Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of Hypocalcemia
TABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of Hypocalcemia
Uploaded by
Rashmeeta ThadhaniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Calcium & Phosphorus AnishDocument52 pagesCalcium & Phosphorus AnishAnish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Major Causes Hypocalcemia - UpToDate PDFDocument2 pagesMajor Causes Hypocalcemia - UpToDate PDFAnita VásquezNo ratings yet
- Serum Calcium: Total Serum Calcium 8.5 - 10.5 MG/DL Ionized Serum Calcium 4.5 - 5.2 MG/DLDocument25 pagesSerum Calcium: Total Serum Calcium 8.5 - 10.5 MG/DL Ionized Serum Calcium 4.5 - 5.2 MG/DLAmrAminNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia 130217123548 Phpapp02Document30 pagesHypocalcemia 130217123548 Phpapp02RAMJIBAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Food-Drug Interaction: Presented By: Deepika Baranwal PHD ScholarDocument29 pagesFood-Drug Interaction: Presented By: Deepika Baranwal PHD ScholarUncu LiviaNo ratings yet
- HYPOCALCEMIADocument27 pagesHYPOCALCEMIAJeffri SetiawanNo ratings yet
- HiperparatiroidDocument15 pagesHiperparatiroidDoni PrasetioNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology, Calcium-PSimmDocument38 pagesEndocrinology, Calcium-PSimmSonia TivadarNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Lab 1 Nilai NormalDocument3 pagesPemeriksaan Lab 1 Nilai NormalSivasangkari AnbalaganNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Gland Diseases: Primary Hyperparathyroidism HypoparathyroidismDocument25 pagesParathyroid Gland Diseases: Primary Hyperparathyroidism HypoparathyroidismZahrah El FaradisaNo ratings yet
- HyperparathyroidismDocument16 pagesHyperparathyroidismkint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid DisordersDocument44 pagesParathyroid DisordersBIAN ALKHAZMARI100% (1)
- Primary and Secondary HyperparathyroidismDocument13 pagesPrimary and Secondary Hyperparathyroidismaileen agustinNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate BalanceDocument20 pagesDisorders of Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate BalanceMarcela HincapiéNo ratings yet
- Agents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisDocument5 pagesAgents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisKoj LozadaNo ratings yet
- HyperphosphatemiaDocument2 pagesHyperphosphatemiatephNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral DisorderDocument25 pagesBone Mineral DisorderAvino Mulana FikriNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral Disorder: Calcium, Vitamin D and Phosphorus: Next Webinar: July 30,2020Document25 pagesBone Mineral Disorder: Calcium, Vitamin D and Phosphorus: Next Webinar: July 30,2020Dr Mehreen LateefNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDocument20 pagesDisorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismAhmed Noureldin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcaemia: Done By: Saja Dmour Supervised By: DR. Ahmad MdallalDocument16 pagesHypocalcaemia: Done By: Saja Dmour Supervised By: DR. Ahmad Mdallalraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDocument20 pagesDisorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismAli TawbeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology - Part 3 Parathyroid GlandDocument30 pagesEndocrine Physiology - Part 3 Parathyroid GlandTerrence Beniasi CharumbiraNo ratings yet
- 0815 Skugor HyperAndHypocalcemiaDocument79 pages0815 Skugor HyperAndHypocalcemiaSirNorman BalinoNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Parathyroid GlandsDocument30 pagesDisorders of The Parathyroid Glandsikram ullah khan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Body Fluids and Fluid TherapyDocument37 pagesPathophysiology of Body Fluids and Fluid TherapyReza Badruun Syahrul HakimNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi SharmaDocument36 pagesRenal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi Sharmanidhi261987No ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia Secondary To Primary HyperparathyroidismDocument26 pagesHypercalcemia Secondary To Primary HyperparathyroidismClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Gout ManagementDocument28 pagesGuideline For Gout ManagementbestmonkeyNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism Review of The Literature 2018 PDFDocument7 pagesHypoparathyroidism Review of The Literature 2018 PDFsajmirNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument40 pagesChronic Renal FailureChristian Valenzuela RojasNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia: Dept of Nephrology PsriDocument40 pagesHypocalcemia: Dept of Nephrology Psriind78No ratings yet
- Hyper Parathyroid IsmDocument20 pagesHyper Parathyroid IsmPartha SarathyNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone, Calcitonin and Vitamin D Testing in Calcium and Bone Metabolic DisordersDocument3 pagesParathyroid Hormone, Calcitonin and Vitamin D Testing in Calcium and Bone Metabolic DisordersVeronika WijayaNo ratings yet
- The Parathyroid GlandDocument66 pagesThe Parathyroid GlandMohammed GamalNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument30 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Parathyroid GlandsDocument52 pagesDisorders of Parathyroid GlandsDr. Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Parathyroid Gland: DR - Umalkhayr Omar, MDDocument36 pagesThe Parathyroid Gland: DR - Umalkhayr Omar, MDgibreilNo ratings yet
- Pathology IcsmDocument84 pagesPathology IcsmAlice TangNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Micro Nutrients ChartDocument2 pagesVitamin and Micro Nutrients ChartsublunderNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia: - Disorder of Mature Bone in Which Mineralisation of New Osteoid Bone Is Inadequate or DelayedDocument48 pagesOsteomalacia: - Disorder of Mature Bone in Which Mineralisation of New Osteoid Bone Is Inadequate or DelayedHimanshu NarangNo ratings yet
- Roberts Week 7 HyperparathyroidismDocument17 pagesRoberts Week 7 Hyperparathyroidismjackie robertsNo ratings yet
- M. AnaemiaDocument44 pagesM. AnaemiaAbdirashidNo ratings yet
- Lab Normal Value Comments: AlbuminDocument4 pagesLab Normal Value Comments: AlbumindelantarzNo ratings yet
- Lec#49 Calcium DisordersDocument105 pagesLec#49 Calcium DisordersKhaldoun AlmomaniNo ratings yet
- RicketsDocument24 pagesRicketsNabrazz SthaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Parathyroid Gland: BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. Soumya BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. SoumyaDocument59 pagesDisorders of Parathyroid Gland: BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. Soumya BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. SoumyaAirdorid LoginidNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Nutrient DepletionDocument75 pagesDrug-Induced Nutrient DepletionValentin Quinteros100% (1)
- Calicum Metabolisim DisoodersDocument12 pagesCalicum Metabolisim DisoodersDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Slide Disorder ParatiroidDocument15 pagesSlide Disorder ParatiroiddradrianramdhanyNo ratings yet
- Complications of Long Term DialysisDocument9 pagesComplications of Long Term Dialysisbazuu mbwegzeNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocument5 pagesHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdNo ratings yet
- Calcium: HypercalcemiaDocument7 pagesCalcium: HypercalcemiaGregNo ratings yet
- LactateDocument2 pagesLactatebrittanymedical3365No ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytesVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- Potassium: Causes of HypokalemiaDocument1 pagePotassium: Causes of HypokalemiaMyra De Guzman PalattaoNo ratings yet
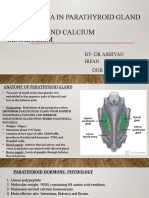
- Anaesthesia in Parathyroid Gland DisordersDocument25 pagesAnaesthesia in Parathyroid Gland DisordersAshiyan IrfanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Review II RevisedDocument37 pagesEndocrine Review II RevisedEdRobertArnadNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRICSDocument70 pagesPEDIATRICSMathewos MekonnenNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Surgery Open Digestive Advance: G. Pasinato, J.-M RegimbeauDocument7 pagesSurgery Open Digestive Advance: G. Pasinato, J.-M RegimbeauRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-19 - Emergency Therapy of HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-19 - Emergency Therapy of HyperkalemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-26 - Symptoms and Signs of HypocalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-26 - Symptoms and Signs of HypocalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-30 - Drugs That Cause Hypophosphatemia and UnderlyingDocument1 pageTABLE 17-30 - Drugs That Cause Hypophosphatemia and UnderlyingRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-29 - Causes of HypophosphatemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-29 - Causes of HypophosphatemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument1 pageTintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Primer: Head and Neck Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument22 pagesPrimer: Head and Neck Squamous Cell CarcinomaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach of Fever in Childhood - Aug 19Document31 pagesDiagnostic Approach of Fever in Childhood - Aug 19Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- (Sici) 1520 6823 (1997) 5:3 93::aid Roi1 3.0.co 2 DDocument4 pages(Sici) 1520 6823 (1997) 5:3 93::aid Roi1 3.0.co 2 DRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- 2011 Article 195Document6 pages2011 Article 195Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers October 2016Document25 pagesTuberculosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers October 2016Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Left BehindDocument1 pageReflection On Left BehindRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- KS 1405 WB03A Energy Systems Modeling Workshop BriefDocument9 pagesKS 1405 WB03A Energy Systems Modeling Workshop BriefRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2020 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument23 pagesEconomics ALevel 2020 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument31 pagesEconomics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Joint Pain (Dr. Stevent, 27th August 2020)Document3 pagesJoint Pain (Dr. Stevent, 27th August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Pemberton Sign in Diagnosis of Retrosternal GoiterDocument3 pagesPemberton Sign in Diagnosis of Retrosternal GoiterRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Cardiology: Micaela Gliozzi, Natalia Malara, Saverio Muscoli, Vincenzo MollaceDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Cardiology: Micaela Gliozzi, Natalia Malara, Saverio Muscoli, Vincenzo MollaceRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Anti Bullying: Love YourselfDocument23 pagesAnti Bullying: Love YourselfRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Document18 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
TABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of Hypocalcemia
TABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of Hypocalcemia
Uploaded by
Rashmeeta ThadhaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of Hypocalcemia
TABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of Hypocalcemia
Uploaded by
Rashmeeta ThadhaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e >Fluids and Electrolytes
Judith E. Tintinalli, J. Stephan Stapczynski, O. John Ma, Donald M. Yealy, Garth D. Meckler, David M. Cline+
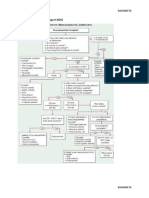
TABLE 17-24Some Causes of Hypocalcemia
Cause Mechanism
Decreased calcium absorption
Vitamin D deficiency
Decreased oral intake Malnutrition
Decreased intestinal absorption Intestinal bypass, gastrectomy
Decreased production of 25(OH)D3 Liver failure
Decreased synthesis of 1,25(OH2)D3 Renal failure, hyperphosphatemia
Malabsorption syndromes
Increased calcium excretion/reduced bone resorption
Alcoholism Hypomagnesemia causing inhibition of PTH secretion, PTH resistance to bone resorption
Hypoparathyroidism Genetic, autoimmune, surgical, tumoral
Pseudohypoparathyroidism Resistance to PTH action
Hypomagnesemia Inhibition of PTH secretion, PTH resistance to bone resorption
Drugs (Table 17-25)
Miscellaneous
Sepsis
Acute pancreatitis Fatty acids combine with [Ca2+] to form insoluble Ca2+ soaps and lead to a reduction of serum [Ca2+]
Massive transfusions
Rhabdomyolysis
Abbreviations: 25(OH)D3 = 25-hydroxyvitamin D3; 1,25(OH2)D3 = 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3; PTH = parathyroid hormone.
Date of download: 03/26/23 from AccessEmergency Medicine: accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Calcium & Phosphorus AnishDocument52 pagesCalcium & Phosphorus AnishAnish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Major Causes Hypocalcemia - UpToDate PDFDocument2 pagesMajor Causes Hypocalcemia - UpToDate PDFAnita VásquezNo ratings yet
- Serum Calcium: Total Serum Calcium 8.5 - 10.5 MG/DL Ionized Serum Calcium 4.5 - 5.2 MG/DLDocument25 pagesSerum Calcium: Total Serum Calcium 8.5 - 10.5 MG/DL Ionized Serum Calcium 4.5 - 5.2 MG/DLAmrAminNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia 130217123548 Phpapp02Document30 pagesHypocalcemia 130217123548 Phpapp02RAMJIBAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Food-Drug Interaction: Presented By: Deepika Baranwal PHD ScholarDocument29 pagesFood-Drug Interaction: Presented By: Deepika Baranwal PHD ScholarUncu LiviaNo ratings yet
- HYPOCALCEMIADocument27 pagesHYPOCALCEMIAJeffri SetiawanNo ratings yet
- HiperparatiroidDocument15 pagesHiperparatiroidDoni PrasetioNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology, Calcium-PSimmDocument38 pagesEndocrinology, Calcium-PSimmSonia TivadarNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Lab 1 Nilai NormalDocument3 pagesPemeriksaan Lab 1 Nilai NormalSivasangkari AnbalaganNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Gland Diseases: Primary Hyperparathyroidism HypoparathyroidismDocument25 pagesParathyroid Gland Diseases: Primary Hyperparathyroidism HypoparathyroidismZahrah El FaradisaNo ratings yet
- HyperparathyroidismDocument16 pagesHyperparathyroidismkint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid DisordersDocument44 pagesParathyroid DisordersBIAN ALKHAZMARI100% (1)
- Primary and Secondary HyperparathyroidismDocument13 pagesPrimary and Secondary Hyperparathyroidismaileen agustinNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate BalanceDocument20 pagesDisorders of Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate BalanceMarcela HincapiéNo ratings yet
- Agents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisDocument5 pagesAgents That Affect Bone Mineral HomeostasisKoj LozadaNo ratings yet
- HyperphosphatemiaDocument2 pagesHyperphosphatemiatephNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral DisorderDocument25 pagesBone Mineral DisorderAvino Mulana FikriNo ratings yet
- Bone Mineral Disorder: Calcium, Vitamin D and Phosphorus: Next Webinar: July 30,2020Document25 pagesBone Mineral Disorder: Calcium, Vitamin D and Phosphorus: Next Webinar: July 30,2020Dr Mehreen LateefNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDocument20 pagesDisorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismAhmed Noureldin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcaemia: Done By: Saja Dmour Supervised By: DR. Ahmad MdallalDocument16 pagesHypocalcaemia: Done By: Saja Dmour Supervised By: DR. Ahmad Mdallalraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDocument20 pagesDisorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismAli TawbeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology - Part 3 Parathyroid GlandDocument30 pagesEndocrine Physiology - Part 3 Parathyroid GlandTerrence Beniasi CharumbiraNo ratings yet
- 0815 Skugor HyperAndHypocalcemiaDocument79 pages0815 Skugor HyperAndHypocalcemiaSirNorman BalinoNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Parathyroid GlandsDocument30 pagesDisorders of The Parathyroid Glandsikram ullah khan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Body Fluids and Fluid TherapyDocument37 pagesPathophysiology of Body Fluids and Fluid TherapyReza Badruun Syahrul HakimNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi SharmaDocument36 pagesRenal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi Sharmanidhi261987No ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia Secondary To Primary HyperparathyroidismDocument26 pagesHypercalcemia Secondary To Primary HyperparathyroidismClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Gout ManagementDocument28 pagesGuideline For Gout ManagementbestmonkeyNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism Review of The Literature 2018 PDFDocument7 pagesHypoparathyroidism Review of The Literature 2018 PDFsajmirNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument40 pagesChronic Renal FailureChristian Valenzuela RojasNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia: Dept of Nephrology PsriDocument40 pagesHypocalcemia: Dept of Nephrology Psriind78No ratings yet
- Hyper Parathyroid IsmDocument20 pagesHyper Parathyroid IsmPartha SarathyNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Hormone, Calcitonin and Vitamin D Testing in Calcium and Bone Metabolic DisordersDocument3 pagesParathyroid Hormone, Calcitonin and Vitamin D Testing in Calcium and Bone Metabolic DisordersVeronika WijayaNo ratings yet
- The Parathyroid GlandDocument66 pagesThe Parathyroid GlandMohammed GamalNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument30 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Parathyroid GlandsDocument52 pagesDisorders of Parathyroid GlandsDr. Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Parathyroid Gland: DR - Umalkhayr Omar, MDDocument36 pagesThe Parathyroid Gland: DR - Umalkhayr Omar, MDgibreilNo ratings yet
- Pathology IcsmDocument84 pagesPathology IcsmAlice TangNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Micro Nutrients ChartDocument2 pagesVitamin and Micro Nutrients ChartsublunderNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia: - Disorder of Mature Bone in Which Mineralisation of New Osteoid Bone Is Inadequate or DelayedDocument48 pagesOsteomalacia: - Disorder of Mature Bone in Which Mineralisation of New Osteoid Bone Is Inadequate or DelayedHimanshu NarangNo ratings yet
- Roberts Week 7 HyperparathyroidismDocument17 pagesRoberts Week 7 Hyperparathyroidismjackie robertsNo ratings yet
- M. AnaemiaDocument44 pagesM. AnaemiaAbdirashidNo ratings yet
- Lab Normal Value Comments: AlbuminDocument4 pagesLab Normal Value Comments: AlbumindelantarzNo ratings yet
- Lec#49 Calcium DisordersDocument105 pagesLec#49 Calcium DisordersKhaldoun AlmomaniNo ratings yet
- RicketsDocument24 pagesRicketsNabrazz SthaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Parathyroid Gland: BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. Soumya BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. SoumyaDocument59 pagesDisorders of Parathyroid Gland: BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. Soumya BY: Dr. Rakesh Dr. Karthik Dr. SoumyaAirdorid LoginidNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Nutrient DepletionDocument75 pagesDrug-Induced Nutrient DepletionValentin Quinteros100% (1)
- Calicum Metabolisim DisoodersDocument12 pagesCalicum Metabolisim DisoodersDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Slide Disorder ParatiroidDocument15 pagesSlide Disorder ParatiroiddradrianramdhanyNo ratings yet
- Complications of Long Term DialysisDocument9 pagesComplications of Long Term Dialysisbazuu mbwegzeNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocument5 pagesHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdNo ratings yet
- Calcium: HypercalcemiaDocument7 pagesCalcium: HypercalcemiaGregNo ratings yet
- LactateDocument2 pagesLactatebrittanymedical3365No ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytesVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- Potassium: Causes of HypokalemiaDocument1 pagePotassium: Causes of HypokalemiaMyra De Guzman PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia in Parathyroid Gland DisordersDocument25 pagesAnaesthesia in Parathyroid Gland DisordersAshiyan IrfanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Review II RevisedDocument37 pagesEndocrine Review II RevisedEdRobertArnadNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRICSDocument70 pagesPEDIATRICSMathewos MekonnenNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Surgery Open Digestive Advance: G. Pasinato, J.-M RegimbeauDocument7 pagesSurgery Open Digestive Advance: G. Pasinato, J.-M RegimbeauRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-19 - Emergency Therapy of HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-19 - Emergency Therapy of HyperkalemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-26 - Symptoms and Signs of HypocalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-26 - Symptoms and Signs of HypocalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-30 - Drugs That Cause Hypophosphatemia and UnderlyingDocument1 pageTABLE 17-30 - Drugs That Cause Hypophosphatemia and UnderlyingRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-29 - Causes of HypophosphatemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-29 - Causes of HypophosphatemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument1 pageTintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Primer: Head and Neck Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument22 pagesPrimer: Head and Neck Squamous Cell CarcinomaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach of Fever in Childhood - Aug 19Document31 pagesDiagnostic Approach of Fever in Childhood - Aug 19Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- (Sici) 1520 6823 (1997) 5:3 93::aid Roi1 3.0.co 2 DDocument4 pages(Sici) 1520 6823 (1997) 5:3 93::aid Roi1 3.0.co 2 DRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- 2011 Article 195Document6 pages2011 Article 195Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers October 2016Document25 pagesTuberculosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers October 2016Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Left BehindDocument1 pageReflection On Left BehindRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- KS 1405 WB03A Energy Systems Modeling Workshop BriefDocument9 pagesKS 1405 WB03A Energy Systems Modeling Workshop BriefRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2020 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument23 pagesEconomics ALevel 2020 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument31 pagesEconomics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Joint Pain (Dr. Stevent, 27th August 2020)Document3 pagesJoint Pain (Dr. Stevent, 27th August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Pemberton Sign in Diagnosis of Retrosternal GoiterDocument3 pagesPemberton Sign in Diagnosis of Retrosternal GoiterRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Cardiology: Micaela Gliozzi, Natalia Malara, Saverio Muscoli, Vincenzo MollaceDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Cardiology: Micaela Gliozzi, Natalia Malara, Saverio Muscoli, Vincenzo MollaceRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Anti Bullying: Love YourselfDocument23 pagesAnti Bullying: Love YourselfRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Document18 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet