Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufactu
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufactu
Uploaded by
Pallabi JaiswalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Module-1 Additive Manufacturing 18 SchemeDocument47 pagesModule-1 Additive Manufacturing 18 SchemeSANTOSH100% (1)
- 3D PRINTING OF BUILDING PresentationDocument19 pages3D PRINTING OF BUILDING PresentationMd Fayazuddin50% (2)
- Study of The Use of 3D Technologies and Associated Social and Ethical Issues in BoeingDocument14 pagesStudy of The Use of 3D Technologies and Associated Social and Ethical Issues in BoeingDebarshi BiswasNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument12 pages3D Printingriddhima.thankiNo ratings yet
- A New Emerging TechnologyDocument16 pagesA New Emerging TechnologyAmey MairalNo ratings yet
- DF Lab ManualDocument80 pagesDF Lab ManualSruthi ChallapalliNo ratings yet
- APM Additive Manufacturing FinalDocument4 pagesAPM Additive Manufacturing FinalAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing: Slicing: From 3D Model To 3D PrinterDocument10 pages3D Printing: Slicing: From 3D Model To 3D PrinterAadil KakarNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Civil EngineeringDocument13 pagesEmerging Trends in Civil EngineeringAyush ShethNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing and Pre - FabricationDocument16 pages3D Printing and Pre - FabricationAyush ShethNo ratings yet
- Am - Unit 1 - NotesDocument14 pagesAm - Unit 1 - NotesNarender NarruNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument7 pages3D PrintingwizardNo ratings yet
- A New Emerging TechnologyDocument16 pagesA New Emerging TechnologyHumanityNo ratings yet
- All About 3d Concrete PrintingDocument6 pagesAll About 3d Concrete Printinggk_kishoree81No ratings yet
- Presented By: Kalpesh Shah M.E. (Design)Document40 pagesPresented By: Kalpesh Shah M.E. (Design)Terminator941988No ratings yet
- Module - 1: Regulation - 2015 (CBCS Scheme) Additive Manufacturing - 15me82Document37 pagesModule - 1: Regulation - 2015 (CBCS Scheme) Additive Manufacturing - 15me82swaroop kenganalNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument6 pagesUnit IDhaneshNo ratings yet
- 3d PrintingDocument74 pages3d PrintingDknargesh 2003No ratings yet
- 3de PrintingDocument17 pages3de PrintingNaveen AnanthNo ratings yet
- English Thesis PresentationDocument2 pagesEnglish Thesis PresentationBhagya sreekumarNo ratings yet
- C1 C Girum Tesfaye Gedecho 3D PrintingDocument5 pagesC1 C Girum Tesfaye Gedecho 3D PrintingGirum TesfayeNo ratings yet
- IAM3D ReportDocument11 pagesIAM3D Reportsiva shankarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Additive ManufacturingDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Additive Manufacturingsuvojitchunari001No ratings yet
- The Art of Additive ManufacturingDocument17 pagesThe Art of Additive ManufacturingHARISHRUTHINo ratings yet
- Exploring The Future: 3D Printing TechnologyDocument9 pagesExploring The Future: 3D Printing Technologyvss.shishirNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document37 pagesModule 1Lokesh Lokesh D SNo ratings yet
- UNIT I-Summary Need of Additive ManufacturingDocument4 pagesUNIT I-Summary Need of Additive ManufacturingRajijackNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument14 pagesUntitled PresentationAyush ShethNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 3D Printing: DT: 06 Apr 20Document2 pagesIntroduction To 3D Printing: DT: 06 Apr 20praveenhegdeNo ratings yet
- Anjuman College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument12 pagesAnjuman College of Engineering & TechnologyZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- 3-D Printing: ContentDocument9 pages3-D Printing: ContentRitik PothareNo ratings yet
- Reverse EngineeringDocument13 pagesReverse Engineeringprashant6942100% (3)
- Design and Fabrication of 3d PrintingDocument23 pagesDesign and Fabrication of 3d PrintingManikanta Venkata100% (1)
- Rapid Prototyping: Kubersuryavanshi BT16MEC004 Nationalinstitute of TechnologyuttarakhandDocument26 pagesRapid Prototyping: Kubersuryavanshi BT16MEC004 Nationalinstitute of TechnologyuttarakhandShubham ChomalNo ratings yet
- 3d PrintingDocument36 pages3d PrintingARJUN MPNo ratings yet
- 3d PrintingDocument19 pages3d PrintingthedooodledenNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Coursera NotesDocument16 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Coursera Notespolladhavan 1No ratings yet
- RP MaterialDocument3 pagesRP MaterialAnantNo ratings yet
- What Is Reverse Engineering?Document15 pagesWhat Is Reverse Engineering?Kuldeep GautamNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666412721000441 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2666412721000441 MainBM20623 Wan Mohamad Danial Bin Wan SyariffudinNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument31 pagesAdditive ManufacturingDaeNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument2 pagesAdditive ManufacturingsmrajbeNo ratings yet
- Metal Additive Manufacturing Explained: Grow by 27.9%Document3 pagesMetal Additive Manufacturing Explained: Grow by 27.9%rodolfoNo ratings yet
- Avances TecnologicosDocument13 pagesAvances TecnologicosSALAZAR VILLEGAS ESTEBAN DAMIANNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATIC BIKE Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesPNEUMATIC BIKE Seminar Reportprajakta chaudhari100% (1)
- 3d Printing AssignmentDocument7 pages3d Printing Assignmentnana100% (1)
- 3d PrintingDocument14 pages3d PrintingRaj SanthoshNo ratings yet
- IJRET20160516038Document4 pagesIJRET20160516038Youssef AliNo ratings yet
- 3D PrinterDocument21 pages3D Printerrajibnaskar425No ratings yet
- Activity On PL SQLDocument3 pagesActivity On PL SQLShubham MoteNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Special Report 1018Document33 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Special Report 1018OARIASCO100% (1)
- General Seminar 3-D PrintingDocument19 pagesGeneral Seminar 3-D PrintingVipul VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Kaushalendra PDFDocument24 pagesKaushalendra PDFharshNo ratings yet
- Maham Lateef: 3D Printers & PrintingDocument16 pagesMaham Lateef: 3D Printers & PrintingRogerHuang100% (1)
- Digital ManufacturingDocument7 pagesDigital ManufacturingAvik K DuttaNo ratings yet
- IJRPR12244Document7 pagesIJRPR12244Sai AnirudhNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 AmDocument127 pagesUnit - 4 AmLalit Banaal100% (1)
- Additive Manufacturing: Making The Quantum Leap To MainstreamDocument2 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: Making The Quantum Leap To Mainstreamdharmender142No ratings yet
- BLEPT 09-2016 Room Assignment Rosales-SecDocument114 pagesBLEPT 09-2016 Room Assignment Rosales-SecPRC Baguio50% (2)
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationTaufik TajudinNo ratings yet
- Materi Komposit - Prof. Anne ZulfiaDocument59 pagesMateri Komposit - Prof. Anne ZulfiaMuhammad ThohariNo ratings yet
- Honorato C. Perez, Sr. Memorial Science High SchoolDocument8 pagesHonorato C. Perez, Sr. Memorial Science High SchoolJOMARI DL. GAVINONo ratings yet
- Mud Max Mud Max Compact: Centrifugal Pump Series 250Document32 pagesMud Max Mud Max Compact: Centrifugal Pump Series 250Hussein MohamedNo ratings yet
- An Essay On AdvertisementDocument6 pagesAn Essay On Advertisementafhbctdfx100% (2)
- AQUARIUS EC DatasheetDocument4 pagesAQUARIUS EC DatasheetÇağlayan TopNo ratings yet
- Insight NDT Equipment LTD - ..Document2 pagesInsight NDT Equipment LTD - ..aoxoxzNo ratings yet
- CCTV PoleDocument180 pagesCCTV PoleAnonymous zMWvcTNo ratings yet
- E0234 PPTDocument41 pagesE0234 PPTjerry.sharma0312No ratings yet
- TALQ White Paper: The Smart City ProtocolDocument14 pagesTALQ White Paper: The Smart City ProtocolFiras KACHROUDINo ratings yet
- Electrode Consumption PDFDocument1 pageElectrode Consumption PDFharold_bhieNo ratings yet
- 2.mean Value TheoremsDocument29 pages2.mean Value TheoremsPratyush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 02 Introduction To Numerical AnalysisDocument27 pages02 Introduction To Numerical AnalysisBruhNo ratings yet
- Emedicine Hypersemesis GravidarumDocument26 pagesEmedicine Hypersemesis GravidarumAnonymous 3OoumAUytNo ratings yet
- Laserjet Professional M1130/M1210: MFP SeriesDocument16 pagesLaserjet Professional M1130/M1210: MFP SeriesDhanesh RamachandramNo ratings yet
- DSP Integrated Circuits 3Document3 pagesDSP Integrated Circuits 3brindkowsiNo ratings yet
- Nanomagnets Versus Nanofiltration in Water Treatement - VSKDocument8 pagesNanomagnets Versus Nanofiltration in Water Treatement - VSKmoganasandeepNo ratings yet
- BCD 16206 e Nu 545 500Document1 pageBCD 16206 e Nu 545 500Rajeesh P RaviNo ratings yet
- Essay On U.N.H.R.C Report On Ficancialization of HousingDocument3 pagesEssay On U.N.H.R.C Report On Ficancialization of HousingMuhammad EhtishamNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic and Respiratory Equipment - Laryngoscopes For Tracheal IntubationDocument2 pagesAnaesthetic and Respiratory Equipment - Laryngoscopes For Tracheal IntubationAisha MughalNo ratings yet
- Linear Guideway: 1. Features of HIWIN Linear Guideways 2 - Series of Linear GuidewaysDocument39 pagesLinear Guideway: 1. Features of HIWIN Linear Guideways 2 - Series of Linear GuidewaysyusufagcatrNo ratings yet
- Exponents, Radicals and LogarithmsDocument32 pagesExponents, Radicals and LogarithmsandrikaNo ratings yet
- SAA17 - Download What The Forecast On Windows PC 11,10,8,7Document4 pagesSAA17 - Download What The Forecast On Windows PC 11,10,8,7Sakshi MishraNo ratings yet
- 8 Weeks To Bigger Pecs 2Document11 pages8 Weeks To Bigger Pecs 2Ryan PanNo ratings yet
- HRCT ProtocolsDocument17 pagesHRCT ProtocolsZezo KaraNo ratings yet
- Geological Chance of SuccessDocument11 pagesGeological Chance of SuccesssarapkanNo ratings yet
- Specsheet It02 07Document2 pagesSpecsheet It02 07Jamel GrineNo ratings yet
- Resistors Module 01Document10 pagesResistors Module 01VinodKumarTummalurNo ratings yet
- NE 242 Syllabus 2013Document4 pagesNE 242 Syllabus 2013Nick VardyNo ratings yet
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufactu
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufactu
Uploaded by
Pallabi JaiswalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufactu
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufactu
Uploaded by
Pallabi JaiswalCopyright:
Available Formats
Pros and Cons of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a manufacturing process that
creates three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer. It has gained
popularity in recent years due to its ability to create complex designs with high
precision. Here are some pros and cons of additive manufacturing:
Pros:
Design flexibility: Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex
and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to produce with
traditional manufacturing techniques.
Cost-effective: Additive manufacturing eliminates the need for tooling,
reducing production costs and making it a cost-effective manufacturing method for
small production runs.
Faster production: Additive manufacturing can produce parts faster than
traditional manufacturing techniques, allowing for faster time-to-market for new
products.
Waste reduction: Additive manufacturing produces less waste than traditional
manufacturing methods because it only uses the exact amount of material needed for
the object being produced.
Customization: Additive manufacturing enables the creation of customized
products with unique features tailored to specific customer needs.
Cons:
Material limitations: Additive manufakcturing is limited in terms of the
range of materials it can use, which can limit the properties of the objects
produced.
Limited size: The size of objects that can be produced through additive
manufacturing is limited by the size of the 3D printer used.
Surface quality: The surface finish of objects produced through additive
manufacturing may not be as smooth as those produced through traditional
manufacturing techniques.
Post-processing requirements: Objects produced through additive manufacturing
may require post-processing, such as polishing or coating, to achieve the desired
surface finish or other properties.
Cost of equipment: The cost of equipment required for additive manufacturing
can be high, making it a less viable option for some businesses.
Briefly Explain Reverse Engineering.
Reverse engineering is the process of deconstructing or analyzing an existing
product or system to understand its design, function, and components. The goal of
reverse engineering is to obtain a detailed understanding of how the product or
system works, with the aim of replicating, improving, or modifying it. Reverse
engineering involves breaking down the product or system into its individual
components, examining each component's design and function, and determining how
they work together to achieve the desired end result. This process often involves
the use of specialized software, tools, and techniques to capture and analyze data,
such as 3D scanning, CAD modeling, and material testing. Reverse engineering is
often used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where
products are complex and have a long lifecycle.
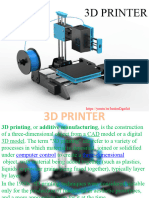
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is a process of creating a physical object from a digital design
or model using a specialized machine known as a 3D printer. The process involves
building up layers of material, such as plastic, metal, or even biological matter,
one at a time, until the desired object is complete. The design is first created
using computer-aided design (CAD) software, and the 3D printer then reads the
digital file and creates the object by depositing layers of material based on the
design specifications. 3D printing has many applications in various industries,
including manufacturing, medicine, architecture, and art, and it allows for the
creation of complex geometries and shapes that would be difficult or impossible to
achieve using traditional manufacturing methods.
Difference between Additive Vs Subtractive Manufacturing
Additive and subtractive manufacturing are two different approaches to
creating physical objects, with the former adding material layer by layer and the
latter removing material from a larger block. The main differences between additive
and subtractive manufacturing are as follows:
Additive Manufacturing:
Adds material layer by layer to create the final object.
Starts with a digital model or design, which is used to guide the printing
process.
Can create complex geometries and shapes that are difficult or impossible to
achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Uses a range of materials, including plastics, metals, and even biological
materials.
Generally slower than subtractive manufacturing but can be more cost-
effective for creating complex designs in small quantities.
Subtractive Manufacturing:
Starts with a larger block of material and removes material to create the
final object.
Uses a range of cutting tools such as drills, lathes, and milling machines to
remove material from the workpiece.
Is often faster than additive manufacturing for producing large quantities of
simpler designs.
Limited in terms of the geometries and shapes that can be created compared to
additive manufacturing.
Generally more wasteful, as the removed material cannot be easily reused.
You might also like
- Module-1 Additive Manufacturing 18 SchemeDocument47 pagesModule-1 Additive Manufacturing 18 SchemeSANTOSH100% (1)
- 3D PRINTING OF BUILDING PresentationDocument19 pages3D PRINTING OF BUILDING PresentationMd Fayazuddin50% (2)
- Study of The Use of 3D Technologies and Associated Social and Ethical Issues in BoeingDocument14 pagesStudy of The Use of 3D Technologies and Associated Social and Ethical Issues in BoeingDebarshi BiswasNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument12 pages3D Printingriddhima.thankiNo ratings yet
- A New Emerging TechnologyDocument16 pagesA New Emerging TechnologyAmey MairalNo ratings yet
- DF Lab ManualDocument80 pagesDF Lab ManualSruthi ChallapalliNo ratings yet
- APM Additive Manufacturing FinalDocument4 pagesAPM Additive Manufacturing FinalAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing: Slicing: From 3D Model To 3D PrinterDocument10 pages3D Printing: Slicing: From 3D Model To 3D PrinterAadil KakarNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Civil EngineeringDocument13 pagesEmerging Trends in Civil EngineeringAyush ShethNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing and Pre - FabricationDocument16 pages3D Printing and Pre - FabricationAyush ShethNo ratings yet
- Am - Unit 1 - NotesDocument14 pagesAm - Unit 1 - NotesNarender NarruNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument7 pages3D PrintingwizardNo ratings yet
- A New Emerging TechnologyDocument16 pagesA New Emerging TechnologyHumanityNo ratings yet
- All About 3d Concrete PrintingDocument6 pagesAll About 3d Concrete Printinggk_kishoree81No ratings yet
- Presented By: Kalpesh Shah M.E. (Design)Document40 pagesPresented By: Kalpesh Shah M.E. (Design)Terminator941988No ratings yet
- Module - 1: Regulation - 2015 (CBCS Scheme) Additive Manufacturing - 15me82Document37 pagesModule - 1: Regulation - 2015 (CBCS Scheme) Additive Manufacturing - 15me82swaroop kenganalNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument6 pagesUnit IDhaneshNo ratings yet
- 3d PrintingDocument74 pages3d PrintingDknargesh 2003No ratings yet
- 3de PrintingDocument17 pages3de PrintingNaveen AnanthNo ratings yet
- English Thesis PresentationDocument2 pagesEnglish Thesis PresentationBhagya sreekumarNo ratings yet
- C1 C Girum Tesfaye Gedecho 3D PrintingDocument5 pagesC1 C Girum Tesfaye Gedecho 3D PrintingGirum TesfayeNo ratings yet
- IAM3D ReportDocument11 pagesIAM3D Reportsiva shankarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Additive ManufacturingDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Additive Manufacturingsuvojitchunari001No ratings yet
- The Art of Additive ManufacturingDocument17 pagesThe Art of Additive ManufacturingHARISHRUTHINo ratings yet
- Exploring The Future: 3D Printing TechnologyDocument9 pagesExploring The Future: 3D Printing Technologyvss.shishirNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document37 pagesModule 1Lokesh Lokesh D SNo ratings yet
- UNIT I-Summary Need of Additive ManufacturingDocument4 pagesUNIT I-Summary Need of Additive ManufacturingRajijackNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument14 pagesUntitled PresentationAyush ShethNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 3D Printing: DT: 06 Apr 20Document2 pagesIntroduction To 3D Printing: DT: 06 Apr 20praveenhegdeNo ratings yet
- Anjuman College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument12 pagesAnjuman College of Engineering & TechnologyZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- 3-D Printing: ContentDocument9 pages3-D Printing: ContentRitik PothareNo ratings yet
- Reverse EngineeringDocument13 pagesReverse Engineeringprashant6942100% (3)
- Design and Fabrication of 3d PrintingDocument23 pagesDesign and Fabrication of 3d PrintingManikanta Venkata100% (1)
- Rapid Prototyping: Kubersuryavanshi BT16MEC004 Nationalinstitute of TechnologyuttarakhandDocument26 pagesRapid Prototyping: Kubersuryavanshi BT16MEC004 Nationalinstitute of TechnologyuttarakhandShubham ChomalNo ratings yet
- 3d PrintingDocument36 pages3d PrintingARJUN MPNo ratings yet
- 3d PrintingDocument19 pages3d PrintingthedooodledenNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Coursera NotesDocument16 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Coursera Notespolladhavan 1No ratings yet
- RP MaterialDocument3 pagesRP MaterialAnantNo ratings yet
- What Is Reverse Engineering?Document15 pagesWhat Is Reverse Engineering?Kuldeep GautamNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666412721000441 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2666412721000441 MainBM20623 Wan Mohamad Danial Bin Wan SyariffudinNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument31 pagesAdditive ManufacturingDaeNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument2 pagesAdditive ManufacturingsmrajbeNo ratings yet
- Metal Additive Manufacturing Explained: Grow by 27.9%Document3 pagesMetal Additive Manufacturing Explained: Grow by 27.9%rodolfoNo ratings yet
- Avances TecnologicosDocument13 pagesAvances TecnologicosSALAZAR VILLEGAS ESTEBAN DAMIANNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATIC BIKE Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesPNEUMATIC BIKE Seminar Reportprajakta chaudhari100% (1)
- 3d Printing AssignmentDocument7 pages3d Printing Assignmentnana100% (1)
- 3d PrintingDocument14 pages3d PrintingRaj SanthoshNo ratings yet
- IJRET20160516038Document4 pagesIJRET20160516038Youssef AliNo ratings yet
- 3D PrinterDocument21 pages3D Printerrajibnaskar425No ratings yet
- Activity On PL SQLDocument3 pagesActivity On PL SQLShubham MoteNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Special Report 1018Document33 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Special Report 1018OARIASCO100% (1)
- General Seminar 3-D PrintingDocument19 pagesGeneral Seminar 3-D PrintingVipul VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Kaushalendra PDFDocument24 pagesKaushalendra PDFharshNo ratings yet
- Maham Lateef: 3D Printers & PrintingDocument16 pagesMaham Lateef: 3D Printers & PrintingRogerHuang100% (1)
- Digital ManufacturingDocument7 pagesDigital ManufacturingAvik K DuttaNo ratings yet
- IJRPR12244Document7 pagesIJRPR12244Sai AnirudhNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 AmDocument127 pagesUnit - 4 AmLalit Banaal100% (1)
- Additive Manufacturing: Making The Quantum Leap To MainstreamDocument2 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: Making The Quantum Leap To Mainstreamdharmender142No ratings yet
- BLEPT 09-2016 Room Assignment Rosales-SecDocument114 pagesBLEPT 09-2016 Room Assignment Rosales-SecPRC Baguio50% (2)
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationTaufik TajudinNo ratings yet
- Materi Komposit - Prof. Anne ZulfiaDocument59 pagesMateri Komposit - Prof. Anne ZulfiaMuhammad ThohariNo ratings yet
- Honorato C. Perez, Sr. Memorial Science High SchoolDocument8 pagesHonorato C. Perez, Sr. Memorial Science High SchoolJOMARI DL. GAVINONo ratings yet
- Mud Max Mud Max Compact: Centrifugal Pump Series 250Document32 pagesMud Max Mud Max Compact: Centrifugal Pump Series 250Hussein MohamedNo ratings yet
- An Essay On AdvertisementDocument6 pagesAn Essay On Advertisementafhbctdfx100% (2)
- AQUARIUS EC DatasheetDocument4 pagesAQUARIUS EC DatasheetÇağlayan TopNo ratings yet
- Insight NDT Equipment LTD - ..Document2 pagesInsight NDT Equipment LTD - ..aoxoxzNo ratings yet
- CCTV PoleDocument180 pagesCCTV PoleAnonymous zMWvcTNo ratings yet
- E0234 PPTDocument41 pagesE0234 PPTjerry.sharma0312No ratings yet
- TALQ White Paper: The Smart City ProtocolDocument14 pagesTALQ White Paper: The Smart City ProtocolFiras KACHROUDINo ratings yet
- Electrode Consumption PDFDocument1 pageElectrode Consumption PDFharold_bhieNo ratings yet
- 2.mean Value TheoremsDocument29 pages2.mean Value TheoremsPratyush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 02 Introduction To Numerical AnalysisDocument27 pages02 Introduction To Numerical AnalysisBruhNo ratings yet
- Emedicine Hypersemesis GravidarumDocument26 pagesEmedicine Hypersemesis GravidarumAnonymous 3OoumAUytNo ratings yet
- Laserjet Professional M1130/M1210: MFP SeriesDocument16 pagesLaserjet Professional M1130/M1210: MFP SeriesDhanesh RamachandramNo ratings yet
- DSP Integrated Circuits 3Document3 pagesDSP Integrated Circuits 3brindkowsiNo ratings yet
- Nanomagnets Versus Nanofiltration in Water Treatement - VSKDocument8 pagesNanomagnets Versus Nanofiltration in Water Treatement - VSKmoganasandeepNo ratings yet
- BCD 16206 e Nu 545 500Document1 pageBCD 16206 e Nu 545 500Rajeesh P RaviNo ratings yet
- Essay On U.N.H.R.C Report On Ficancialization of HousingDocument3 pagesEssay On U.N.H.R.C Report On Ficancialization of HousingMuhammad EhtishamNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic and Respiratory Equipment - Laryngoscopes For Tracheal IntubationDocument2 pagesAnaesthetic and Respiratory Equipment - Laryngoscopes For Tracheal IntubationAisha MughalNo ratings yet
- Linear Guideway: 1. Features of HIWIN Linear Guideways 2 - Series of Linear GuidewaysDocument39 pagesLinear Guideway: 1. Features of HIWIN Linear Guideways 2 - Series of Linear GuidewaysyusufagcatrNo ratings yet
- Exponents, Radicals and LogarithmsDocument32 pagesExponents, Radicals and LogarithmsandrikaNo ratings yet
- SAA17 - Download What The Forecast On Windows PC 11,10,8,7Document4 pagesSAA17 - Download What The Forecast On Windows PC 11,10,8,7Sakshi MishraNo ratings yet
- 8 Weeks To Bigger Pecs 2Document11 pages8 Weeks To Bigger Pecs 2Ryan PanNo ratings yet
- HRCT ProtocolsDocument17 pagesHRCT ProtocolsZezo KaraNo ratings yet
- Geological Chance of SuccessDocument11 pagesGeological Chance of SuccesssarapkanNo ratings yet
- Specsheet It02 07Document2 pagesSpecsheet It02 07Jamel GrineNo ratings yet
- Resistors Module 01Document10 pagesResistors Module 01VinodKumarTummalurNo ratings yet
- NE 242 Syllabus 2013Document4 pagesNE 242 Syllabus 2013Nick VardyNo ratings yet