Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LESSON 5.3: Principles of Scientific Research Design: Capstone
LESSON 5.3: Principles of Scientific Research Design: Capstone
Uploaded by
BIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNOCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Study Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsFrom EverandStudy Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Principles of Experimental Design Types of Experimental Research DesignDocument1 pagePrinciples of Experimental Design Types of Experimental Research DesignHabeeb UddinNo ratings yet
- Design of Experiment (G2)Document26 pagesDesign of Experiment (G2)YANA UPADHYAYNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument6 pagesResearch DesignFatima-Ridziana AbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Experimental Designs in Statistics - Replication, Randomization & Local ControlDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Experimental Designs in Statistics - Replication, Randomization & Local ControlImran Afzal BhatNo ratings yet
- ECOLAPP NotesDocument29 pagesECOLAPP NotesyarahbitangNo ratings yet
- Research Cha 4 Long Essay-......Document11 pagesResearch Cha 4 Long Essay-......RINU E ONo ratings yet
- RM Unit 2Document10 pagesRM Unit 2Twinkal loteNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Engineering Experiments: Douglas C. MontgomeryDocument48 pagesDesign and Analysis of Engineering Experiments: Douglas C. MontgomeryRandhyRinconNo ratings yet
- 3rd QuarterDocument4 pages3rd Quarteriedon533No ratings yet
- Experimental Research 3.1Document3 pagesExperimental Research 3.1Jims CudinyerahNo ratings yet
- Research Reviewer Q2Document3 pagesResearch Reviewer Q2senjiNo ratings yet
- Syahrul Research DesignDocument5 pagesSyahrul Research DesignfahrurizasyahrulNo ratings yet
- 1 Doe TerminologiesDocument3 pages1 Doe TerminologiesSethu Malaravan K ENo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Design of Experiments PDFDocument9 pagesA Brief Introduction To Design of Experiments PDFjonathan2788No ratings yet
- Caps 12 Q2 0503 FDDocument15 pagesCaps 12 Q2 0503 FDUbertreffen SolilapsiNo ratings yet
- Experimental DesignDocument8 pagesExperimental DesignLavenia SarcenaNo ratings yet
- Munagapati V Experimentaldesign SummaryDocument3 pagesMunagapati V Experimentaldesign Summaryapi-694251611No ratings yet
- FINAL (PPT) - PR2 11-12 Q1 0101 - UNIT 1 - LESSON 1 - Qualities of Quantitative Research-2Document37 pagesFINAL (PPT) - PR2 11-12 Q1 0101 - UNIT 1 - LESSON 1 - Qualities of Quantitative Research-2irishcauilan27No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Designing ExperimentsDocument13 pagesGuidelines For Designing ExperimentsupenderNo ratings yet
- First Semester - MidtermsDocument28 pagesFirst Semester - MidtermsAshtey RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Anova Experimental Design AnalysisDocument31 pagesChapter4 Anova Experimental Design AnalysisAnup ŠářkarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoDocument36 pagesExperimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoTonette ArlesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 IntroductionDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Introductionmoneyheistberlin09No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Research Design 1 PDFDocument43 pagesLesson 5 Research Design 1 PDFjhonel ballerasNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- PR2 (Note - Reviewer)Document9 pagesPR2 (Note - Reviewer)Woxi BedineNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR 2Document2 pagesReviewer PR 2jet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Definition and Types of Quantitative ResearchDocument43 pagesDefinition and Types of Quantitative ResearchCrosel DavidNo ratings yet
- PSS - Researcj Methodology FinalsDocument2 pagesPSS - Researcj Methodology FinalsRuthyNo ratings yet
- Statistic 2018 Session2Document104 pagesStatistic 2018 Session2Mutiara KhalishNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Experimental DesignsDocument2 pagesBasic Principles of Experimental DesignsAnonymous AuvmxB100% (2)
- Design Experiments For MQL1Document15 pagesDesign Experiments For MQL1VishalDabhadeNo ratings yet
- ABE 057 ManualDocument84 pagesABE 057 ManualAlisidiq A. DisomaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Research DesignDocument28 pagesTopic 5 - Research DesignILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design ProcessDocument44 pagesEngineering Design ProcessQuyền PhạmNo ratings yet
- Pre Experimental DesignDocument6 pagesPre Experimental DesignJonn EngueroNo ratings yet
- Informative Digital Poster SampleDocument1 pageInformative Digital Poster Samplekcx6g8dzdjNo ratings yet
- Module IIIDocument49 pagesModule IIIdanielkeziah77No ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument12 pagesResearch ReviewerAlexis GarraezNo ratings yet
- Expp WSDDocument1 pageExpp WSD정유노No ratings yet
- Research II Q1 M5Document15 pagesResearch II Q1 M5eikomedleyNo ratings yet
- Design of ExperimentsDocument32 pagesDesign of Experimentsmeryroselicaros525No ratings yet
- (APP 2) Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchDocument1 page(APP 2) Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchMJ AlolorNo ratings yet
- Assignment PresentationDocument15 pagesAssignment Presentation21P410 - VARUN MNo ratings yet
- Methods of Research (Part Iii)Document6 pagesMethods of Research (Part Iii)Lala LalaNo ratings yet
- 9 Part32Document3 pages9 Part32arashameem60No ratings yet
- Experimental ResearchDocument50 pagesExperimental Researchliz8585100% (5)
- CHAPTER 9 - EXPERIMENTS - FinalDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 9 - EXPERIMENTS - FinalVJ DecanoNo ratings yet
- RCT3Document20 pagesRCT3siddhartha senNo ratings yet
- Main Goals of Research Quasi-Experimental Research DesignDocument8 pagesMain Goals of Research Quasi-Experimental Research DesignseanakkigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - ExperimentsDocument22 pagesChapter 9 - ExperimentsVALEN JOY DECANONo ratings yet
- Research II 3rd Quarter Reviewer Grade 8Document4 pagesResearch II 3rd Quarter Reviewer Grade 8Amelia Ria CanlasNo ratings yet
- Sampling TheoryDocument108 pagesSampling TheoryAbduli SalimuNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research DesignDocument51 pagesQuantitative Research DesignFarah BasemNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument24 pagesResearch DesignFiona Ashley MasanqueNo ratings yet
- Action Research and Experimental ResearchDocument16 pagesAction Research and Experimental ResearchVinjel LibradillaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 RevDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 RevChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Experimental Economics: Rethinking the RulesFrom EverandExperimental Economics: Rethinking the RulesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- GGGGGGGGGG: LESSON 2.3: Safety and Environmental Issues Related To ResearchDocument2 pagesGGGGGGGGGG: LESSON 2.3: Safety and Environmental Issues Related To ResearchBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.2: Plagiarism and Intellectual Property: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 2.2: Plagiarism and Intellectual Property: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
LESSON 5.3: Principles of Scientific Research Design: Capstone
LESSON 5.3: Principles of Scientific Research Design: Capstone
Uploaded by
BIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNOOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 5.3: Principles of Scientific Research Design: Capstone
LESSON 5.3: Principles of Scientific Research Design: Capstone
Uploaded by
BIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNOCopyright:
Available Formats
CAPSTONEIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
LESSON 5.3: Principles of Scientific Research Design
2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023
LECTURER: MR. ERIC PALMEROLA
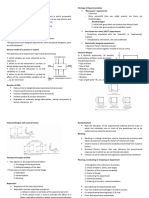
PRINCIPLES OF RESEARCH DESIGN C. LOCAL CONTROL
➢ Is the amount of balancing, blocking, and
A. RANDOMIZATION grouping of the experimental units.
➢ Is a random process of designation ➢ The primary purpose of local control is to
treatments to the experimental units or increase the efficiency of each assigned
samples in the study. experimental design by simply decreasing
➢ The main purpose of randomization is to the experimental error.
remove any form of bias and extraneous ➢ This involves the organization of groups
variation that cannot be controlled by the based on homogeneity and is somewhat
researchers. similar to creating a replicate.
➢ An example that can be used for
randomization is the assignment of a
number to each subject and randomly
drawing numbers as a selection process.
B. REPLICATION
➢ Is the process of repeating one basic
experiment. To simplify, it refers to another
set of complete runs for all the treatments
being tested in the experiment.
➢ Is important to secure a more accurate
estimate of the possible error present in
the experiment. At the same time, it
decreases the experimental error, while
increasing the precision of the measured
data.
➢ Example: each color of pot signifies a
different measurement to be done in the
experiment. The removal of variations in
this process is important for eliminating
errors.
Transcripted by: Bianca Leona Marie Puno
12 - Aristarchus Lessons
You might also like
- Study Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsFrom EverandStudy Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Principles of Experimental Design Types of Experimental Research DesignDocument1 pagePrinciples of Experimental Design Types of Experimental Research DesignHabeeb UddinNo ratings yet
- Design of Experiment (G2)Document26 pagesDesign of Experiment (G2)YANA UPADHYAYNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument6 pagesResearch DesignFatima-Ridziana AbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Experimental Designs in Statistics - Replication, Randomization & Local ControlDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Experimental Designs in Statistics - Replication, Randomization & Local ControlImran Afzal BhatNo ratings yet
- ECOLAPP NotesDocument29 pagesECOLAPP NotesyarahbitangNo ratings yet
- Research Cha 4 Long Essay-......Document11 pagesResearch Cha 4 Long Essay-......RINU E ONo ratings yet
- RM Unit 2Document10 pagesRM Unit 2Twinkal loteNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Engineering Experiments: Douglas C. MontgomeryDocument48 pagesDesign and Analysis of Engineering Experiments: Douglas C. MontgomeryRandhyRinconNo ratings yet
- 3rd QuarterDocument4 pages3rd Quarteriedon533No ratings yet
- Experimental Research 3.1Document3 pagesExperimental Research 3.1Jims CudinyerahNo ratings yet
- Research Reviewer Q2Document3 pagesResearch Reviewer Q2senjiNo ratings yet
- Syahrul Research DesignDocument5 pagesSyahrul Research DesignfahrurizasyahrulNo ratings yet
- 1 Doe TerminologiesDocument3 pages1 Doe TerminologiesSethu Malaravan K ENo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Design of Experiments PDFDocument9 pagesA Brief Introduction To Design of Experiments PDFjonathan2788No ratings yet
- Caps 12 Q2 0503 FDDocument15 pagesCaps 12 Q2 0503 FDUbertreffen SolilapsiNo ratings yet
- Experimental DesignDocument8 pagesExperimental DesignLavenia SarcenaNo ratings yet
- Munagapati V Experimentaldesign SummaryDocument3 pagesMunagapati V Experimentaldesign Summaryapi-694251611No ratings yet
- FINAL (PPT) - PR2 11-12 Q1 0101 - UNIT 1 - LESSON 1 - Qualities of Quantitative Research-2Document37 pagesFINAL (PPT) - PR2 11-12 Q1 0101 - UNIT 1 - LESSON 1 - Qualities of Quantitative Research-2irishcauilan27No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Designing ExperimentsDocument13 pagesGuidelines For Designing ExperimentsupenderNo ratings yet
- First Semester - MidtermsDocument28 pagesFirst Semester - MidtermsAshtey RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Anova Experimental Design AnalysisDocument31 pagesChapter4 Anova Experimental Design AnalysisAnup ŠářkarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoDocument36 pagesExperimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoTonette ArlesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 IntroductionDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Introductionmoneyheistberlin09No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Research Design 1 PDFDocument43 pagesLesson 5 Research Design 1 PDFjhonel ballerasNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- PR2 (Note - Reviewer)Document9 pagesPR2 (Note - Reviewer)Woxi BedineNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR 2Document2 pagesReviewer PR 2jet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Definition and Types of Quantitative ResearchDocument43 pagesDefinition and Types of Quantitative ResearchCrosel DavidNo ratings yet
- PSS - Researcj Methodology FinalsDocument2 pagesPSS - Researcj Methodology FinalsRuthyNo ratings yet
- Statistic 2018 Session2Document104 pagesStatistic 2018 Session2Mutiara KhalishNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Experimental DesignsDocument2 pagesBasic Principles of Experimental DesignsAnonymous AuvmxB100% (2)
- Design Experiments For MQL1Document15 pagesDesign Experiments For MQL1VishalDabhadeNo ratings yet
- ABE 057 ManualDocument84 pagesABE 057 ManualAlisidiq A. DisomaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Research DesignDocument28 pagesTopic 5 - Research DesignILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design ProcessDocument44 pagesEngineering Design ProcessQuyền PhạmNo ratings yet
- Pre Experimental DesignDocument6 pagesPre Experimental DesignJonn EngueroNo ratings yet
- Informative Digital Poster SampleDocument1 pageInformative Digital Poster Samplekcx6g8dzdjNo ratings yet
- Module IIIDocument49 pagesModule IIIdanielkeziah77No ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument12 pagesResearch ReviewerAlexis GarraezNo ratings yet
- Expp WSDDocument1 pageExpp WSD정유노No ratings yet
- Research II Q1 M5Document15 pagesResearch II Q1 M5eikomedleyNo ratings yet
- Design of ExperimentsDocument32 pagesDesign of Experimentsmeryroselicaros525No ratings yet
- (APP 2) Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchDocument1 page(APP 2) Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchMJ AlolorNo ratings yet
- Assignment PresentationDocument15 pagesAssignment Presentation21P410 - VARUN MNo ratings yet
- Methods of Research (Part Iii)Document6 pagesMethods of Research (Part Iii)Lala LalaNo ratings yet
- 9 Part32Document3 pages9 Part32arashameem60No ratings yet
- Experimental ResearchDocument50 pagesExperimental Researchliz8585100% (5)
- CHAPTER 9 - EXPERIMENTS - FinalDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 9 - EXPERIMENTS - FinalVJ DecanoNo ratings yet
- RCT3Document20 pagesRCT3siddhartha senNo ratings yet
- Main Goals of Research Quasi-Experimental Research DesignDocument8 pagesMain Goals of Research Quasi-Experimental Research DesignseanakkigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - ExperimentsDocument22 pagesChapter 9 - ExperimentsVALEN JOY DECANONo ratings yet
- Research II 3rd Quarter Reviewer Grade 8Document4 pagesResearch II 3rd Quarter Reviewer Grade 8Amelia Ria CanlasNo ratings yet
- Sampling TheoryDocument108 pagesSampling TheoryAbduli SalimuNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research DesignDocument51 pagesQuantitative Research DesignFarah BasemNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument24 pagesResearch DesignFiona Ashley MasanqueNo ratings yet
- Action Research and Experimental ResearchDocument16 pagesAction Research and Experimental ResearchVinjel LibradillaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 RevDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 RevChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Experimental Economics: Rethinking the RulesFrom EverandExperimental Economics: Rethinking the RulesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- GGGGGGGGGG: LESSON 2.3: Safety and Environmental Issues Related To ResearchDocument2 pagesGGGGGGGGGG: LESSON 2.3: Safety and Environmental Issues Related To ResearchBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.2: Plagiarism and Intellectual Property: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 2.2: Plagiarism and Intellectual Property: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.2: Scientific Research Design: CapstoneBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet