Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
61 views© Medi - Lectures DR Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures DR Shubham Upadhyay
Uploaded by
HemanthDiarrhea management in children
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Full Download Ebook PDF Lehnes Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Providers PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Lehnes Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Providers PDFeleanor.jones934100% (40)
- Homoeopathic Clinic-CASE RECORD FORMDocument27 pagesHomoeopathic Clinic-CASE RECORD FORMAtit ShethNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Consumer ProductsDocument3 pagesEnzymes and Consumer ProductsMAC STACEY CAVENo ratings yet
- Signature Not VerifiedDocument1 pageSignature Not VerifiedSudharsan MohanNo ratings yet
- Weekly AssignmentDocument7 pagesWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaNo ratings yet
- The NASDAQ DozenDocument8 pagesThe NASDAQ Dozenrodolfo leivaNo ratings yet
- PSYC4009 Introduction To Counselling Semester 2 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTDocument13 pagesPSYC4009 Introduction To Counselling Semester 2 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTAhmad QawwamNo ratings yet
- I A Comenii Vestibuli Linguarum AuctariumDocument42 pagesI A Comenii Vestibuli Linguarum AuctariumRuben William Da Silva AndradeNo ratings yet
- GodMan 10236902Document177 pagesGodMan 1023690212monkeyzNo ratings yet
- HPCL Application FormDocument3 pagesHPCL Application FormPriyank PatelNo ratings yet
- 192-TNPSC History - Study Materials 1 - RK IAS Academy - Tamil Medium PDF DownloadDocument104 pages192-TNPSC History - Study Materials 1 - RK IAS Academy - Tamil Medium PDF DownloadKumaresan DhineshNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Biology Investigatory Project Class Xii Breast CancerDocument14 pagesVdocuments - MX Biology Investigatory Project Class Xii Breast CancerPooja TikaniaNo ratings yet
- Ahmes Secondary School General Studies Form-Vi Holiday Package: December 2021Document1 pageAhmes Secondary School General Studies Form-Vi Holiday Package: December 2021Aden.No ratings yet
- Menu FoodDocument3 pagesMenu FoodMarcellinda SteviNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument2 pagesNutritionVishu MehtaNo ratings yet
- Steps Carried Out Comparison: ObservationDocument9 pagesSteps Carried Out Comparison: ObservationJovan Paul DeldaNo ratings yet
- PT. Ikon Surabaya Farmamart (ISF)Document4 pagesPT. Ikon Surabaya Farmamart (ISF)Anonymous aaAQ6dgNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument72 pagesUntitleddojiveNo ratings yet
- PFMS Generated Print Payment Advice: To, The Branch HeadDocument2 pagesPFMS Generated Print Payment Advice: To, The Branch HeadIpsita SahaNo ratings yet
- Billet PDF V2Document2 pagesBillet PDF V2Md ShahedNo ratings yet
- Palm SundayDocument15 pagesPalm Sundayapi-286204923No ratings yet
- Ret Chhattisgarh 10 11Document29 pagesRet Chhattisgarh 10 11Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Microbiotricks - MmeDocument21 pagesMicrobiotricks - MmesiddhantaNo ratings yet
- QUOTATIONDocument4 pagesQUOTATIONCak Bash MkfNo ratings yet
- Rural MarketingDocument25 pagesRural Marketingbls.chitra6152No ratings yet
- Price Et Al., International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2022Document16 pagesPrice Et Al., International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2022Radu CiprianNo ratings yet
- 5 - 4 19 - 48) Oop-WPS OfficeDocument3 pages5 - 4 19 - 48) Oop-WPS OfficeWidara TaubatinNo ratings yet
- Larah Catalogue October 2022 - LR-1Document104 pagesLarah Catalogue October 2022 - LR-1Saif JamalNo ratings yet
- E Max Computer Education ProspectusDocument24 pagesE Max Computer Education ProspectusPratyush AryaNo ratings yet
- Isbt 18 Dec Deh - DelhiDocument1 pageIsbt 18 Dec Deh - DelhiKabir PantNo ratings yet
- DGS DGSDocument1 pageDGS DGSlalunaku nakurNo ratings yet
- Krsnaa Diagnostics - Full Form of ResidentDocument12 pagesKrsnaa Diagnostics - Full Form of ResidentAbisekNo ratings yet
- Robc Reviewed 2021Document56 pagesRobc Reviewed 2021Harmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- PCWB-2316 FLXL Black N100-IdDocument4 pagesPCWB-2316 FLXL Black N100-IdFindora InternusaNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Document4 pagesShanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- Ritshidze State of Healthcare For Key Populations 2023Document60 pagesRitshidze State of Healthcare For Key Populations 2023Krash KingNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportDocument7 pagesProgress ReportRizki LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Merritt Morning Market 3809 - Mar 24Document2 pagesMerritt Morning Market 3809 - Mar 24Kim LeclairNo ratings yet
- DVM Thesis PublishedDocument14 pagesDVM Thesis PublishedRedwanNo ratings yet
- SGS.G20 5.SewMachines - DurexDocument56 pagesSGS.G20 5.SewMachines - DurexNguyễn BáNo ratings yet
- Scoring Package 3rd Eng 2021-22-1Document48 pagesScoring Package 3rd Eng 2021-22-1Tayab TayabNo ratings yet
- FASH235 Document 2Document2 pagesFASH235 Document 2siibnuNo ratings yet
- Program A CaoDocument44 pagesProgram A CaoSalvi MascaroNo ratings yet
- Inggris Pat Kelas 3Document10 pagesInggris Pat Kelas 3Septiana anggrianiNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease - The Indian PerspectiveDocument209 pagesSickle Cell Disease - The Indian PerspectiveV L Gupta100% (2)
- Verbos en Presente Simple PDFDocument6 pagesVerbos en Presente Simple PDFwladapalsilva2495No ratings yet
- 10sm SST Eng 2021 22Document439 pages10sm SST Eng 2021 22vidushiNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument5 pagesEmotional IntelligenceKavitha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Introduction To Web Programming and PHPDocument12 pagesLab 9 Introduction To Web Programming and PHPMisbah UllahNo ratings yet
- L&T Mutual Fund Application FormDocument5 pagesL&T Mutual Fund Application Formnanduverma100% (1)
- Carp PolycultureDocument22 pagesCarp PolycultureMd.Tanvirul EhsanNo ratings yet
- Https Onetimeregn - Haryana.gov - in PrintApp - AspxDocument3 pagesHttps Onetimeregn - Haryana.gov - in PrintApp - AspxYogita TanwarNo ratings yet
- Star Laminates 0 8mm 1 0mm LaminatesDocument60 pagesStar Laminates 0 8mm 1 0mm Laminatesfosoce7719No ratings yet
- Extraterrestrial and Extradimensional Beings - How They Travel Space and TimeDocument1 pageExtraterrestrial and Extradimensional Beings - How They Travel Space and TimeStep T.No ratings yet
- BIO224 Chapter 7Document5 pagesBIO224 Chapter 7Muh. RidwanNo ratings yet
- Nylon Carpet. Harrington Catalogue.2022Document41 pagesNylon Carpet. Harrington Catalogue.2022Nikhil Chawla100% (1)
- Ipe UasDocument5 pagesIpe UasEben HaezerNo ratings yet
- Pet Bereavement and Coping MechanismsDocument16 pagesPet Bereavement and Coping MechanismsSophia JoseNo ratings yet
- Pests of CitrusDocument29 pagesPests of CitrusPalash MondalNo ratings yet
- Desensitization To Media Violence Links HiDocument17 pagesDesensitization To Media Violence Links HiJustinNo ratings yet
- Diare Dehidrasi BeratDocument40 pagesDiare Dehidrasi BeratcutietimothyNo ratings yet
- Farhan ChaudharyDocument1 pageFarhan ChaudharyHemanthNo ratings yet
- NBC Guidelines For Healthcare FacilityDocument17 pagesNBC Guidelines For Healthcare FacilityHemanthNo ratings yet
- STEMIDocument29 pagesSTEMIHemanthNo ratings yet
- WPW SyndromeDocument8 pagesWPW SyndromeHemanthNo ratings yet
- Acute Adrenal CrisisDocument27 pagesAcute Adrenal CrisisHemanthNo ratings yet
- Offtag Assessment 2Document12 pagesOfftag Assessment 2chooNo ratings yet
- Key Points - Peds Vital SignsDocument1 pageKey Points - Peds Vital SignsRaman kangNo ratings yet
- Yamamoto 2010Document2 pagesYamamoto 2010Ferdi ArdiNo ratings yet
- MeatinniDocument11 pagesMeatinnivinadata01No ratings yet
- Eng 2008 MedDocument43 pagesEng 2008 MedLucia BogNo ratings yet
- SSTIDocument1 pageSSTITan ShenNo ratings yet
- 1) CPG Management Major Depressive Disorder (Second Edition)Document83 pages1) CPG Management Major Depressive Disorder (Second Edition)Meena ViswaNo ratings yet
- 6Document5 pages6ρενα μινορεNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases EpidemiologyDocument44 pagesCommunicable Diseases EpidemiologyIrum QureshiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisGaming BoyNo ratings yet
- National AIDS Control ProgramDocument29 pagesNational AIDS Control ProgramMonalisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Artikel Keluarga Berencana, Izzatul Ummah FhadillaDocument6 pagesArtikel Keluarga Berencana, Izzatul Ummah FhadillaAQFAL storyNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review NotesDocument76 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Review Notesnot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- SPED QuizDocument4 pagesSPED QuizJennevive Micabalo CabugsaNo ratings yet
- The Shaken Baby SyndromeDocument9 pagesThe Shaken Baby SyndromeDiana LoloiuNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care For CHO - SN - Introduction To Emergency CareDocument28 pagesEmergency Care For CHO - SN - Introduction To Emergency CareAditi JainNo ratings yet
- 10 51982-Bagimli 1399294-3574178Document9 pages10 51982-Bagimli 1399294-3574178yahya kemalNo ratings yet
- NeuroblastomaDocument9 pagesNeuroblastomasamantha mccoyNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in Pulmonary MedicineDocument4 pagesThesis Topics in Pulmonary Medicinegj6sr6d7100% (2)
- Medicine FMGE Sprint by Dr. Santosh Patil (PW Med Ed)Document31 pagesMedicine FMGE Sprint by Dr. Santosh Patil (PW Med Ed)Stella ParkerNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Pain and Symptoms in PregnancyDocument6 pagesMusculoskeletal Pain and Symptoms in PregnancyDzaki Prakoso RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrain Systm Question 1 ST DayDocument15 pagesEndocrain Systm Question 1 ST DayJohn AjishNo ratings yet
- Soal Soal Latihan Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesSoal Soal Latihan Bahasa InggrisMIKA OKENo ratings yet
- AmnesiaDocument4 pagesAmnesiaHsnysbvNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mental Health and Coping - Dealing With Anxiety and DepressionDocument49 pagesUnit 4 - Mental Health and Coping - Dealing With Anxiety and DepressionAundrei ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cellular AbrasionDocument3 pagesCellular AbrasionFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Testicular Tumors: Dr. Ricardo Isip March 26, 2021Document19 pagesDiagnosis of Testicular Tumors: Dr. Ricardo Isip March 26, 2021Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Septic ArthritisDocument21 pagesSeptic ArthritisDawex IsraelNo ratings yet
- Ref 31 Meningeal LeukemiaDocument9 pagesRef 31 Meningeal LeukemiamuarifNo ratings yet
© Medi - Lectures DR Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures DR Shubham Upadhyay
Uploaded by
Hemanth100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
61 views37 pagesDiarrhea management in children
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiarrhea management in children
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
61 views37 pages© Medi - Lectures DR Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures DR Shubham Upadhyay
Uploaded by
HemanthDiarrhea management in children
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 37
Dr Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
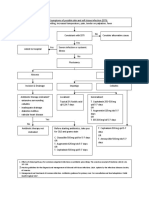
OVERVIEW
• Introduction
• Classification of Diarrhea
• Small Intestinal vs Large Intestinal diarrhea
• Acute Diarrhea
• Toxin Induced
• Inflammatory
• Chronic Diarrhea
• Non- Inflammatory
• Inflammatory
• High Yielding points
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
INTRODUCTION
• Passage of abnormally liquid or unformed stools at an increased
frequency
• Stool wt. >200 gm/day on western diet
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
INTRODUCTION
• Passage of abnormally liquid or unformed stools at an increased
frequency
• Stool wt. >200 gm/day on western diet
• Pseudodiarrhea - ↑ Frequency + ↑Liquidity + wt. <200 gm/day
• Fecal Incontinence - Involuntary discharge of fecal contents (NM
disorders or structural anorectal problems)
• Overflow diarrhea - Due to Fecal impaction
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
CLASSIFICATION
ACUTE PERSISTENT CHRONIC
<2 WEEKS 2 - 4 WEEKS > 4 WEEKS
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
CLASSIFICATION
ACUTE PERSISTENT CHRONIC
<2 WEEKS 2 - 4 WEEKS > 4 WEEKS
USUALLY INEFCTIOUS USUALLY NON-
INEFCTIOUS
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
SMALL vs LARGE INTESTINAL DIARRHEA
FEATURE SMALL BOWEL DIARRHEA LARGE BOWEL DIARRHEA
Volume Large Small
Colour Light Dark
Smell Very Foul Foul
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
SMALL vs LARGE INTESTINAL DIARRHEA
FEATURE SMALL BOWEL DIARRHEA LARGE BOWEL DIARRHEA
Volume Large Small
Colour Light Dark
Smell Very Foul Foul
Nature Watery/greasy Mucoid
Steatorrhea Present Absent
Blood in stools Rare Common
Pus in stools Rare Common
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
SMALL vs LARGE INTESTINAL DIARRHEA
FEATURE SMALL BOWEL DIARRHEA LARGE BOWEL DIARRHEA
Volume Large Small
Colour Light Dark
Smell Very Foul Foul
Nature Watery/greasy Mucoid
Steatorrhea Present Absent
Blood in stools Rare Common
Pus in stools Rare Common
Abdominal pain Mid abdomen (colic) Lower abdomen (continuous)
Tenesmus Absent Present
Urgency Absent Often Present
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
SMALL vs LARGE INTESTINAL DIARRHEA
FEATURE SMALL BOWEL DIARRHEA LARGE BOWEL DIARRHEA
Volume Large Small
Colour Light Dark
Smell Very Foul Foul
Nature Watery/greasy Mucoid
Steatorrhea Present Absent
Blood in stools Rare Common
Pus in stools Rare Common
Abdominal pain Mid abdomen (colic) Lower abdomen (continuous)
Tenesmus Absent Present
Urgency Absent Often Present
Pathogens V. cholera, E. coli, Viral, giardia, Shigella, E. histolytica, U. colitis,
TB(ileum), Crohn’s disease(ileum)
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
Rectal colitis
ACUTE DIARRHEA
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
ACUTE DIARRHEA
TOXIN INDUCED INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
ACUTE DIARRHEA
TOXIN INDUCED INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA
↑ electrolytes + water secretion into the lumen Exudation in the lumen
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
ACUTE DIARRHEA
TOXIN INDUCED INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA
↑ electrolytes + water secretion into the lumen Exudation in the lumen
PREFORMED TOXIN ENTEROTOXIN
• B. cereus (IP < 6 Hr) (IP 1 -2 days)
• S. aureus (IP < 6 Hr) • ETEC
• C. perfringens (IP 12-16 • V. Cholerae
Hr)
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
ACUTE DIARRHEA
TOXIN INDUCED INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA
↑ electrolytes + water secretion into the lumen Exudation in the lumen
PREFORMED TOXIN ENTEROTOXIN MILD MODERATE SEVERE
• B. cereus (IP < 6 Hr) (IP 1 -2 days) (only mucosa) (submucosa) (deeper)
• S. aureus (IP < 6 Hr) • ETEC • Rotavirus • Salmonella • Shigella
• C. perfringens (IP 12-16 • V. Cholerae • Norovirus • C. jejuni • E. histolytica
Hr) • Y. enterocolitica
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• B. cereus
• 2 forms of food poisoning
IP 1-6 hrs IP 6-12 hrs
• Uncooked Fried rice (Chinese • Pudding, Meat balls, dried
Restaurant Diarrhea) potato
• Preformed toxin • Toxin formed inside small
• Vomiting predominant intestine
• Diarrhea predominant
Requires only conservative management
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Staphylococcus aureus
• Preformed toxin
• IP: 1-6 hrs
• Pork, Canned meat, custard
• Vomiting- predominant symptom with abdominal cramps due to preformed
toxins (vagal stimulation)
• Fever, Hypotension - Never seen
• Diarrhea- rare
• No role of antibiotics
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Enterotoxic E. coli
• MCC of
1. Traveller’s diarrhea
2. Community acquired diarrhea
3. Toxigenic Diarrhea
• Produces heat labile toxin (LT) --> ↑ cAMP
• EHEC produces O157:H7 (Shiga like toxin) --> HUS
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Vibrio cholerae:
• Pathogenesis
• Toxin A - + cAMP (inhibits Na in villus cell + activates Cl in crypt cells)
• Toxin B - bind toxin receptor
• Clinical features
• IP 1-2 days
• Cholera gravis(severe form)
• Rice water stools
• Loss of K and HCO3 - Hypokalemia + Metabolic acidosis
• Treatment
• iv fluid of choice- Ringer lactate
• DOC- Doxycycline
• DOC in pregnancy- Azithromycin
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Salmonella
RISK FACTORS CLINICAL FEATURES INVESTIGATIONS & TREATMENT
• ↓ stomach • Most prominent - Fever (>75%) • Blood Culture - 40-80%
acidity • Abd pain - 30-40% sensitivity
• IBD • Cough - 30% • >15 org/ml should be present in
• Antibiotic use • Diarrhea - 25% blood for culture to be positive
• Constipation - 15% • Bone marrow culture - 55-90%
• HSM - 5% positive (positive upto 5 days
• rose spots - 30% even after antibiotic use)
• GI bleed - 10-20% • culture of intestinal secretions
• Neurological - Muttering delirium or (Duodenal string test)
coma vigil
• meningitis, GBS
• Chronic asymptomatic carrier- 1-4%
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• DOC- Ceftrixone
• Campylobacter jejuni
PATHOGENESIS CLINICAL FEATURES & COMPLICATIONS INVESTIGATIONS & TREATMENT
• IP - 1-7 days • Prodrome followed by diarrhea • Darting motility
• Site - SI+LI • Pseudoappendicitis • Culture
• Crypt abscess
• Hepatitis
• GBS (20-40% cases of GBS) • DOC- Erythromycin
• Alpha chain disease • For systemic infection -
(Immunoproliferative SI disease) Gentamycin
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Yersinia enterocolitica
• Causes multiple autoimmune reactions - Thyroiditis, Pericarditis,
Glomerulonephritis
• Pseudoappendicitis
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Shigella
PATHOGENESIS CLINICAL FEATURES & COMPLICATIONS INVESTIGATIONS & TREATMENT
• Feco-oral route, • Watery diarrhea (enterotoxin at jejunal • Gold std- Stool Culture
sexual route level) • Blood culture <5% sensitive
• Inoculum size - • Dysentry (distal colon+rectum)
100 • Resolve within 1 week untreated
• DOC- Ciprofloxacin
• Toxic megacolon
• Rectal prolapse
• Perforation
• Hypoglycemia
• Hyponatremia
• HUS - S. dysentriae type 1
• Reactive arthritis - S. flexneri
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Entamoeba histolytica
PATHOGENESIS CLINICAL FEATURES & INVESTIGATIONS & TREATMENT
COMPLICATIONS
• 10% world population • MC symptom- Diarrhea • PCR for DNA in stool samples
• 10% symptomatic • MC extraintestinal symptom - • Endemic areas- ELISA to detect
• Male> Female (less Liver abscess (mortality 1-3%) Entamoeba Ag
effective complement • Other complications - Toxic • Liver abscess- USG
mediated killing of megacolon, Amebomas,
amoebic Cerebral abscess
trophozoites) • Asymptomatic carrier -Luminal
• IP - 2-6 weeks agent(Ioqoquinol/Paromomycin)
• Flask shaped ulcers • Acute colitis - Metronidazole +
Luminal agent
• Liver abscess- Metronidazole +
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
Luminal agent
ACUTE DIARRHEA - TREATMENT
REHYDRATION ANTIBIOTICS ANTIMOTILITY DRUGS
• Essential in all cases, Indications Indications: Moderate to
etiologies 1. Moderate to Severe Severe dehydration
• IV fluid of choice- ringer inflammatory diarrhea despite iv fluids eg
Lactate Any 1 out of 3 Oliguria
features:- Contraindication:
a.fever>101 F Moderate to sever
b. Blood in stools inflammatory diarrhea
c. Pus in stools ( risk of perforation)
2. Immunocompromised Drug : Loperamide
(HIV)
3. Prosthetic Valves
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
CHRONIC DIARRHEA
NON-INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
CHRONIC DIARRHEA
NON-INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA INFLAMMATORY DIARRHEA
• Secretory Diarrhea • Ulcerative Colitis
• Osmotic Diarrhea • Crohn’s Disease
• Malabsorption induced Diarrhea
• Dysmotile causes
• Iatrogenic Causes
• Factitial causes
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
SECRETORY vs OSMOTIC DIARRHEA
SECRETORY OSMOTIC
MECHANISM ↑ electrolytes + water in lumen Due to osmotically active agent in gut
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
SECRETORY vs OSMOTIC DIARRHEA
SECRETORY OSMOTIC
MECHANISM ↑ electrolytes + water in lumen Due to osmotically active agent in gut
CLINICAL • Watery (>10 lit/day)
FEATURES • Painless/Effortless • Painful
• Persist with fasting • Stops with fasting
INVESTIGATIONS Stool Osmotic Gap <25 mOsm/kg Stool Osmotic Gap >50 mOsm/kg
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
SECRETORY vs OSMOTIC DIARRHEA
SECRETORY OSMOTIC
MECHANISM ↑ electrolytes + water in lumen Due to osmotically active agent in gut
CLINICAL • Watery (>10 lit/day)
FEATURES • Painless/Effortless • Painful
• Persist with fasting • Stops with fasting
INVESTIGATIONS Stool Osmotic Gap <25 mOsm/kg Stool Osmotic Gap >50 mOsm/kg
EXAMPLES 1. Hormone Hypersecretion 1. Laxatives (eg Lactulose, PEG)
2. Small Intestine resection 2. Lactose Intolerance
3. Alcoholics
4. SAIO
5. Chronic Shigella infection
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
HIGH YIELDING POINTS
• Organisms sensitive to acidic gastric pH - Salmonella, Giardia,
Heminths
• Organism resistant to acidic gastric pH - Rotavirus
• Cruise ship diarrhea- Norovirus
• Salami diarrhea - EHEC
• Inoculum size
• Shigella, EHEC, Giardia, Entamoeba = 10-100
• Salmonella = 103 - 106
• Vibrio >105
• HUS --> EHEC>Shigella dysentriae
• Reactive Arthritis
• MC Worldwide - Chlamydia trachomatis
• MC India - Shigella dysentria
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
• Bone marrow supression -Salmonella
• GBS - C. jejuni
• Toxic megacolon - Clostridium difficile
• Intestinal hmg. - Salmonella
• Small bowel lymphoproliferative disorder - Campylobacter
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
QUESTION
• Which of the following drug use is most commonly implicated in
development of pseudomembranous Colitis?
1. Cephalosporins
2. Clindamycin
3. Amoxicillin
4. Fluoroquinolones
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
© Medi - Lectures Dr Shubham Upadhyay
You might also like
- Full Download Ebook PDF Lehnes Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Providers PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Lehnes Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Providers PDFeleanor.jones934100% (40)
- Homoeopathic Clinic-CASE RECORD FORMDocument27 pagesHomoeopathic Clinic-CASE RECORD FORMAtit ShethNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Consumer ProductsDocument3 pagesEnzymes and Consumer ProductsMAC STACEY CAVENo ratings yet
- Signature Not VerifiedDocument1 pageSignature Not VerifiedSudharsan MohanNo ratings yet
- Weekly AssignmentDocument7 pagesWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaNo ratings yet
- The NASDAQ DozenDocument8 pagesThe NASDAQ Dozenrodolfo leivaNo ratings yet
- PSYC4009 Introduction To Counselling Semester 2 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTDocument13 pagesPSYC4009 Introduction To Counselling Semester 2 2022 Bentley Perth Campus INTAhmad QawwamNo ratings yet
- I A Comenii Vestibuli Linguarum AuctariumDocument42 pagesI A Comenii Vestibuli Linguarum AuctariumRuben William Da Silva AndradeNo ratings yet
- GodMan 10236902Document177 pagesGodMan 1023690212monkeyzNo ratings yet
- HPCL Application FormDocument3 pagesHPCL Application FormPriyank PatelNo ratings yet
- 192-TNPSC History - Study Materials 1 - RK IAS Academy - Tamil Medium PDF DownloadDocument104 pages192-TNPSC History - Study Materials 1 - RK IAS Academy - Tamil Medium PDF DownloadKumaresan DhineshNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Biology Investigatory Project Class Xii Breast CancerDocument14 pagesVdocuments - MX Biology Investigatory Project Class Xii Breast CancerPooja TikaniaNo ratings yet
- Ahmes Secondary School General Studies Form-Vi Holiday Package: December 2021Document1 pageAhmes Secondary School General Studies Form-Vi Holiday Package: December 2021Aden.No ratings yet
- Menu FoodDocument3 pagesMenu FoodMarcellinda SteviNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument2 pagesNutritionVishu MehtaNo ratings yet
- Steps Carried Out Comparison: ObservationDocument9 pagesSteps Carried Out Comparison: ObservationJovan Paul DeldaNo ratings yet
- PT. Ikon Surabaya Farmamart (ISF)Document4 pagesPT. Ikon Surabaya Farmamart (ISF)Anonymous aaAQ6dgNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument72 pagesUntitleddojiveNo ratings yet
- PFMS Generated Print Payment Advice: To, The Branch HeadDocument2 pagesPFMS Generated Print Payment Advice: To, The Branch HeadIpsita SahaNo ratings yet
- Billet PDF V2Document2 pagesBillet PDF V2Md ShahedNo ratings yet
- Palm SundayDocument15 pagesPalm Sundayapi-286204923No ratings yet
- Ret Chhattisgarh 10 11Document29 pagesRet Chhattisgarh 10 11Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Microbiotricks - MmeDocument21 pagesMicrobiotricks - MmesiddhantaNo ratings yet
- QUOTATIONDocument4 pagesQUOTATIONCak Bash MkfNo ratings yet
- Rural MarketingDocument25 pagesRural Marketingbls.chitra6152No ratings yet
- Price Et Al., International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2022Document16 pagesPrice Et Al., International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2022Radu CiprianNo ratings yet
- 5 - 4 19 - 48) Oop-WPS OfficeDocument3 pages5 - 4 19 - 48) Oop-WPS OfficeWidara TaubatinNo ratings yet
- Larah Catalogue October 2022 - LR-1Document104 pagesLarah Catalogue October 2022 - LR-1Saif JamalNo ratings yet
- E Max Computer Education ProspectusDocument24 pagesE Max Computer Education ProspectusPratyush AryaNo ratings yet
- Isbt 18 Dec Deh - DelhiDocument1 pageIsbt 18 Dec Deh - DelhiKabir PantNo ratings yet
- DGS DGSDocument1 pageDGS DGSlalunaku nakurNo ratings yet
- Krsnaa Diagnostics - Full Form of ResidentDocument12 pagesKrsnaa Diagnostics - Full Form of ResidentAbisekNo ratings yet
- Robc Reviewed 2021Document56 pagesRobc Reviewed 2021Harmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- PCWB-2316 FLXL Black N100-IdDocument4 pagesPCWB-2316 FLXL Black N100-IdFindora InternusaNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Document4 pagesShanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- Ritshidze State of Healthcare For Key Populations 2023Document60 pagesRitshidze State of Healthcare For Key Populations 2023Krash KingNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportDocument7 pagesProgress ReportRizki LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Merritt Morning Market 3809 - Mar 24Document2 pagesMerritt Morning Market 3809 - Mar 24Kim LeclairNo ratings yet
- DVM Thesis PublishedDocument14 pagesDVM Thesis PublishedRedwanNo ratings yet
- SGS.G20 5.SewMachines - DurexDocument56 pagesSGS.G20 5.SewMachines - DurexNguyễn BáNo ratings yet
- Scoring Package 3rd Eng 2021-22-1Document48 pagesScoring Package 3rd Eng 2021-22-1Tayab TayabNo ratings yet
- FASH235 Document 2Document2 pagesFASH235 Document 2siibnuNo ratings yet
- Program A CaoDocument44 pagesProgram A CaoSalvi MascaroNo ratings yet
- Inggris Pat Kelas 3Document10 pagesInggris Pat Kelas 3Septiana anggrianiNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease - The Indian PerspectiveDocument209 pagesSickle Cell Disease - The Indian PerspectiveV L Gupta100% (2)
- Verbos en Presente Simple PDFDocument6 pagesVerbos en Presente Simple PDFwladapalsilva2495No ratings yet
- 10sm SST Eng 2021 22Document439 pages10sm SST Eng 2021 22vidushiNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument5 pagesEmotional IntelligenceKavitha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Introduction To Web Programming and PHPDocument12 pagesLab 9 Introduction To Web Programming and PHPMisbah UllahNo ratings yet
- L&T Mutual Fund Application FormDocument5 pagesL&T Mutual Fund Application Formnanduverma100% (1)
- Carp PolycultureDocument22 pagesCarp PolycultureMd.Tanvirul EhsanNo ratings yet
- Https Onetimeregn - Haryana.gov - in PrintApp - AspxDocument3 pagesHttps Onetimeregn - Haryana.gov - in PrintApp - AspxYogita TanwarNo ratings yet
- Star Laminates 0 8mm 1 0mm LaminatesDocument60 pagesStar Laminates 0 8mm 1 0mm Laminatesfosoce7719No ratings yet
- Extraterrestrial and Extradimensional Beings - How They Travel Space and TimeDocument1 pageExtraterrestrial and Extradimensional Beings - How They Travel Space and TimeStep T.No ratings yet
- BIO224 Chapter 7Document5 pagesBIO224 Chapter 7Muh. RidwanNo ratings yet
- Nylon Carpet. Harrington Catalogue.2022Document41 pagesNylon Carpet. Harrington Catalogue.2022Nikhil Chawla100% (1)
- Ipe UasDocument5 pagesIpe UasEben HaezerNo ratings yet
- Pet Bereavement and Coping MechanismsDocument16 pagesPet Bereavement and Coping MechanismsSophia JoseNo ratings yet
- Pests of CitrusDocument29 pagesPests of CitrusPalash MondalNo ratings yet
- Desensitization To Media Violence Links HiDocument17 pagesDesensitization To Media Violence Links HiJustinNo ratings yet
- Diare Dehidrasi BeratDocument40 pagesDiare Dehidrasi BeratcutietimothyNo ratings yet
- Farhan ChaudharyDocument1 pageFarhan ChaudharyHemanthNo ratings yet
- NBC Guidelines For Healthcare FacilityDocument17 pagesNBC Guidelines For Healthcare FacilityHemanthNo ratings yet
- STEMIDocument29 pagesSTEMIHemanthNo ratings yet
- WPW SyndromeDocument8 pagesWPW SyndromeHemanthNo ratings yet
- Acute Adrenal CrisisDocument27 pagesAcute Adrenal CrisisHemanthNo ratings yet
- Offtag Assessment 2Document12 pagesOfftag Assessment 2chooNo ratings yet
- Key Points - Peds Vital SignsDocument1 pageKey Points - Peds Vital SignsRaman kangNo ratings yet
- Yamamoto 2010Document2 pagesYamamoto 2010Ferdi ArdiNo ratings yet
- MeatinniDocument11 pagesMeatinnivinadata01No ratings yet
- Eng 2008 MedDocument43 pagesEng 2008 MedLucia BogNo ratings yet
- SSTIDocument1 pageSSTITan ShenNo ratings yet
- 1) CPG Management Major Depressive Disorder (Second Edition)Document83 pages1) CPG Management Major Depressive Disorder (Second Edition)Meena ViswaNo ratings yet
- 6Document5 pages6ρενα μινορεNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases EpidemiologyDocument44 pagesCommunicable Diseases EpidemiologyIrum QureshiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisGaming BoyNo ratings yet
- National AIDS Control ProgramDocument29 pagesNational AIDS Control ProgramMonalisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Artikel Keluarga Berencana, Izzatul Ummah FhadillaDocument6 pagesArtikel Keluarga Berencana, Izzatul Ummah FhadillaAQFAL storyNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review NotesDocument76 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Review Notesnot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- SPED QuizDocument4 pagesSPED QuizJennevive Micabalo CabugsaNo ratings yet
- The Shaken Baby SyndromeDocument9 pagesThe Shaken Baby SyndromeDiana LoloiuNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care For CHO - SN - Introduction To Emergency CareDocument28 pagesEmergency Care For CHO - SN - Introduction To Emergency CareAditi JainNo ratings yet
- 10 51982-Bagimli 1399294-3574178Document9 pages10 51982-Bagimli 1399294-3574178yahya kemalNo ratings yet
- NeuroblastomaDocument9 pagesNeuroblastomasamantha mccoyNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in Pulmonary MedicineDocument4 pagesThesis Topics in Pulmonary Medicinegj6sr6d7100% (2)
- Medicine FMGE Sprint by Dr. Santosh Patil (PW Med Ed)Document31 pagesMedicine FMGE Sprint by Dr. Santosh Patil (PW Med Ed)Stella ParkerNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Pain and Symptoms in PregnancyDocument6 pagesMusculoskeletal Pain and Symptoms in PregnancyDzaki Prakoso RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrain Systm Question 1 ST DayDocument15 pagesEndocrain Systm Question 1 ST DayJohn AjishNo ratings yet
- Soal Soal Latihan Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesSoal Soal Latihan Bahasa InggrisMIKA OKENo ratings yet
- AmnesiaDocument4 pagesAmnesiaHsnysbvNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mental Health and Coping - Dealing With Anxiety and DepressionDocument49 pagesUnit 4 - Mental Health and Coping - Dealing With Anxiety and DepressionAundrei ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cellular AbrasionDocument3 pagesCellular AbrasionFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Testicular Tumors: Dr. Ricardo Isip March 26, 2021Document19 pagesDiagnosis of Testicular Tumors: Dr. Ricardo Isip March 26, 2021Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Septic ArthritisDocument21 pagesSeptic ArthritisDawex IsraelNo ratings yet
- Ref 31 Meningeal LeukemiaDocument9 pagesRef 31 Meningeal LeukemiamuarifNo ratings yet