Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STD 6 Chem
STD 6 Chem
Uploaded by
tasnimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STD 6 Chem
STD 6 Chem
Uploaded by
tasnimCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 6 Physics: (Lesson details for Final exams)
Syllabus: Atoms, elements and the periodic table
States of matter
Atoms:
Atom: An atom is a tiny particle that makes up everything around us, starting from living things like humans to
non-living things like a table and a chair.
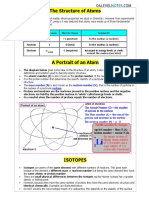
An atom contains three even tinier particles called subatomic particles; they are electron, proton and neutron.
Subatomic particles: An electron has a negative charge (-ve) and The structure of an atom:
is found in (electronic) shells in an atom.
An also electron has no mass. A proton has a positive charge (+ve) and
a neutron has no charge. Both are found inside a space called the
nucleus in an atom. Both also have the same mass that is 1.
Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom determines it’s
atomic or proton number.
Atomic mass: The total number of proton and neutron (proton +
neutron) in atom determines its atomic
mass.
Arrangement of electrons: The electrons are arranged in electronic shells as following -
The first shell can contain at most 2 electrons and the later shells can contain up to 8 electrons.
Why an atom is neutral: An atom is always neutral (has no charge) even though the electrons and protons inside
it have charges. This is because inside an atom, the total number of protons and electrons are always equal. So
the charges cancel out.
Elements:
Element: An element is a pure substance containing only one type of atom. Example: The element sodium
contains only sodium atoms. Some other examples are: Lithium, Carbon, Oxygen, Boron etc. There are two types
of elements: metals and non-metals.
Symbol: An element is often represented by a symbol. For example, sodium is represented by Na which comes
from its Latin name Natrium. Whereas the symbol of oxygen is “O” and it comes from its English name.
The Periodic Table:
The periodic table: is a chart in which the elements are arranged or displayed. In the table there are numbered
(horizontal) rows and (vertical) columns.
The rows are called periods and the columns are called groups. The elements in a group have similar chemical
properties.
The metal elements and non-metal elements are separated by a zigzag line in the table.
Two factors of the periodic table are:
1. The group number indicates the number of outer shell electrons. Meaning group 1 elements all contain one
electron in their outermost shell.
2. The period number indicates the number of electron shells. Meaning all period 4 elements have 4 electron
shells.
(For your syllabus you only need to know the first 20 elements)
States of Matter:
Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies space is called matter. There are three states of matter. They are:
solid, liquid and gas.
Solids: The particles in a solid are close together and can only vibrate about fixed positions. Solids have fixed
shape and volume.
Liquids: The particles in a liquid are farther apart and can move about each other. Liquids have fixed volume but
no fixed shape.
Gases: The particles in a gas are far apart from each other and move freely in all directions. Gases do not have
fixed shape or volume.
You might also like
- Laboratory Testing Manual (2000) PDFDocument330 pagesLaboratory Testing Manual (2000) PDFandressaoliveira2301100% (8)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument13 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsChemistryKlipz93% (29)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Atoms, Elements and MoleculesDocument16 pagesAtoms, Elements and MoleculesshantaebabydolltaylorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document11 pagesChapter 7Hend HamedNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesAtoms and Elements: ObjectivesAngel RingorNo ratings yet
- Biology Chemistry DoccxDocument3 pagesBiology Chemistry Doccxmaddi.ellistonNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY CHEMISTRY doccv 582Document3 pagesBIOLOGY CHEMISTRY doccv 582maddi.ellistonNo ratings yet
- Matter:: Revision Class Notes Grade VI Subject: ChemistryDocument9 pagesMatter:: Revision Class Notes Grade VI Subject: ChemistryKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Tableeugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Chemistry For PhysiciansDocument14 pagesChemistry For PhysiciansenzlibraryNo ratings yet
- Topic 3. Additional NotesDocument28 pagesTopic 3. Additional NotesChai MingzeNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 NotesDocument4 pagesChap 2 NotesAe AeNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Building Blocks of Molecules: AtomsDocument10 pages2.1 The Building Blocks of Molecules: AtomsLiezl Cutchon CaguiatNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahDocument46 pagesThe Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahYouseffNo ratings yet
- Grade 9-Chem. Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument10 pagesGrade 9-Chem. Atomic Structure and Periodic TableMusfira zaibNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument27 pagesChemistryErica LeNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and Compounds: Part TwoDocument45 pagesAtoms, Elements and Compounds: Part TwoBerylNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesChapter 2. Atomic StructureUmerNo ratings yet
- Atoms and IonsDocument13 pagesAtoms and IonsYousuf Al ManjiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Material Structure and BondingDocument34 pagesChapter 2-Material Structure and BondingMohd AziziNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Physics First UnitDocument18 pagesCambridge Physics First Unitmusic LenzoNo ratings yet
- Peroidic ClassificationDocument13 pagesPeroidic ClassificationAman RajNo ratings yet
- Css Atom StructureDocument20 pagesCss Atom StructureHaris AzizNo ratings yet
- Chemis IX Chapter-04 PDFDocument5 pagesChemis IX Chapter-04 PDFJsusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Atomic Number / Proton NumberDocument15 pagesChemistry: Atomic Number / Proton NumberZeynep AkıNo ratings yet
- AIDSDocument15 pagesAIDSMohit PathakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PDFDocument19 pagesChemistry Notes PDFAman RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Atoms and MatterDocument44 pagesChapter 2-Atoms and MatterNajma AqilahNo ratings yet
- Outline CH 3Document4 pagesOutline CH 3lexusredpbNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table5Document31 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic Table5Angelica Beltran LazagaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Atoms: Mass Number (A) Nucleon Number (N), IsotopeDocument5 pagesThe Structure of Atoms: Mass Number (A) Nucleon Number (N), Isotopelqq889No ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic TableDocument13 pagesAtoms and The Periodic TableAnonymous Bv0YpFNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Take Notes Assesment Answer RefelctionDocument6 pagesScience 8 Take Notes Assesment Answer RefelctionMary Ellain Sorima DaelNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument1 pageAtomstasnimNo ratings yet
- Elements and CompoundsDocument6 pagesElements and CompoundsVIX 07No ratings yet
- MY3 AtomsDocument6 pagesMY3 AtomserikaNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Foundation of LIfeDocument29 pagesThe Chemical Foundation of LIfehurainsahar21No ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 2 - Part 1Document15 pagesChemistry Module 2 - Part 1Francis RecocoNo ratings yet
- 20 Page GCSE To AS Transition BookletDocument20 pages20 Page GCSE To AS Transition BookletHanaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Elements McgrawhillDocument46 pagesPeriodic Table and Elements Mcgrawhillapi-230328718100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Ronel PanchooNo ratings yet
- Anh Văn Chuyên Ngành Hóa Học 1Document26 pagesAnh Văn Chuyên Ngành Hóa Học 1Nguyen TuanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 CHM3100 Basic Quantum Theory-1Document41 pages1.1 CHM3100 Basic Quantum Theory-1NicholasYeohNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic StructureDocument13 pages1.3 Atomic StructureLionel MigrinoNo ratings yet
- 2.atoms, Elements & CompoundDocument6 pages2.atoms, Elements & CompoundhenryNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds & MixturesDocument35 pagesElements, Compounds & MixturesSherazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Student Reading: Parts of The AtomDocument12 pagesChapter 4-Student Reading: Parts of The AtomShimmy LimmyNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument21 pagesThe Periodic Tableapi-286079895No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Atoms, Elements and IsotopesDocument10 pagesThe Periodic Table Atoms, Elements and IsotopesRubén De Gracia SantoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Action Note PackageDocument21 pagesChemistry in Action Note Packageapi-235471411No ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument2 pagesPDF DocumentSirupyEwe GamerNo ratings yet
- 4 1 - Atomic Theory BondingDocument38 pages4 1 - Atomic Theory Bondingapi-309810985No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 GED TrialDocument67 pagesChapter 9 GED TrialKaung KhantNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Atoms: Mass Number (A) Nucleon Number (N), IsotopeDocument5 pagesThe Structure of Atoms: Mass Number (A) Nucleon Number (N), IsotopeYusra RasoolNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureMuhammadAbutalibKazmiNo ratings yet
- Course: BIO 101: Introduction To Biology Matter and ElementsDocument9 pagesCourse: BIO 101: Introduction To Biology Matter and ElementsAhamadul Islam OnonnoNo ratings yet
- Inside The AtomDocument13 pagesInside The AtomAnita VardhanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 - Atoms and ElementsDocument38 pagesCh. 1 - Atoms and Elementslejode9724No ratings yet
- Metals and ExtractionDocument1 pageMetals and ExtractiontasnimNo ratings yet
- M/s M/s M/S: Newton's Second LawDocument1 pageM/s M/s M/S: Newton's Second LawtasnimNo ratings yet
- Newtons Second Law and WeightDocument1 pageNewtons Second Law and WeighttasnimNo ratings yet
- Elements and The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesElements and The Periodic TabletasnimNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledtasnimNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument1 pageForcestasnimNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument1 pageAtomstasnimNo ratings yet
- Elements:: Element: An Element Is A Pure Substance Containing Only One Type of Atom. Example: The Element Sodium ContainsDocument1 pageElements:: Element: An Element Is A Pure Substance Containing Only One Type of Atom. Example: The Element Sodium ContainstasnimNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 5.11, 5.13 To 5.15Document1 pageClass 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 5.11, 5.13 To 5.15tasnimNo ratings yet
- Class 4 Science: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Chapter: 13 (The Weather)Document2 pagesClass 4 Science: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Chapter: 13 (The Weather)tasnimNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Science: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Chapter: 13 (Pollution)Document3 pagesClass 5 Science: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Chapter: 13 (Pollution)tasnimNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10Document2 pagesClass 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10tasnimNo ratings yet
- Sour Corrosion Control in Refinery 1597351611Document1 pageSour Corrosion Control in Refinery 1597351611Akshat AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Cycloalkanes and AlkenesDocument3 pagesAlkanes Cycloalkanes and AlkenesDorota ZębikNo ratings yet
- Cam MechDocument24 pagesCam MechmarcglebNo ratings yet
- T. Y. Civil Minor Project Report - 3Document55 pagesT. Y. Civil Minor Project Report - 3Rs 31 Pavan PawarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: For Class X (Marks 65)Document5 pagesChemistry: For Class X (Marks 65)Asif AyazNo ratings yet
- CBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2Document4 pagesCBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2R roseNo ratings yet
- Brunner Suddarths Textbook of Medical Surgical Nursing 14th Edition Hinkle Cheever Test BankDocument37 pagesBrunner Suddarths Textbook of Medical Surgical Nursing 14th Edition Hinkle Cheever Test Bankpoetrycloudyzjm12q100% (29)
- CorrosionDocument79 pagesCorrosionaakash sharma100% (1)
- Naseeb Scale - Up and Post Approval ChangesDocument32 pagesNaseeb Scale - Up and Post Approval ChangesshivaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Drag On AircraftDocument20 pagesTypes of Drag On AircraftPramod DhaigudeNo ratings yet
- TCC TR 9 P4 Q1 M Lu EF8 WAHHDocument13 pagesTCC TR 9 P4 Q1 M Lu EF8 WAHHspbarathrajNo ratings yet
- Science6 DLP Week7 Day1 5Document19 pagesScience6 DLP Week7 Day1 5Jocelle FallarcunaNo ratings yet
- Emf PDFDocument84 pagesEmf PDFDr-Anamika YadavNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument31 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureAtul VermaNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (Stem)Document3 pagesScience, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (Stem)Alvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Logs, Xi+175 Pp. Glasgow, London: Blackie New: RiderDocument1 pageLogs, Xi+175 Pp. Glasgow, London: Blackie New: RiderAnonymous DNuC9GeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentsDocument3 pagesChemistry AssignmentsKishan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cadao, Lynjie T. SEPT.10, 2O19 1 Year-Nme3 Ms. Marisa BienvenidoDocument10 pagesCadao, Lynjie T. SEPT.10, 2O19 1 Year-Nme3 Ms. Marisa BienvenidoDenmar OriñaNo ratings yet
- Transamination - Wikipedia PDFDocument12 pagesTransamination - Wikipedia PDFkuldeep sainiNo ratings yet
- 444 StainlessDocument4 pages444 StainlessSH1961No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Bhopal Region Preboard Examination 2020-21 Class Xii - Question Paper - Set ADocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Bhopal Region Preboard Examination 2020-21 Class Xii - Question Paper - Set AMeghesh SamadhiyaNo ratings yet
- CAGI ElectHB ch7Document259 pagesCAGI ElectHB ch7Alejandro GilNo ratings yet
- Sartorius Economy Hand-Held PH Meter PT-15Document1 pageSartorius Economy Hand-Held PH Meter PT-15Evan JustinNo ratings yet
- IIT Delhi Assistant ProfessorDocument21 pagesIIT Delhi Assistant Professorpdrfbq46rxNo ratings yet
- Laws of Thermodynamics and The Human BodyDocument2 pagesLaws of Thermodynamics and The Human BodyCHANDRA SHEKAR BESTA100% (3)
- Thermal Performance of Nanofluid Filled Solar Flat Plate CollectorDocument8 pagesThermal Performance of Nanofluid Filled Solar Flat Plate CollectorDriss Miral AchemlalNo ratings yet
- Design Centrifugal Pump Assisted by CF Turbo 10.4 SoftwareDocument8 pagesDesign Centrifugal Pump Assisted by CF Turbo 10.4 Softwareomaimahaya12No ratings yet
- AQA AS Physics A Chapter 9 Textbook AnswersDocument4 pagesAQA AS Physics A Chapter 9 Textbook Answerscathylister100% (1)
- 11th-Physics Standard Planner-JEEDocument5 pages11th-Physics Standard Planner-JEEMuhammed NehanNo ratings yet