Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decision Analysis: Monday, 5 September 2022 11:09 Am
Decision Analysis: Monday, 5 September 2022 11:09 Am
Uploaded by
Timothy james PalermoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Decision Analysis: Monday, 5 September 2022 11:09 Am
Decision Analysis: Monday, 5 September 2022 11:09 Am
Uploaded by
Timothy james PalermoCopyright:
Available Formats
Decision Analysis
Monday, 5 September 2022 11:09 am
Decision analysis - used to develop and optimal strategy when a decision makers is faced with
several decision alternatives and uncertain or risk-filled pattern of future events
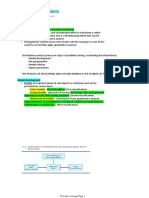
Problem Formulation
- Chance events - uncertain future events
- Consequences - combination of decision alternative and chance event outcomes
- Decision alternatives - different possible strategies the decision maker can employ
- States of nature - future events that are not under the control of the decision maker
Influence diagrams - graphical device that shows the relationships among the decisions, chance
events, and the consequences for a decision problem
Nodes- represent decisions, chance events, and consequences
- Decision nodes
- chance nodes
- consequence nodes
- referred to as arcs; shows the direction of influence
Payoff tables
Payoff - consequence resulting from a specific combination of a decision alternative and a state
of nature; a table that shows payoffs is called a payoff table
Decision trees
- Graphical representation for the decision-making process
DECISION MAKING WITHOUT PROBABILITIES
• Optimistic approach - decision with the largest payoff or lowest cost; also known as maximax
Pre-mid coverage Page 1
• Conservative approach - evaluates in terms of the worst payoff that can occur. Alternative recommended is the one that
provides the best of the worst possible payoff
• Minimax regret approach - decision making one would choose the decision alternative that minimizes the maximum state of
regret that could occur over all possible states of nature
○ Regret - represents how much potential payoff one would forgo by selecting a particular decision alternative; referred to
as opportunity loss
DECISION MAKING WITH PROBABILITIES
- When probability assessments for the states of nature are available, use the expected
value approach
Expected value of a decision alternative is the sum of weighted payoffs for the decision
alternative
Decision Tree - chronological representation of the decision problem
Expected value with perfect information (EVwPI) -
Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI) - increase in the expected profit that would
result if one knew with certainty which state of nature would occur
FORMULAS TO REMEMBER:
Efficiency = (EVSI/EVPI)x100
EVPI = |EVwPI - EVwoPI
EVSI ={ [ Probability favorable( EV) + probability unfavorable(EV) ] - EVwoPI }
Joint probability P(Sₐ I F/U) : Prior probability P(Sₐ) X Conditional Probability P(F or
U I Sₐ)
Pre-mid coverage Page 2
Posterior Probability: ∑ Joint probability P (F or U I Sₐ) / Joint probability of Sₐ P(F I
Sₐ)
Pre-mid coverage Page 3
You might also like
- Stage 1 Visual Art Task SheetDocument4 pagesStage 1 Visual Art Task Sheetapi-321385393No ratings yet
- Functions of Management: PlanningDocument46 pagesFunctions of Management: PlanningKharen JaneNo ratings yet
- Topic: Howard Sheth ModelDocument12 pagesTopic: Howard Sheth ModelPhaniraj Lenkalapally100% (1)
- Nursing ManagementDocument17 pagesNursing Managementdivya anoop100% (5)
- Chap 3 QMREviewerDocument3 pagesChap 3 QMREviewerRenalyn FabilaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Decision AnalysisDocument11 pagesUnit 2 - Decision AnalysisAlyana GeriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document3 pagesChapter 13Gio BurburanNo ratings yet
- Decision Tree AnalysisDocument4 pagesDecision Tree AnalysisRESMI VNo ratings yet
- TOMTATPTDLTDLDocument30 pagesTOMTATPTDLTDLAnh ThyNo ratings yet
- Team Exercise 3 - c3 2022-23Document8 pagesTeam Exercise 3 - c3 2022-23Eric Kevin LecarosNo ratings yet
- Minimum Payoff For Each Alternative. Select Maximum NumberDocument3 pagesMinimum Payoff For Each Alternative. Select Maximum NumberValerie AnnNo ratings yet
- QMB12 CH 04Document49 pagesQMB12 CH 04Syed AliNo ratings yet
- Decision Theory (Or-Assignment)Document3 pagesDecision Theory (Or-Assignment)Saurabh Nlyk100% (1)
- Risk and UncertainityDocument28 pagesRisk and UncertainityAnnie NadarNo ratings yet
- Decision TreeDocument26 pagesDecision TreePriya GaNo ratings yet
- Decision TheoryDocument24 pagesDecision TheoryShimul HossainNo ratings yet
- Decision AnalysisDocument19 pagesDecision AnalysisThian Patrice EviaNo ratings yet
- What Is Decision AnalysisDocument4 pagesWhat Is Decision AnalysisMc RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2Soonyoung KwonNo ratings yet
- OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT WILLIAM STEVENSON 9eDocument19 pagesOPERATIONS MANAGEMENT WILLIAM STEVENSON 9eSagar MurtyNo ratings yet
- Stevenson9e Ch5s PDFDocument19 pagesStevenson9e Ch5s PDFGanessa RolandNo ratings yet
- Four Decision Theory: Tebek-Aau-Fbe-MgmtDocument30 pagesFour Decision Theory: Tebek-Aau-Fbe-MgmtbikilahussenNo ratings yet
- Decision TheoryDocument20 pagesDecision TheoryChikadibia OkoroNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods For MarketersDocument41 pagesQuantitative Methods For MarketersYeshambel EwunetuNo ratings yet
- Decision MakerDocument3 pagesDecision Makerkhfgf;lNo ratings yet
- Unit I 2 DTDocument43 pagesUnit I 2 DTPravah ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Decision Theory Model - Lec03.1Document29 pagesDecision Theory Model - Lec03.1Libres Twin100% (1)
- Decision Analysis: Quantitative TechniquesDocument7 pagesDecision Analysis: Quantitative TechniquesDennisBrionesNo ratings yet
- Decision Theory: Defective Chips at A Rate of 1 in 3Document6 pagesDecision Theory: Defective Chips at A Rate of 1 in 3swatiraj05No ratings yet
- OR2 Project - 3BSIE C - Group 3 - Decision TheoryDocument21 pagesOR2 Project - 3BSIE C - Group 3 - Decision TheoryJhayemm QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques Quick NotesDocument9 pagesQuantitative Techniques Quick NotesAlliah Mae ArbastoNo ratings yet
- OR Unit 4Document14 pagesOR Unit 4sakshi narayanNo ratings yet
- Decision AnalysisDocument19 pagesDecision Analysissamim25feb2904No ratings yet
- LBO Finals Notes (Concepts)Document9 pagesLBO Finals Notes (Concepts)nikkaangelikapuatuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2.doc ReadyDocument3 pagesQuiz 2.doc ReadyKuma AguirreNo ratings yet
- ch08 IsmDocument19 pagesch08 Ismsaraaqil75% (4)
- DMRiskDocument2 pagesDMRisksinhapalak1002No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Decision-Making Under Conditions of Risk and UncertaintyDocument5 pagesChapter 12 Decision-Making Under Conditions of Risk and UncertaintykellyNo ratings yet
- 8 PazekDocument9 pages8 Pazekchirag_vaswaniNo ratings yet
- Managers Use Quantitative Approaches in Decision Making WhenDocument6 pagesManagers Use Quantitative Approaches in Decision Making WhenIda Katrina FiecasNo ratings yet
- Notes (Quanti)Document6 pagesNotes (Quanti)Althea JeanNo ratings yet
- G Decision TheoryDocument25 pagesG Decision TheoryUtkarsh Sethi100% (5)
- Notes 2. Decision Theory - ToDocument13 pagesNotes 2. Decision Theory - Tostephen mwendwaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Techniques PPT at Mba Opreatiop MGMTDocument61 pagesDecision Making Techniques PPT at Mba Opreatiop MGMTBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- FASE I - Tema 2Document52 pagesFASE I - Tema 2Angela MelgarNo ratings yet
- 10e 15 Chap Student Workbook PDFDocument18 pages10e 15 Chap Student Workbook PDFEdison CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Decision Making OMDocument4 pagesDecision Making OMwubeNo ratings yet
- Chap 015 ETTODocument29 pagesChap 015 ETTOjologsNo ratings yet
- W7-8 Module 5 - Decision Making Under RiskDocument6 pagesW7-8 Module 5 - Decision Making Under RiskVirgilio Jay CervantesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Decision AnalysisDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Decision AnalysisJade BelenNo ratings yet
- Activity6 Decision TheoryDocument6 pagesActivity6 Decision Theorynisperos.majanelleNo ratings yet
- Audine - Laurence - Rue - Presentation 1 Decision Theory MME321Document25 pagesAudine - Laurence - Rue - Presentation 1 Decision Theory MME321Laurence Rue AudineNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Enviornment & Decision TreeDocument11 pagesDecision Making Enviornment & Decision Treesarveshshukla20016No ratings yet
- CH 4Document24 pagesCH 4Yosef KetemaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in International Bussiness: Munich Personal Repec ArchiveDocument15 pagesRisk Management in International Bussiness: Munich Personal Repec ArchiveOleg FrunzeNo ratings yet
- Evans Analytics3e PPT 16 AccessibleDocument60 pagesEvans Analytics3e PPT 16 AccessibleAarti HaswaniNo ratings yet
- CH 2 QuantatativeDocument14 pagesCH 2 QuantatativeAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- MANSI BHARNE 16/10/2020: Unit X: Statistical Decision TheoryDocument4 pagesMANSI BHARNE 16/10/2020: Unit X: Statistical Decision TheoryVrushab PunjabiNo ratings yet
- 1decision TheoryDocument33 pages1decision Theoryadesh guliaNo ratings yet
- Sns College of Technology: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument21 pagesSns College of Technology: Department of Civil EngineeringSathya SankarNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis: Facilitating and Analysis Guidelines for Capital Expenditure ProjectsFrom EverandRisk Analysis: Facilitating and Analysis Guidelines for Capital Expenditure ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Comparison Among Defective ContractsDocument1 pageComparison Among Defective ContractsTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- PAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureDocument3 pagesPAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Decision Making With Probabilities: Expected Value ApproachDocument1 pageDecision Making With Probabilities: Expected Value ApproachTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument2 pagesRisk and ReturnTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Decision MakingDocument1 pageProblem Solving and Decision MakingTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Risk ProfileDocument1 pageRisk ProfileTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Without ProbabilitiesDocument1 pageDecision Making Without ProbabilitiesTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative AnalysisDocument6 pagesQuantitative AnalysisTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Quantative Studies For MGMTDocument507 pagesQuantative Studies For MGMTMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus JDM CourseDocument4 pagesSyllabus JDM CourseAlberto ForteNo ratings yet
- Key Project Management Skills Interpersonal Skills: © Dr. Farrukh ArifDocument6 pagesKey Project Management Skills Interpersonal Skills: © Dr. Farrukh ArifM.Usama MustafaNo ratings yet
- Decision Under UncertanityDocument28 pagesDecision Under UncertanityTheaNo ratings yet
- Management Introduction Questions and Answers 11 To 20Document5 pagesManagement Introduction Questions and Answers 11 To 20chakshu vaidNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Management: Definition, Purpose, Objectives and Components of MIS Unit I - Chapter-2Document26 pagesInformation Systems Management: Definition, Purpose, Objectives and Components of MIS Unit I - Chapter-2Vardeep Singh SidhuNo ratings yet
- CVAC MultidisciplinaryDocument14 pagesCVAC Multidisciplinaryksucheta013No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument13 pagesUntitled DocumentKavya PandyaNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics Workshop - Abbey & JaiDocument15 pagesCode of Ethics Workshop - Abbey & JaiJai PhookanNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument18 pagesManagerial EconomicsPrathu PondeNo ratings yet
- MELC HG Junior HighDocument6 pagesMELC HG Junior HighAirah Joy SantiaguelNo ratings yet
- Keeping Your Balance - 08 - Coping With Psychosocial Stressors and Self-ManagementDocument13 pagesKeeping Your Balance - 08 - Coping With Psychosocial Stressors and Self-ManagementBogdanMînjinăNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument11 pagesDecision Making ProcessLakshayNo ratings yet
- Cases in Indian Management Turn Around IndiaDocument35 pagesCases in Indian Management Turn Around IndiaDharma RaoNo ratings yet
- Product DesignDocument11 pagesProduct DesignParamasivam VeerappanNo ratings yet
- Carroll 11e CH05Document40 pagesCarroll 11e CH05Adrienne SmithNo ratings yet
- Building Moral Robots 2019Document17 pagesBuilding Moral Robots 2019XxBestxX 23No ratings yet
- Decision AnalysisDocument28 pagesDecision AnalysisAshley MorrisNo ratings yet
- Faa Ada280477 Dot Faa Rd-93 5Document411 pagesFaa Ada280477 Dot Faa Rd-93 5anantiaNo ratings yet
- Soft ComputingDocument52 pagesSoft ComputingEco Frnd Nikhil ChNo ratings yet
- White Paper Contract Bidding and Technology EvaluationDocument14 pagesWhite Paper Contract Bidding and Technology EvaluationApplied BinaryNo ratings yet
- Research Methods PDFDocument48 pagesResearch Methods PDFsophiasisaac119100% (1)
- Keri Pearlson & Carol Saunders: Strategic Management of Information Systems Fifth EditionDocument41 pagesKeri Pearlson & Carol Saunders: Strategic Management of Information Systems Fifth EditionSap 155155No ratings yet
- Solomon cb11 ppt02Document30 pagesSolomon cb11 ppt02karishma asharNo ratings yet
- Subject: Principles of Management Topic: Types of OrganisationDocument34 pagesSubject: Principles of Management Topic: Types of OrganisationVindraj ChopdekarNo ratings yet
- Describe The Concept of Leadership Skills and The 6 Key Leadership SkillsDocument2 pagesDescribe The Concept of Leadership Skills and The 6 Key Leadership SkillsPeter LawNo ratings yet