Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Bob0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThis document discusses various concepts related to the movement of substances through cell membranes via diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It defines key terms like selectively permeable membrane, diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It also provides examples of how these processes occur in plant cells specifically, allowing water and minerals to enter the root cells and move throughout the plant. The selectively permeable membranes in plant cells, like the cell membrane and vacuole membrane, control the movement of substances and help maintain turgor pressure.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various concepts related to the movement of substances through cell membranes via diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It defines key terms like selectively permeable membrane, diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It also provides examples of how these processes occur in plant cells specifically, allowing water and minerals to enter the root cells and move throughout the plant. The selectively permeable membranes in plant cells, like the cell membrane and vacuole membrane, control the movement of substances and help maintain turgor pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
BobThis document discusses various concepts related to the movement of substances through cell membranes via diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It defines key terms like selectively permeable membrane, diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It also provides examples of how these processes occur in plant cells specifically, allowing water and minerals to enter the root cells and move throughout the plant. The selectively permeable membranes in plant cells, like the cell membrane and vacuole membrane, control the movement of substances and help maintain turgor pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
2.2.
6 Movement through Membranes FMQuiz Homework Solution
Q. Water enters the outermost cells of the root by Q. Explain the term turgor.
osmosis. What does this tell you about the cell sap A. Pressure of cell contents on cell wall
of these outermost cells?
A. Lower water concentration or higher solute Q. Give an example of osmosis in plants.
concentration A. Water movement between cells or from soil to
root
Q. Osmosis has been described as a special case of
diffusion. Explain why. Q. Name a substance found in a plant cell vacuole.
A. Movement of water along a concentration A. Water or sugar or sap or salt(s) or protein
gradient through a selectively permeable
membrane Q. Give a feature of a plant cell that allows it to
remain turgid for long periods.
Q. What is meant by a selectively permeable A. Vacuole or cell wall or cell sap
membrane?
A. Allowing some substances to pass through Q. True or False. Plant cell walls are fully
permeable.
Q. Give locations in a cell at which there is a A. TRUE
selectively permeable membrane.
A. Chloroplast, mitochondrion, nucleus, vacuole Q. Water for photosynthesis enters the roots of
plants by what process?
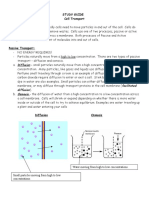
Q. What is diffusion? A. Osmosis
A. Movement of molecules from area of high
concentration to area of lower concentration Q. Suggest a way in which turgor is of value to
plants.
Q. Why is diffusion alternatively known as passive A. Support
transport?
A. No energy (ATP) required Q. Name the terms used in biology to describe the
movement of substances through cell membranes.
Q. Explain the biological basis for the use of high A. Diffusion; Osmosis; Active transport
sugar or high salt concentrations in the
preservation of food. Q. What process is responsible for the uptake of
A. Bacteria lose water by osmosis; this leads to minerals in a plant?
inactivity or death A. Active transport
Q. What did you use as the selectively permeable Q. What is meant by osmoregulation?
membrane in your investigation of osmosis? A. Controlling the water/salt balance within an
A. Visking tubing organism
Q. What is active transport? Q. Where precisely does water enter a plant?
A. Movement of molecules against a concentration A. Root hairs
gradient using energy
Q. The drooping of the leaves of a plant resulting
Q. Name two substances that enter a human from loss of turgidity due to lack of water is known
muscle cell by diffusion. as …
A. Oxygen; glucose; water; amino acids; phosphate; A. Wilting
iron
Q. In which tissue does water ascend through the
Q. Suggest an advantage to the cell of having a plant?
selectively permeable membrane. A. Xylem
A. Substances can be kept in (or out) or substances
can be let in (or out)
Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- Inter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFDocument8 pagesInter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFsingoj.bhargava chary100% (10)
- Jack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryDocument52 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryLora100% (2)
- Passive Transports: Osmosis and DiffusionDocument2 pagesPassive Transports: Osmosis and DiffusionAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Transport in Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter-1 Transport in Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsajayNo ratings yet
- MF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2Document33 pagesMF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Diffusion: AlveoliDocument5 pagesDiffusion: Alveoliaby251188No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document11 pagesChapter 11Atharva SchoolsNo ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherDocument20 pagesChap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherSulochana Devi PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument9 pagesMovement Into and Out of CellsMuhammad Ahmad NoorNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsPrakriti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement Into and Out of CellsAnanya MujumdarNo ratings yet
- Means of TransportDocument2 pagesMeans of Transportsridevikamaraj16No ratings yet
- Review 3 Cell Transport Advanced ZDocument4 pagesReview 3 Cell Transport Advanced ZOlyad EmanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Expect EssayDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Expect Essayrilahasniy48No ratings yet
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocument414 pagesMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Test: Biology Name: - Topic: Movement of Molecules Across Plasma MembraneDocument2 pagesClass 9 Test: Biology Name: - Topic: Movement of Molecules Across Plasma MembranearifaasadNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants IIDocument19 pagesTransport in Plants IIMarko ĆaletaNo ratings yet
- GR 7 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument9 pagesGR 7 Diffusion and OsmosisSHANNo ratings yet
- KimaniwamiangaDocument4 pagesKimaniwamiangaagwonadavidNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membranes Sheet AnswersDocument3 pagesPlasma Membranes Sheet Answerskim szymanskiNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- 03 Movement in and Out of CellsDocument26 pages03 Movement in and Out of Cells张查No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantMuskan VarlaniNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument19 pagesTransport MechanismAaron Roxas100% (2)
- 6 OsmosisDocument3 pages6 OsmosisQuino AmarelaNo ratings yet
- Biological Uptake Worksheet KeyDocument4 pagesBiological Uptake Worksheet KeyHanna MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Water and Solute Movements in PlantsDocument19 pagesLecture 3 Water and Solute Movements in PlantsnindaleNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyDocument51 pagesCell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyChester WengerNo ratings yet
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranNo ratings yet
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Functionapi-455371000No ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearDocument13 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearFrancisco Samarco100% (1)
- MOVEMENT IN & OUT OF CELLS - Ch.3Document48 pagesMOVEMENT IN & OUT OF CELLS - Ch.3Yassin Al fekyNo ratings yet
- Biology 110 (Section 152) - Intro To Biology & Society (Fall 2019)Document3 pagesBiology 110 (Section 152) - Intro To Biology & Society (Fall 2019)John MixerNo ratings yet
- Articles Move Across Membran Es by Simple Diffusion, Facilitat Ed Diffusion, Osmosis and Activ e TransportDocument34 pagesArticles Move Across Membran Es by Simple Diffusion, Facilitat Ed Diffusion, Osmosis and Activ e TransportApollo AdairNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoNo ratings yet
- B2.2 Revision Notes Zzsc27Document2 pagesB2.2 Revision Notes Zzsc27GwendaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function HomeworkDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Function Homeworkqrqvw98482No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDocument35 pagesCell Membrane and Cell Transportaayesha.fatima.rajaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument26 pagesTransport in Plants PDFMasOom Si ChuRail100% (2)
- Biology Form 6-1Document200 pagesBiology Form 6-1Justine MakolokaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion Lab FormativeDocument4 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion Lab Formativeapi-674548860No ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Cell Organelles A. Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument3 pagesBiology Notes: Cell Organelles A. Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesweeeeeshNo ratings yet
- Bio Exchange of MaterialsDocument12 pagesBio Exchange of Materials3.4 (2022) LAU JING XUAN DESTINEENo ratings yet
- 7.3 Cell TransportDocument3 pages7.3 Cell TransportSafa-99No ratings yet
- Movement of Materials in CellsDocument4 pagesMovement of Materials in CellsDaniel KidaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Water Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesWater Transport in PlantsPaula IscarNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument1 pageTransport MechanismsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Membrane TransportDocument28 pagesMembrane TransportLena WęglarzNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells - NOTESDocument5 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells - NOTESAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants I PUC - Biology Chapter - 11 One MarkDocument7 pagesTransport in Plants I PUC - Biology Chapter - 11 One MarkPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3Document8 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3MSKNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Plant Phy Lab ReportDocument9 pagesDiffusion Plant Phy Lab ReportBenjune RoseladaNo ratings yet
- How Translocation WorksDocument23 pagesHow Translocation WorksAqeela SyakiraNo ratings yet
- Water MovementDocument13 pagesWater Movementroteromano5No ratings yet
- 1 Cellular Transport VidDocument57 pages1 Cellular Transport Vidchizy bananaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Transport Through Cell MembraneDocument6 pagesModule 3 - Transport Through Cell MembraneGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Evolution and Escalation: An Ecological History of LifeFrom EverandEvolution and Escalation: An Ecological History of LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
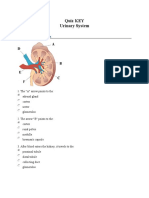
- QUIZ: Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesQUIZ: Urinary SystemBobNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Test Review Questions 2017Document1 pageCell Membrane Test Review Questions 2017BobNo ratings yet
- C. LysosomesDocument3 pagesC. LysosomesBobNo ratings yet
- B01 Cells and OrganellesDocument39 pagesB01 Cells and OrganellesBobNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledBobNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Project: Minimum Information To IncludeDocument3 pagesHuman Body Systems Project: Minimum Information To IncludeBobNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Cell TransportDocument2 pagesStudy Guide Cell TransportBobNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledBobNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Response Exam Qs FOUNDATION MarkschemeDocument16 pagesHomeostasis Response Exam Qs FOUNDATION MarkschemeBobNo ratings yet
- Cornell Note Taking FormatDocument1 pageCornell Note Taking FormatBobNo ratings yet
- Nervoustestreview Fall2014Document2 pagesNervoustestreview Fall2014BobNo ratings yet
- AMH and PCODocument10 pagesAMH and PCOwaleedaliNo ratings yet
- Contoh B.ingDocument3 pagesContoh B.ingQhaisya Binasanjaya67% (3)
- 1D - Thyroid Gland AssessmentDocument35 pages1D - Thyroid Gland AssessmentSadeem AbbasNo ratings yet
- NEET PG 2014 Question Paper With SolutionsDocument2,472 pagesNEET PG 2014 Question Paper With SolutionsSK RaulNo ratings yet
- Personality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteDocument8 pagesPersonality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteCzarina Ciara AndresNo ratings yet
- Reaction TimeDocument7 pagesReaction TimeMantaj GillNo ratings yet
- Ciccarelli 6e CH09 IPPTDocument63 pagesCiccarelli 6e CH09 IPPTz55nhgckwsNo ratings yet
- Ste 2103 General Biology Quiz On Cell (Camota)Document3 pagesSte 2103 General Biology Quiz On Cell (Camota)Angelo Paolo CamotaNo ratings yet
- STD 7 12.the Muscular System and Digestive Systemin Human BeingDocument3 pagesSTD 7 12.the Muscular System and Digestive Systemin Human BeingtechnoNo ratings yet
- Allen 2013, Revisión TSSTDocument31 pagesAllen 2013, Revisión TSSTSara Puig PérezNo ratings yet
- Coronary CirculationDocument33 pagesCoronary CirculationAayushman YadavNo ratings yet
- Life Science Grade10 To 12 FINALDocument20 pagesLife Science Grade10 To 12 FINALOsborn AgyemangNo ratings yet
- CPE203 Practice Problems 2Document4 pagesCPE203 Practice Problems 2Evita Angelina Putri JumaNo ratings yet
- Lect.8 HyperaldosteronismDocument10 pagesLect.8 HyperaldosteronismShubhamNo ratings yet
- 2023 Specimen Paper 4Document17 pages2023 Specimen Paper 4joumanaaa beckNo ratings yet
- 44 Impact of Salt and Metallic Stress On The Sodium and Potassium Uptake by The Vicia Faba L. PlantsDocument5 pages44 Impact of Salt and Metallic Stress On The Sodium and Potassium Uptake by The Vicia Faba L. PlantsAmina BelguendouzNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation - Operon Theory - Microbiology - OpenStaxDocument12 pagesGene Regulation - Operon Theory - Microbiology - OpenStaxAleksandra Sanja MartinovicNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: FK Uph May26, 2022Document52 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis: FK Uph May26, 2022FirmanHidayatNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 and 2Document447 pagesBiology 1 and 2Emmar MukisaNo ratings yet
- Aakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020Document12 pagesAakash Rank Booster Test Series For NEET-2020VedNo ratings yet
- Absorption of LipidsDocument22 pagesAbsorption of LipidsEmm Noman100% (1)
- Morphology and Anatomy of Sylleptic Shoots of Plum Trees (Prunus Domestica L.) As in Uenced by Different Dates of Shoot Heading During Summer PruningDocument11 pagesMorphology and Anatomy of Sylleptic Shoots of Plum Trees (Prunus Domestica L.) As in Uenced by Different Dates of Shoot Heading During Summer Pruningilicradmila320No ratings yet
- Mazi's Project Work K PDFDocument106 pagesMazi's Project Work K PDFIbogu TimothyNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument16 pagesFetal CirculationRESHMA AJAYNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Problems in Breast Pathology, 2009, PGDocument362 pagesDiagnostic Problems in Breast Pathology, 2009, PGMarin Ionut100% (1)
- Quarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sDocument17 pagesQuarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sTristan Paul PagalananNo ratings yet
- Ex 5 Act 2 - FisioexDocument4 pagesEx 5 Act 2 - FisioexIvanny RosadoNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone PerioDocument32 pagesAlveolar Bone PerioFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Grade 8 MitosisDocument5 pagesGrade 8 MitosisJay r DomingoNo ratings yet