Disorder Clark Capacity to adapt
therapy, and the ability to Barlow model
Socratic questioning interventions in
understand and employ the response to client
model in practice Ability to explain and demonstrate feedback
rationale for CBT to client Ability to use thought records OCD Steketee/ Kozac & Capacity to use and
Foa model respond to humour
Ability to engage client
Ability to agree goals for the Ability to identify and work
Borkovec model
intervention with safety behaviours
Clark
Ability to foster and maintain GAD Dugas/ Ladouceur
a good therapeutic alliance, Ability to structure sessions Ability to detect, examine and kmodel
and to grasp the client’s help client reality test Clark
Zinbarg/Craske/ CBT-specific
perspective and ‘world view’ Sharing responsibility for automatic thoughts/images Barlow model metacompentencies
session structure & content
Foa/Rothbaum model
Ability to elicit key cognitions/ Capacity to implement
Ability to manage emotional CBT in a manner
Ability to adhere to an agreed images Resick model
content of sessions PTSD consonant with its
agenda Clark
Ehlers model underlying philosophy
Ability to identify and help
Ability to manage endings Ability to plan and to review client modify assumptions, Clark
Capacity to formulate
practice assignments attitudes and rules Depression – High and apply CBT models
(‘homework’) intensity interventions to the individual client
Ability to undertake generic
assessment (relevant Using summaries and feedback Ability to identify and help
to structure the session client modify core beliefs Cognitive Therapy (Beck) Capacity to select and
history and identifying
apply most appropriate
suitability for intervention)
BT & CBT method
Ability to employ imagery Behavioural Activation
techniques (Jacobson)
Ability to use measures and self Capacity to structure
Ability to make use of
monitoring to guide therapy and ) sessions and maintain
supervision Ability to plan and conduct
to monitor outcome appropriate pacing
behavioural experiments Behavioural Activation
Depression – Low Capacity to manage
(Jacobson)
Ability to devise a maintenance intensity interventions obstacles to CBT
cycle and use this to set targets
therapy
Ability to develop formulation
and use this to develop Behavioural Activation
Problem solving treatment plan /case
conceptualisation
Ability to end therapy in a Ability to understand client’s Guided CBT self-help
planned manner, and to plan for inner world and response to
long-term maintenance of gains therapy
after treatment ends
You might also like
- Syllabus - Strategic Business AnalysisDocument10 pagesSyllabus - Strategic Business AnalysisEfren100% (4)
- The Mindfulness & Acceptance Workbook For AnxietyDocument286 pagesThe Mindfulness & Acceptance Workbook For AnxietyMarian González García100% (49)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (Group Counselling)Document28 pagesCognitive Behavioral Therapy (Group Counselling)Zed Idiaz100% (2)
- Oet StudyDocument36 pagesOet StudyFatima Zehra Nishad86% (36)
- Critical Thinking Skills Developing Effective Anal... - (12 Critical Reflection)Document26 pagesCritical Thinking Skills Developing Effective Anal... - (12 Critical Reflection)Steven JonathanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 11Document2 pagesGeneral Biology 11Lester EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8-Curriculum MapDocument6 pagesGrade 8-Curriculum MapCrystal Gayle Afos-MedranoNo ratings yet
- The Goodman Battery Part 1Document21 pagesThe Goodman Battery Part 1Olivia MNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy RevisitedDocument1 pageBlooms Taxonomy RevisitedMuhammad Zaka EmadNo ratings yet
- Module 16 The Revised Bloom'Staxonomy of EducationalobjectivesDocument18 pagesModule 16 The Revised Bloom'Staxonomy of EducationalobjectivesAli Takahasii (lilibibi)No ratings yet
- OT2 M1 Philo ConceptsDocument3 pagesOT2 M1 Philo ConceptsPalo, Patricia RamonaNo ratings yet
- Pink Pastel Textured Compay Mind Map BrainstormDocument2 pagesPink Pastel Textured Compay Mind Map BrainstormWindhy CabadingNo ratings yet
- Region4A - Validity and Falsity of Real-Life Argument - SalandananDocument3 pagesRegion4A - Validity and Falsity of Real-Life Argument - SalandananJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Authors: Sathish Kumar Mudedla Abdennour Braka Sangwook WuDocument4 pagesAuthors: Sathish Kumar Mudedla Abdennour Braka Sangwook WuHabaekNo ratings yet
- Generic Assessment Rubric TemplateDocument6 pagesGeneric Assessment Rubric TemplateNur Hidayah Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Training Manajemen StratejikDocument11 pagesTraining Manajemen Stratejikalfa rahmatNo ratings yet
- Cidam - PR2Document6 pagesCidam - PR2crystalNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity No. 4-5 Learning Environment: Name: CourseDocument2 pagesLearning Activity No. 4-5 Learning Environment: Name: CourseRomiNo ratings yet
- Marking RubricDocument1 pageMarking RubricMary KarmacharyaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour and Marketing Strategy - Course OutlineDocument17 pagesConsumer Behaviour and Marketing Strategy - Course OutlineMichal MitchellsNo ratings yet
- PGDPM Project Scope and Schedule Case Study RubricDocument3 pagesPGDPM Project Scope and Schedule Case Study RubricedsonNo ratings yet
- If You Want To Build A Ship, Don't Drum Up People To Gather Wood, Saw It and Nail The Planks Together. Instead, Build in Them A Passionate Desire For The SeaDocument20 pagesIf You Want To Build A Ship, Don't Drum Up People To Gather Wood, Saw It and Nail The Planks Together. Instead, Build in Them A Passionate Desire For The SeaNajad SalahudeenNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapDocument3 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapMindanao Community School0% (1)
- Bloom's Taxonomy (Learning Domains) Related With Knowledge and Knowledge Management (KM)Document1 pageBloom's Taxonomy (Learning Domains) Related With Knowledge and Knowledge Management (KM)Md SantoNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Development of Borderline Personality Disorder: A ProposedmodelDocument6 pagesThe Structure and Development of Borderline Personality Disorder: A Proposedmodelh_julietNo ratings yet
- Grad E Level Subject Top 3 Least Learned Melcs Percentage Root Cause Analysis (Why)Document2 pagesGrad E Level Subject Top 3 Least Learned Melcs Percentage Root Cause Analysis (Why)Cherry CarlosNo ratings yet
- LO & Konsep Dasar Pembelajaran KlinikDocument23 pagesLO & Konsep Dasar Pembelajaran KlinikRahmawati NaloleNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapDocument3 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapMindanao Community SchoolNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test - Part ADocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test - Part AAnkitNo ratings yet
- BA Course OutlineDocument6 pagesBA Course OutlineASHI JAINNo ratings yet
- The Revised TaxonomyDocument6 pagesThe Revised TaxonomyFlornel Joy MacahineNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge "Involves The Recall of Specifics and Universals, The Recall of MethodsDocument7 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge "Involves The Recall of Specifics and Universals, The Recall of Methodsshagufta moosaNo ratings yet
- Ii Shadow Master PartDocument48 pagesIi Shadow Master PartScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Government of Canada Executive Group: Guide Chart For EvaluatingDocument1 pageGovernment of Canada Executive Group: Guide Chart For EvaluatingMojtabaNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Level of Knowledge With Description (Assignment)Document2 pagesRubric For Level of Knowledge With Description (Assignment)sivenday21No ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument3 pagesGeneral ChemistryLester Estoquia75% (4)
- MCS Program Learning OutlinesDocument14 pagesMCS Program Learning OutlinesRyan X RoseNo ratings yet
- Klein Et Al MacrocognitionDocument5 pagesKlein Et Al MacrocognitionMac HusseyNo ratings yet
- Wisc - IV-recommendations To ParentsDocument5 pagesWisc - IV-recommendations To ParentsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Conceptual/ Theoritical FrameworkDocument4 pagesConceptual/ Theoritical FrameworkAhmad Fitri AyubNo ratings yet
- Graduate AttibuteDocument2 pagesGraduate AttibuteKrame LuluNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 8 - Unit 1.2 Appropriatenes of Assessment MethodsDocument2 pagesProf Ed 8 - Unit 1.2 Appropriatenes of Assessment MethodsMarjorie MendozaNo ratings yet
- CFLM 2 Lesson 1 To 8Document118 pagesCFLM 2 Lesson 1 To 8Dave Chan100% (2)
- B9MK123 Module GuideDocument7 pagesB9MK123 Module GuideYash BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Commercial Cooking Nciii Training PlanDocument20 pagesCommercial Cooking Nciii Training Planjazzy mallariNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER6 Human Behavior in Organization: Learning and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesCHAPTER6 Human Behavior in Organization: Learning and DevelopmentUltraviolet RemarkeyableNo ratings yet
- Y12 Sylabus PsychologyDocument9 pagesY12 Sylabus Psychologykm6jzq7tt6No ratings yet
- Using Different Methods, Tools and TasksDocument18 pagesUsing Different Methods, Tools and Tasksnissi guingabNo ratings yet
- Obtl Strat 1Document6 pagesObtl Strat 1Christian PiguerraNo ratings yet
- Y7 DT Mobile Hanger Project PresentationDocument58 pagesY7 DT Mobile Hanger Project PresentationLebario MosesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 2 PROJECT-CONSTRUCTION AND SITE MANAGEMENTDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Part 2 PROJECT-CONSTRUCTION AND SITE MANAGEMENTdimitrihemmingsNo ratings yet
- INSET 2019 - TLE 7 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesINSET 2019 - TLE 7 3rd QuarterJennylyn Alumbro DiazNo ratings yet
- 18MBA21 Human Resource Management VTUDocument6 pages18MBA21 Human Resource Management VTUVishnu PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Brief: Subject Code and Title Assessment Individual/Group Length Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesAssessment 1 Brief: Subject Code and Title Assessment Individual/Group Length Learning OutcomeshammadNo ratings yet
- CMAP - Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCMAP - Course OutlineChaitanya JethaniNo ratings yet
- CBL and Habits of Mindv6Document1 pageCBL and Habits of Mindv6api-342501740No ratings yet
- Region 4A - Establishing The Validity and Falsity of Real-Life Argument - SalandananDocument3 pagesRegion 4A - Establishing The Validity and Falsity of Real-Life Argument - SalandananJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Rubric Marking For ISM AssignmentDocument1 pageRubric Marking For ISM AssignmentDipraj KayasthaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - FIDPDocument1 pageBiomolecules - FIDPAustin Capal Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Handouts (Jean Piaget) (Personal Development)Document1 pageHandouts (Jean Piaget) (Personal Development)CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Scenario Thinking: Preparing Your Organization for the Future in an Unpredictable WorldFrom EverandScenario Thinking: Preparing Your Organization for the Future in an Unpredictable WorldNo ratings yet
- Essay On WarDocument8 pagesEssay On Warfesegizipej2100% (2)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy For Negative SymptomsDocument7 pagesCognitive Behavioral Therapy For Negative SymptomsKorn IbraNo ratings yet
- Australian Clinical Psychosis GuidelinesDocument18 pagesAustralian Clinical Psychosis Guidelinessolomon1234567No ratings yet
- Learning CBT An Illustrated Guide PDFDocument21 pagesLearning CBT An Illustrated Guide PDFMaria BagourdiNo ratings yet
- Thesis RRLDocument15 pagesThesis RRLjohn ferrerNo ratings yet
- Student Workbook PDFDocument80 pagesStudent Workbook PDFajkdnfkjdhkjsndNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Ranche and YapDocument10 pagesCognitive Behavioral Therapy Ranche and YapChristian MirandaNo ratings yet
- PhobiasDocument4 pagesPhobiasOti VuraNo ratings yet
- CBT in Cancer Patients ST PDFDocument16 pagesCBT in Cancer Patients ST PDFMerve ApaydınNo ratings yet
- Albert EllisDocument4 pagesAlbert ElliskinlangksNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology - Model 16-Mark EssayDocument1 pagePsychopathology - Model 16-Mark Essaycrosbieiona86No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PerDevDocument22 pagesLesson 2 PerDevCes Reyes100% (1)
- No. 3 - June 2018 - A Second Special Issue On EMDR in PTSD and Other Psychopathological ConditionsDocument2 pagesNo. 3 - June 2018 - A Second Special Issue On EMDR in PTSD and Other Psychopathological ConditionsYolanda BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document5 pagesPaper 2fernanda cornejoNo ratings yet
- Adapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumDocument3 pagesAdapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumVini PezzinNo ratings yet
- Sample Adhd Research PaperDocument7 pagesSample Adhd Research Paperfvhqqm3b100% (1)
- Depression and Cognitive Behavioural TherapyDocument20 pagesDepression and Cognitive Behavioural TherapySandra NgNo ratings yet
- Energy Psychology The Future of Therapy Issue Thirteen, August 2011 Noetic Now Institute of Noetic SciencesDocument5 pagesEnergy Psychology The Future of Therapy Issue Thirteen, August 2011 Noetic Now Institute of Noetic SciencesAbhijith MarathakamNo ratings yet
- Behavioral/ Cognitive Family TherapyDocument6 pagesBehavioral/ Cognitive Family Therapymiji_ggNo ratings yet
- Vantage Sensitivity: A Framework For Individual Differences in Response To Psychological InterventionDocument10 pagesVantage Sensitivity: A Framework For Individual Differences in Response To Psychological InterventionThiago PrimoNo ratings yet
- Logo e Stress Pós TraumaticoDocument77 pagesLogo e Stress Pós Traumaticoedson miazatoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For Adult Anxiety Disorders in Clinical Practice: A Meta-Analysis of Effectiveness StudiesDocument13 pagesCognitive-Behavioral Therapy For Adult Anxiety Disorders in Clinical Practice: A Meta-Analysis of Effectiveness StudiesMaria Inês de AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Suicide Among YouthsDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Suicide Among YouthsRanbom GuyNo ratings yet
- British Gestalt Journal 2020 VOLUME 29 No.1Document70 pagesBritish Gestalt Journal 2020 VOLUME 29 No.1Антон ГромовNo ratings yet
- Generalised Anxiety DisorderDocument5 pagesGeneralised Anxiety DisorderSantosh ParabNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Dan Nasional IntanDocument12 pagesJurnal Internasional Dan Nasional Intanherli padli wijayaNo ratings yet
- CS 410 Assignment On Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesCS 410 Assignment On Literature Reviewsimi chongNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavioral Play TheraphyDocument14 pagesCognitive Behavioral Play TheraphygjavierperezNo ratings yet