Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evaluation Exam 7 April2023
Evaluation Exam 7 April2023
Uploaded by
Michael MercadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evaluation Exam 7 April2023
Evaluation Exam 7 April2023
Uploaded by
Michael MercadoCopyright:
Available Formats
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. Mark only one answer
for each item by shading the box corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet
provided. STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED.
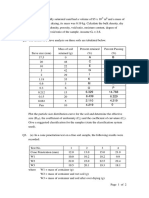
Situation I: Following are the results of a sieve analysis.
Sieve Opening Percent finer
No. (mm) (grams)
4 4.75 100
10 2.00 94.5
20 0.85 86.3
40 0.425 74.1
60 0.25 54.9
80 0.18 38.1
100 0.15 9.3
200 0.075 1.7
Pan - 0
1. Determine the effective size (mm).
a. 0.10 c. 0.15
b. 0.30 d. 0.72
2. Determine the uniformity coefficient.
a. 1.5 c. 2.1
b. 1.9 d. 1.8
3. Determine the coefficient of curvature.
a. 0.13 c. 0.42
b. 0.67 d. 0.72
Situation II: Classify the following soils according to the USDA textural classification system. Refer to
FIG. CS35 for this problem.
Particle-size
distribution A B C
(%)
Gravel 10 21 0
Sand 20 12 18
Silt 41 35 24
Clay 29 32 58
4. Soil A
a. Silty clay c. Clay
b. Gravelly clay d. Gravelly clay loam
5. Soil B
a. Silty clay c. Sandy loam
b. Gravelly Silty Clay d. Gravelly clay loam
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
6. Soil C
a. Silty clay c. Clay
b. Gravelly Silty Clay d. Gravelly clay loam
7. The results of the particle-size analysis of a soil are as follows:
Percent passing the No. 10 sieve = 100
Percent passing the No. 40 sieve = 80
Percent passing the No. 200 sieve = 58
The liquid limit and plasticity index of the soil are 30 and 10, respectively. Classify the soil by
the AASHTO Classification system in the FIG. COS43
a. A-4 (3) c. A-1-a (2)
b. A-2-7 (4) d. A-3 (0)
Situation III: For a vibroflotation project, the following backfill material specification must be satisfied.
The difference between D30 and D25 is 70𝜇𝑚.
So = 1.6
CU = 3.75
CC = 0.80
D10 = 0.25 D75
D20 = 0.55 mm
D50 = 1.30 mm.
8. Calculate the required suitability number.
a. 5.6 c. 2.4
b. 4.2 d. 6.4
9. What is the condition of the backfill?
a. Excellent c. Fair
b. Good d. Unsuitable
10. An embankment for a highway is to be constructed from a soil compacted to a dry unit weight
of 18 kN/m^3. The clay has to be trucked to the site from a borrow pit. The bulk unit weight of
the soil in the borrow pit is 17 kN/m^3 and its natural water content is 5%. Calculate the
volume of clay from the borrow pit required for 1 cubic meter of embankment. The swell factor
is 1.2 (20% free swell). Assume Gs 5 2.7.
a. 0.45 c. 2.15
b. 4.67 d. 1.33
11. An ASTM D 854 test was conducted on a sand. The data are as shown below. Calculate the
specific gravity.
Mass of pycnometer 38.2 grams
Mass of pycnometer and dry soil 64.3 grams
Mass of pycnometer, dry soil and water 154.8 grams
Mass of pycnometer and water 138.5 grams
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
a. 2.66 c. 1.79
b. 3.75 d. 1.85
12. An earth dam require one hundred cubic meter of soil compacted with unit weight of 20.5
KN/m^3 and moisture content of 8%, choose two from the three borrow pits given in the table
below, knowing that the first must be one of the two borrow pits, the specific gravity of solid
particles is 2.7. Which of the following is the most economical choice.
Borrow pit
Void Ratio Cost (P/m^3) Available Volume (m^3)
No.
1 0.6 1 80
2 1 1.5 100
3 0.75 1.7 100
a. Borrow pit 2 c. Borrow pit 1
b. Borrow pit 3 d. Borrow pit 1 and 2
Situation IV: A dry sand is placed in a container having a volume of 0.3 ft^3. The dry weight of the
sample is 31 Ib. Water is carefully added to the container so as not to disturb the
condition of the sand. When the container is filled, the combined weight of soil plus
water is 38.2 Ib. From these data,
13. Compute the void ratio of soil in the container,
a. 0.624 c. 0.426
b. 0.733 d. 0.235
14. And the specific gravity of the soil particles.
a. 4.65 c. 2.69
b. 2.45 d. 1.46
Situation V: The in-situ(field) moisture content of a soil is 18% and it’s moisture unit weight is 105 pcf
(Ib/ft^3). The specific gravity of soil solids is 2.75. This soil is to be excavated and
transported to a construction site and then compacted to a minimum dry weight of 103.5
pcf at a moisture content of 20 %.
15. How many cubic yards of excavated soil are needed to produce 10,000 yd^3 of compacted
fill?
a. 9,346.4 yd^3 c. 14,667.1 yd^3
b. 10,064.6 yd^3 d. 11,631.4 yd^3
16. How many truckloads are needed to transport the excavated soil if each truck can carry 20
tons? ( 1ton = 2000lb, 1yd = 3ft )
a. 825 c. 815
b. 820 d. 845
Situation VI: A liquid limit test is conducted and the data from each trial are shown below:
Moisture Content Number of
Trials
% blows
Trials 1 35 20
Trials 2 31 36
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
Plastic limit test is conducted and the data from each trial are shown below:
Test No. 1 2
Mass of wet Soil + Container 22.3g 21.9g
Mass of dry soil + Container 20.2g 20.1g
Mass of Container 13.05g 13.05g
17. Determine the flow index
a. -25.3 c. -2.2
b. -15.7 d. -30.4
18. Determine the toughness index
a. 0.67 c. 0.22
b. 0.38 d. 0.43
19. In a project, soil A has the following atterberg limits; LL=118%, PL=42%, Percentage of clay
particles 50. Classify soil A based on its activity.
a. Inactive c. Abnormal
b. Normal d. Active
Situation VII: For a certain soil profile, a uniformly distributed load, ΔP = 50 kPa, is applied at the
ground surface. Assume CS = 0.20CC. Take e = 0.95, LL = 50, height of clay layer = 8
m and PO = 136.9 kPa. Determine the settlement of the clay layer caused by primary
consolidation if:
20. The clay is normally consolidated.
a. 200mm c. 40mm
b. 153mm d. 131mm
21. The preconsolidated pressure PC is 210 kPa.
a. 200mm c. 40mm
b. 153mm d. 131mm
22. The preconsolidated pressure PC is 150 kPa.
a. 200mm c. 40mm
b. 153mm d. 131mm
Situation VIII: Two footings rest in layer of sand 2.7m thick. The bottoms of the footings are 0.90m
below the ground surface. Beneath the sand layer is a 1.8m thick clay layer.
Underneath the clay layer is solid rock. Water table is at a depth of 1.8m below the
ground surface. The load on the footings are: Pa = 450 kN and Pb = 900 kN. . The
corresponding characteristics of the soil is given as follows:
𝑘𝑁 𝑘𝑁
For sand: 𝛾𝑠𝑎𝑛𝑑 = 18.5 𝑚3 , 𝛾𝑠𝑎𝑡 = 20.8 𝑚3
𝑘𝑁
For clay: 𝛾𝑐𝑙𝑎𝑦 = 18.8 , 𝑒 = 1.03, 𝐶𝑐 = 0.3
𝑚3
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
23. Compute the stress increase in kPa below footing A (1.5m x 1.5m) at the center of the clay
layer. Assume that the pressure beneath footing A is spread at an angle of 2 vertical to 1
horizontal.
a. 20.15 c. 22.50
b. 30.75 d. 25.51
24. Determine the size of footing B so that the settlement in the clay layer is the same beneath
footings A and B.
a. 2.85m x 2.85m c. 1.8m x 1.8m
b. 3.24m x 3.24m d. 3.63m x 3.63m
25. Determine the settlement in mm beneath footing A.
a. 34.70 c. 58.10
b. 30.85 d. 46.65
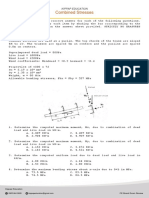
Situation IX: Find the following, all the dimensions are in cm:
26. Determine the pressure head at B
a. 19.30 cm c. 16.17 cm
b. 12 cm d. 24 cm
27. Determine the pressure head at C
a. 19.30 cm c. 16.17 cm
b. 12 cm d. 24 cm
28. Equivalent hydraulic conductivity in cm/s
a. 0.334 c. 0.0547
b. 0.0647 d. 0.0798
Situation X: In a consolidation test of a soil the following results have been obtained. When the load
was changed from 50 kN/m2 to 100 kN/m2, the void ratio changed from 0.70 to 0.65. The
coefficient of permeability is 3.55 x 10^-3 m/day
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
29. Determine the coefficient of compressibility.
a. 0.001 c. 0.023
b. 0.002 d. 0.45
30. Determine the coefficient of volume compressibility.
a. 2.79×10^(-4) c. 0.64×10^(-3)
b. 3.64×10^(-4) d. 5.88×10^(-4)
31. How long will it take for 50% consolidation to occur if the layer is drained on both ends? The
thickness of a clay layer is 8m.
a. 5.1 days c. 2.5 days
b. 8.3 days d. 3.4 days
SITUATION XI. The coefficient of permeability below a dam is 4m/day. The water on the upstream side
is 20 meters higher than on the downstream side. To estimate the seepage below the dam, a flow net
was graphically drawn such that the number of potential drops, Nd=10 and the number of flow channels
Nf=4. The base of the dam is founded 1m below the ground. Between the heel and the toe of the dam,
a distance of 30 meters, there are 8 potential drops.
32. Evaluate the seepage flow per meter width of dam, in liters/min.
a. 18.5 c. 20.6
b. 32.5 d. 22.2
33. Determine the uplift pressure at the heel of the dam, in KPa.
a. 114 c. 177
b. 181 d. 198
34. Determine the uplift pressure at the toe of the dam, in KPa.
a. 11.4 c. 14.7
b. 19.6 d. 17.6
SITUATION XII. A confined aquifer has a hydraulic conductivity of 40m/day and a porosity of 25%.
The piezometer surface in two observation wells are at elevation 65m and 60m,
respectively from common datum. The first and second observation well are 3.65km
and 5km from the source of recharge respectively. The aquifer has an average
thickness of 25m and average width of 4km.
35. Which of the following most nearly gives the flow rate of water through the aquifer?
a. 14814.8 c. 11448.8
b. 18814.4 d. 14448.8
36. Which of the following most nearly gives the interstitial velocity of the flow?
a. 0.04 c. 0.59
b. 0.16 d. 0.15
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
37. Which of the following most nearly gives the time travel from the head of the aquifer to a point
4km downstream?
a. 3319 c. 6750
b. 4242 d. 7250
𝑔
SITUATION XIII. In a field density test the following result are obtained: 𝜌𝑚 = 1.95 𝑐𝑚3 , 𝑤 = 16%. The
speficic gravity of solids is 2.7.
38. Calculate the percent air voids.
a. 23.3 c. 31.8
b. 19.1 d. 28.7
39. Calculate the air content.
a. 9.33 c. 10.8
b. 11.9 d. 8.11
40. Volume change in saturated soils cause by the expulsion of pore water from loading?
a. Primary Consolidation c. Permeability
b. Secondary Consolidation d. Effective stress
FIG. COS43
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
KIPPAP EDUCATION
Evaluation Exam 7
FIG. COS35
Kippap Education
0905 664 2628 kippapeducation@gmail.com CE Board Exam Review
You might also like
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 9th Edition Das Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 9th Edition Das Solutions ManualSarahJonesgkoey87% (15)
- Solution Manual For Soil Mechanics and Foundations 3rd Ed - Muni BudhuDocument12 pagesSolution Manual For Soil Mechanics and Foundations 3rd Ed - Muni BudhuAfshar Arabi11% (9)
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 9th Edition Das Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 9th Edition Das Solutions Manualpithlessriverp4d6100% (30)
- Problem Set in GEotechnical EngineeringDocument15 pagesProblem Set in GEotechnical EngineeringRachel DelosreyesNo ratings yet
- Screening, Size Reduction, Flotation, AgitationDocument496 pagesScreening, Size Reduction, Flotation, Agitationscarlett67% (3)
- PS2 4Document10 pagesPS2 4Karl Alexis TumibayNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Sem II Sesi20182019 (Answer Scheme)Document7 pagesTest 1 Sem II Sesi20182019 (Answer Scheme)Ashyra JamilNo ratings yet
- Assignments and Tutorials - Soil Mechanics - Spring NewDocument42 pagesAssignments and Tutorials - Soil Mechanics - Spring NewmanthanNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering I - Soil Mechanics Quiz 1 Batch 2021-2022 INSTRUCTION (S) : Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following QuestionsDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering I - Soil Mechanics Quiz 1 Batch 2021-2022 INSTRUCTION (S) : Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following QuestionsCarjez LoveNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials and TestingDocument4 pagesConstruction Materials and TestingNicole May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Problem Set11Document10 pagesProblem Set11Habyer47No ratings yet
- Mock Exam GeoDocument3 pagesMock Exam Geoorigin.zerefNo ratings yet
- 2 Soil Classification - S21Document3 pages2 Soil Classification - S21hassanNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document12 pagesCH 02Nadia Zaman SrutiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry - Print - Quizizz2Document10 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry - Print - Quizizz2andieNo ratings yet
- XPERTZ - Evaluation & RefresherDocument23 pagesXPERTZ - Evaluation & RefresherCatherine Shaina Pasion50% (2)
- Mix Design SpecificationDocument38 pagesMix Design SpecificationRohan Dhatbale100% (1)
- Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyDocument3 pagesJomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyTinaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios para Practicar ch3 PDFDocument5 pagesEjercicios para Practicar ch3 PDFCindy Lorena PachecoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios para Practicar Ch3Document5 pagesEjercicios para Practicar Ch3Cindy Lorena PachecoNo ratings yet
- Answers To Selected Problems: Sieve No. Percent FinerDocument10 pagesAnswers To Selected Problems: Sieve No. Percent FinerLucas Cavalcante de AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- PS1 Without AnswerDocument3 pagesPS1 Without Answerbrian galangNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Problems PDFDocument2 pagesSet 1 Problems PDFKristin Argosino0% (1)
- Policarpio 4 - Refresher GEODocument2 pagesPolicarpio 4 - Refresher GEOJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics RefresherDocument14 pagesSoil Mechanics Refresherfrancis bautistaNo ratings yet
- Civ 40Document5 pagesCiv 40jean willieNo ratings yet
- MKCP 313 Midterm QuizDocument3 pagesMKCP 313 Midterm QuizasdfqwertyNo ratings yet
- US Sieve No. Mass of Soil Retained On Each Sieve: Situation-1: Following Are The Results of A Sieve AnalysisDocument1 pageUS Sieve No. Mass of Soil Retained On Each Sieve: Situation-1: Following Are The Results of A Sieve Analysispj390No ratings yet
- Elective - II: Pavement Analysis & Design: B.E.Eighth Semester (Civil Engineering) (C.B.S.)Document12 pagesElective - II: Pavement Analysis & Design: B.E.Eighth Semester (Civil Engineering) (C.B.S.)Uday PatilNo ratings yet
- PT 2023 Past QuestionDocument7 pagesPT 2023 Past QuestionTSOG MHNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics - Problems 1Document2 pagesSoil Mechanics - Problems 1MJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3: Highway Engineering-II 2011 E.CDocument4 pagesAssignment - 3: Highway Engineering-II 2011 E.CABexample GgideyNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 1Document3 pagesCE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 1rando12345No ratings yet
- CEGE205P - Soils and Eng Geology LSA 2018Document7 pagesCEGE205P - Soils and Eng Geology LSA 2018Sarah SmithNo ratings yet
- Responsi 3 Mekanika Tanah 1Document2 pagesResponsi 3 Mekanika Tanah 1Rene KurniadiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Tutorial 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1: Tutorial 1smithson JoeNo ratings yet
- RefM 18 - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument1 pageRefM 18 - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsusueNo ratings yet
- ESE 2020: Prelims Exam: Test 6Document21 pagesESE 2020: Prelims Exam: Test 6Anurag SinghNo ratings yet
- Cie - 20047 P2 - 20exam Answer - 20key 1S Sy2324Document9 pagesCie - 20047 P2 - 20exam Answer - 20key 1S Sy232424ks72xn8jNo ratings yet
- Piping Materials 1Document1 pagePiping Materials 1AlenNo ratings yet
- Dec 2019Document6 pagesDec 2019uloveNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Science Remove Class Summative Test 2020 No. Answer Marks Section ADocument1 pageAnswer Scheme Science Remove Class Summative Test 2020 No. Answer Marks Section AMexlyn AdnanNo ratings yet
- 08 Ch-8 PDFDocument6 pages08 Ch-8 PDFMANJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document2 pagesTutorial Chapter 1Muhammad Azrul AzuwanNo ratings yet
- Geotechnics 1 (BFC 21702) Tutorial Chapter 1Document2 pagesGeotechnics 1 (BFC 21702) Tutorial Chapter 1wendyNo ratings yet
- Division of Taguig City and PaterosDocument2 pagesDivision of Taguig City and Paterosriela dhee lagramaNo ratings yet
- Highway and Airports EngineeringDocument1 pageHighway and Airports EngineeringAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 - Hydro GeoDocument9 pagesExam 1 - Hydro GeoRenz PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical QuizDocument41 pagesGeotechnical QuizAminulIslamNo ratings yet
- Accreditation Exam 3Document12 pagesAccreditation Exam 3Andrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Nor Faizah BawadiNo ratings yet
- Ce 36-B (Q1)Document2 pagesCe 36-B (Q1)GintokiNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 1-12: Tutorial Sheet 1Document11 pagesTutorials 1-12: Tutorial Sheet 1NarasimharaoNo ratings yet
- TRB Test SeriesDocument12 pagesTRB Test SeriesGokul ParthibanNo ratings yet
- Tle 8 CarpentryDocument4 pagesTle 8 CarpentryKristine Mae Vitor LargoNo ratings yet
- Geotechincal Engineering NotesDocument7 pagesGeotechincal Engineering NotesThesis ConsultantNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document2 pagesExercise 2Ahmed NasserNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document1 pageSheet 2Rawaa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Soil Assign PDFDocument7 pagesSoil Assign PDFtilahun Mersha0% (1)
- University of PeradeniyaDocument7 pagesUniversity of Peradeniyanaveen daluwattaNo ratings yet
- Kippap-Handout-Evaluation Exam 5Document6 pagesKippap-Handout-Evaluation Exam 5Michael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 9Document7 pagesEvaluation Exam 9Michael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 6Document9 pagesEvaluation Exam 6Michael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 8Document8 pagesEvaluation Exam 8Michael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Combined Stresses: Kippap EducationDocument2 pagesCombined Stresses: Kippap EducationMichael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationDocument22 pagesEvaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationMichael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationDocument8 pagesEvaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationMichael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Soft Clay:: Slow Draining. Slow To Warm in The Spring. Compacts Easily, Making It Difficult For PlantDocument15 pagesSoft Clay:: Slow Draining. Slow To Warm in The Spring. Compacts Easily, Making It Difficult For PlantMoudud Ul Islam AwanNo ratings yet
- L3 - Hardening Soil Models in PlaxisDocument33 pagesL3 - Hardening Soil Models in PlaxisOng Tai BoonNo ratings yet
- 17-Soft Soil Model - PlaxisDocument5 pages17-Soft Soil Model - PlaxisVa Ni SkyNo ratings yet
- GATE Previous Year Solved Paper PDFDocument74 pagesGATE Previous Year Solved Paper PDFBipradipDeyNo ratings yet
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument11 pagesInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringFabrizio MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Foundation Settlement ElasticDocument14 pagesFoundation Settlement Elasticxingze luNo ratings yet
- D4767.1278696-1 Compresion Triaxial CUDocument14 pagesD4767.1278696-1 Compresion Triaxial CUJuan Mario Claros QuispeNo ratings yet
- DDA JE Syllabus 2023Document3 pagesDDA JE Syllabus 2023Rahul ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- FoundationsDocument4 pagesFoundationsjo100% (2)
- Report-L & T-ALH-162-R3-okDocument32 pagesReport-L & T-ALH-162-R3-okShubham MauryaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering. 02 Soil CompressibilityDocument63 pagesFoundation Engineering. 02 Soil Compressibilitysammy lopezNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II Partial Differentiation 12 Hrs PDFDocument350 pagesUNIT - II Partial Differentiation 12 Hrs PDFbarbara_ropeNo ratings yet
- Copy Civil Eng Paper 2 JuneDocument35 pagesCopy Civil Eng Paper 2 JuneSamiullah M QaisraniNo ratings yet
- Astm D2850 23Document4 pagesAstm D2850 23Mence RistovskaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction and A Historical PerspectiveDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction and A Historical PerspectiveanittamariaroNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Settlement Analysis: 2B Influence of Plate 2B of Actual Footing Sand Soft Clay Illustration of Influence ZonesDocument6 pages3.3 Settlement Analysis: 2B Influence of Plate 2B of Actual Footing Sand Soft Clay Illustration of Influence ZoneslenanaNo ratings yet
- ARMA-18-462-Permeability and Porosity Changes in Unconsolidated Porous Medium Due To Variations of Confining Stress and TemperatureDocument7 pagesARMA-18-462-Permeability and Porosity Changes in Unconsolidated Porous Medium Due To Variations of Confining Stress and TemperatureAlejandra Arbelaez LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Settlement Calculation Data Refer To BH-3 For Settelment CalculationDocument4 pagesSettlement Calculation Data Refer To BH-3 For Settelment Calculationardian difaxNo ratings yet
- Pre-Bid Attach02-GB 50021-2009 Code For Investigation of Geotechnical EngineeringDocument276 pagesPre-Bid Attach02-GB 50021-2009 Code For Investigation of Geotechnical EngineeringArdion Fikri ZatamiNo ratings yet
- Settlement Behaviour of A Major Dam: November 2006Document11 pagesSettlement Behaviour of A Major Dam: November 2006Isabela BalanNo ratings yet
- 2D and 3D Consolidation - Biot Theory (OCT2011 Color)Document42 pages2D and 3D Consolidation - Biot Theory (OCT2011 Color)bsitlerNo ratings yet
- IS :2720 (Part 15) - 1986 (Reaffirmed 1997)Document19 pagesIS :2720 (Part 15) - 1986 (Reaffirmed 1997)giriNo ratings yet
- Prefabricated Vertical Drains, Volume 1Document124 pagesPrefabricated Vertical Drains, Volume 1Osvaldo VargasNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Settlement and ConsolidationDocument25 pages1.3 Settlement and ConsolidationBlessingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Discussion On Undrained Shear Strength of Soft SoilsDocument14 pagesChapter 3. Discussion On Undrained Shear Strength of Soft SoilsanasNo ratings yet
- Consolidation Behavior of Natural Soils Around PC Value - Long Term Consolidation TestDocument13 pagesConsolidation Behavior of Natural Soils Around PC Value - Long Term Consolidation TestJunaidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Op-13. Procedures For Design of Embankment: Work Instructions For EngineersDocument8 pagesOp-13. Procedures For Design of Embankment: Work Instructions For Engineersjinwook75No ratings yet
- Constant Rate of Strain ConsolidationDocument2 pagesConstant Rate of Strain ConsolidationDương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Dissipation Test - ENGDocument3 pagesDissipation Test - ENGADS ADSNo ratings yet