Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost Acc - BSA 2-01, Untalasco
Cost Acc - BSA 2-01, Untalasco
Uploaded by
Julienne Untalasco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesThis document discusses different ways that costs can be classified for accounting and managerial purposes. It outlines classifications based on whether costs are manufacturing or non-manufacturing, fixed or variable, direct or indirect, joint or common, capital or operating, and for planning, control, or analysis. Specific types of costs are defined within each classification, such as direct materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs. The purpose of cost classification is to support cost accounting, budgeting, and decision making.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different ways that costs can be classified for accounting and managerial purposes. It outlines classifications based on whether costs are manufacturing or non-manufacturing, fixed or variable, direct or indirect, joint or common, capital or operating, and for planning, control, or analysis. Specific types of costs are defined within each classification, such as direct materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs. The purpose of cost classification is to support cost accounting, budgeting, and decision making.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesCost Acc - BSA 2-01, Untalasco
Cost Acc - BSA 2-01, Untalasco
Uploaded by
Julienne UntalascoThis document discusses different ways that costs can be classified for accounting and managerial purposes. It outlines classifications based on whether costs are manufacturing or non-manufacturing, fixed or variable, direct or indirect, joint or common, capital or operating, and for planning, control, or analysis. Specific types of costs are defined within each classification, such as direct materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs. The purpose of cost classification is to support cost accounting, budgeting, and decision making.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
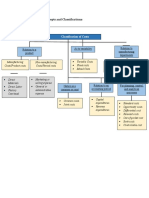
COST CLASSIFICATION IN RELATION TO PRODUCT
a) Manufacturing and non- manufacturing
- Manufacturing costs are the costs incurred during the production of a product. costs include the
cost of direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overheads. Non-manufacturing costs are
expenditures not associated with product costs .Costs include administrative costs, marketing and
selling costs, finance costs etc.
- Manufacturing costs initially form part of product inventory and are expensed out as cost of
goods sold only when the inventory is sold out. Non-manufacturing costs, on the other hand,
never get included in inventory rather are expensed out immediately as incurred.
b) Cost classified as to variability
- Variability of cost is estimated in relation to the volume of production. Some costs vary in
accordance with production while some remain constant. Under this classification, costs are
classified into three groups: Fixed cost. Variable costs, semi-variable costs
- FIXED COST - is that cost that is not affected by any variation in the volume of
output. The amount of fixed cost tends to remain constant for all volumes or
production within the fixed capacity of the plant.
- VARIABLE COST - this is a cost that varies directly with variations in the volume of
output. Such cost increases when the production goes up and correspondingly the cost
decreases when the production declines. However, variations may not always be in the
same proportion.
- SEMI - VARIABLE COST - This cost is partly variable and partly fixed. It possesses
the characteristics of both the fixed and variable.
c) Cost classified as to relation to manufacturing departments
- Production costs refer to the costs a company incurs from manufacturing a product or providing a
service that generates revenue for the company. Production costs can include a variety of expenses,
such as labor, raw materials, consumable manufacturing supplies, and general overhead.
- DIRECT MATERIAL COST- Direct materials are the raw materials that become a
part of the finished product. Manufacturing adds value to raw materials by applying a
chain of operations to maintain a deliverable product. There are many operations that
can be applied to raw materials such as welding, cutting and painting. It is important to
differentiate between direct materials and indirect materials.
- DIRECT LABOR COST - The direct labor cost is the cost of workers who can be
easily identified with the unit of production. Types of labor who are considered to be
part of the direct labor cost are the assembly workers on an assembly line.
- MANUFACTURING OVERHEAD - Manufacturing overhead is any manufacturing
cost that is neither direct materials cost nor direct labor cost. Manufacturing overhead
includes all charges that provide support to manufacturing.
d) Cost classified to their nature as to joint and common
- Joint costs arise when the same resource results in two or more different products at the same time.
Common costs are harder to identify, but include all costs that keep the business running but
which cannot be attributed to one product, department, project, territory or other specific cost
center.
- Some costs benefit more than one product or process in the manufacturing process. These costs are
called Joint costs. Almost all manufacturers incur joint costs at some level the manufacturing
process. It can also be defined as the cost to operate joint-product processes including the disposal
of waste.
- Common costs are business expenses that multiple departments share. Usually, common costs
aren't attributable to a single individual, product or team. Instead, they might benefit multiple
departments, processes or business offerings
e) Cost classified as to relation to an accounting period
- The capital expenditure and revenue expenditure are classified under it. Revenue expenses relate to
the current accounting period. Capital expenditures are the benefits beyond the accounting period.
- In managerial accounting, costs are classified into fixed costs, variable costs or mixed costs (based on
behavior); product costs or period costs (for external reporting); direct costs or indirect costs (based
on traceability); and sunk costs, opportunity costs or incremental costs (for decision-making)
f) Cost for planning, control and analytical process
- Cost planning and control is the estimation of costs, the setting of an agreed budget, and
management of actual and forecast costs against that budget.
- Cost control is the method of reducing business expenses by managing and analyzing financial data.
Collecting costs in a consolidated format allows organizations to make more accurate and informed
projections, know where they can minimize costs, and identify areas of overspending.
- Analytical costs are those costs that are taken into account for analyzing the production activities of
an organization. These costs are the deciding criteria for carrying out business activities.
You might also like
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Assessment YearDocument1 pageIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement 2021-22: Assessment YearDirector GGINo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument18 pagesInternship Reportaamirqaisar10No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Completing The Accounting Cycle PDFDocument142 pagesChapter 4 Completing The Accounting Cycle PDFhakuaNo ratings yet
- Cost Classification or Cost Flow in An OrgaizationDocument8 pagesCost Classification or Cost Flow in An OrgaizationvaloruroNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and ClassificationDocument54 pagesCost Concepts and ClassificationShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 The-Manager-and-Management-AccountingDocument11 pagesChap 2 The-Manager-and-Management-Accountingqgminh7114No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2Sarah Jane Dice DegonesNo ratings yet
- ACG2071 - Chapter 1Document4 pagesACG2071 - Chapter 1Fabian NonesNo ratings yet
- NOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlDocument11 pagesNOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlHanna CasasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Cost Management ConceptsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 Cost Management Conceptsestihdaf استهدافNo ratings yet
- Classification of Costs - TutorialDocument1 pageClassification of Costs - TutorialAnimesh MayankNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Introduction To Cost ConceptsDocument51 pagesModule 2 - Introduction To Cost Conceptskaizen4apexNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter IDocument6 pagesNotes Chapter Iadiebeduya53No ratings yet
- The COST Concept in Managerial Accounting: For Planning, Budgeting, Cost Control, Decision-MakingDocument8 pagesThe COST Concept in Managerial Accounting: For Planning, Budgeting, Cost Control, Decision-MakingRobin LlagunoNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Management ConceptsDocument4 pagesBasic Cost Management ConceptsElvie Abulencia-BagsicNo ratings yet
- MAF Notes Mid ExamDocument8 pagesMAF Notes Mid ExamPenguin Da Business GooseNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts & Classification ShailajaDocument30 pagesCost Concepts & Classification ShailajaPankaj VyasNo ratings yet
- 2 - Terms, Concepts, ClassificationsDocument5 pages2 - Terms, Concepts, ClassificationsALLYSON BURAGANo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesCost AccountingClarivelle NonesNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Management ConceptsDocument7 pagesBasic Cost Management ConceptsHeizeruNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting - Different Kinds of CostsDocument3 pagesCost Accounting - Different Kinds of CostsPam Alem Caval PlarisanNo ratings yet
- FIN600 Module 3 Notes - Financial Management Accounting ConceptsDocument20 pagesFIN600 Module 3 Notes - Financial Management Accounting ConceptsInés Tetuá TralleroNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts: Cost: Lecture Notes On Module-2Document18 pagesCost Concepts: Cost: Lecture Notes On Module-2ramanarao susarlaNo ratings yet
- ACT121 - Topic 2Document2 pagesACT121 - Topic 2Juan FrivaldoNo ratings yet
- ME Unit 2Document53 pagesME Unit 2Rutvij GiteNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Cap. 1.: (Introducción y Tipos de Costos)Document15 pagesManagerial Accounting and Cost Concepts Cap. 1.: (Introducción y Tipos de Costos)Eugenio CamposNo ratings yet
- 2B - Unit 2 - Cost Classification Behaviour & Estimation - Workbook SOLUTIONS - 2022Document47 pages2B - Unit 2 - Cost Classification Behaviour & Estimation - Workbook SOLUTIONS - 2022Bono magadaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Hania M. CalandadaNo ratings yet
- Atp 106 LPM Accounting - Topic 6 - Costing and BudgetingDocument17 pagesAtp 106 LPM Accounting - Topic 6 - Costing and BudgetingTwain JonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Hilton 10th Instructor NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Hilton 10th Instructor NotesKD MV100% (1)
- Cost Concepts HandoutDocument5 pagesCost Concepts HandoutNovilyn LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Cost Accounting: Unit-IDocument65 pagesCost Accounting Cost Accounting: Unit-IPriyanshu JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Cost Classification and ConceptsDocument11 pagesChapter2 - Cost Classification and ConceptsshubhNo ratings yet
- Ca&c NotesDocument6 pagesCa&c NotesLourdes Sabuero TampusNo ratings yet
- Costing For A Spinning Mill PDFDocument13 pagesCosting For A Spinning Mill PDFyogesh kumawatNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and ClassificationsDocument3 pagesCost Concepts and ClassificationsCONCORDIA RAFAEL IVANNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Cost Concept and Classification RevisedDocument48 pagesSession 2 - Cost Concept and Classification Revisedsakshi upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Reviewer)Document3 pagesChapter 2 (Reviewer)Erika May EndencioNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounitng NotesDocument17 pagesCost Accounitng NotesDarlene JoyceNo ratings yet
- Costing For A Spinning MillDocument14 pagesCosting For A Spinning Millvijay100% (1)
- CA Notes2Document3 pagesCA Notes2jeyoon13No ratings yet
- DSFDFJM LLKDocument27 pagesDSFDFJM LLKDeepak R GoradNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2Hk100% (1)
- MA ÔnDocument4 pagesMA ÔnDương Xuân ĐạtNo ratings yet
- CostDocument33 pagesCostversmajardoNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Reviewer Chapter 1-4Document10 pagesCost Accounting Reviewer Chapter 1-4hanaNo ratings yet
- Costing: Prepared By: Dr. B. K. MawandiyaDocument26 pagesCosting: Prepared By: Dr. B. K. MawandiyaNamanNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing Unit IIIDocument22 pagesMarginal Costing Unit IIIAarchi SinghNo ratings yet
- Cost ConceptDocument6 pagesCost ConceptDeepti KumariNo ratings yet
- In Production, Research, Retail, and Accounting, A Cost Is The Value of Money That Has Been Used Up To Produce Something or Deliver A ServiceDocument20 pagesIn Production, Research, Retail, and Accounting, A Cost Is The Value of Money That Has Been Used Up To Produce Something or Deliver A ServiceBHUSHAN PATILNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and ClassificationDocument3 pagesCost Concepts and ClassificationPrincess PilNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and ClassificationDocument3 pagesCost Concepts and ClassificationPrincess PilNo ratings yet
- Cost ConceptsDocument32 pagesCost Conceptsamira samirNo ratings yet
- A.3. Cost ClassificationsDocument57 pagesA.3. Cost ClassificationsTiyas KurniaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting SeminarDocument2 pagesManagerial Accounting SeminarIbrahimm Denis FofanahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Manufacturing BusinessDocument4 pagesLesson 10 - Manufacturing BusinessVISITACION JAIRUS GWENNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument28 pagesCost Accountinglove_oct22100% (1)
- (2330) M Abdullah Amjad BCOM (B)Document9 pages(2330) M Abdullah Amjad BCOM (B)Amna Khan YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- ACC2022 SummaryDocument44 pagesACC2022 Summary7jpvqnk7fkNo ratings yet
- Cost Concept and Classification of CostDocument31 pagesCost Concept and Classification of CostRujean Salar AltejarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Cost Accounting PDFDocument19 pagesUnit - 3 Cost Accounting PDFShreyash PardeshiNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Ferlin Acol Quiz 2 Intact 3Document1 pageFerlin Acol Quiz 2 Intact 3Julienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Julienne Untalasco - Ano Ang Natutunan Ko Sa Leksyon Natin NgayonDocument1 pageJulienne Untalasco - Ano Ang Natutunan Ko Sa Leksyon Natin NgayonJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Nature and Form of The ContractDocument25 pagesChapter1 Nature and Form of The ContractJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Julienne Untalasco - FINAL OUTPUT - FILM CRITQUEDocument3 pagesJulienne Untalasco - FINAL OUTPUT - FILM CRITQUEJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Income Taxation Individual TaxpayersDocument58 pagesWeek 3 Income Taxation Individual TaxpayersJulienne Untalasco100% (1)
- Computations AE 04 2Document17 pagesComputations AE 04 2Julienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- AE 12 (Group Activity) - Capistrano, Par, UntalascoDocument73 pagesAE 12 (Group Activity) - Capistrano, Par, UntalascoJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- First Pencils Ever Made by Nicholas-Jacques Conte PDFDocument1 pageFirst Pencils Ever Made by Nicholas-Jacques Conte PDFJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Articles of Partnership For General Partnerships 2Document4 pagesArticles of Partnership For General Partnerships 2Julienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Myka Eleonor Estole Quiz 5Document8 pagesMyka Eleonor Estole Quiz 5Julienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Why Cant Language Be Separated From Culture and Culture - Not Be Separated From LanguageDocument5 pagesWhy Cant Language Be Separated From Culture and Culture - Not Be Separated From LanguageJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Julienne Untalasco - OPPOSITIONAL INFERENCEDocument1 pageJulienne Untalasco - OPPOSITIONAL INFERENCEJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Ferlin Acol Quiz 2 Gross Estate Part 1Document3 pagesFerlin Acol Quiz 2 Gross Estate Part 1Julienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- BLAW01 - Maceda Law ScriptDocument7 pagesBLAW01 - Maceda Law ScriptJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument17 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents SummaryDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents SummaryJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Bank Recon and Petty CashDocument44 pagesBank Recon and Petty CashJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare Gravestone PDFDocument1 pageShakespeare Gravestone PDFJulienne UntalascoNo ratings yet
- Is We Work A Fraud?Document18 pagesIs We Work A Fraud?AdamNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2019 PDFDocument188 pagesAnnual Report 2019 PDFowen.rijantoNo ratings yet
- People V Kintanar Case DigestDocument3 pagesPeople V Kintanar Case DigestaiceljoyNo ratings yet
- ACCA P6 Mind MapDocument9 pagesACCA P6 Mind MapreaderNo ratings yet
- Acctg 105 Finals Answer KeyDocument13 pagesAcctg 105 Finals Answer KeySusana GarciaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Ericsson Telecommunications, Inc. v. City of Pasig GR No 176667 PDFDocument8 pages12 - Ericsson Telecommunications, Inc. v. City of Pasig GR No 176667 PDFEmelie Marie DiezNo ratings yet
- Adidas Case AnalysisDocument9 pagesAdidas Case AnalysismsklggNo ratings yet
- TATA Motors Final AccountsDocument4 pagesTATA Motors Final AccountsjayanathNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document32 pagesCH 12Abood AlissaNo ratings yet
- Problem 31 1Document3 pagesProblem 31 1CodeSeeker100% (1)
- Financial and Managerial AccountingDocument1 pageFinancial and Managerial Accountingcons theNo ratings yet
- Introductory Financial Accounting - Mock PaperDocument12 pagesIntroductory Financial Accounting - Mock PaperSuyash DixitNo ratings yet
- Max's Group Inc.Document35 pagesMax's Group Inc.Venz LacreNo ratings yet
- Antique2 CUTDocument33 pagesAntique2 CUTrchawdhry123No ratings yet
- Ethiopian Tax SystemDocument26 pagesEthiopian Tax SystemAsfaw WossenNo ratings yet
- Dec2017Document8 pagesDec2017dhande mayurNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting B N GaurDocument85 pagesCost Accounting B N GaurSK LashariNo ratings yet
- Saln TemplateDocument6 pagesSaln TemplateAllan TomasNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS MATHEMATICS 2ND QUARTER 5th WEEK LESSON GROSS NET INCOMEDocument15 pagesBUSINESS MATHEMATICS 2ND QUARTER 5th WEEK LESSON GROSS NET INCOMEDearla BitoonNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco Annual Report 2009 - tcm10-1201956Document144 pagesAtlas Copco Annual Report 2009 - tcm10-1201956Siva Nageswara Rao Chebrolu0% (1)
- Final CDP DanapurDocument191 pagesFinal CDP DanapurdrpklalNo ratings yet
- Taxation - Income TaxDocument158 pagesTaxation - Income Taxnaren197667% (6)
- Ratio AnalysisDocument22 pagesRatio AnalysisUvuvwevwevwe Onyetenyevwe Ugwemubwem Ossas100% (1)
- BASF Report 2018Document290 pagesBASF Report 2018Dridi BadreddineNo ratings yet
- De La Salle Araneta UniversityDocument7 pagesDe La Salle Araneta UniversityBryent GawNo ratings yet
- Tds in Tally - Erp 9Document81 pagesTds in Tally - Erp 9DAKSHPREET17100% (1)
- Equity Trader Before and After Resume SampleDocument2 pagesEquity Trader Before and After Resume SamplepsmadhusudhanNo ratings yet