Professional Documents
Culture Documents
???? ??? ?????????
???? ??? ?????????
Uploaded by
Zoya AdnanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dwnload Full Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFschmitzerallanafx100% (13)
- Physical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document32 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3Jerome Manaig Suelto83% (12)
- 2) Cementing AdditivesDocument41 pages2) Cementing Additiveseng20072007100% (1)
- Food Science Invisible Fats Lab ReportDocument5 pagesFood Science Invisible Fats Lab Reportapi-286256497No ratings yet
- Material Guide For Horizontal and Vertical In-Line PumpsDocument1 pageMaterial Guide For Horizontal and Vertical In-Line PumpsEr Bishwonath Shah100% (1)
- Atoms and Molecules Handout 2Document3 pagesAtoms and Molecules Handout 2Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Formulas of Common Chemical SubstancesDocument11 pagesModule 2 Formulas of Common Chemical SubstancesIcarusNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972Document32 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972lindseyallenizqtgdakmw100% (22)
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972christopher.manteca185100% (14)
- Expt. No. 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reaction - For On LineDocument8 pagesExpt. No. 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reaction - For On LineJames Val SalazarNo ratings yet
- Las Atoms Molecules IonsDocument7 pagesLas Atoms Molecules IonsPrince Dave NievesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Activity 7 Lessons 3 7Document5 pagesChemistry Activity 7 Lessons 3 7Nikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesIntroductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualEdwardMasseyentky100% (14)
- General-Chemistry1 Quarter1 Week2Document24 pagesGeneral-Chemistry1 Quarter1 Week2Rose RepuestoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualBrettStoutxcqdi100% (13)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualrussellsmithnjcoydzkfm100% (9)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (30)
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Slabaugh 1133605133 9781133605133 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Slabaugh 1133605133 9781133605133 Full Chapter PDFlois.payne328100% (18)
- Name/identify What Is Asked in Every Item Below. Choose Your Answer On The Box BelowDocument1 pageName/identify What Is Asked in Every Item Below. Choose Your Answer On The Box BelowDonna RemitarNo ratings yet
- AP C S W: Hemistry Ummer ORKDocument28 pagesAP C S W: Hemistry Ummer ORKLeslie BenetezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (25)
- Gateways Institute of Science & Technology: Configuration of The Following Nuclides. (2pts - Each)Document2 pagesGateways Institute of Science & Technology: Configuration of The Following Nuclides. (2pts - Each)Donna RemitarNo ratings yet
- Bonds and Type of ReactionsDocument7 pagesBonds and Type of ReactionsAlwyn Dave AmbataliNo ratings yet
- Full Download Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualhaineytattiis100% (28)
- Elements and Compounds Outcomes:: WriteDocument4 pagesElements and Compounds Outcomes:: WriterayNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 StudentDocument34 pagesTopic 1 Studentnayana wanasingheNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Editionrepastgraffitie17pv100% (18)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manualwarlyyersthdvmv100% (38)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (26)
- Activity 4NamingCompoundsDocument5 pagesActivity 4NamingCompoundsSamantha RicoNo ratings yet
- Writting and Naming Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument13 pagesWritting and Naming Ionic and Covalent Compoundsshamiervalo2No ratings yet
- Jai Shree RamDocument10 pagesJai Shree RamRenu YadavNo ratings yet
- Full Download Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterforcingcureless.z93zi7100% (20)
- Grade 7: First Term Examination-2018Document3 pagesGrade 7: First Term Examination-2018ApoorvaNo ratings yet
- Activity Binary Compounds Set 1Document2 pagesActivity Binary Compounds Set 1Zian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- Try This!Document5 pagesTry This!Almudi TallingNo ratings yet
- Yaga Nga ScienceDocument4 pagesYaga Nga ScienceChristelle PabiranNo ratings yet
- WS - Practice Problems Quantitative Chemistry - IB ChemistryDocument13 pagesWS - Practice Problems Quantitative Chemistry - IB ChemistryShaakirah JafferNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Properties of MatterDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Properties of MatterKen Christian As a StudentNo ratings yet
- Atoms 4 - Task SheetDocument3 pagesAtoms 4 - Task SheetShinto BabuNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Lesson 4 - Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds Name - Section - Score - I. Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Lesson 4 - Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds Name - Section - Score - I. Practice ProblemsLeslie BenetezNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Pre-TestDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Pre-TestMae Pia Flor CawalingNo ratings yet
- Last Name: ID# # On The Signature List: First Name: Chemistry 205/4 Mid Term ExaminationDocument7 pagesLast Name: ID# # On The Signature List: First Name: Chemistry 205/4 Mid Term Examinationb76xxn4rdjNo ratings yet
- Self Practice - Block Test IIDocument2 pagesSelf Practice - Block Test IIDwayneNo ratings yet
- Draw A Line Between The Molecule and Its NameDocument58 pagesDraw A Line Between The Molecule and Its NameJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Editionunwill.eadishvj8p100% (51)
- Midterms PSDocument3 pagesMidterms PSvstxllaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Moles & StoichiometryDocument39 pagesUnit 5: Moles & StoichiometryNico Theodorus SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Element and CompoundDocument21 pagesElement and CompoundJoey PotterNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly Chapterwise Important Questionsfood loverNo ratings yet
- Application Task - Compounds and FormulaeDocument2 pagesApplication Task - Compounds and Formulaeandrei2108w800No ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition PDF Full Chaptermeow.switchel.2kjze7100% (25)
- 10 ReviewDocument4 pages10 Reviewapi-248454170No ratings yet
- KimDocument104 pagesKimBayby SiZzle'zNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDavina MarstonNo ratings yet
- Ap Chem Summer AssignmentDocument5 pagesAp Chem Summer Assignmentapi-310338634No ratings yet
- Element CompoundDocument51 pagesElement CompoundVilma Hebron CruzNo ratings yet
- Learner'S Activity Sheet in Grade 12 General Chemistry 1 For Quarter 1, Week 3Document7 pagesLearner'S Activity Sheet in Grade 12 General Chemistry 1 For Quarter 1, Week 3cutiepie creampieNo ratings yet
- Is It Balanced and Ch-12 Lesson 1 Content PracticeDocument3 pagesIs It Balanced and Ch-12 Lesson 1 Content Practicejeehoonkim78No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument37 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsSeth CapellanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chm131Document52 pagesChapter 2 Chm131araso100% (1)
- (Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsDocument1 page(Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsJarar VirkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula and NomenclatureDocument16 pagesChemical Formula and NomenclatureFlorie CaballoNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Unit 1-3 Elements, Atomic Structure Exam QuestionDocument1 pageUnit 1-3 Elements, Atomic Structure Exam QuestionZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- ???? ??? ????????? ?????????Document1 page???? ??? ????????? ?????????Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Karachi Grammar School Middle Section First Term Examination, 2019 Syllabus Class IxDocument6 pagesKarachi Grammar School Middle Section First Term Examination, 2019 Syllabus Class IxZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Atomic STRCDocument2 pagesAtomic STRCZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Density NotesDocument1 pageDensity NotesZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules Handout 2Document3 pagesAtoms and Molecules Handout 2Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument5 pagesPDF DocumentZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Physical QuanitiesDocument8 pagesPhysical QuanitiesZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- DensityDocument4 pagesDensityZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Science SA2 Juying Sec 2018Document44 pagesSec 1 Science SA2 Juying Sec 2018Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Light Test Paper2Document2 pagesLight Test Paper2Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Science SA2 Hua Yi Sec 2018Document33 pagesSec 1 Science SA2 Hua Yi Sec 2018Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- SaltsDocument4 pagesSaltsZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Foam PDFDocument15 pagesFoam PDFShivaram SuppiahNo ratings yet
- Thermax Demineralisation BrochureDocument8 pagesThermax Demineralisation Brochuremathesis-2No ratings yet
- TPL Call No:-HRRL/CDU-VDU/TR-JOHN ZINK/2959 Dated 18.11.2022Document1 pageTPL Call No:-HRRL/CDU-VDU/TR-JOHN ZINK/2959 Dated 18.11.2022PRASHANTNo ratings yet
- What Is Mirachem 500 Cleaner / Degreaser Concentrate?Document18 pagesWhat Is Mirachem 500 Cleaner / Degreaser Concentrate?Ras-Sherwin A. JalaniNo ratings yet
- Coolant SelectionsDocument35 pagesCoolant SelectionsAntony MorenoNo ratings yet
- Ok Tubrod 14.30a PDFDocument1 pageOk Tubrod 14.30a PDFqaNo ratings yet
- Tube Products of India Cold Rolling DivisionDocument45 pagesTube Products of India Cold Rolling DivisionAditya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Forging PDF NotesDocument51 pagesForging PDF Notesaman prasadNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0920410522010956 MainDocument37 pages1 s2.0 S0920410522010956 MainHNo ratings yet
- CreolinDocument4 pagesCreolinJean RisquezNo ratings yet
- EN24 and EN24T SteelDocument3 pagesEN24 and EN24T Steelpatrik710No ratings yet
- Spiropyrans Synthesis PropertiesDocument31 pagesSpiropyrans Synthesis PropertiesXuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Atomic Structure Formulas and Names of CompoundsDocument11 pagesLesson 2. Atomic Structure Formulas and Names of CompoundsRandel MontielNo ratings yet
- Casquillos INADocument55 pagesCasquillos INAFrancisco PalomeroNo ratings yet
- MSDS NAOH FLAKE (Kop LTL)Document5 pagesMSDS NAOH FLAKE (Kop LTL)PT. CITA RASA PALEMBANGNo ratings yet
- Aqua SILENCERDocument28 pagesAqua SILENCERAnandu Pm100% (5)
- Le Chatelier'S Principle PDFDocument37 pagesLe Chatelier'S Principle PDFNaveenDarwinNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hardness and Wear Resistance On en 353 Steel by Heat TreatmentDocument4 pagesEffect of Hardness and Wear Resistance On en 353 Steel by Heat TreatmentIJMERNo ratings yet
- Title: Minimum Requirements On Welding From Supplier and Sub-SupplierDocument10 pagesTitle: Minimum Requirements On Welding From Supplier and Sub-SupplierDeepak DasNo ratings yet
- 05 IR Chart PDFDocument1 page05 IR Chart PDFKonstantina MsNo ratings yet
- Chem Woot Diagnostic So LNDocument4 pagesChem Woot Diagnostic So LNRSLNo ratings yet
- Rasa BinduDocument27 pagesRasa Bindupyam143No ratings yet
- Siemens Lining Material Water WP PDFDocument4 pagesSiemens Lining Material Water WP PDFJorgeNo ratings yet
- Lycasin®80/55 - Maltitol SyrupDocument3 pagesLycasin®80/55 - Maltitol SyrupAmol Amritkar NASIKNo ratings yet
- General Presentation: Chemical Composition C Si MN Ni CR Cu Mo N P SDocument7 pagesGeneral Presentation: Chemical Composition C Si MN Ni CR Cu Mo N P SCan ERTANNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fastener Pretreatment: Co., OHDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Fastener Pretreatment: Co., OHsuksesNo ratings yet
???? ??? ?????????
???? ??? ?????????
Uploaded by
Zoya AdnanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
???? ??? ?????????
???? ??? ?????????
Uploaded by
Zoya AdnanCopyright:
Available Formats
𝐀𝐭𝐨𝐦 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐌𝐨𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐞𝐬
Sunday, 3 January 2021 2:51 AM
𝐌𝐨𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐞
A group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental
unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction.
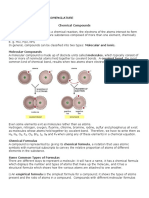
𝐓𝐲𝐩𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐦𝐨𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐞𝐬
𝐌𝐨𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐚𝐧 𝐞𝐥𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭
Molecule of an element consists of same kind of atoms (element) or
identical atoms combined chemically in a fixed ratio.
𝐌𝐨𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐚 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐝
Molecule of a compound consists of different kinds of atoms (element)
combined chemically in a fixed ratio.
𝐂𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐅𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐮𝐥𝐚
Chemical formula describes the chemical reactions.
Difference between an atom and a molecule:
Atom is the smallest particle (basic unit) of an element. Example,
Copper is an element and it is used to make electrical wire. Every
individual atom of this element has identical atoms.
Molecule is the smallest particle (basic unit) of a compound.
Molecule is the group of atoms, which is formed when identical
(same) atoms e.g. H2 (Hydrogen) or different kind (type) of atoms
combine chemically in a fixed ratio. Such as H2O (water), CO2
(Carbon Dioxide)
Difference between Mixture and Compound:
Mixture: It is formed when two or more substance combine
physically in a variable (different) ratio by mass. Examples, air,
ketchup, tooth-paste, milk, jelly, blood, sea-water, etc.
Compound: It is formed when two or more substance combine
chemically in a fixed ratio by mass. Examples, water forms with two
Hydrogen atoms and one Oxygen atom i.e chemically in a fixed
ratio.
Types of Molecules:
i. Molecule of an element.
ii. Molecule in a compound
Exercise No. 1 State the type of molecule
S. No. Name of Chemical Type of molecule
molecule Formula
1. Water H2O Molecule of a
compound
2. Oxygen gas O2 Molecule of an
element
3. Carbon Dioxide CO2
4. Ammonia gas NH3
5. Sulfur S8
6. Methane gas CH4
7. Ozone O3
8. Ethanol C2H5OH
Exercise No. 2 State the number of each kind of atoms in
molecules
S. No. Name of Chemical Number of each kind of atoms
molecule Formula in a molecule
1. Water H2O 2 Hydrogen atoms, 1
Oxygen atom
2. Hydrogen gas H2
3. Carbon CO
Monoxide
4. Carbon CCl4
Tetrachloride
5. Phosphorus P4
6. Sulfur Dioxide SO2
gas
7. Ozone O3
8. Methanol CH3OH
Exercise No. 3 Name the elements present in the following
molecules.
S. No. Name of Chemical Name of each kind of
molecule Formula atoms in a molecule
1. Carbon CO2 Carbon, Oxygen
Dioxide
2. Chlorine gas Cl2
3. Methane gas CH4
4. Carbon CCl4
Tetrachloride
5. Hydrogen HCl
Chloride
6. Nitrogen Oxide NO
gas
7. Ammonia gas NH3
8. Methanol CH3OH
Exercise No. 4 Total number of atoms in each
molecule
S. No. Name of Chemical Total number of
molecule Formula atoms in each
molecule
1. Carbon CO2 3 atoms
Dioxide
2. Magnesium MgO
Oxide
3. Ethane gas C2H6
4. Carbon CCl4
Tetrachlorid
e
5. Hydrogen HF
Fluoride
6. Sodium NaCl
Chloride
7. Ammonia NH3
gas
8. Glucose C6H12O6
Exercise No. 5 Describe the following
molecules.
i. Ethanol: It is a molecule of a compound. It
consists of two atoms of carbon, one atom of
Oxygen and six atoms of Hydrogen
combined chemically.
ii. Ammonia:
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
iii. Ozone: _____________________________
__________________________________________
_____________
iv. Glucose: _____________________________
__________________________________________
_____________
v. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S):
__________________________________________
___________________________
vi. Phosphorus
molecule: ________________________________
_____________________________________
vii. Methane: _____________________________
__________________________________________
_____________
viii. Calcium Carbonate
(CaCO3): __________________________________
_____________________________
Exercise No. 6 Write chemical formula of
the following molecules.
Magnesium Oxide Methane
Ammonia Nitrogen gas
Ethanol Sodium Fluoride
Exercise No. 7 Draw model diagram of the
following molecules.
i.
ii. Sulfur molecule
iii. Ammonia iv. Carbon
Dioxide v. Methane vi. Phosphorus vii. Carbon
Tetrachloride
viii. Sodium Chloride ix. Ozone x. Hydrogen
molecule
Exercise No. 8
Fig. below shows some of the molecules in the air above
an active volcano. For example, a water molecule has
the formula H2O and is shown in the diagram. Write the
formulae for the other molecules in the air above the
volcano.
𝐂𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐅𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐬
Water:H2O
Hydrogen:H2
Hydrogen chloride:HCL
Carbon Monoxide:CO
Carbon Dioxide:CO2
Sulfur:S8
Phosphorus:P4
Carbon Tetrachloride:CCL4
Ammonia:NH3
Methane:CH4
Methanol:CH3OH
Glucose:C6H12O6
Sucrose:C12H22O11
Potassium Permanganate:KMnO₄
Sulfuric Acid:H₂SO₄
Sugar:C12H22O11
Ethanol: C. 2H. 6O
Ozone:O3
Oxygen:O2
Nitrogen:N2
Sodium Fluoride: NaF
Sodium:Na
Calcium Carbonate:CaCO3
Sodium Carbonate:Na₂CO₃
Calcium oxide:CaO
Nitric Acid:HNO₃
Chlorine:Cl2
Sodium Chloride:
Hydrogen Flouride:HF
Sulfur Dioxide gas:SO2
Completed
You might also like
- Dwnload Full Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFschmitzerallanafx100% (13)
- Physical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document32 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 3Jerome Manaig Suelto83% (12)
- 2) Cementing AdditivesDocument41 pages2) Cementing Additiveseng20072007100% (1)
- Food Science Invisible Fats Lab ReportDocument5 pagesFood Science Invisible Fats Lab Reportapi-286256497No ratings yet
- Material Guide For Horizontal and Vertical In-Line PumpsDocument1 pageMaterial Guide For Horizontal and Vertical In-Line PumpsEr Bishwonath Shah100% (1)
- Atoms and Molecules Handout 2Document3 pagesAtoms and Molecules Handout 2Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Formulas of Common Chemical SubstancesDocument11 pagesModule 2 Formulas of Common Chemical SubstancesIcarusNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972Document32 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972lindseyallenizqtgdakmw100% (22)
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972christopher.manteca185100% (14)
- Expt. No. 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reaction - For On LineDocument8 pagesExpt. No. 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reaction - For On LineJames Val SalazarNo ratings yet
- Las Atoms Molecules IonsDocument7 pagesLas Atoms Molecules IonsPrince Dave NievesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Activity 7 Lessons 3 7Document5 pagesChemistry Activity 7 Lessons 3 7Nikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesIntroductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualEdwardMasseyentky100% (14)
- General-Chemistry1 Quarter1 Week2Document24 pagesGeneral-Chemistry1 Quarter1 Week2Rose RepuestoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualBrettStoutxcqdi100% (13)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualrussellsmithnjcoydzkfm100% (9)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (30)
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Slabaugh 1133605133 9781133605133 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Slabaugh 1133605133 9781133605133 Full Chapter PDFlois.payne328100% (18)
- Name/identify What Is Asked in Every Item Below. Choose Your Answer On The Box BelowDocument1 pageName/identify What Is Asked in Every Item Below. Choose Your Answer On The Box BelowDonna RemitarNo ratings yet
- AP C S W: Hemistry Ummer ORKDocument28 pagesAP C S W: Hemistry Ummer ORKLeslie BenetezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (25)
- Gateways Institute of Science & Technology: Configuration of The Following Nuclides. (2pts - Each)Document2 pagesGateways Institute of Science & Technology: Configuration of The Following Nuclides. (2pts - Each)Donna RemitarNo ratings yet
- Bonds and Type of ReactionsDocument7 pagesBonds and Type of ReactionsAlwyn Dave AmbataliNo ratings yet
- Full Download Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualhaineytattiis100% (28)
- Elements and Compounds Outcomes:: WriteDocument4 pagesElements and Compounds Outcomes:: WriterayNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 StudentDocument34 pagesTopic 1 Studentnayana wanasingheNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Editionrepastgraffitie17pv100% (18)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manualwarlyyersthdvmv100% (38)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (26)
- Activity 4NamingCompoundsDocument5 pagesActivity 4NamingCompoundsSamantha RicoNo ratings yet
- Writting and Naming Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument13 pagesWritting and Naming Ionic and Covalent Compoundsshamiervalo2No ratings yet
- Jai Shree RamDocument10 pagesJai Shree RamRenu YadavNo ratings yet
- Full Download Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterforcingcureless.z93zi7100% (20)
- Grade 7: First Term Examination-2018Document3 pagesGrade 7: First Term Examination-2018ApoorvaNo ratings yet
- Activity Binary Compounds Set 1Document2 pagesActivity Binary Compounds Set 1Zian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- Try This!Document5 pagesTry This!Almudi TallingNo ratings yet
- Yaga Nga ScienceDocument4 pagesYaga Nga ScienceChristelle PabiranNo ratings yet
- WS - Practice Problems Quantitative Chemistry - IB ChemistryDocument13 pagesWS - Practice Problems Quantitative Chemistry - IB ChemistryShaakirah JafferNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Properties of MatterDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Properties of MatterKen Christian As a StudentNo ratings yet
- Atoms 4 - Task SheetDocument3 pagesAtoms 4 - Task SheetShinto BabuNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Lesson 4 - Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds Name - Section - Score - I. Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Lesson 4 - Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds Name - Section - Score - I. Practice ProblemsLeslie BenetezNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Pre-TestDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Pre-TestMae Pia Flor CawalingNo ratings yet
- Last Name: ID# # On The Signature List: First Name: Chemistry 205/4 Mid Term ExaminationDocument7 pagesLast Name: ID# # On The Signature List: First Name: Chemistry 205/4 Mid Term Examinationb76xxn4rdjNo ratings yet
- Self Practice - Block Test IIDocument2 pagesSelf Practice - Block Test IIDwayneNo ratings yet
- Draw A Line Between The Molecule and Its NameDocument58 pagesDraw A Line Between The Molecule and Its NameJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Editionunwill.eadishvj8p100% (51)
- Midterms PSDocument3 pagesMidterms PSvstxllaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Moles & StoichiometryDocument39 pagesUnit 5: Moles & StoichiometryNico Theodorus SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Element and CompoundDocument21 pagesElement and CompoundJoey PotterNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly Chapterwise Important Questionsfood loverNo ratings yet
- Application Task - Compounds and FormulaeDocument2 pagesApplication Task - Compounds and Formulaeandrei2108w800No ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition PDF Full Chaptermeow.switchel.2kjze7100% (25)
- 10 ReviewDocument4 pages10 Reviewapi-248454170No ratings yet
- KimDocument104 pagesKimBayby SiZzle'zNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDavina MarstonNo ratings yet
- Ap Chem Summer AssignmentDocument5 pagesAp Chem Summer Assignmentapi-310338634No ratings yet
- Element CompoundDocument51 pagesElement CompoundVilma Hebron CruzNo ratings yet
- Learner'S Activity Sheet in Grade 12 General Chemistry 1 For Quarter 1, Week 3Document7 pagesLearner'S Activity Sheet in Grade 12 General Chemistry 1 For Quarter 1, Week 3cutiepie creampieNo ratings yet
- Is It Balanced and Ch-12 Lesson 1 Content PracticeDocument3 pagesIs It Balanced and Ch-12 Lesson 1 Content Practicejeehoonkim78No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument37 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsSeth CapellanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chm131Document52 pagesChapter 2 Chm131araso100% (1)
- (Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsDocument1 page(Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsJarar VirkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula and NomenclatureDocument16 pagesChemical Formula and NomenclatureFlorie CaballoNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Unit 1-3 Elements, Atomic Structure Exam QuestionDocument1 pageUnit 1-3 Elements, Atomic Structure Exam QuestionZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- ???? ??? ????????? ?????????Document1 page???? ??? ????????? ?????????Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Karachi Grammar School Middle Section First Term Examination, 2019 Syllabus Class IxDocument6 pagesKarachi Grammar School Middle Section First Term Examination, 2019 Syllabus Class IxZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Atomic STRCDocument2 pagesAtomic STRCZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Density NotesDocument1 pageDensity NotesZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules Handout 2Document3 pagesAtoms and Molecules Handout 2Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument5 pagesPDF DocumentZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Physical QuanitiesDocument8 pagesPhysical QuanitiesZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- DensityDocument4 pagesDensityZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Science SA2 Juying Sec 2018Document44 pagesSec 1 Science SA2 Juying Sec 2018Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Light Test Paper2Document2 pagesLight Test Paper2Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Science SA2 Hua Yi Sec 2018Document33 pagesSec 1 Science SA2 Hua Yi Sec 2018Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- SaltsDocument4 pagesSaltsZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Foam PDFDocument15 pagesFoam PDFShivaram SuppiahNo ratings yet
- Thermax Demineralisation BrochureDocument8 pagesThermax Demineralisation Brochuremathesis-2No ratings yet
- TPL Call No:-HRRL/CDU-VDU/TR-JOHN ZINK/2959 Dated 18.11.2022Document1 pageTPL Call No:-HRRL/CDU-VDU/TR-JOHN ZINK/2959 Dated 18.11.2022PRASHANTNo ratings yet
- What Is Mirachem 500 Cleaner / Degreaser Concentrate?Document18 pagesWhat Is Mirachem 500 Cleaner / Degreaser Concentrate?Ras-Sherwin A. JalaniNo ratings yet
- Coolant SelectionsDocument35 pagesCoolant SelectionsAntony MorenoNo ratings yet
- Ok Tubrod 14.30a PDFDocument1 pageOk Tubrod 14.30a PDFqaNo ratings yet
- Tube Products of India Cold Rolling DivisionDocument45 pagesTube Products of India Cold Rolling DivisionAditya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Forging PDF NotesDocument51 pagesForging PDF Notesaman prasadNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0920410522010956 MainDocument37 pages1 s2.0 S0920410522010956 MainHNo ratings yet
- CreolinDocument4 pagesCreolinJean RisquezNo ratings yet
- EN24 and EN24T SteelDocument3 pagesEN24 and EN24T Steelpatrik710No ratings yet
- Spiropyrans Synthesis PropertiesDocument31 pagesSpiropyrans Synthesis PropertiesXuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Atomic Structure Formulas and Names of CompoundsDocument11 pagesLesson 2. Atomic Structure Formulas and Names of CompoundsRandel MontielNo ratings yet
- Casquillos INADocument55 pagesCasquillos INAFrancisco PalomeroNo ratings yet
- MSDS NAOH FLAKE (Kop LTL)Document5 pagesMSDS NAOH FLAKE (Kop LTL)PT. CITA RASA PALEMBANGNo ratings yet
- Aqua SILENCERDocument28 pagesAqua SILENCERAnandu Pm100% (5)
- Le Chatelier'S Principle PDFDocument37 pagesLe Chatelier'S Principle PDFNaveenDarwinNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hardness and Wear Resistance On en 353 Steel by Heat TreatmentDocument4 pagesEffect of Hardness and Wear Resistance On en 353 Steel by Heat TreatmentIJMERNo ratings yet
- Title: Minimum Requirements On Welding From Supplier and Sub-SupplierDocument10 pagesTitle: Minimum Requirements On Welding From Supplier and Sub-SupplierDeepak DasNo ratings yet
- 05 IR Chart PDFDocument1 page05 IR Chart PDFKonstantina MsNo ratings yet
- Chem Woot Diagnostic So LNDocument4 pagesChem Woot Diagnostic So LNRSLNo ratings yet
- Rasa BinduDocument27 pagesRasa Bindupyam143No ratings yet
- Siemens Lining Material Water WP PDFDocument4 pagesSiemens Lining Material Water WP PDFJorgeNo ratings yet
- Lycasin®80/55 - Maltitol SyrupDocument3 pagesLycasin®80/55 - Maltitol SyrupAmol Amritkar NASIKNo ratings yet
- General Presentation: Chemical Composition C Si MN Ni CR Cu Mo N P SDocument7 pagesGeneral Presentation: Chemical Composition C Si MN Ni CR Cu Mo N P SCan ERTANNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fastener Pretreatment: Co., OHDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Fastener Pretreatment: Co., OHsuksesNo ratings yet