Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch. 16 SCD - GR
Ch. 16 SCD - GR
Uploaded by
Baxton Paul GarzaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 9 Week Power BodybuildingDocument20 pages9 Week Power BodybuildingelaminwriterNo ratings yet
- Pilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFDocument17 pagesPilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFbrunoduartefr100% (1)
- Scope and SequenceDocument4 pagesScope and Sequenceapi-251763981No ratings yet
- CARE of ADOLESCENTSDocument15 pagesCARE of ADOLESCENTSaprilkate banagodosNo ratings yet
- Assessing Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesAssessing Musculo-Skeletal SystemLentic, Charmie JaneNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision Making in Evaluation of Shoulder DysfunctionDocument27 pagesClinical Decision Making in Evaluation of Shoulder DysfunctionSanjanaa ZadNo ratings yet
- LOW BACK PAIN EditedDocument55 pagesLOW BACK PAIN EditedMaiden I. Sotelo100% (1)
- Pembekalan BPI Sem 5Document40 pagesPembekalan BPI Sem 5Mukhtar Ali MuktiNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida Hydrocephalus Presentation 0Document75 pagesSpina Bifida Hydrocephalus Presentation 0Emanuel PopoviciNo ratings yet
- LDM Balandra-MobiityDocument79 pagesLDM Balandra-MobiityJOHAIMAH CABUGATANNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and LordosisDocument17 pagesAbnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and LordosisBheru LalNo ratings yet
- 15.spina BifidaDocument37 pages15.spina BifidaAbdullah AzamNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Impairment HandoutsDocument2 pagesOrthopedic Impairment HandoutsCaress EusebioNo ratings yet
- Good Posture and Postural DeformitiesDocument13 pagesGood Posture and Postural DeformitiesAnne NashNo ratings yet
- Weebly Questions Week TwoDocument3 pagesWeebly Questions Week Twoapi-459697337No ratings yet
- Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal Disorders in ChildhoodDocument11 pagesOrthopedic and Musculoskeletal Disorders in ChildhoodMateo GeoffNo ratings yet
- The Child With Neuromuscular or Muscular Dysfunction NOTESDocument27 pagesThe Child With Neuromuscular or Muscular Dysfunction NOTESERIKA BOOTS CABALUNANo ratings yet
- Rekapan Kuis CPPDS Orthopedi Periode Januari 2023Document82 pagesRekapan Kuis CPPDS Orthopedi Periode Januari 2023Indra Anwari RukmanNo ratings yet
- BackproblemsDocument14 pagesBackproblemsAshvin PatelNo ratings yet
- Difficulty in Mobility 2022 Final Presentation As of 08-18-2022Document84 pagesDifficulty in Mobility 2022 Final Presentation As of 08-18-2022arianmay.tiongcoNo ratings yet
- Posture and Body Composition: Fitt 1Document22 pagesPosture and Body Composition: Fitt 1BERNARD LARRACASNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Scoliosis PDFDocument9 pages3.3 Scoliosis PDFDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Muscular DystrophyDocument21 pagesMuscular DystrophyIqra Iftikhar100% (4)
- A Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Postural Deviations: Kinesiology RHS 341 Dr. Einas Al-EisaDocument40 pagesPostural Deviations: Kinesiology RHS 341 Dr. Einas Al-EisaStephanie GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: Michael C. Koester, MD, Michael S. George, MD, John E. Kuhn, MDDocument4 pagesShoulder Impingement Syndrome: Michael C. Koester, MD, Michael S. George, MD, John E. Kuhn, MDraniNo ratings yet
- Assessment Treatment LBP InterventionalDocument64 pagesAssessment Treatment LBP InterventionalAbdillah Akbar KyugaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Children and Women in SportsDocument9 pagesChapter-2 Children and Women in SportsLakshaya YadavNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Dysfunction in ChildrenDocument40 pagesMusculoskeletal Dysfunction in Childrensanakhan091197No ratings yet
- Understanding Learners With Difficulty in Mobility (LDM) : Department of EducationDocument60 pagesUnderstanding Learners With Difficulty in Mobility (LDM) : Department of EducationCherry Bobier100% (1)
- Lee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Document25 pagesLee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Star CruiseNo ratings yet
- 3RD TERM JSS2 PHE LESSON NOTES UsuavsDocument19 pages3RD TERM JSS2 PHE LESSON NOTES UsuavsIdeji EkemenaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes Affecting Various Sytem in Older AdultsDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes Affecting Various Sytem in Older AdultsDERRICKKEANNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis - DR P K Sahoo PDFDocument3 pagesScoliosis - DR P K Sahoo PDFManish MauryaNo ratings yet
- Department of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofDocument24 pagesDepartment of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofShahbaz RainaNo ratings yet
- SoNH BACK CAREDocument30 pagesSoNH BACK CARESafetyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation ScoliosisDocument7 pagesCase Presentation ScoliosisKhrizjan RebloraNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352Document17 pagesAbnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352alyyn2045No ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: PediatricsDocument50 pagesCerebral Palsy: PediatricsRANJIT GOGOINo ratings yet
- Types of Spine Curvature DisordersDocument7 pagesTypes of Spine Curvature DisordersNicu MacariNo ratings yet
- Yoga and Movement Re-Education For The Treatment oDocument1 pageYoga and Movement Re-Education For The Treatment oAndré Bento SantosNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar DisordersDocument29 pagesCerebellar DisordersArslan Aslam100% (1)
- Spinal Muscle AtrophyDocument33 pagesSpinal Muscle AtrophyAaliyah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy of The Vertebral ColumnDocument53 pagesApplied Anatomy of The Vertebral Columnpramodyasithumini202No ratings yet
- Hands On: Management of Shoulder Disorders in Primary CareDocument8 pagesHands On: Management of Shoulder Disorders in Primary CareCambriaChicoNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis by Dr. AbbasDocument11 pagesScoliosis by Dr. AbbasAbbas AliNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiDocument13 pagesScoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiWillie100% (1)
- Handout Orthopedic Nursing ScoliosisDocument3 pagesHandout Orthopedic Nursing ScoliosisPaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (3)
- Erb's PalsyDocument18 pagesErb's PalsyMegha PataniNo ratings yet
- Pediatric RehabilitationDocument36 pagesPediatric RehabilitationFrayen BlaugranaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury FinalDocument3 pagesSpinal Cord Injury FinalAa AaNo ratings yet
- Functional Examinations & Impact of Lumbar Radiculopathy: Dr. Aditya Wahyudi, SP.K.F.R., FIPM (USG)Document55 pagesFunctional Examinations & Impact of Lumbar Radiculopathy: Dr. Aditya Wahyudi, SP.K.F.R., FIPM (USG)shintiasspNo ratings yet
- 9 TalipesDocument33 pages9 TalipesPY 01No ratings yet
- Health Related FitnessDocument24 pagesHealth Related FitnessKali AndresNo ratings yet
- The Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbarDocument32 pagesThe Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbartryasNo ratings yet
- The Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbarDocument32 pagesThe Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbartryasNo ratings yet
- Sport Injuries: ShoulderDocument67 pagesSport Injuries: ShoulderNabiha AjmalNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityDocument8 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityGeremie Magno Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spine CurvaturesDocument7 pagesAbnormal Spine CurvaturesMartin SageNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Cerebral Palsy & Motor DelayDocument49 pagesRehabilitation of Cerebral Palsy & Motor DelayasloocltNo ratings yet
- wk3 Category 2Document8 pageswk3 Category 2api-508474347No ratings yet
- Scoliosis, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandScoliosis, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Practice Questions-10 - 22 - Update-1Document11 pagesCapital Budgeting Practice Questions-10 - 22 - Update-1Baxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Nutrition CalculationsDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Nutrition CalculationsBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Training Program AssignmentDocument4 pagesTraining Program AssignmentBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- XIO M9) : - Xl"e - 3/ O) KR (JDocument10 pagesXIO M9) : - Xl"e - 3/ O) KR (JBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Energy SystemsDocument44 pagesAnaerobic Energy SystemsBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study QuestionDocument3 pagesChemistry Study QuestionBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Rhythmic Activities SourcesDocument8 pagesRhythmic Activities SourcesYan MahusayNo ratings yet
- FCE SchPrTests 1 SsDocument19 pagesFCE SchPrTests 1 Sspompiliamaraloiu408No ratings yet
- Soal Greeting and Leave and Taking (Students)Document7 pagesSoal Greeting and Leave and Taking (Students)Rizky efandra100% (1)
- Activity Tracking and Calories Burn - Lab AssignmentDocument14 pagesActivity Tracking and Calories Burn - Lab AssignmentStephanie PonceNo ratings yet
- Pilates Pregnancy and BeyondDocument3 pagesPilates Pregnancy and BeyondRiyan WahyudoNo ratings yet
- Full-Body Weight-Loss Home WorkoutsDocument6 pagesFull-Body Weight-Loss Home Workoutsmohamed aliNo ratings yet
- Contoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tema KesehatanDocument1 pageContoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tema KesehatanJejak KakikuNo ratings yet
- Uniform Standards For The Universal Design of Fitness Equipment (UDFE)Document101 pagesUniform Standards For The Universal Design of Fitness Equipment (UDFE)Mehdi Bostan ShirinNo ratings yet
- My Family Went To The Beach and at This Time I Think... : at Four O'clock (She) ... at Five O'clock (I) ..Document4 pagesMy Family Went To The Beach and at This Time I Think... : at Four O'clock (She) ... at Five O'clock (I) ..sflay nexNo ratings yet
- Sun Salutations Ebook - 5.5.21Document31 pagesSun Salutations Ebook - 5.5.21muragesh.tubakiNo ratings yet
- Snapping Hip Syndrome Exercises - tcm28-180743Document5 pagesSnapping Hip Syndrome Exercises - tcm28-180743josephNo ratings yet
- Phed Week Pre-Lim ModuleDocument21 pagesPhed Week Pre-Lim ModuleFerndale AlimondoNo ratings yet
- Manifesting Secret FormulaDocument6 pagesManifesting Secret FormulaDavid HinojosaNo ratings yet
- PPL Programme - KopieDocument20 pagesPPL Programme - KopieQuý VũNo ratings yet
- Eastern Mindoro CollegeDocument4 pagesEastern Mindoro Collegecarmela leonidaNo ratings yet
- #Noomhabitoverhaul: Week 1Document4 pages#Noomhabitoverhaul: Week 1Prashant KCNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: I. Objectives A. Content StandardsDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: I. Objectives A. Content StandardsCharmaine JanorasNo ratings yet
- Guide To Beginner StrenghtDocument24 pagesGuide To Beginner StrenghtBaitel IrinaNo ratings yet
- 6 Week Lean MassDocument1 page6 Week Lean Massnimish prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Skills in VolleyballDocument22 pagesFundamental Skills in VolleyballKurt Christian Diaz0% (1)
- Department of Education: Summative Test in Mapeh 7 Music: Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Summative Test in Mapeh 7 Music: Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Space ProvidedChai BarcelonNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 6 - Q4 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Mapeh 6 - Q4 - W3RICXIENo ratings yet
- LAS10 Week 4 7 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesLAS10 Week 4 7 2nd QuarterGleamor DaagNo ratings yet
- Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: What Is GTPS?Document4 pagesGreater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: What Is GTPS?Sebastiano SerraNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Realization After Watching The Presentation of Vincent Lam?Document2 pagesWhat Is Your Realization After Watching The Presentation of Vincent Lam?Rachel Ann DayananNo ratings yet
- Program Australia JudôDocument17 pagesProgram Australia JudôFernando Lima GuimaraesNo ratings yet
- Grammar U5 L2Document3 pagesGrammar U5 L2uzielNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION - Attempt 3 Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 2Document21 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION - Attempt 3 Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 2johnmiguelgallardoNo ratings yet
Ch. 16 SCD - GR
Ch. 16 SCD - GR
Uploaded by
Baxton Paul GarzaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch. 16 SCD - GR
Ch. 16 SCD - GR
Uploaded by
Baxton Paul GarzaCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 16 – Spinal Cord Disabilities
Wesley J. Wilson and Luke E. Kelly
Complete the blanks with definitions or the keyword throughout the
document.
Classification Systems of SCI:
Medical Classification –
Sport Classification –
Relevant Factors
Respiration Hip, knee, and ankle control and
Shoulder, arm, and hand control and sensation
sensation Bowel and bladder control
Trunk Stability Quadriplegia and paraplegia
Loss of movement and sensation
Handling Potential Spine Injuries
• Treat all injuries as potentially • Restore breathing and circulation.
serious. • Summon medical help.
• Immobilize neck. • Keep victim warm.
Treatment phases
Hospitalization –
Rehabilitation –
Return to home –
Secondary issues
Psychosocial acceptance o Urinary tract infections
Health Conditions o Spasticity
o Decubitus ulcers o Contractures
o Bruising o Obesity
Spina Bifida:
Congenital birth defect – Neural tube fails to close completely in the first 4 weeks of
fetal development.
Classifications of Spina Bifida:
Most severe, most common; covering of the spinal cord, cerebrospinal fluid, and part
of the spinal cord protrudes through the opening and forma visible sac on the back –
Spinal cord covering and cerebrospinal fluid protrude into the sac; rarely has
neurological damage; surgically corrected –
Mildest, least common; defect in the posterior arch of vertebra/ no protrusion
through the opening; no neurological damage; surgically corrected –
Similarities and Differences of SPIs
• Acquired spinal cord impairments • Congenital impairments—spina
• Psychosocial acceptance and bifida
development • Psychosocial acceptance and
• Physical and motor development
development • Physical and motor
development
Chapter 16 – Spinal Cord Disabilities
Wesley J. Wilson and Luke E. Kelly
Fitness and Spinal Cord Injuries
Obesity Fitness and safety
General level of fitness Hypotension –
Flexibility, Strength, Endurance Thermoregulation –
Muscle imbalances Autonomic dysreflexia –
Spinal Column Deviations
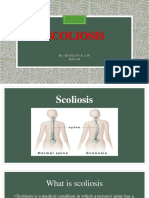
Scoliosis –
Kyphosis –
Lordosis –
Scoliosis Classification
1. Permanent or fixed changes in the alignment of the vertebrae that cannot be altered
through physical manipulation, positioning, or exercise –
2. Functional deviations, vertebrae can be realigned through positioning or removal of
primary cause –
Causes of scoliosis
Idiopathic – cause is unknown
o S-shaped curve; one major curve and two minor curves
o Progressive
Neuromuscular – result of a nerve or muscle problem
o C-shaped curve
o Balance difficulties
o Pressure on internal organs
o Seating problems
Treatment of scoliosis
Treatment varies with degree of curvature
Mild –
Severe –
Extremely severe (curve greater than 40 degrees) –
Treatment of spinal deviations
Work on both strength and Encourage them to watch
flexibility. themselves in mirrors when they
Make routines fun and motivating. exercise.
Employ appropriate warm-up and Make sure program is followed
cool-down periods. outside of your setting.
Emphasize static over dynamic Emphasize symmetrical exercises.
stretching. Be aware of limitations imposed by
Make sure they understand and can braces
do the exercises correctly.
Chapter 16 – Spinal Cord Disabilities
Wesley J. Wilson and Luke E. Kelly
Inclusion
• Focus on abilities.
• Substitute objectives (e.g., wheelchair skills for locomotor skills).
• Make accommodations to ensure success and learning.
• Teach self-advocacy.
• Does the student feel a sense of value, belonging, and acceptance in physical
education?
You might also like
- 9 Week Power BodybuildingDocument20 pages9 Week Power BodybuildingelaminwriterNo ratings yet
- Pilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFDocument17 pagesPilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFbrunoduartefr100% (1)
- Scope and SequenceDocument4 pagesScope and Sequenceapi-251763981No ratings yet
- CARE of ADOLESCENTSDocument15 pagesCARE of ADOLESCENTSaprilkate banagodosNo ratings yet
- Assessing Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesAssessing Musculo-Skeletal SystemLentic, Charmie JaneNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision Making in Evaluation of Shoulder DysfunctionDocument27 pagesClinical Decision Making in Evaluation of Shoulder DysfunctionSanjanaa ZadNo ratings yet
- LOW BACK PAIN EditedDocument55 pagesLOW BACK PAIN EditedMaiden I. Sotelo100% (1)
- Pembekalan BPI Sem 5Document40 pagesPembekalan BPI Sem 5Mukhtar Ali MuktiNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida Hydrocephalus Presentation 0Document75 pagesSpina Bifida Hydrocephalus Presentation 0Emanuel PopoviciNo ratings yet
- LDM Balandra-MobiityDocument79 pagesLDM Balandra-MobiityJOHAIMAH CABUGATANNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and LordosisDocument17 pagesAbnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and LordosisBheru LalNo ratings yet
- 15.spina BifidaDocument37 pages15.spina BifidaAbdullah AzamNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Impairment HandoutsDocument2 pagesOrthopedic Impairment HandoutsCaress EusebioNo ratings yet
- Good Posture and Postural DeformitiesDocument13 pagesGood Posture and Postural DeformitiesAnne NashNo ratings yet
- Weebly Questions Week TwoDocument3 pagesWeebly Questions Week Twoapi-459697337No ratings yet
- Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal Disorders in ChildhoodDocument11 pagesOrthopedic and Musculoskeletal Disorders in ChildhoodMateo GeoffNo ratings yet
- The Child With Neuromuscular or Muscular Dysfunction NOTESDocument27 pagesThe Child With Neuromuscular or Muscular Dysfunction NOTESERIKA BOOTS CABALUNANo ratings yet
- Rekapan Kuis CPPDS Orthopedi Periode Januari 2023Document82 pagesRekapan Kuis CPPDS Orthopedi Periode Januari 2023Indra Anwari RukmanNo ratings yet
- BackproblemsDocument14 pagesBackproblemsAshvin PatelNo ratings yet
- Difficulty in Mobility 2022 Final Presentation As of 08-18-2022Document84 pagesDifficulty in Mobility 2022 Final Presentation As of 08-18-2022arianmay.tiongcoNo ratings yet
- Posture and Body Composition: Fitt 1Document22 pagesPosture and Body Composition: Fitt 1BERNARD LARRACASNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Scoliosis PDFDocument9 pages3.3 Scoliosis PDFDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Muscular DystrophyDocument21 pagesMuscular DystrophyIqra Iftikhar100% (4)
- A Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Posture, Spine Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Postural Deviations: Kinesiology RHS 341 Dr. Einas Al-EisaDocument40 pagesPostural Deviations: Kinesiology RHS 341 Dr. Einas Al-EisaStephanie GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: Michael C. Koester, MD, Michael S. George, MD, John E. Kuhn, MDDocument4 pagesShoulder Impingement Syndrome: Michael C. Koester, MD, Michael S. George, MD, John E. Kuhn, MDraniNo ratings yet
- Assessment Treatment LBP InterventionalDocument64 pagesAssessment Treatment LBP InterventionalAbdillah Akbar KyugaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Children and Women in SportsDocument9 pagesChapter-2 Children and Women in SportsLakshaya YadavNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Dysfunction in ChildrenDocument40 pagesMusculoskeletal Dysfunction in Childrensanakhan091197No ratings yet
- Understanding Learners With Difficulty in Mobility (LDM) : Department of EducationDocument60 pagesUnderstanding Learners With Difficulty in Mobility (LDM) : Department of EducationCherry Bobier100% (1)
- Lee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Document25 pagesLee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Star CruiseNo ratings yet
- 3RD TERM JSS2 PHE LESSON NOTES UsuavsDocument19 pages3RD TERM JSS2 PHE LESSON NOTES UsuavsIdeji EkemenaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes Affecting Various Sytem in Older AdultsDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes Affecting Various Sytem in Older AdultsDERRICKKEANNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis - DR P K Sahoo PDFDocument3 pagesScoliosis - DR P K Sahoo PDFManish MauryaNo ratings yet
- Department of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofDocument24 pagesDepartment of Anatomy:: Physiological and Pathological Curvatures ofShahbaz RainaNo ratings yet
- SoNH BACK CAREDocument30 pagesSoNH BACK CARESafetyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation ScoliosisDocument7 pagesCase Presentation ScoliosisKhrizjan RebloraNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352Document17 pagesAbnormal Spinal Postures Kyphosis and Lordosis4352alyyn2045No ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: PediatricsDocument50 pagesCerebral Palsy: PediatricsRANJIT GOGOINo ratings yet
- Types of Spine Curvature DisordersDocument7 pagesTypes of Spine Curvature DisordersNicu MacariNo ratings yet
- Yoga and Movement Re-Education For The Treatment oDocument1 pageYoga and Movement Re-Education For The Treatment oAndré Bento SantosNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar DisordersDocument29 pagesCerebellar DisordersArslan Aslam100% (1)
- Spinal Muscle AtrophyDocument33 pagesSpinal Muscle AtrophyAaliyah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy of The Vertebral ColumnDocument53 pagesApplied Anatomy of The Vertebral Columnpramodyasithumini202No ratings yet
- Hands On: Management of Shoulder Disorders in Primary CareDocument8 pagesHands On: Management of Shoulder Disorders in Primary CareCambriaChicoNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis by Dr. AbbasDocument11 pagesScoliosis by Dr. AbbasAbbas AliNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiDocument13 pagesScoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiWillie100% (1)
- Handout Orthopedic Nursing ScoliosisDocument3 pagesHandout Orthopedic Nursing ScoliosisPaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (3)
- Erb's PalsyDocument18 pagesErb's PalsyMegha PataniNo ratings yet
- Pediatric RehabilitationDocument36 pagesPediatric RehabilitationFrayen BlaugranaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury FinalDocument3 pagesSpinal Cord Injury FinalAa AaNo ratings yet
- Functional Examinations & Impact of Lumbar Radiculopathy: Dr. Aditya Wahyudi, SP.K.F.R., FIPM (USG)Document55 pagesFunctional Examinations & Impact of Lumbar Radiculopathy: Dr. Aditya Wahyudi, SP.K.F.R., FIPM (USG)shintiasspNo ratings yet
- 9 TalipesDocument33 pages9 TalipesPY 01No ratings yet
- Health Related FitnessDocument24 pagesHealth Related FitnessKali AndresNo ratings yet
- The Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbarDocument32 pagesThe Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbartryasNo ratings yet
- The Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbarDocument32 pagesThe Patient History and Physical Examination: Cervical, Thoracic, and LumbartryasNo ratings yet
- Sport Injuries: ShoulderDocument67 pagesSport Injuries: ShoulderNabiha AjmalNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityDocument8 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityGeremie Magno Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Spine CurvaturesDocument7 pagesAbnormal Spine CurvaturesMartin SageNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Cerebral Palsy & Motor DelayDocument49 pagesRehabilitation of Cerebral Palsy & Motor DelayasloocltNo ratings yet
- wk3 Category 2Document8 pageswk3 Category 2api-508474347No ratings yet
- Scoliosis, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandScoliosis, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Practice Questions-10 - 22 - Update-1Document11 pagesCapital Budgeting Practice Questions-10 - 22 - Update-1Baxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Nutrition CalculationsDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Nutrition CalculationsBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Training Program AssignmentDocument4 pagesTraining Program AssignmentBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- XIO M9) : - Xl"e - 3/ O) KR (JDocument10 pagesXIO M9) : - Xl"e - 3/ O) KR (JBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Energy SystemsDocument44 pagesAnaerobic Energy SystemsBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study QuestionDocument3 pagesChemistry Study QuestionBaxton Paul GarzaNo ratings yet
- Rhythmic Activities SourcesDocument8 pagesRhythmic Activities SourcesYan MahusayNo ratings yet
- FCE SchPrTests 1 SsDocument19 pagesFCE SchPrTests 1 Sspompiliamaraloiu408No ratings yet
- Soal Greeting and Leave and Taking (Students)Document7 pagesSoal Greeting and Leave and Taking (Students)Rizky efandra100% (1)
- Activity Tracking and Calories Burn - Lab AssignmentDocument14 pagesActivity Tracking and Calories Burn - Lab AssignmentStephanie PonceNo ratings yet
- Pilates Pregnancy and BeyondDocument3 pagesPilates Pregnancy and BeyondRiyan WahyudoNo ratings yet
- Full-Body Weight-Loss Home WorkoutsDocument6 pagesFull-Body Weight-Loss Home Workoutsmohamed aliNo ratings yet
- Contoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tema KesehatanDocument1 pageContoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tema KesehatanJejak KakikuNo ratings yet
- Uniform Standards For The Universal Design of Fitness Equipment (UDFE)Document101 pagesUniform Standards For The Universal Design of Fitness Equipment (UDFE)Mehdi Bostan ShirinNo ratings yet
- My Family Went To The Beach and at This Time I Think... : at Four O'clock (She) ... at Five O'clock (I) ..Document4 pagesMy Family Went To The Beach and at This Time I Think... : at Four O'clock (She) ... at Five O'clock (I) ..sflay nexNo ratings yet
- Sun Salutations Ebook - 5.5.21Document31 pagesSun Salutations Ebook - 5.5.21muragesh.tubakiNo ratings yet
- Snapping Hip Syndrome Exercises - tcm28-180743Document5 pagesSnapping Hip Syndrome Exercises - tcm28-180743josephNo ratings yet
- Phed Week Pre-Lim ModuleDocument21 pagesPhed Week Pre-Lim ModuleFerndale AlimondoNo ratings yet
- Manifesting Secret FormulaDocument6 pagesManifesting Secret FormulaDavid HinojosaNo ratings yet
- PPL Programme - KopieDocument20 pagesPPL Programme - KopieQuý VũNo ratings yet
- Eastern Mindoro CollegeDocument4 pagesEastern Mindoro Collegecarmela leonidaNo ratings yet
- #Noomhabitoverhaul: Week 1Document4 pages#Noomhabitoverhaul: Week 1Prashant KCNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: I. Objectives A. Content StandardsDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: I. Objectives A. Content StandardsCharmaine JanorasNo ratings yet
- Guide To Beginner StrenghtDocument24 pagesGuide To Beginner StrenghtBaitel IrinaNo ratings yet
- 6 Week Lean MassDocument1 page6 Week Lean Massnimish prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Skills in VolleyballDocument22 pagesFundamental Skills in VolleyballKurt Christian Diaz0% (1)
- Department of Education: Summative Test in Mapeh 7 Music: Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Summative Test in Mapeh 7 Music: Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Space ProvidedChai BarcelonNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 6 - Q4 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Mapeh 6 - Q4 - W3RICXIENo ratings yet
- LAS10 Week 4 7 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesLAS10 Week 4 7 2nd QuarterGleamor DaagNo ratings yet
- Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: What Is GTPS?Document4 pagesGreater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: What Is GTPS?Sebastiano SerraNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Realization After Watching The Presentation of Vincent Lam?Document2 pagesWhat Is Your Realization After Watching The Presentation of Vincent Lam?Rachel Ann DayananNo ratings yet
- Program Australia JudôDocument17 pagesProgram Australia JudôFernando Lima GuimaraesNo ratings yet
- Grammar U5 L2Document3 pagesGrammar U5 L2uzielNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION - Attempt 3 Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 2Document21 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION - Attempt 3 Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 2johnmiguelgallardoNo ratings yet