Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System (U - Gyl K - 0Ffnl)
Endocrine System (U - Gyl K - 0Ffnl)
Uploaded by
Sugandhi SahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System (U - Gyl K - 0Ffnl)
Endocrine System (U - Gyl K - 0Ffnl)
Uploaded by
Sugandhi SahCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System ( u|GyL k|0ffnL )
Endocrine gland & Nervous system is the co-ordinating and regulating system of our body.
Endo - Ductless (gnLljxLg), Crine - Gland ( u|GyL )
There are major 9 gland of the Endocrine gland
Gland :-
/; pTkfbgug{ ;Sg] Epithelial cell sf] ;d'xnfO{ Gland elgG5 . o; /;n] Target organ sf Structurejf
FunctionnfO{ Modify u5{ . of] @ k|sf/sf x'G5 .
1. Endocrine gland :-
It is Also called Ductless gland( glnlalxgu|lGy) , o;n] HormonepTkfbgub{5 .
Hormone n] lgoGq0f ug]{ tissue or organ nfO{Target organ or Target siteelgG5 f
Hormone are chemical messanger which produce in a organ and use or work at target organ
Hormone chemically 2 types
a) Protein nature :- All hormone except produced by Adrenal cortex & sex gland
b) Steroid nature :- produced by Adrenal cortex & sex gland
Hormone/utdfDirecthfG5 .
Hormone is made of :- Steroid, Peptide, Amono acid
laxfglaxfgdflg; p7gsf] sf/0f ;- Hormonal activation
2. Exocrine gland :-
It is Also Duct full gland , which Production of Enzyme.
of] gnLeP/ Target organ eP/ /utsfdfWodn] hfG5 . e.g. Liver, Salivery Gland, Sebacious Gland,
Sweet gland .
Mixed gland / Heterocrinegland :-o;df Exocrine / Endocrine b'O6} x'G5 . E.g. Pancrease
Notes:-
Largest Gland of the body :– Liver ( 1.5-2.5 kg)
Largest Oran in our body :– Skin ( 4 kg )
Smallest organ of Our body :- Pineal gland
Largest Exocrine gland :- Liver
Largest Visceral organ :– Liver
Largest Endocrine gland :– Thyroid (0.5gm)
Largest Mixed gland :– Pancrease (60gm)
Endocrine gland :-
Gland x?sf] ;d'xh;n] k}bf u/]sf] /; ljgfglnl;w} /utdf hfG5 . To:tfGlandx?nfO{ Endocrine gland
elgG5
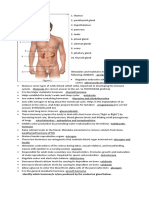
z/L/dfkfpg] Endocrine gland x? :-
Pituitory gland 1
Pineal gland 1
Thyroid gland 1
Parathyroid gland 4
Thymus gland 1
Pancreas 1
Adrenal gland 2
Gonads (Female gonads (overy)- 2 , Male gonads (Testies ) 2
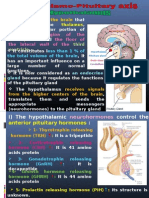
Hypothamus( Supermaster gland )
Heart of Endocrine gland :- Hypothalamus
it is also called Biological clock
It is located below the Thalamus , it is about the size of an almond
Fore brain sf] part xf].h'g3rdventricaldf/x]sf] x'G5 .
Hypothalamus have vascular connection with Anterior pituitary and neural connection with posterior
pituitary by infundibulum /salk.
Junction of pos. pipuitory gland & Hypothalamus :- Infundibulam stalk/Pituitory stalk
o;nfO{Pitiutory Gland sf]ControllarePsf]n] Super-master of gland elgG5 .
o;nfO{ Sleeping and wake –upk|lqmofnfO{ Maintain u/]sf] x'gfn] o;nfO{ Biological clock elgG5 .
The Hypothalamus is the link between the Endocrine & Nervous system
Whatsapp : 9821133890 Birgunj,Parsa
The Hypothalamus produce Releasing & inhibitinghormone , Which stop and start the production
of orther hormone through the body
Hypothalamus releasing hormone are :-Gonodotrophicrelising hormone[GHRH], Corticotrophic
Releasing Hormone, Thyroid trophic hormone
Function of Hypothalamus @ EATS
E = Emotion and Endocrine activities. - ?g], xf:g], s/fpg], sfo{nfO{ af]w _
A = Autonomic Function and appetite. - ef]s / A.N.S sf] sfo{sf] jf]w _
T = Thermo-regulation and trusty. - Temp andltvf{sf] jf]w u/fp5 _
S = Sexual activities, Sleep and wake-up pattern. - Sexk|ltsf] ls|ofsnfk, ;'Tg] / p7g] s'/fsf] af]w u/fp5
Pituitory Gland / Hypophysis cerebri - 1
of] Sphenoid bone sf] Hypophysical fossa/ pituitary fossa (sellaturcica)df /x]sf] x'G5 .
of] Pea shape - s]/fpsf] bfgf _ h:tf] uf9f v}/f] /Ës]f [ Raddish Brown] x'G5 .
Weight :- 500mg (0.5gm)& Diameter :- 1 cm
Length :- 12mm & Breath :- 8mm
o;n] ;a} gland sf] sfdnfO{ lgoGq0f u/]sf] x'gfn] o;nfO{ Master gland elgG5 .
It have 3 lobes:-
a. Anterior Lobe / (Adinohypophysis)- Vascular connection
It is Largest lobe of pituitary gland
of] Hypothalamus df Blood vessels;+u hf]l8Psf] x'G5 .
o; lobenfO{ Hypothalamus af6 lgl:sg] Hormone(releasing and inhibiting) n] lgoGq0f ub{5 .
Anterior Lobe af6 lg:sg] Hormone x?:- 5 .
A. Growth hormone :- o;n] zf/Ll/s a[l4ljsf; ub{5 t/ Sextissueafx]s
Target organ:- Bone and all tissue but without sex organ., of] ;'t]sf] j]nf a9L lg:sLG5.
Deficiency :- Dwarfism/ growth retardation/ simmonds disease [ <4ft ]
Excess :-Child- Gigantism , Adult- Acromegaly
B.T S H (Thyroid Stimulating / Releasing Hormone
o;n] Thyroid GlandnfO{ Stimulate -pt]h_ u/L T3 , T4/ Calcitonine sf] pTkfbgub{5 .
Target organ :- Thyroid Gland .
AdrinoCorticotrophic Hormone . (ACTH)
o;n] Adrinal glandnfO{ Stimulatu/fOHormonepTkfbg u/fpb5 .
Target organ :- Adrenal cortex .
Prolacting / Maternity/ Lactogenic Hormone
o;n] :tg / kf7]3/df /fd|f] c;/ kb{5 h;n] ubf{ :tgaf6 b'wpTkfbg x'g5 eg] kf7]3/af6 Placentajflx/
lgsfN5 .
Target organ :- Breast , Uterus .
Excess :- infertility , Amenorrhoea , Glactorrhoea But in male loss of libido
Ganado Trophic Hormone (G T H )
o;dfb'O{ cf]6f Hormone x'G5 ;- FSH(Follicle Stimulating hormone) and LHS
1. F S H (Follicle Stimulating Hormone):-
Female:- Female dfo;n] Ovarian FolliclesnfO{ k'0f{ ljsl;t u/fp5 / Oestrogen
HormonepTkfbgub{5
Male:-o;n] Testis sf] Somniferous tubules nfO{ Stimulate u/fOSpermatozoajf Spermsf] pTkfbgu/fp5 .
2. L H( Leutinizing Hormone ):-
Female :- female dfo;n] Ovulation u/fp5 / OvaljxLg Follicles nfO{ Corpus Lutiumdf Convert
ub{5 ,h:fn] Progesterone Hormone pTkfbgub{5 .
Male :- Male dfo;n] Testis sf] Interstitial cellof LeydignfO{ pQ]lht u/fOTestosterone Hormone
sf] pTkfbg u/fp5 . h;n] Secondary Character lbG5 .
2)Posterior Lobe (Neurohypophysis ):- o;n] b'O{ cf]6f Hormone lgsfNb5 . :-;'q - O. A
A. Oxytocine / Pitocine
Also called Lovehormone / Birth hormone / Milk ejection hormone
Contraction and Relaxation of Uterus and Lactiferous duct of Breast .
To help out of Fetus to uterus and Ejaculate of milk to Breast .
Notes :-
Milk secretion / production:- Prolactin
Milk letdown / out :- Oxytocin
Whatsapp : 9821133890 Birgunj,Parsa
B. Antidiuretic Hormone (A.D. H) of Vasopressin.
Target :-Nephrone
o;n]] D C T af6 kfgLsf] zf]if0f a9L u/fp5 . / o;n] Peripheral Blood Vessels -5flt , k]6 , 5fnf _
nfO{ Constraction -v'lDrofpg' _ u/fO{ Blood Presuer a9fp5 .
A D H :-o;s]f a9L ePdfLittle and Concentration Urine /water and salt retention.
A D H :- o;sf] sdLePdfDiabetic insipidus -lk;fa w]/} nfUg'_
c. Intermediate Lobe / Mid Lobe
o;n] Melanocyte Stimulate HormonepTkfbgub{5 h'gSkin s]f Epidermis df /x]sf] x'G5 / of]
Scrotamdf ;aeGbf a9L kfOG5 .
Melanocyte Stimulate Hormonen]melaninepigmintlgsfNb5 / 5fnfsf] /Ë lbG5 .
o;sf] al9 ePdf :- Hyper pigmentation -sfnf]_
Thyroid gland
Highly vascular gland &Largest Endocrine gland.
Butterfly shape , Weight :- 25gm , Size :- 5x3 cm
Located :- infront of larynx & trachea ( C5- T1)
o;sf] 2 j6f Lobe x'G5 Right Lobe and Left Lobe b'O6} LobenfO{ Esthmus n] hf]l8Psf] x'G5 .
o;n] TSH lgsfNb5 . E.g. ( T3 , T4/ Calcitonin)
Metabolic rate is controlled by Thyroid
o;dfb'Ocf]6f Cell /x]sf] x'G5 .
A.FolicallsCell :-o; Follicles cell n] 2 j6f Hormone lgsfNb5 .
T3 – Tri-ido Thyroxin Hormone & T4 - Thyroxin Hormone.
T3 and T4 Hormone Iodine sf] pkl:yltdfpTkfbg x'G5 cyf{t T3 and T4aGgIodine sf] cfjZostf
kb{5.
T3 -10 % x'G5 eg] T4 -90 % /x]sf] x'G5 &T4eGbf T3 Hormone a9L active x'G5 .
a.
Para Note:- Follicles df Iodine Trapping eP/ /x]sf] x'G5 . 3 j6f Iodine sf] pkl:yltdf Follicles n]
lgsfNg] Hormone nfO{T3= Triido Thyroxin Hormone and 4 j6f Iodine sf] pkl:yltdf Follicles
n] lgsfNg] Hormone nfO{T4elgG5 .
Follicles:-of] Follicles cell sf] ljr-ljrdfʽCʼ shapesf] /x]sf] x'G5 h;n] Calcitonine HormonelgsfNb5
Calcitonine Hormonen] Kidney df Calcium sf] Re-Absorbotion36fO{ Blood df Calcium sf]
dfqf 36gfn] Bone af6 Calcium Release x'G5 / Osteoporosis x'G5 .
Function of Thyroid Gland
1. Metabolism (Carbohydrate , Protein , Fat )
2. Mental development up to 5 yrs
3. Maintain normal basal Metabolic rate .
-hltVitamin h'gorganx?nfO{ rflxG5 Toltdfqlbg] aflsnfO{ /fVg] jfkmfNg]_
Deficiency :-Hypothyrodism
Child - Cretinism (mental retardation)
In adult – Myxo edema (Non pitting )
Excess:-Hyperthyrodism/ Thyrotoxicosis
Graves disease (exothalmic- cfFvfafxL/ cfpg' )
Goiter/ ufnuf8
Enlargment of Thyroid Gland . due to Excessive and deficiency of thyroid secration
primary deficiency in Goiter Iodine.
Graps disease / Goiter Male eGbf Female df a9L x'G5 .
Goiter commonly seen in mountain area( lxdfln
Para thyroid gland(PTH)
Thyroid Gland sf] k5f8L /x]sf] x'G5 .
Number of parathyroid gland – 4each Wt- 50 mg , Size- 6 ꭖ 4 ꭖ 2 cm3
of] xfd|f] zl//dfcalcium metabolismug}{ k|d'vu|Glyxf]
o;n] Paratharmon Hormone / Parathyroxine Hormone lgsfNb5 h;n] Blood df Calcium / Phosphorus
sf] Reabsorb a9fp5 .
Paratharmon Hormone n]calcium and phosphorussf] dfqfa9fp5 .
Excess secretion –Brittle bone( osteoporosis), muscular pain,
Deficiency – Muscular rigidity , muscular tetany
Whatsapp : 9821133890 Birgunj,Parsa
Adrenal gland
Also called Suprarenal gland / Emergency gland / 4s gland / 3f gland / life saving gland.
of] k|To]s d[uf}nfsf] dfly /x]sf] x'G5 / Renal fosian] 9fFs]sf] x'G5 .
weight- 5 gm , Size - 5 X 3 X 1 cm
4 S Means :- Salt Retention, Sugar Metrabolism, Sexual function, Safety
o;dfaflx/L lelqul/ b'O{ cf]6f tx x'G5 .
Adrenal medulla-lelqkq_;-of]10 %dfq x'G5 o;af6 lgl:sg] Hormone Adrenaline , Nor adrenaline
Catecholamine.
Function -3f :- Fight -emu8f ug'{ , Fright -u{hg' , Flight -efUg'_
Adrenal Cortex -aflx/L kq -of]80 % x'G5 / o;n]3 j6f HormonelgsfNb5 .
Glucocarticosteroido;n] /utdf Glucose sf] dfqf a9fp5, Delayed wound healing
Minarlocorticoid / Aldestoren :-o;n] kidneydfsodium / potassium sf] dfqfnfO{ ;+t'ng u{5 /
water sf] Reabsorption u/fp5 .
Androgen (Sex hormone):-o;n] Testosteroneand estrogen sf] sfo{nfO{ ;+t'ng u{5 / o;n]
Protein and Nitrogen sf] ;~ro -e08f/0f_ u{5 .
Pancreases / Hetrocrine / MixedGland :-
Largest mixed gland
o;sf] 2 j6f part x'G5 , Exocrine – 80 %&Endocrine – 20 %
Endocrine gland sf] ?kdfinsulin, Glucagon , & SomatostatinlgsfNb5f
Exocrine gland sf] ?kdfpancreatic juicelgsfNb5f
Endocrine cell sf] ;d'xnfO{ islets of langerhans elGG5
Islets of langerhans contain:- Alpha - Glucagon, Beta- insulin , Delta – Somatostatin
Notes:-
Glucagon is catabolic hormone that increase blood glucose by glycogenesis,
Excess glucose- Hyperglycemia
Insulin is Anabolic hormone that decrease blood glucose by glucogenesis, storage of protein & fat
Excess glucose-Hypoglycaemia&Deficiency – Diabetes myelitis
Somatostatin is growth hormone inhibiting hormone & control the secretion of both glucagon and
somatostatin
Gonadotrophic Hormone
Female gonads :-
Overy – 2 j6f , weight – 7 gm,Size – 3x2x1 cm3 , Shape – Almond shape
o;nfO{ Graffine/ ovarian follicles x'G5 h;n] OestrogenpTkfbgub{5 .
Function of Oesterogen :- Proliferation ofEndomatarium wall
Mammay glandnfO{ 7"nf] agfp5 .
Corpus Luetium (ova ljxLg Follicles) secrete Progesterone Hormone .(pregnancy hormone)
Thickest of endometrium wall .
Uterus secretion nfO{afSnf] agfpF5 &Uterus nfO{ implantation sf] nflutof/ u5{ .
Male gonads :-
Testis – 2 :- Weight :- 10-14 gm , shape :- oval , Location :- Scortum
o;dfePsf] Interstitial cellof Leyding n] Testosterone Hormone product u5{ h;n] MaledfSexual
secondary character lbG5 . 9fx|L , hËf , u'KtfËdf /f} cfpg' , ljk/Lt lnËlt/ cfs{ifgx'g' , formation &
maturation of sperm,
Pineal gland
Also called Third Eye
Smallest organ of our body ;- Pineal gland
of] Brainleq /x]sf] x'G5 (Fore brain sf] 3rd Ventricledf) ,Length :- 10mmjf 1 cm.
o;n] Melatonin Hormone lgsfN5 / Melatonin Hormone n] Puberty cj:yfcfpg' eGbf cufl8
Reproductive organ sf] ljsf; x'glbb}g .
Puberty ca:yf cufl8 of] Brain df Atrophy eP/ hfG5 / Sand bad - afnjfsf] l9sf] s]f ?kdf /x]sf]
x'G5 . / of] /ftf v}/f] /Ësf] x'G5 .
Pineal gland Atrophy after puberty known asbrain sand
Thymus gland :-
It is primary Lymphatic organ
Located in upper Mediastenum behind the sternum .
Whatsapp : 9821133890 Birgunj,Parsa
It secreted is called Thymosin which help in maturation of t cell
Weight:-30-40 gm. But At during afterpuberty 10-15gm
Thymus & Pineal gland atrophy after puberty.
It secrets thymocine hormone which is active the T. Lymphocyte.
Tips:-
4 s gland :- Salt Retention, Sugar Metabolism, Sexual Function , Safety
placenta secretes :- HCG( human chorionic gonadotrophic]
Kidney secrete :– Erythropoetin , Renin , vit D ( Kidney Hormone )
Mast cell secrete Histamine
Calcium level balanced by parathyroid Hormone
Iodine store in Thyroid gland
Muscle spasm due to Deficiency ofParathermone Hormone
Development of Mustache[ bflx|] in female due to excess of Suprarenal gland
Diabetiesincipidius due to deficiency of ADH
Gluconeogenesis & glycogenesis causes of Glucagon
Portal system is present in Pituitary gland
Muscular tetany due to deficiency of Parathyroxin
Which hormone require zinc for synthesis :- Insulin
Pineal gland secrete Melatonin
Regulation of metabolic rate of body cell :- Thyroid Hormone
Conns Syndsromepresent due excessive production of Aldosterone
Duct and gland are internally lined by Cuboidal epithelium
Hormone and Disorder
Hormone Excess Deficiency
G.H Gigantism( Child), Acromegaly[ Adult] Dwarfism
Prolactin Infertility, Amenorrhoea –
Female,DecreseLabido, Galactorrhoea-
Male
Aldosterone Conn,s syndrome Addition syndrome
Glucocorticoids Cushings Syndrome Hyponatraemia, shock
Androgen Hirsutism, pseudohermophoditism –
virilizationpseudohermophoditism – Male
female
Insulin Hypoglycemia Dibetes Myelitis
Glucagon Hyperglycemia Diabetes Myelitis
Prepared By:-MukeshRazMahto,
Health Assistant Gov of Nepal
Whatsapp : 9821133890 Birgunj,Parsa
You might also like
- Anterior and Posterio Pituitary GlandDocument7 pagesAnterior and Posterio Pituitary GlandAnny AlvrzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 21 The Sensory SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 21 The Sensory SystemThanh Nguyen VanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewDocument9 pagesEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- Energy of YouDocument29 pagesEnergy of YouIulia Palimaru100% (4)
- Note Midwifery NewDocument59 pagesNote Midwifery NewAn ZeelaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemSugandhi SahNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Endocrine GlandDocument73 pagesUnit 13 Endocrine GlandChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Human and Animal Physiology Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine GlandsDocument21 pagesHuman and Animal Physiology Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine Glandshitmanno5No ratings yet
- Unit 13 Endocrine GlandDocument73 pagesUnit 13 Endocrine GlandChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesEndocrine SystemPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument86 pagesEndocrine PhysiologySabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Act SheetDocument3 pagesEndocrine Act SheetTrisha ArdedNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Disorders (Final Draft)Document17 pagesPituitary Disorders (Final Draft)Kiprono Keitany TimothyNo ratings yet
- Unit IXDocument10 pagesUnit IXPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chem Coordination and Integration PDFDocument37 pages11 - Chem Coordination and Integration PDFANo ratings yet
- ENDODocument141 pagesENDOearldem1996No ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument172 pagesEndocrine DrugsAlvim Tiel FactorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: EndocrineDocument210 pagesPharmacology: EndocrineSharifa Darayan100% (1)
- MRGR Endocrine System Ysh17Document29 pagesMRGR Endocrine System Ysh17Yash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland - WikipediaDocument29 pagesEndocrine Gland - WikipediaSumaya FarheenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document3 pagesChapter 10Zoe DorothyNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Growth Axis: Source Site of Action Hormone Struct Receptor Post-Rece ActivityDocument5 pagesPituitary Growth Axis: Source Site of Action Hormone Struct Receptor Post-Rece Activitykep1313No ratings yet
- Part 3 - MEDTERM-117 LECDocument6 pagesPart 3 - MEDTERM-117 LECfrechel kimNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus & PituitaryDocument61 pagesHypothalamus & PituitaryShreya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Indocrine SystemsDocument59 pagesAnatomy Indocrine SystemsibrooavcNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction of EndocrineDocument35 pages1.introduction of EndocrineCabdiladif Ahmed McrfNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesEndocrine SystemAkshat RastogiNo ratings yet
- HistoEndocrineSystem by DR - NaDocument64 pagesHistoEndocrineSystem by DR - NaAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology FinalDocument25 pagesEndocrine Physiology FinalVondNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis: - Oleh: - I Dewa Made RuspawanDocument33 pagesHypothalamic-Pituitary Axis: - Oleh: - I Dewa Made RuspawanherlinaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Deference Between Hormone and EnzymeDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Deference Between Hormone and EnzymeCurex QANo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument5 pagesEndocrinologyAliehsEiram18No ratings yet
- BSC Anterior Pituitary HormonesDocument27 pagesBSC Anterior Pituitary HormonesThalapathy PrakashNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument50 pagesEndocrine DrugsJohney DoeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Raghu Prasada M S MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCDocument27 pagesDr. Raghu Prasada M S MBBS, MD Assistant Professor Dept. of Pharmacology Ssims & RCNastase Daniela EcaterinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25 - The Endocrine SystemDocument40 pagesLecture 25 - The Endocrine SystemEarle Jimenez Niervo RNNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary GlandDocument29 pagesAnterior Pituitary GlandSyed Mohammad Osama AhsanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 Endocrine Diseases Lecture 1 January 10-020Document68 pagesLECTURE 1 Endocrine Diseases Lecture 1 January 10-020aleen qawareetNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentrain_puvNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Some TerminologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Some TerminologySugandhi SahNo ratings yet
- Neuroendokrin: Oleh: Dr. Budi SeptiawanDocument43 pagesNeuroendokrin: Oleh: Dr. Budi SeptiawanMeldy Muzada ElfaNo ratings yet
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocument32 pagesM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Sections: Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis)Document4 pagesSections: Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis)chiqui_salazarNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument114 pagesReproductive SystembookaccountNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi EndokrinDocument118 pagesFisiologi Endokrinyoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Endocrine Guided NotesDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Endocrine Guided NotesJeanette IrambonaNo ratings yet
- Human Endocrene SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Endocrene SystemmaroonblekiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Endocrine: Which Have No Duct and ReleaseDocument36 pagesEndocrine System: Endocrine: Which Have No Duct and Releasedr_saleh77No ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument101 pagesThe Endocrine SystemLeônidas ZazelisNo ratings yet
- 6-TheR 608# Hormones & Reprod-IIDocument15 pages6-TheR 608# Hormones & Reprod-IIHamza HassanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument4 pagesEndocrine Glandakash_zizouNo ratings yet
- Endocrinol Pred 02Document7 pagesEndocrinol Pred 02api-3706483No ratings yet
- AP-2 Lab Report - Lab 01 The Endrocine SystemDocument15 pagesAP-2 Lab Report - Lab 01 The Endrocine Systemrcdunfee86% (7)
- Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesEndocrine SystemYary MayorNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NOTESDocument2 pagesEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNo ratings yet
- Learning Reproduction in Farm AnimalsDocument5 pagesLearning Reproduction in Farm AnimalsBharathi DasanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Part 1.Document57 pagesEndocrine System Part 1.Jonathan Young XDNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemHerlene Suelto Tingle100% (1)
- Worksheet 1, AnaphyDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1, AnaphycelynjasminegNo ratings yet
- Unit2-Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument80 pagesUnit2-Hypothalamus and Pituitarypranutan739No ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPituitary Gland, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- National List of Essential Medicines Nepal 2021Document72 pagesNational List of Essential Medicines Nepal 2021Sugandhi SahNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemSugandhi SahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (ZJF K - ZJF K - 0ffln)Document4 pagesRespiratory System (ZJF K - ZJF K - 0ffln)Sugandhi SahNo ratings yet
- Important of Body Fluid &electrolyteDocument1 pageImportant of Body Fluid &electrolyteSugandhi SahNo ratings yet
- Hormonal CoordinationDocument4 pagesHormonal CoordinationKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Biology Matura Workbook - Biológia Érettségi Feladatok Tematikus Csoportosítás Angol NyelvenDocument22 pagesBiology Matura Workbook - Biológia Érettségi Feladatok Tematikus Csoportosítás Angol NyelvenOmer Belfaqih100% (2)
- Koordinasi Badan: Body CoordinationDocument9 pagesKoordinasi Badan: Body CoordinationReeta BanifaceNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - MedDocument124 pagesEndocrine System - Medrediet shimekachNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ClarkDocument834 pagesEndocrine ClarkKhaled AbdelgalelNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)Document34 pagesEndocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)ayaessam392002No ratings yet
- Insect Control Using Hormones and PheromonesDocument15 pagesInsect Control Using Hormones and PheromonesPatricia Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Secondary School Biology Short Notes and Exercises For Grade 10Document22 pagesSecondary School Biology Short Notes and Exercises For Grade 10Gashaw Fikir AdugnaNo ratings yet
- RPT Biology Form 5 2020Document21 pagesRPT Biology Form 5 2020izeliwaniismailNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands PDFDocument99 pagesEndocrine Glands PDFXochitl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Biology Sample Paper 1Document6 pagesICSE Class 8 Biology Sample Paper 1Chhavi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Std08 I MSSS EM 2 PDFDocument56 pagesStd08 I MSSS EM 2 PDFSenthilmurugan RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ResonanceDocument51 pagesEndocrine ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- XII Zoology PC ReasoningDocument6 pagesXII Zoology PC ReasoningAmrah ShahNo ratings yet
- 9th Sci 2 CH 15 NotesDocument10 pages9th Sci 2 CH 15 NotesnilNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemJamie BagundolNo ratings yet
- The Brain, Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDocument13 pagesThe Brain, Nervous System and Endocrine SystemMark Lorenzo A RuizNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument144 pagesEndocrinedaffodilrachagNo ratings yet
- EMRGI 5 - EndcorineDocument7 pagesEMRGI 5 - EndcorineCindy CabrerosNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document15 pagesBiology 1maielsherif2020No ratings yet
- Lecture Note Asas Psikologi (The Biological Perspective)Document66 pagesLecture Note Asas Psikologi (The Biological Perspective)Muhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 2011Document30 pagesHyperthyroidism 2011Elyza MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- M2 Lesson 3 Endocrine System Animals and PlantsDocument35 pagesM2 Lesson 3 Endocrine System Animals and PlantsSophia Grace VicenteNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 10 Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesAnaphy Chapter 10 Endocrine SystemJohnNo ratings yet
- Yoga Notes For Serious StudentsDocument10 pagesYoga Notes For Serious StudentsDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -KNo ratings yet
- Exocrine Glands-Endocrine GlandsDocument8 pagesExocrine Glands-Endocrine GlandsneerleoNo ratings yet
- Hormones General Characteristics, Classification.Document13 pagesHormones General Characteristics, Classification.Jihan NurainiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemMabes100% (1)
- Promotion-Past-Questions For Ges CandidatesDocument315 pagesPromotion-Past-Questions For Ges Candidatesyaw19750% (2)