Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
Ann Margarette MoralesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HydromechanicsDocument183 pagesHydromechanicsReza GoldaranNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1st Assignment RenrenDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics 1st Assignment RenrenReynald MatiasNo ratings yet
- FMDocument78 pagesFMindumathijayakaranNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicssajjaddr0% (1)
- Buoyancy Force ReportDocument9 pagesBuoyancy Force Reportah3422No ratings yet
- Module 4Document15 pagesModule 4Gabriel CortesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-3Document66 pagesLesson 1-3Andrich Rey CortesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Pressure QDocument16 pagesChapter 7 Pressure QKaung Pyae SoneNo ratings yet
- Phy 061 Chapter 7 Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesPhy 061 Chapter 7 Fluid MechanicsAngel Lou LiwagonNo ratings yet
- Module 16 - Phys 13 Fluid StaticsDocument24 pagesModule 16 - Phys 13 Fluid StaticsRamnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet
- 6 Hydro Static DynamicDocument15 pages6 Hydro Static DynamiclundNo ratings yet
- Fluid StaticsDocument79 pagesFluid Staticsmahirtanjim50No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics WK 1Document63 pagesFluid Mechanics WK 1JAMES CLEARNo ratings yet
- 2019/2020 MECH2414 Thermofluids PART 2 - Fluids Yuguo Li: Chapter 1 Introduction To Fluid MechanicsDocument22 pages2019/2020 MECH2414 Thermofluids PART 2 - Fluids Yuguo Li: Chapter 1 Introduction To Fluid MechanicsLeo WongNo ratings yet
- Static FluidsDocument16 pagesStatic Fluidspabo.gagute.upNo ratings yet
- Adv Fluid HandoutDocument9 pagesAdv Fluid Handoutarfat_ahmad_khanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: Chris Race January 27, 2005Document21 pagesProperties of Fluids: Chris Race January 27, 2005Rahul PatwaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesFluid MechanicsDEEPAK TNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Lecture Part I (Introduction)Document46 pagesHydraulics Lecture Part I (Introduction)Kristal AbalosNo ratings yet
- FluMechMOD1 2Document13 pagesFluMechMOD1 2Trisha ServanoNo ratings yet
- Fluid PropertiesDocument10 pagesFluid PropertiesTokki TokkiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.1B-Introduction and Basic ConceptsDocument31 pagesLecture 1.1B-Introduction and Basic ConceptsBảo Tín TrầnNo ratings yet
- CE17304 Fluid Mechanics Part-A With AnswersDocument40 pagesCE17304 Fluid Mechanics Part-A With Answersநாம் தமிழர்No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: 1 2 HydrostaticsDocument18 pagesFluid Mechanics: 1 2 HydrostaticsAnant KumarNo ratings yet
- College Physics 2e 30 38Document9 pagesCollege Physics 2e 30 38diversidadcristianprimeNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Physics Liquid Liquid Is One of The Four Fundamental States of Matter (The Others Being Solid, Gas, and Plasma), and IsDocument3 pagesAssignment in Physics Liquid Liquid Is One of The Four Fundamental States of Matter (The Others Being Solid, Gas, and Plasma), and IsAlyssa MauricioNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicsAngelicaNo ratings yet
- General Physics IDocument19 pagesGeneral Physics ITiểu Quản GiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument45 pagesFluid MechanicsSean Eric CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics, ASU QRO Summer 2022, Course MaterialDocument256 pagesFluid Mechanics, ASU QRO Summer 2022, Course MaterialxREDCivicCometxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document34 pagesChapter 14sapriadilrocketNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFluid MechanicsRex FortezaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - 1Document35 pagesFluid Mechanics - 1kkiyo2113No ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes ch10 PDFDocument3 pages11 Physics Notes ch10 PDFManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument55 pagesFluid MechanicsRixzyli Coqui SalcedoNo ratings yet
- 001 Hydraulics Module 1 Common Properties of Fluids Part 2 of 2Document7 pages001 Hydraulics Module 1 Common Properties of Fluids Part 2 of 2Anjie CabalcarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Fluid MechanicsDocument12 pagesModule 5 Fluid MechanicsJai FloresNo ratings yet
- AnsDocument9 pagesAnsPrathiba R • XII - ANo ratings yet
- PHY 111aDocument29 pagesPHY 111aCharisse StevensNo ratings yet
- Agustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW2Document5 pagesAgustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW2mark agustinNo ratings yet
- 1 - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid PropertiesDocument21 pages1 - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Propertiesسيمو بشيريNo ratings yet
- Flu Mach NotesDocument22 pagesFlu Mach NotesJohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes I On Applied HydraulicsDocument143 pagesLecture Notes I On Applied HydraulicsAlex GHNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction (CH 1+2)Document23 pages1-Introduction (CH 1+2)YazeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - GasesDocument3 pagesChapter 11 - GasesscolarokNo ratings yet
- HydrostaticsDocument12 pagesHydrostaticsbman0051401No ratings yet
- Cec 107 Lecture NoteDocument12 pagesCec 107 Lecture NoteJamilu Adamu SalisuNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Thermal Physics: Kebede Shogile. June 3, 2021Document29 pagesFluid and Thermal Physics: Kebede Shogile. June 3, 2021Usmaan Gammachuu0% (1)
- Fluids NotezDocument47 pagesFluids Notezharshita21pvtNo ratings yet
- Biufluidmechanics 1Document19 pagesBiufluidmechanics 1Osarobo IghodaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1afaq ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Canute - Hydrostatics and Hydraulic CalculationsDocument4 pagesCanute - Hydrostatics and Hydraulic CalculationsEdgardo EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Fluids - 3Document8 pagesChapter 13 - Fluids - 3Adiyat MakrufiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics (Fluid Properties)Document18 pagesHydraulics (Fluid Properties)Natnael SitotaNo ratings yet
- Module-1-FLUID PROPERTIESDocument7 pagesModule-1-FLUID PROPERTIESFerry CaballasNo ratings yet
- Energy of A Liquid in MotionDocument25 pagesEnergy of A Liquid in MotionRafie MohammedNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 FluidsDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 1 FluidsIvan JadeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Physics Class 11 Part 1Document28 pagesNCERT Physics Class 11 Part 1ABC1234No ratings yet
- ET6018 Lecture 1 Fluid IntroDocument16 pagesET6018 Lecture 1 Fluid IntrolishadNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 4 Specific Tests For CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesLab Activity 4 Specific Tests For CarbohydratesAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- I. Human Body OrientationDocument10 pagesI. Human Body OrientationAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument3 pagesRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nature and Background of Social DancesDocument2 pagesNature and Background of Social DancesAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Folk DanceDocument5 pagesFolk DanceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- CalorimetryDocument2 pagesCalorimetryAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and DielectricsDocument2 pagesCapacitance and DielectricsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Center of MassDocument2 pagesCenter of MassAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Center of Mass (Momentum, Impulse, and Collision)Document2 pagesCenter of Mass (Momentum, Impulse, and Collision)Ann Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Current, Resistance, and Electromotive ForceDocument3 pagesCurrent, Resistance, and Electromotive ForceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnaPhy ReviewerAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Electrical PotentialDocument2 pagesElectrical PotentialAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument3 pagesElectric ChargeAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lab RepoertDocument11 pagesLab RepoertIhtisham GhazanferNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2 Set ADocument22 pagesCircuits 2 Set AJoan LorenNo ratings yet
- Time 12C. P. Test-6. Electrostatics Marks 35: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesTime 12C. P. Test-6. Electrostatics Marks 35: Page 1 of 2Gaurav BajpeyeeNo ratings yet
- Lab 06 Electrostatic Energy Stored in CapacitorsDocument10 pagesLab 06 Electrostatic Energy Stored in CapacitorsAmjadNo ratings yet
- RISHMaster 6100Document5 pagesRISHMaster 6100Aarif Patel0% (1)
- Module ThreeDocument59 pagesModule ThreeAndrei Jose GilNo ratings yet
- Complete NSO - SOF Physics (Part 1) - Practice Sheet Notes - (Only PDFDocument5 pagesComplete NSO - SOF Physics (Part 1) - Practice Sheet Notes - (Only PDFsrijanapple5No ratings yet
- 2016 Engineer AMethodologyto Developa Distribution TransformerDocument10 pages2016 Engineer AMethodologyto Developa Distribution TransformerFirdaus AzmiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual I Sem Basic ElectricalDocument48 pagesLab Manual I Sem Basic ElectricalGoutami T SunthankarNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 1 Objective Problems - NEET: Basic Mathematics, Units & Dimension - 1Document13 pagesExercise - 1 Objective Problems - NEET: Basic Mathematics, Units & Dimension - 1Shweta GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Load Frequency Control LFCPower System Operation ControlDocument23 pagesLoad Frequency Control LFCPower System Operation Controlsaifur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Tetra TR EngDocument42 pagesCatalogue Tetra TR EngArun KumarNo ratings yet
- MCQs Answers With Explanations U20AE301 AET SDocument127 pagesMCQs Answers With Explanations U20AE301 AET SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field: Principle of DC MotorDocument15 pagesMagnetic Field: Principle of DC Motorcode scribd100% (1)
- Csa 100 Gen. Ed. Maths (Ratio and Proportion)Document4 pagesCsa 100 Gen. Ed. Maths (Ratio and Proportion)Krishna Angela CabrasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Energy Balances: 9.2. Types of Energy To Be Included in Energy BalancesDocument7 pagesChapter 9. Energy Balances: 9.2. Types of Energy To Be Included in Energy Balancesاحمد ماجد زبنNo ratings yet
- Three Phase AC Circuits: King Saud UniversityDocument7 pagesThree Phase AC Circuits: King Saud Universityjove_1981100% (1)
- ES 112 Last Topic For FinalDocument5 pagesES 112 Last Topic For FinalBAJO, FRANSHUA RICA A.No ratings yet
- Analisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal (1222Document84 pagesAnalisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal (1222Jorge Luis Huahuachampi CayllahuaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential: General Physics 2 STE 2206Document28 pagesElectric Potential: General Physics 2 STE 2206Vincent LumaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesThermodynamicsKommraju Sravan KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Revision QuestionsDocument17 pagesElectrical Circuits Revision QuestionsOrlando ScottNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysicsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To PhysicsMuhamad Zahid AzisNo ratings yet
- Eng - 6.1 Analogue InstrumentsDocument42 pagesEng - 6.1 Analogue InstrumentsJohn VernonNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 General Physics 1Document4 pagesQuiz 1 General Physics 1Arcturus PolluxNo ratings yet
- Fat GensetDocument5 pagesFat GensetYoga AsmaraNo ratings yet
- Study of Electromagnetic DampingDocument6 pagesStudy of Electromagnetic DampingSoham MishraNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional, Steady-State Heat ConductionDocument53 pagesOne Dimensional, Steady-State Heat ConductionG. Dancer GhNo ratings yet
- II IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 13 - Heat Trans & Thermal RadiationDocument5 pagesII IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 13 - Heat Trans & Thermal RadiationAshwin KumarNo ratings yet
- Void Fractions in Two-Phase FlowsDocument0 pagesVoid Fractions in Two-Phase FlowsMohsen AghaeiNo ratings yet
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
Ann Margarette MoralesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
Ann Margarette MoralesCopyright:
Available Formats
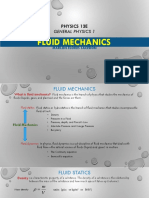
Fluid Mechanics EQUATIONS
DEFINITION OF TERMS Archimedes’ Principle
1. Fluid Mechanics
It is the branch of physics concerned with
the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and
plasmas) and the forces on them. Pascals’ Principle
2. Fluid
any liquid or gas or generally any material
that cannot sustain a tangential, or shearing,
force when at rest and that undergoes a
Density
continuous change in shape when subjected
to such a stress
3. Fluid Statics
Bernoulli’s Equation
The fluid which is in state of rest is called as
static fluid and its study is called as fluid
statics.
4. Fluid Dynamics
The branch of science which studies the
effect of all pressures including the external
pressures on the moving fluid is called as
fluid dynamics. SAMPLE PROBLEMS
5. Density
defined as mass per unit volume 1. What is the density in g/mL of a 0.4 L of
6. Pressure solution weighing 150 grams.
the amount of force exerted on a given area. Given: Find:
7. Atmospheric pressure
it is the force exerted on a surface by the
air above its gravity pulls it to Earth. Solution:
8. Pascal's principle
Pascal's law says that pressure applied to an
enclosed fluid will be transmitted without a
change in magnitude to every point of the
fluid and to the walls of the container.
9. Buoyant force 2. A rectangular block of wood has a mass of
the buoyant force is the upward force 130kg and dimensions of the block are 21cm,
exerted on an object wholly or partly 50cm and 62cm. The block of the wood is
immersed in a fluid. placed at the bottom of a tank filled with
10. Archimedes Law water (p = 1000 kg/m3). What is the upward
The upward buoyant force that is exerted on buoyant force?
a body immersed in a fluid Given: Find:
11. Bernoulli's Equation
a relation between pressure, kinetic energy,
and gravitational potential energy of a fluid
in a container.
Solution:
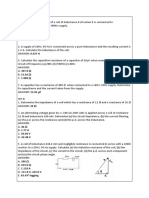
3. The hydraulic lift has a large cross section
and a small cross section. Large cross -
sectional area is 27 times the small cross-
sectional area. If on the small cross section
is given an input force of 38 N, then
determine the output force.
Given: Find:
Solution:
QUIZ
1. It is the branch of physics concerned with the
mechanics of fluids and the forces on them.
2. It is the force exerted on a surface by the air
above it as gravity pulls it to earth.
3. This law states that pressure applied to an
enclosed fluid will be transmitted without a change
in magnitude to every point of the fluid and to the
walls of the container.
4. A relation between pressure, kinetic energy, and
gravitational potential energy of a fluid in a
container.
5. Any liquid or gas or generally any material that
cannot sustain a tangential or shearing, force when
at rest and.that undergoes a continuous change in
shape when subjected to such a stress.
You might also like
- HydromechanicsDocument183 pagesHydromechanicsReza GoldaranNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1st Assignment RenrenDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics 1st Assignment RenrenReynald MatiasNo ratings yet
- FMDocument78 pagesFMindumathijayakaranNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicssajjaddr0% (1)
- Buoyancy Force ReportDocument9 pagesBuoyancy Force Reportah3422No ratings yet
- Module 4Document15 pagesModule 4Gabriel CortesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-3Document66 pagesLesson 1-3Andrich Rey CortesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Pressure QDocument16 pagesChapter 7 Pressure QKaung Pyae SoneNo ratings yet
- Phy 061 Chapter 7 Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesPhy 061 Chapter 7 Fluid MechanicsAngel Lou LiwagonNo ratings yet
- Module 16 - Phys 13 Fluid StaticsDocument24 pagesModule 16 - Phys 13 Fluid StaticsRamnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet
- 6 Hydro Static DynamicDocument15 pages6 Hydro Static DynamiclundNo ratings yet
- Fluid StaticsDocument79 pagesFluid Staticsmahirtanjim50No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics WK 1Document63 pagesFluid Mechanics WK 1JAMES CLEARNo ratings yet
- 2019/2020 MECH2414 Thermofluids PART 2 - Fluids Yuguo Li: Chapter 1 Introduction To Fluid MechanicsDocument22 pages2019/2020 MECH2414 Thermofluids PART 2 - Fluids Yuguo Li: Chapter 1 Introduction To Fluid MechanicsLeo WongNo ratings yet
- Static FluidsDocument16 pagesStatic Fluidspabo.gagute.upNo ratings yet
- Adv Fluid HandoutDocument9 pagesAdv Fluid Handoutarfat_ahmad_khanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: Chris Race January 27, 2005Document21 pagesProperties of Fluids: Chris Race January 27, 2005Rahul PatwaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesFluid MechanicsDEEPAK TNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Lecture Part I (Introduction)Document46 pagesHydraulics Lecture Part I (Introduction)Kristal AbalosNo ratings yet
- FluMechMOD1 2Document13 pagesFluMechMOD1 2Trisha ServanoNo ratings yet
- Fluid PropertiesDocument10 pagesFluid PropertiesTokki TokkiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.1B-Introduction and Basic ConceptsDocument31 pagesLecture 1.1B-Introduction and Basic ConceptsBảo Tín TrầnNo ratings yet
- CE17304 Fluid Mechanics Part-A With AnswersDocument40 pagesCE17304 Fluid Mechanics Part-A With Answersநாம் தமிழர்No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: 1 2 HydrostaticsDocument18 pagesFluid Mechanics: 1 2 HydrostaticsAnant KumarNo ratings yet
- College Physics 2e 30 38Document9 pagesCollege Physics 2e 30 38diversidadcristianprimeNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Physics Liquid Liquid Is One of The Four Fundamental States of Matter (The Others Being Solid, Gas, and Plasma), and IsDocument3 pagesAssignment in Physics Liquid Liquid Is One of The Four Fundamental States of Matter (The Others Being Solid, Gas, and Plasma), and IsAlyssa MauricioNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicsAngelicaNo ratings yet
- General Physics IDocument19 pagesGeneral Physics ITiểu Quản GiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument45 pagesFluid MechanicsSean Eric CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics, ASU QRO Summer 2022, Course MaterialDocument256 pagesFluid Mechanics, ASU QRO Summer 2022, Course MaterialxREDCivicCometxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document34 pagesChapter 14sapriadilrocketNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFluid MechanicsRex FortezaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - 1Document35 pagesFluid Mechanics - 1kkiyo2113No ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes ch10 PDFDocument3 pages11 Physics Notes ch10 PDFManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument55 pagesFluid MechanicsRixzyli Coqui SalcedoNo ratings yet
- 001 Hydraulics Module 1 Common Properties of Fluids Part 2 of 2Document7 pages001 Hydraulics Module 1 Common Properties of Fluids Part 2 of 2Anjie CabalcarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Fluid MechanicsDocument12 pagesModule 5 Fluid MechanicsJai FloresNo ratings yet
- AnsDocument9 pagesAnsPrathiba R • XII - ANo ratings yet
- PHY 111aDocument29 pagesPHY 111aCharisse StevensNo ratings yet
- Agustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW2Document5 pagesAgustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW2mark agustinNo ratings yet
- 1 - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid PropertiesDocument21 pages1 - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Propertiesسيمو بشيريNo ratings yet
- Flu Mach NotesDocument22 pagesFlu Mach NotesJohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes I On Applied HydraulicsDocument143 pagesLecture Notes I On Applied HydraulicsAlex GHNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction (CH 1+2)Document23 pages1-Introduction (CH 1+2)YazeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - GasesDocument3 pagesChapter 11 - GasesscolarokNo ratings yet
- HydrostaticsDocument12 pagesHydrostaticsbman0051401No ratings yet
- Cec 107 Lecture NoteDocument12 pagesCec 107 Lecture NoteJamilu Adamu SalisuNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Thermal Physics: Kebede Shogile. June 3, 2021Document29 pagesFluid and Thermal Physics: Kebede Shogile. June 3, 2021Usmaan Gammachuu0% (1)
- Fluids NotezDocument47 pagesFluids Notezharshita21pvtNo ratings yet
- Biufluidmechanics 1Document19 pagesBiufluidmechanics 1Osarobo IghodaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1afaq ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Canute - Hydrostatics and Hydraulic CalculationsDocument4 pagesCanute - Hydrostatics and Hydraulic CalculationsEdgardo EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Fluids - 3Document8 pagesChapter 13 - Fluids - 3Adiyat MakrufiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics (Fluid Properties)Document18 pagesHydraulics (Fluid Properties)Natnael SitotaNo ratings yet
- Module-1-FLUID PROPERTIESDocument7 pagesModule-1-FLUID PROPERTIESFerry CaballasNo ratings yet
- Energy of A Liquid in MotionDocument25 pagesEnergy of A Liquid in MotionRafie MohammedNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 FluidsDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 1 FluidsIvan JadeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Physics Class 11 Part 1Document28 pagesNCERT Physics Class 11 Part 1ABC1234No ratings yet
- ET6018 Lecture 1 Fluid IntroDocument16 pagesET6018 Lecture 1 Fluid IntrolishadNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 4 Specific Tests For CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesLab Activity 4 Specific Tests For CarbohydratesAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- I. Human Body OrientationDocument10 pagesI. Human Body OrientationAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument3 pagesRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nature and Background of Social DancesDocument2 pagesNature and Background of Social DancesAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Folk DanceDocument5 pagesFolk DanceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- CalorimetryDocument2 pagesCalorimetryAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and DielectricsDocument2 pagesCapacitance and DielectricsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Center of MassDocument2 pagesCenter of MassAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Center of Mass (Momentum, Impulse, and Collision)Document2 pagesCenter of Mass (Momentum, Impulse, and Collision)Ann Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Current, Resistance, and Electromotive ForceDocument3 pagesCurrent, Resistance, and Electromotive ForceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnaPhy ReviewerAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Electrical PotentialDocument2 pagesElectrical PotentialAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument3 pagesElectric ChargeAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lab RepoertDocument11 pagesLab RepoertIhtisham GhazanferNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2 Set ADocument22 pagesCircuits 2 Set AJoan LorenNo ratings yet
- Time 12C. P. Test-6. Electrostatics Marks 35: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesTime 12C. P. Test-6. Electrostatics Marks 35: Page 1 of 2Gaurav BajpeyeeNo ratings yet
- Lab 06 Electrostatic Energy Stored in CapacitorsDocument10 pagesLab 06 Electrostatic Energy Stored in CapacitorsAmjadNo ratings yet
- RISHMaster 6100Document5 pagesRISHMaster 6100Aarif Patel0% (1)
- Module ThreeDocument59 pagesModule ThreeAndrei Jose GilNo ratings yet
- Complete NSO - SOF Physics (Part 1) - Practice Sheet Notes - (Only PDFDocument5 pagesComplete NSO - SOF Physics (Part 1) - Practice Sheet Notes - (Only PDFsrijanapple5No ratings yet
- 2016 Engineer AMethodologyto Developa Distribution TransformerDocument10 pages2016 Engineer AMethodologyto Developa Distribution TransformerFirdaus AzmiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual I Sem Basic ElectricalDocument48 pagesLab Manual I Sem Basic ElectricalGoutami T SunthankarNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 1 Objective Problems - NEET: Basic Mathematics, Units & Dimension - 1Document13 pagesExercise - 1 Objective Problems - NEET: Basic Mathematics, Units & Dimension - 1Shweta GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Load Frequency Control LFCPower System Operation ControlDocument23 pagesLoad Frequency Control LFCPower System Operation Controlsaifur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Tetra TR EngDocument42 pagesCatalogue Tetra TR EngArun KumarNo ratings yet
- MCQs Answers With Explanations U20AE301 AET SDocument127 pagesMCQs Answers With Explanations U20AE301 AET SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field: Principle of DC MotorDocument15 pagesMagnetic Field: Principle of DC Motorcode scribd100% (1)
- Csa 100 Gen. Ed. Maths (Ratio and Proportion)Document4 pagesCsa 100 Gen. Ed. Maths (Ratio and Proportion)Krishna Angela CabrasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Energy Balances: 9.2. Types of Energy To Be Included in Energy BalancesDocument7 pagesChapter 9. Energy Balances: 9.2. Types of Energy To Be Included in Energy Balancesاحمد ماجد زبنNo ratings yet
- Three Phase AC Circuits: King Saud UniversityDocument7 pagesThree Phase AC Circuits: King Saud Universityjove_1981100% (1)
- ES 112 Last Topic For FinalDocument5 pagesES 112 Last Topic For FinalBAJO, FRANSHUA RICA A.No ratings yet
- Analisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal (1222Document84 pagesAnalisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal (1222Jorge Luis Huahuachampi CayllahuaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential: General Physics 2 STE 2206Document28 pagesElectric Potential: General Physics 2 STE 2206Vincent LumaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesThermodynamicsKommraju Sravan KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Revision QuestionsDocument17 pagesElectrical Circuits Revision QuestionsOrlando ScottNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysicsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To PhysicsMuhamad Zahid AzisNo ratings yet
- Eng - 6.1 Analogue InstrumentsDocument42 pagesEng - 6.1 Analogue InstrumentsJohn VernonNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 General Physics 1Document4 pagesQuiz 1 General Physics 1Arcturus PolluxNo ratings yet
- Fat GensetDocument5 pagesFat GensetYoga AsmaraNo ratings yet
- Study of Electromagnetic DampingDocument6 pagesStudy of Electromagnetic DampingSoham MishraNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional, Steady-State Heat ConductionDocument53 pagesOne Dimensional, Steady-State Heat ConductionG. Dancer GhNo ratings yet
- II IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 13 - Heat Trans & Thermal RadiationDocument5 pagesII IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 13 - Heat Trans & Thermal RadiationAshwin KumarNo ratings yet
- Void Fractions in Two-Phase FlowsDocument0 pagesVoid Fractions in Two-Phase FlowsMohsen AghaeiNo ratings yet