Professional Documents
Culture Documents
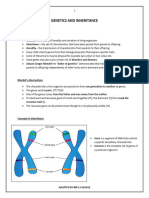
Method
Method
Uploaded by
Em0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThis document outlines different biology methods for studying inheritance patterns based on phenotypes and gender. It describes:
1) X-linked inheritance which affects both males and females and can determine recessive vs dominant traits.
2) Y-linked inheritance which only affects males.
3) Autosomal inheritance to determine dominant and recessive alleles.
4) Co-dominance and incomplete dominance inheritance which involve 3 phenotypes in specific ratios through cross-breeding.
5) Multiple allele inheritance involving 3+ phenotypes to construct Punnett squares and determine dominance hierarchies.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines different biology methods for studying inheritance patterns based on phenotypes and gender. It describes:
1) X-linked inheritance which affects both males and females and can determine recessive vs dominant traits.
2) Y-linked inheritance which only affects males.
3) Autosomal inheritance to determine dominant and recessive alleles.
4) Co-dominance and incomplete dominance inheritance which involve 3 phenotypes in specific ratios through cross-breeding.
5) Multiple allele inheritance involving 3+ phenotypes to construct Punnett squares and determine dominance hierarchies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageMethod
Method
Uploaded by
EmThis document outlines different biology methods for studying inheritance patterns based on phenotypes and gender. It describes:
1) X-linked inheritance which affects both males and females and can determine recessive vs dominant traits.
2) Y-linked inheritance which only affects males.
3) Autosomal inheritance to determine dominant and recessive alleles.
4) Co-dominance and incomplete dominance inheritance which involve 3 phenotypes in specific ratios through cross-breeding.
5) Multiple allele inheritance involving 3+ phenotypes to construct Punnett squares and determine dominance hierarchies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
BIOLOGY METHOD
FIRST
1. Change the way the organisms are viewed. (Sort by phenotypes and view by gender)
2. Look for phenotype (physical features) and gender, and check the number of alleles (2, 3 or 3+)
X-LINKED (2 PHENOTYPES) (MALES AND FEMALE EFFECTED)
1. Cross same phenotypes for both phenotypes
2. Cross different phenotypes
If all of one phenotype is male when the female was affected, then it is X linked
Bread the opposite female and male phenotypes to tell which is recessive and which is dominate
Y-LINKED (2 PHENOTYPES) (ONLY MEN AFFECTED)
1. Cross same phenotypes for both phenotypes
2. Cross different phenotypes
Only men will be affected
AUTOSOMAL (2 PHENOTYPES)
1. Cross same phenotypes for both phenotypes
2. Cross different phenotypes to determine which allele is dominate and which is recessive
CO-DOMINACE (3 PHENOTYPES)
1. Cross same phenotypes for all three
1 should show a range of all three populate types at the rough ratio of 1:2:1
2. Breed two different phenotypes until you get a third (spotty)
INCOMPLETE DOMINACY (3 PHENOTYPES) (MALES AND FEMALE EFFECTED)
1. Cross same phenotypes for all three
1 should show a range of all three populate types at the rough ratio of 1:2:1
2. Breed two different phenotypes until you get a third (hybrid)
MULTIPLE ALLES (3+ PHENOTYPES)
1. Cross same phenotypes for all
2. Cross different alleles to determine dominance
3. Construct a Punnett square to determine the dominance hierarchy and check in simulator
4. 25% means recessive 75% means dominate 100% means dominate but with heterozygous
You might also like
- BIOL 239 Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesBIOL 239 Lecture NoteskcqywNo ratings yet
- Sex DeterminationDocument20 pagesSex DeterminationYhurrie Mae EranNo ratings yet
- L2 Biol261F2014Document37 pagesL2 Biol261F2014jdazuelosNo ratings yet
- Study Material Unit 2Document27 pagesStudy Material Unit 2api-264649244No ratings yet
- Lab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian GeneticsDocument6 pagesLab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian Genetics13ucciNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument6 pagesGenetics NotesShane Tang100% (2)
- Cheat Sheet Quiz 1Document2 pagesCheat Sheet Quiz 1Ryan ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Genetics ActivityDocument3 pagesGenetics ActivityBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - NonmendelianDocument5 pagesSummary Notes - NonmendelianBonachita YamNo ratings yet
- 9 InheritanceDocument6 pages9 InheritanceTalita KumalaNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument20 pagesGenetics Noteslebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter - GenesDocument57 pages1st Quarter - Genesreinko9019No ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument50 pagesInheritanceLawrence MarquezNo ratings yet
- Biology Synopsis Bridge Course (8.5.18 To19.5.18)Document37 pagesBiology Synopsis Bridge Course (8.5.18 To19.5.18)Anil Kumar ANo ratings yet
- Module 3 Mendelian GeneticsDocument14 pagesModule 3 Mendelian GeneticsRaiza AwatNo ratings yet
- Unraveling The Roles of Systematics and The Cladistic System PDFDocument3 pagesUnraveling The Roles of Systematics and The Cladistic System PDFjer montillaNo ratings yet
- 1937 Fdoc-1Document8 pages1937 Fdoc-1tyleryawh2072No ratings yet
- Notes of HERIDITY2020Document5 pagesNotes of HERIDITY2020Shubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2ND Sem 3RD QDocument30 pagesReviewer 2ND Sem 3RD QJohn Mathew ReynanteNo ratings yet
- Lab-3-Mendelian Genetics: Human GeneticDocument14 pagesLab-3-Mendelian Genetics: Human Geneticdhoha alawsiNo ratings yet
- Bio 511 c4Document88 pagesBio 511 c4Athirah JeffryNo ratings yet
- (Lec3 - Modified Mendelian Dihybrid (Dominance, Lethal GenDocument18 pages(Lec3 - Modified Mendelian Dihybrid (Dominance, Lethal Genبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Phenotypes and Genotypes 7Document4 pagesPhenotypes and Genotypes 7Rashed Aiman Sameer Alsayyed AlalqamawiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Classical GeneticsDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts of Classical Geneticsganesandec27No ratings yet
- Genetics and InheritanceDocument78 pagesGenetics and Inheritanceapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 5 Notes (Grade 11)Document3 pagesBio Chapter 5 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (1)
- Kami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSISDocument11 pagesKami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSISgefegNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Document7 pagesInheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Leah HerbertNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Non Mendelian Inheritance IC and CodominanceDocument120 pagesScience 9 - Non Mendelian Inheritance IC and CodominanceClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- 4.3.1 Monohybrid N DihybridDocument5 pages4.3.1 Monohybrid N DihybridNurul Adnin Nor AzmiNo ratings yet
- Genetic SymbolsDocument3 pagesGenetic SymbolsHoney McRueloNo ratings yet
- Incomplete DominanceDocument15 pagesIncomplete Dominancecarmi lacuestaNo ratings yet
- Pp6 Genetics An Inheritance JangeDocument31 pagesPp6 Genetics An Inheritance JangeoptimallethumusaNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Traits OnlineDocument34 pagesHeredity and Traits OnlineAltheaNo ratings yet
- PP9. Sex ChromosomesDocument53 pagesPP9. Sex Chromosomeslebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- Introduction To Genetics and Dna & RnaDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Genetics and Dna & Rnamonzer elsamadonyNo ratings yet
- 9 InheritanceDocument6 pages9 InheritancePeter TingNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Week 1Document5 pagesLecture Notes - Week 1aclarke0806No ratings yet
- Genetics) 2Document12 pagesGenetics) 2m6rjssoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Solutions Manualbeliechopper05srz100% (44)
- Genetics-Some-Basic-Fundamentals-1Document6 pagesGenetics-Some-Basic-Fundamentals-1Kamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Classical Mendelian GeneticsDocument33 pagesClassical Mendelian GeneticsAngel Pearl DeneroNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual PDFzaridyaneb100% (13)
- Life Sciences GR 12 Theory Booklet GeneticsDocument9 pagesLife Sciences GR 12 Theory Booklet GeneticschiomsonzahNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics PowerPointDocument41 pagesMendelian Genetics PowerPointShiella Mae Baltazar BulauitanNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Experiments: Worked On Pisum SativumDocument33 pagesMendel's Experiments: Worked On Pisum SativumashhhhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Notes Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument26 pagesChapter - 5 Notes Principles of Inheritance and VariationSARVESH VERMANo ratings yet
- Module 8-Dysmorphism and Developmental Delay: Christina Singh S150385Document30 pagesModule 8-Dysmorphism and Developmental Delay: Christina Singh S150385Artika MalaNo ratings yet
- Genes and DiseasesDocument31 pagesGenes and DiseasesT FNo ratings yet
- DrosophilaGenetics PDFDocument14 pagesDrosophilaGenetics PDFPutriErvina100% (1)
- The Study of Epistasis and Complementation Led To The Genetic Analysis of Metabolic PathwaysDocument37 pagesThe Study of Epistasis and Complementation Led To The Genetic Analysis of Metabolic PathwaysjdazuelosNo ratings yet
- Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesGenetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Solutions ManualCraigVelasquezmcot100% (53)
- Flashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument75 pagesFlashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSERinen ParacadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document14 pagesLecture 5Teflon SlimNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination & Sex Linkage (3 HRS)Document76 pagesSex Determination & Sex Linkage (3 HRS)SITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Linkage and Sex DeterminationDocument33 pagesLinkage and Sex DeterminationSwapna GirishNo ratings yet
- Botany GeneticsDocument6 pagesBotany GeneticsCyrene SagumNo ratings yet
- Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument39 pagesNon Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceRichiel Angulo SungaNo ratings yet