Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
NCP
Uploaded by
Jasmine Aliamen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesThe document describes a nursing diagnosis of anxious behavior and interventions to address it. The short-term goal is for the patient to be free from injury and discuss feelings of anxiety within 48 hours. Interventions include remaining with the patient, moving them to a quiet area, using relaxation techniques, and avoiding forcing choices. The long-term goal is for the patient to demonstrate relaxation techniques and manage anxiety without assistance within days. Dependent interventions may include medications and instructing their appropriate use.
Original Description:
NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes a nursing diagnosis of anxious behavior and interventions to address it. The short-term goal is for the patient to be free from injury and discuss feelings of anxiety within 48 hours. Interventions include remaining with the patient, moving them to a quiet area, using relaxation techniques, and avoiding forcing choices. The long-term goal is for the patient to demonstrate relaxation techniques and manage anxiety without assistance within days. Dependent interventions may include medications and instructing their appropriate use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesNCP
NCP
Uploaded by
Jasmine AliamenThe document describes a nursing diagnosis of anxious behavior and interventions to address it. The short-term goal is for the patient to be free from injury and discuss feelings of anxiety within 48 hours. Interventions include remaining with the patient, moving them to a quiet area, using relaxation techniques, and avoiding forcing choices. The long-term goal is for the patient to demonstrate relaxation techniques and manage anxiety without assistance within days. Dependent interventions may include medications and instructing their appropriate use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
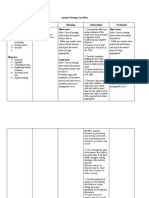
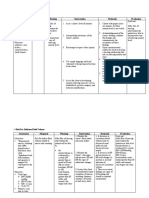
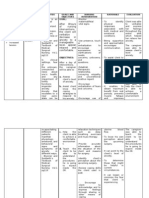
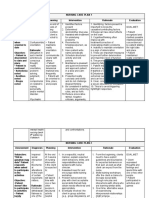
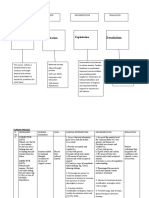
Nursing Diagnosis: ANXIOUS BEHAVIOR
Assessment Desired Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
● Decreasec Short-term: Independent Independent Short-term:
attention After 12-hour shift of 1. Remain with the client at all 1. The client’s safety is a priority. A After 12-hour shift of
span giving effective times when levels of anxiety are highly anxious client should not be left giving effective
● Restleness, nursing interventions high (severe panic) alone; his or her anxiety will escalate. nursing interventions
irritability the patient will be able 2. Move the client to a quiet are 2. Anxious behavior can be escalated the patient will be able
● Poor to: with minimal or decreased stimuli by external stimuli. In a large area, the to:
impulse - Be free from injury such as a small room or seclusion client can feel lost and panicky, but a - Be free from injury
control throughout area. smaller room can enhance a sense of throughout
● Feelings of hospitalization. 3. Remain calm in your approach security. hospitalization.
discomfort, - Discuss feelings of to the client 3. The client will feel more secure if - Discuss feelings of
apprehensio dread, anxiety, and so 4. Use short, simple, and clear you are calm and if the client feels dread, anxiety, and so
n, or forth within 24 to 48 statement. you are in control of the situation forth within 24 to 48
helplessnes hours 5. Avoid asking or forcing the client 4. The client’s ability to deal with hours
s - Respond to to make choices. abstractions or complexity is impaired - Respond to
● Hyperactivit relaxation techniques 6. Be aware of your own feelings 5. The client may not make sound relaxation techniques
y, pacing with staff assistance and level of discomfort. decisions or may be unable to make with staff assistance
● Wringing and demonstrate a 7. Teach the client to use decisions or solve problems. and demonstrate a
hands decreased anxiety relaxation techniques 6. Anxiety is communicated decreased anxiety
● Perceptual level within 2 to 3 independently. interpersonally. Being with an anxious level within 2 to 3
field deficits days. client can raise your own anxiety days.
● Decreased Long Term: Dependent level. Long Term:
ability to After 24-hour shift of 1. PRN medications may be 7. Using relaxation techniques can After 24-hour shift of
communicat giving effective indicated for high levels of anxiety, give the client confidence in having giving effective
e verbally nursing interventions delusions, disorganized thoughts, control over anxiety. nursing interventions
the patient will be able and so forth. Dependent the patient will be able
to: 2. Instruct the patient in the 1. Medications may be necessary to to:
- Demonstrate the appropriate use of antianxiety decrease anxiety to a level at which - Demonstrate the
ability to perform medications. the client can feel safe. ability to perform
relaxation techniques 3. Benzodiazepines such as: 2. Short-term use of antianxiety relaxation techniques
- Reduce own anxiety ● Diazepam(Valium) medications can enhance patient - Reduce own anxiety
level without staff ● Alprazolam coping and reduce physiological level without staff
assistance ● Chlordiazepoxide manifestations of anxiety. assistance
- Be free from anxiety ● Clonazepam 3. Most of these drugs are - Be free from anxiety
attacks ● Lorazepam benzodiazepines, which are attacks
- Manage the anxiety ● Oxazepam commonly prescribed for anxiety. - Manage the anxiety
response to stress 4. Buspirone (BuSpar) These drugs are designed to relieve response to stress
effectively anxiety so that the person can deal effectively
Collaborative more effectively with whatever crisis
1. Encourage the client to identify or situation is causing stress.
supportive resources in the 4. This drug has fewer side effects
community or on the internet. and less risk for dependence than the
2. Encourage the client to identify benzodiazepines. The drug has a
and pursue relationships, personal slower onset of action and may take 1
interests, hobbies, or recreational to 2 weeks to produce a noticeable
activities that may appeal to the therapeutic effect.
client. Collaborative
1. Supportive resources can assist the
client in the ongoing management of
his or her anxiety and decrease social
isolation.
2. The client’s anxiety may have
prevented him or her from engaging in
relationships or activities recently, but
these can be helpful in building
confidence and having a focus on
something other than anxiety.
You might also like
- Psychiatric History Taking FormatDocument10 pagesPsychiatric History Taking Formatleena_awi100% (3)
- Chapter 14 Anxiety and Anxiety DisordersDocument4 pagesChapter 14 Anxiety and Anxiety DisordersCatia Fernandes100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective CopingDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective CopingChiara Fajardo0% (3)
- 1 Example of A Clinical Assessment FormDocument5 pages1 Example of A Clinical Assessment FormMichelle Crawford100% (1)
- Icd 11Document22 pagesIcd 11Shubhangi Vats100% (1)
- History and Evolution of Psychiatric NursingDocument4 pagesHistory and Evolution of Psychiatric Nursingkaren carpio100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Example of Nursing Care Plan: Dr. Evelyn M Del MundoDocument20 pagesExample of Nursing Care Plan: Dr. Evelyn M Del MundoteuuuuNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Stress HspitaiztionDocument1 pageAnxiety Related To Stress HspitaiztionEunice Lan Sandoval Ardiente100% (3)
- HESI Study Guide Psychiatric NursingDocument26 pagesHESI Study Guide Psychiatric NursingDean Winchester100% (5)
- Module 3 Case Analysis 1Document6 pagesModule 3 Case Analysis 1joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (3)
- NCP For ROMDocument7 pagesNCP For ROMampalNo ratings yet
- NCM117 NCPDocument2 pagesNCM117 NCPHANNAH MICOLE GAERLANNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 - Graded SeatworkDocument7 pagesNCM 117 - Graded SeatworkShamsa AfdalNo ratings yet
- Date Cues Nsg. DX Scientific Basis Goal of Care NSG Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesDate Cues Nsg. DX Scientific Basis Goal of Care NSG Intervention Rationale EvaluationWenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPeleinsamNo ratings yet
- DELIRIUMDocument7 pagesDELIRIUMSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationChristine Denise Venus ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument5 pagesPsych NCPJannen Casas100% (3)
- NCP Inffective Individual CopingDocument1 pageNCP Inffective Individual CopingNatalie DulawanNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Nursing Care Plan 1. Separation Anxiety Disorder Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument13 pagesAnxiety Nursing Care Plan 1. Separation Anxiety Disorder Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermMa. Gianella ParduchoNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument3 pagesPsych NCPJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Schizophrenic PatientsDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Schizophrenic PatientsHARVEY SELIMNo ratings yet
- Ncm112a Allncpforcancers BalangueDocument11 pagesNcm112a Allncpforcancers BalangueNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Schiz NCPDocument5 pagesSchiz NCPCharisse LuteroNo ratings yet
- NCP PsychDocument2 pagesNCP PsychGeovi MitreNo ratings yet
- GRPD SomaticNCP-1Document2 pagesGRPD SomaticNCP-1Macmac GalabacNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument1 pageNCP Disturbed Thought Processfretzie azoteNo ratings yet
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 pagesND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," AsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," Asunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument8 pagesAnxiety NCPJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- NSG Care Plan - BipolarDocument17 pagesNSG Care Plan - BipolaraijelethdaldeavilaNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument1 pageDisturbed Thought Processfretzie azoteNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Scizophrenia NCP2Document12 pagesScizophrenia NCP2Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinNo ratings yet
- Winda Suryaningtyas-Resume Bahasa Inggris Kuliah PakarDocument5 pagesWinda Suryaningtyas-Resume Bahasa Inggris Kuliah PakarWinda SuryaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Pilar College of Zamboanga City, IncDocument14 pagesPilar College of Zamboanga City, IncIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Ellen Adarna, Borikat Na Siya. Ga Igat Igat Lang Na Siya"Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ellen Adarna, Borikat Na Siya. Ga Igat Igat Lang Na Siya"dubouzettheresaNo ratings yet
- Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument24 pagesGeneralized Anxiety DisorderEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For SchizophreniaDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan For SchizophreniaJoseph MuzabulaNo ratings yet
- Case Study SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesCase Study SchizophreniaCHRISANTO ARZANANNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument11 pagesNursing Diagnosisseife slassieNo ratings yet
- NCP, 3 Case StudyDocument9 pagesNCP, 3 Case StudyKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument5 pagesRisk For InjuryAllene PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationnipheyy dananNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Depression PDFDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Depression PDFtanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- Ortho NCPDocument1 pageOrtho NCPErjohn Vincent Lim100% (1)
- NCP For CSDocument2 pagesNCP For CSIris Coronel AdamosNo ratings yet
- Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperac Tivity/ph Ysical Agitatio NDocument2 pagesRisk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperac Tivity/ph Ysical Agitatio NCindy BelmesNo ratings yet
- NCP Checked FinalDocument8 pagesNCP Checked FinalyasiraNo ratings yet
- NCP SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesNCP Schizophreniajoshua canja100% (6)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Alcoholism Care PlanDocument11 pagesAlcoholism Care Planilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Inability To Bear Down: Problems With The Psyche FactorsDocument4 pagesInability To Bear Down: Problems With The Psyche FactorsErvina Luisa Delias CampusNo ratings yet
- CounselingDocument5 pagesCounselingIrene Demegillo Salonga100% (2)
- NCP Psyche2Document6 pagesNCP Psyche2Nica RTNo ratings yet
- Mokalid, Bkom NCPDocument7 pagesMokalid, Bkom NCPKC Olaizzah MokalidNo ratings yet
- NCP-and-Drug-study For MENDocument8 pagesNCP-and-Drug-study For MENVillie SumandeNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Rogue Hypnotist's Powerful Hypnosis - Revealing Confessions of a Rogue HypnotistFrom EverandSummary of The Rogue Hypnotist's Powerful Hypnosis - Revealing Confessions of a Rogue HypnotistNo ratings yet
- How to Stop Overthinking Your Relationship and Heal from Narcissistic AbuseFrom EverandHow to Stop Overthinking Your Relationship and Heal from Narcissistic AbuseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Case Study 2 (PTSD)Document12 pagesCase Study 2 (PTSD)Atul MishraNo ratings yet
- Admin,+25 29+JPS+Rini+1Document5 pagesAdmin,+25 29+JPS+Rini+1YAHYA Al-HILALNo ratings yet
- European Clinical Guidelines For Tourette Syndrome and Other Tic DisordersDocument43 pagesEuropean Clinical Guidelines For Tourette Syndrome and Other Tic Disorderscaleidoscopio_saludmentalNo ratings yet
- PhobiaDocument6 pagesPhobiaVirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Social Anxiety Disorder 1.editedDocument4 pagesSocial Anxiety Disorder 1.editedmoureenNo ratings yet
- What Are Monocular CuesDocument1 pageWhat Are Monocular CuesIsaiah TalensNo ratings yet
- On SchizophreniaDocument30 pagesOn SchizophreniaRanieska GoNo ratings yet
- 3 Flippin2010Document19 pages3 Flippin2010Psicoterapia InfantilNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument1 pageSchizophreniaBrittNo ratings yet
- Depresión (Dos Semanas)Document3 pagesDepresión (Dos Semanas)AcdaNo ratings yet
- Hypersexual Disorder - A Proposed Diagnosis For DSM-VDocument25 pagesHypersexual Disorder - A Proposed Diagnosis For DSM-VGabriela GomesNo ratings yet
- 8-Somatic Symptom and Related DisorderDocument31 pages8-Somatic Symptom and Related DisorderZ26No ratings yet
- List of Books: S.N Author Title Publication ISBN QTY RemarkDocument2 pagesList of Books: S.N Author Title Publication ISBN QTY RemarkTemesgen EndalewNo ratings yet
- Association Between Psychotic Experiences and Traumatic Life Events The Role of The Intention To HarmDocument12 pagesAssociation Between Psychotic Experiences and Traumatic Life Events The Role of The Intention To HarmTinaNo ratings yet
- Mental Satus Exam FormDocument3 pagesMental Satus Exam FormRej GarbosaNo ratings yet
- Met 4 Powers of The MindDocument9 pagesMet 4 Powers of The MindSophia BompatNo ratings yet
- Narcissistic Personality DisorderDocument7 pagesNarcissistic Personality DisorderRoxiiJANo ratings yet
- Experience With Homoeopathy in A Case of Intrusive ThoughtsDocument3 pagesExperience With Homoeopathy in A Case of Intrusive ThoughtsHomoeopathic Pulse100% (2)
- Pe Substance Use Disorder Compressed 1Document21 pagesPe Substance Use Disorder Compressed 1David Aldrich LimNo ratings yet
- Trauma in Schools PresentationDocument84 pagesTrauma in Schools Presentationapi-252538062No ratings yet
- Cluster Word Web 2Document1 pageCluster Word Web 2api-430754451100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis PDFDocument42 pagesChapter 3 Clinical Assessment and Diagnosis PDFGabriel Jeremy OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Paralysis PresentationDocument12 pagesSleep Paralysis Presentationdpreston1441No ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument89 pagesPsychiatric NursingJoyVee Pillagara-De LeonNo ratings yet
- (2021) Cognitive Behavioral Analysis System of Psychotherapy Reduces Loneliness in Patients With Persistent Depressive DisorderDocument9 pages(2021) Cognitive Behavioral Analysis System of Psychotherapy Reduces Loneliness in Patients With Persistent Depressive DisorderJúlio César SouzaNo ratings yet
- Feldman10 PPT ch14Document26 pagesFeldman10 PPT ch14hamza_shaukatNo ratings yet