Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Democracy - Concept Map
Democracy - Concept Map
Uploaded by
Shealtiel Kyze Cahilig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
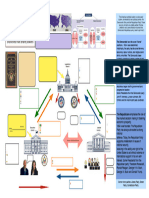
276 views1 pageAncient Athens is considered the birthplace of democracy. The Ekklesia, or People's Assembly, was the supreme governing body where citizens directly participated in decision making, embodying the principle of self-government. However, Athenian democracy had flaws as citizenship was restricted and participation was not extensive. Scholars identify three waves of democratization from the 19th century onward, with new democracies emerging in Europe and Latin America after periods of dictatorship or military rule.
Original Description:
Original Title
Democracy - concept map
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAncient Athens is considered the birthplace of democracy. The Ekklesia, or People's Assembly, was the supreme governing body where citizens directly participated in decision making, embodying the principle of self-government. However, Athenian democracy had flaws as citizenship was restricted and participation was not extensive. Scholars identify three waves of democratization from the 19th century onward, with new democracies emerging in Europe and Latin America after periods of dictatorship or military rule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
276 views1 pageDemocracy - Concept Map
Democracy - Concept Map
Uploaded by
Shealtiel Kyze CahiligAncient Athens is considered the birthplace of democracy. The Ekklesia, or People's Assembly, was the supreme governing body where citizens directly participated in decision making, embodying the principle of self-government. However, Athenian democracy had flaws as citizenship was restricted and participation was not extensive. Scholars identify three waves of democratization from the 19th century onward, with new democracies emerging in Europe and Latin America after periods of dictatorship or military rule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Ancient Athens - Birthplace of Demoracy A group of transitions from non-
democratic to democratic regimes
Each to rule and be ruled in return
USA, Britain, and France - examples of
Nearly 30 countries established at least consolidated democracies emerging
First Wave 1828 -1926
Ekklesia (People's Assembly) - supreme minimally democratic national institutions during the first nineteenth-century wave
over all causes) of democratization
These postwar democracies were
Highly Political Legal System Huntingson's three wave of Established democracies emerge after
introduced by the victorious allies, led by Examples - India, Israel, Japan, West
democratization Second Wave 1943 - 1962 1945 from the ashes of defeated Parties - leading democratic instrument
the USA and usually acting with the Germany
dictatorship
The principle of self-government did not support of domestic partners
Flaws in Athen's Democracy Citizenship was restricted to a small elite Participation was not practice extensively Hardly an exercise in lean government
always lead to decisive and coherent policy
The collapse of communism in the Soviet
The end of right-wing dictatorships in The retreat of the generals in much of Examples - Southern and Eastern Europe,
Third Wave 1974-1991 Union and Eastern Europe at the end of Transformed the global political landscape
Southern Europe in the 70s Latin America in the 1980s Latin America, parts of Africa
Athenian contribution to Western politics Idea of citizen Democracy the 1980s
Democracy Origin of Democracy Forms of Democracy Waves of Democratization
Ekklesia (People's Assembly) - Symbol of Government by, and not just for, the
Direct Democracy State and society become one
Direct Democracy citizens - Principle of Direct Democracy
Desirable brake on democracy, served to
refine and enlarge the public view by
Scapability - key strength of representative passing them through the medium of a
Representative Democracy Elected government Form of expression Modify traditional ideas of representation Representation
democracy chosen body of citizens whose wisdom
may best discern the true interest of their
country
Both the representative and liberal
elements of modern democracy dilute the
It seek to integrate the authority of original principle of self- rule
Based on liberal philosophy in which Liberal democracy is a democracy
Liberal Democracy Constitution - Supreme over all causes democratic government with limits on the Limited government - Central feature System of checks and balances Government of laws rather than men
states scope is restricted by constitution disarmed
scope of their action
Political problems associated with an
Consolidated by one crucial test: A illiberal inheritance
One that has not yet had time to
New Democracy peaceful transfer of power through Difficulties facing new democracy Potical Challenge, Economic Challenge,
consolidate; that is, democracy has not yet
election Economic problems caused by the and Challenge of Timing
become the only game in town
combination of limited development and
extreme iniquality
Consolidated democracy which provides
The outcome of free election is accepted
Established Democracy an accepted framework for political
by the losers as well as the winner
competition.
First - an elected party or leader sets the
framework for political competition, Illiberal or electoral democracy Power is concentrated in a few hands
The outcome than a return to governing in an illiberal fashion
Blend both democratic and authoritarian
Semi-Democracy authoritarianism for those new Operating methods of semi-democracies
elements
democracies that do not consolidate Second - an elected rulers have too little Power is shifted to the military,
Supervised or facade democracy
rather than too much power bureaucracy or top business group
You might also like
- Three Visions For Achieving Equal RightsDocument3 pagesThree Visions For Achieving Equal RightsIan WilsonNo ratings yet
- Boq For Box CulvertDocument2 pagesBoq For Box CulvertDaniel Okere100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Mapeh 4a'sDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Mapeh 4a'sJhayzki Asuncion100% (3)
- DahlDocument50 pagesDahlSergio Fabian LizarazoNo ratings yet
- COMM234 - Communication Media Laws and EthicsDocument6 pagesCOMM234 - Communication Media Laws and EthicsChristine Joyce PelonioNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage 4Document2 pagesReading Passage 411Toán1-06-Phạm Lê Bá DươngNo ratings yet
- The Russian Revolution: Russia Became The First Country in The Word To Form A Communist GovermentDocument2 pagesThe Russian Revolution: Russia Became The First Country in The Word To Form A Communist GovermentbereniceNo ratings yet
- Posthuman Tendencies in Performance ArtDocument86 pagesPosthuman Tendencies in Performance Artchristie rdNo ratings yet
- India's Journey From Civic To Cultural NationalismDocument7 pagesIndia's Journey From Civic To Cultural NationalismDiXit JainNo ratings yet
- Page 36-37Document1 pagePage 36-37api-3707851No ratings yet
- CW2Document1 pageCW2hanna bannanaNo ratings yet
- культураDocument1 pageкультураkazarinaelizaveta01No ratings yet
- Propaganda Model A Critical Approach To Analysing Mass Media Behaviour PDFDocument15 pagesPropaganda Model A Critical Approach To Analysing Mass Media Behaviour PDFMuhammad AchlisonNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 12 May 2021Document1 pageAdobe Scan 12 May 2021Tiyasa MajumdarNo ratings yet
- CommunismDocument9 pagesCommunismSurya GayathriNo ratings yet
- The Art of The Possible: Power Sharing and Post-Civil War DemocracyDocument35 pagesThe Art of The Possible: Power Sharing and Post-Civil War DemocracyKakaNo ratings yet
- Narratives of Resistance WilmerDocument25 pagesNarratives of Resistance WilmerJose Manuel Oyola BallesterosNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Communism and SocialismDocument8 pagesThe Difference Between Communism and SocialismJennifer Marie Columna BorbonNo ratings yet
- Print 3Document3 pagesPrint 3bever 209No ratings yet
- Ucsp ReviewerDocument3 pagesUcsp ReviewerJohn Carlo D MedallaNo ratings yet
- Prewriting NicolasDocument3 pagesPrewriting NicolascazzmereNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy SLM - LAS Week 4Document12 pagesMedia and Information Literacy SLM - LAS Week 4Mark Christian BrlNo ratings yet
- Van de Sande - PrefigurationDocument3 pagesVan de Sande - Prefigurationyagiddippeigoi-4743No ratings yet
- Never Again, Never Forget: Reconstructing Memories and Imagining Democracy in Post-Authoritarian PhilippinesDocument64 pagesNever Again, Never Forget: Reconstructing Memories and Imagining Democracy in Post-Authoritarian PhilippinesseaNo ratings yet
- Classical To Modern Political IdeologiesDocument14 pagesClassical To Modern Political IdeologiesLizette AngelesNo ratings yet
- Classical To Modern Political IdeologiesDocument14 pagesClassical To Modern Political IdeologiesLizette AngelesNo ratings yet
- Reverse Sting in The Media Tale: A Season of India-Pak Spy ThrillersDocument1 pageReverse Sting in The Media Tale: A Season of India-Pak Spy ThrillerskiranNo ratings yet
- Critical Theory On Mass Media-PPT-36Document36 pagesCritical Theory On Mass Media-PPT-36Keith Knight100% (1)
- Adam Smith Filosofo de La Razon PracticaDocument36 pagesAdam Smith Filosofo de La Razon Practicapedroperez10011991No ratings yet
- Marx, Gramsci and HegemonyDocument18 pagesMarx, Gramsci and HegemonyRitik BhandariNo ratings yet
- SYSTEMS CHAP 1 EN JUL 31 2023 - Copy C.Document47 pagesSYSTEMS CHAP 1 EN JUL 31 2023 - Copy C.Gabriela PachecoNo ratings yet
- Democracy in BriefDocument32 pagesDemocracy in Briefsierra_tsNo ratings yet
- Electoral System Andrew HeywoodDocument10 pagesElectoral System Andrew HeywoodHIMANI YADAVNo ratings yet
- JP and The Problem of Representative DemocrcayDocument11 pagesJP and The Problem of Representative DemocrcaytayaltaniNo ratings yet
- A Aluna: Jandira Lopes AraújoDocument4 pagesA Aluna: Jandira Lopes AraújoJose Manuel Lopes TavaresNo ratings yet
- Hegemonic ApparatusDocument8 pagesHegemonic ApparatussaucepanchessboardNo ratings yet
- GRANTER E Critical Theory and Organization StudiesDocument31 pagesGRANTER E Critical Theory and Organization StudiesAnggie MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Apsr 2003Document11 pagesApsr 2003Ethan PuttermanNo ratings yet
- IR Theories Tang 2011 Foundational ParadigmsDocument2 pagesIR Theories Tang 2011 Foundational ParadigmsTeltel TagudandoNo ratings yet
- Government and Politics of Southeast AsiaDocument13 pagesGovernment and Politics of Southeast AsiaGlydel Kate AndresNo ratings yet
- Secondary Socialisation In: Key Functionalists Include: Emile Durkheim, Talcott Parsons and Robert K MertonDocument5 pagesSecondary Socialisation In: Key Functionalists Include: Emile Durkheim, Talcott Parsons and Robert K MertonAdam DjerouniNo ratings yet
- Black Liberation Army Political DictionaryDocument15 pagesBlack Liberation Army Political DictionaryMosi Ngozi (fka) james harris100% (1)
- System. If I Try To Distinguish It From Other Economic Systems Like Capitalist or Socialist, ThisDocument18 pagesSystem. If I Try To Distinguish It From Other Economic Systems Like Capitalist or Socialist, ThisRahimahameedNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Two Types of Dictatorship Year 9 History IGCSEDocument5 pages4.2 Two Types of Dictatorship Year 9 History IGCSEVisalachi Menon SudhakaranNo ratings yet
- Alain Pengam Anarchist CommunismDocument15 pagesAlain Pengam Anarchist CommunismNicolas FerreiraNo ratings yet
- National DifferencesDocument31 pagesNational DifferencesAtif AliNo ratings yet
- Whatever Has Happened To Civil SocietyDocument7 pagesWhatever Has Happened To Civil SocietydevyaniNo ratings yet
- Gramsci - Prison Notebooks - Intellectuals PDFDocument5 pagesGramsci - Prison Notebooks - Intellectuals PDFshagun aggarwalNo ratings yet
- An AnthologyDocument5 pagesAn AnthologyceliaNo ratings yet
- Anarchist Communism, It's Basis and Principles - Peter KropotkinDocument11 pagesAnarchist Communism, It's Basis and Principles - Peter KropotkinRoric ThomasNo ratings yet
- International Ir Singer 1Document20 pagesInternational Ir Singer 1КсенияNo ratings yet
- Lijphart 1999Document14 pagesLijphart 1999Elizabeth MatoshkinaNo ratings yet
- Rulebook en Print SmallDocument32 pagesRulebook en Print SmallDan L'étron TurconNo ratings yet
- Social Theory and Political Thought EssayDocument5 pagesSocial Theory and Political Thought EssaykwisNo ratings yet
- Deliberative Democracy and Digital Sphere (For Book Bind)Document3 pagesDeliberative Democracy and Digital Sphere (For Book Bind)Arvhie SantosNo ratings yet
- 02 JPO-AS Media TheoriesDocument36 pages02 JPO-AS Media TheoriesYeahNo ratings yet
- International Contemporary AnalysisDocument48 pagesInternational Contemporary AnalysisAndres GiraldoNo ratings yet
- GarcialovinkDocument3 pagesGarcialovinkapi-205724572No ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Politics and PowerDocument29 pagesLecture 3-Politics and PowerKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Post-Structuralism Guide-Map6Document1 pagePost-Structuralism Guide-Map6Maxfield WeirNo ratings yet
- Practice SetDocument6 pagesPractice SetShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- SEAL 2 Session 2 #TOTGA - Worksheet-1Document2 pagesSEAL 2 Session 2 #TOTGA - Worksheet-1Shealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- PE4 Hand Outs Unit 1 4Document15 pagesPE4 Hand Outs Unit 1 4Shealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of ArnisDocument4 pagesOrigin and Development of ArnisShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- House of RepresentativesDocument13 pagesHouse of RepresentativesShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Arnis TerminologiesDocument1 pageArnis TerminologiesShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Basic Military CorrespondenceDocument36 pagesBasic Military CorrespondenceShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Democratic RepublicDocument1 pageDemocratic RepublicShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- President's ProfileDocument6 pagesPresident's ProfileShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Istambay AnalysisDocument3 pagesIstambay AnalysisShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Sample Dance Routine With Basic Dance Step in 2Document1 pageSample Dance Routine With Basic Dance Step in 2Shealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Bar Boys Movie ReviewDocument3 pagesBar Boys Movie ReviewShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- CoronavirusDocument2 pagesCoronavirusShealtiel Kyze CahiligNo ratings yet
- Specific Issues in Science, Technology and SocietyDocument27 pagesSpecific Issues in Science, Technology and SocietyRaven Evangelista Cana100% (1)
- Execute PlanDocument1 pageExecute PlanMayline LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - AnswerDocument10 pagesChapter 03 - AnswerMinsky GoceNo ratings yet
- Ayobami Kehinde An Aesthetics of Realism The Image of Postcolonial Africa in Meja Mwangis Going Down River Road An EssayDocument31 pagesAyobami Kehinde An Aesthetics of Realism The Image of Postcolonial Africa in Meja Mwangis Going Down River Road An EssayMedara MosesNo ratings yet
- The Simple Past Practice 3 - ANSWER KEYDocument1 pageThe Simple Past Practice 3 - ANSWER KEYwbfqkrgh6jNo ratings yet
- Week 3 & 4Document12 pagesWeek 3 & 4elbaNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychological Assessment in Illiterates: II. Language and Praxic AbilitiesDocument16 pagesNeuropsychological Assessment in Illiterates: II. Language and Praxic AbilitiesroxanaNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Territory Manager: User Guide Release 12.1Document80 pagesOracle® Territory Manager: User Guide Release 12.1Marcelo MestiNo ratings yet
- Hall Management - Rules, Procedures and GuidelinesDocument27 pagesHall Management - Rules, Procedures and GuidelinesNitish ShankarNo ratings yet
- Applications of Graph Theory inDocument18 pagesApplications of Graph Theory invidulaNo ratings yet
- Social LoafingDocument15 pagesSocial LoafingAkash MeenaNo ratings yet
- Pile CapDocument44 pagesPile Capbhavik modiNo ratings yet
- Mas PrelimsDocument8 pagesMas PrelimsChristopher NogotNo ratings yet
- 03 Amandeep Notifiable Occupational DiseasesDocument6 pages03 Amandeep Notifiable Occupational DiseasesAmandeep DuaNo ratings yet
- Hirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - LiDocument227 pagesHirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - Litrue dreamNo ratings yet
- Wits Visual StorytellingDocument4 pagesWits Visual Storytellingapi-238364900No ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Wah Campus: Herzberg's Theory Alignment To The Case Study TESCODocument2 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Wah Campus: Herzberg's Theory Alignment To The Case Study TESCOiqra khanNo ratings yet
- Metaphysics of AristotleDocument60 pagesMetaphysics of AristotleJaimon Thadathil100% (4)
- Tuned To Yesterday Schedule May 2021Document5 pagesTuned To Yesterday Schedule May 2021Mark L.No ratings yet
- HW1-time Value of Money SOLUÇÃODocument6 pagesHW1-time Value of Money SOLUÇÃOSahid Xerfan NetoNo ratings yet
- INCREASE CARDIAC OUTPUT Related To Altered Heart Rate RythmDocument3 pagesINCREASE CARDIAC OUTPUT Related To Altered Heart Rate RythmSenyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement Cafeteria FoodDocument7 pagesThesis Statement Cafeteria Foodafbwszvft100% (1)
- English Rough Draft 1Document4 pagesEnglish Rough Draft 1api-463048454No ratings yet
- Full Download Essentials of Management Information Systems 10th Edition Laudon Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Essentials of Management Information Systems 10th Edition Laudon Test Bankchetah.cciraz5cz100% (44)
- Diagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test Untuk Siswa Baru Kelas ViiZendy PradiktaNo ratings yet
- Synthesizeable VerilogDocument18 pagesSynthesizeable VerilogQuang Anh VuNo ratings yet
- Alemar's Vs Court of Appeals GR No. 94996Document5 pagesAlemar's Vs Court of Appeals GR No. 94996Darrel John SombilonNo ratings yet