Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulas
Formulas
Uploaded by
Nujhat TabassumCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyDocument64 pagesNephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyMohammed Risq100% (2)
- Nephrology FormulasDocument3 pagesNephrology FormulasM Patel0% (1)
- Disorders of SodiumDocument38 pagesDisorders of SodiumMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Children's Purification CourseDocument160 pagesChildren's Purification Coursemujtabatm1662100% (1)
- Pediatric NotesDocument45 pagesPediatric NoteskkkssbbNo ratings yet
- Dripselec ImbalancesDocument46 pagesDripselec ImbalancesJennicaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Haerani Rasyid FK Unhas 2016Document46 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Haerani Rasyid FK Unhas 2016Ana Yusriana AzzahraNo ratings yet
- 1-Must Be Withen Normal Body Temperature 2-Must Be Clear, Strile, No Turbidity &no P.P.T 3-Must Be Injected Slowly I/VDocument3 pages1-Must Be Withen Normal Body Temperature 2-Must Be Clear, Strile, No Turbidity &no P.P.T 3-Must Be Injected Slowly I/VMorad ImadNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes SummaryDocument23 pagesElectrolytes SummaryDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- RCPCH TAS Renal Anatomy and Physiology Patrick DaviesDocument25 pagesRCPCH TAS Renal Anatomy and Physiology Patrick DaviesWaleed abdul hayeeNo ratings yet
- Nephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyDocument64 pagesNephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafyrazan moneerNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Renal SystemDocument30 pagesFunctions of The Renal SystemBlessing ChirwaNo ratings yet
- Nursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2Document6 pagesNursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2chubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Urine FormationDocument49 pagesUrine FormationMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Fluid - Electrolytes Cram SheetDocument20 pagesFluid - Electrolytes Cram SheetMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Water Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticDocument3 pagesWater Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticMark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument42 pagesAcute Kidney InjurysushmaNo ratings yet
- Biohemija Bubrega2011Document94 pagesBiohemija Bubrega2011Dejan Todorovic100% (1)
- ELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Document3 pagesELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Alondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan Pada AnakDocument48 pagesTerapi Cairan Pada AnakAstri Novia RizqiNo ratings yet
- DKA in AdultsDocument1 pageDKA in AdultsAhmed AdelNo ratings yet
- Fluid & Electrolytes Cram SheetDocument20 pagesFluid & Electrolytes Cram SheetTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- MS - Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesMS - Fluids and ElectrolytesJOHN LOYD CASTILLONo ratings yet
- ADA Management Adults DKA - UpToDateDocument1 pageADA Management Adults DKA - UpToDatewaldirNo ratings yet
- W2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Document6 pagesW2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Syximsh FPNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan Dalam Praktek Sehari-Hari Oleh DR - Sumara Niman, SP - AnDocument49 pagesTerapi Cairan Dalam Praktek Sehari-Hari Oleh DR - Sumara Niman, SP - AnRiony GusbaniansyahNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument84 pagesRenal PhysiologyFauzan HafizNo ratings yet
- Clinical MicroDocument9 pagesClinical Microbelle navalNo ratings yet
- Intern Survival GuideDocument12 pagesIntern Survival GuideHunter RossNo ratings yet
- Kidney Dysfunction: Copotoiu SmaDocument44 pagesKidney Dysfunction: Copotoiu SmaAdriana VillarrealNo ratings yet
- D - Water and Electrolyte Balance of KidneyDocument6 pagesD - Water and Electrolyte Balance of KidneyNav ThiranNo ratings yet
- LS607 Module 7 Renal PhysiologyDocument24 pagesLS607 Module 7 Renal PhysiologyasmaaalmesaifriNo ratings yet
- Creatinine EstimationDocument16 pagesCreatinine Estimationishapriyadarshini2004No ratings yet
- EarDocument11 pagesEarakku.rajvanshi86No ratings yet
- AKI, CKD SummaryDocument4 pagesAKI, CKD SummaryMuathNo ratings yet
- The Patient With Hypokalemia or HyperkalemiaDocument5 pagesThe Patient With Hypokalemia or HyperkalemiaJennifer MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Balance Cairan Final.Document41 pagesBalance Cairan Final.Niqko Bayu PrakarsaNo ratings yet
- EPALS DKA Flowchart Jan 23 V4Document1 pageEPALS DKA Flowchart Jan 23 V4Miguel BaiaNo ratings yet
- Urine Electrolytes PDFDocument26 pagesUrine Electrolytes PDFNyomanGinaHennyKristiantiNo ratings yet
- Resuscitare Sepsis RezidentiDocument51 pagesResuscitare Sepsis RezidentiMihai PopescuNo ratings yet
- 2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityDocument16 pages2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityGoez Aditya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- CirrhosisDocument2 pagesCirrhosisKaja MatovinovicNo ratings yet
- 3.3 KidneyDocument54 pages3.3 KidneySurvin KandhariNo ratings yet
- Aki - CKDDocument51 pagesAki - CKDAyu Luh Ratri WeningNo ratings yet
- Biokimia KardioDocument98 pagesBiokimia KardioirmaNo ratings yet
- DKACalculatorDocument1 pageDKACalculatorRitch BassNo ratings yet
- Kdigo Criteria For Aki: (Pick Highest Stage) : Stage 1: Inc in Serum CreatinineDocument3 pagesKdigo Criteria For Aki: (Pick Highest Stage) : Stage 1: Inc in Serum CreatinineJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument36 pagesUrinalysisMarl EstradaNo ratings yet
- CC1 LAB Creatinine PDFDocument34 pagesCC1 LAB Creatinine PDFAlan Daniel EspañaNo ratings yet
- ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY. 2016m UNISMUHDocument26 pagesACUTE KIDNEY INJURY. 2016m UNISMUHWhulandary DyaswaraNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument32 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryPremKumar ShamugamNo ratings yet
- NA 01 - Renal PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesNA 01 - Renal PathophysiologyMaggie CacieNo ratings yet
- 11.0 Acute Kidney InjuryDocument26 pages11.0 Acute Kidney InjuryHeny KsNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Urine Production. Urine Composition in Health and Pathologies. Biochemistry of Water and Salts TurnoverDocument73 pagesMechanism of Urine Production. Urine Composition in Health and Pathologies. Biochemistry of Water and Salts TurnoverRAJA RAJANNo ratings yet
- Sia DH FinalDocument26 pagesSia DH FinalJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- GA4420 00 - Creatinine Enzymatic - 0Document2 pagesGA4420 00 - Creatinine Enzymatic - 0Abdalrhman FarajNo ratings yet
- Di, Siadh, CSW Tabel PerbedaanDocument17 pagesDi, Siadh, CSW Tabel PerbedaanMichael Tambunan100% (1)
- Urinary Stones: Medical and Surgical ManagementFrom EverandUrinary Stones: Medical and Surgical ManagementMichael GrassoNo ratings yet
- How To Collect Anterior Nasal Specimen For COVID 19Document2 pagesHow To Collect Anterior Nasal Specimen For COVID 19Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 15 Jan 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 15 Jan 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Drug Dose Pediatrics NephrologyDocument16 pagesDrug Dose Pediatrics NephrologyNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Vvimp: Investigationsto Differentiate Ypes of Renal (Rta)Document1 pageVvimp: Investigationsto Differentiate Ypes of Renal (Rta)Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Editor Deputy EditorDocument1 pageEditor Deputy EditorNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum: Kidney International (2023) 103, 798Document1 pageCorrigendum: Kidney International (2023) 103, 798Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment of ReviewersDocument7 pagesAcknowledgment of ReviewersNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- 2.5 EnzymesDocument42 pages2.5 EnzymesHelena GlanvilleNo ratings yet
- B5M2Q1 CompilationDocument22 pagesB5M2Q1 CompilationMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Soalan BK1 Finalyre15Document12 pagesSoalan BK1 Finalyre15hanafizaNo ratings yet
- cc2861 PDFDocument6 pagescc2861 PDFArturo Eduardo Huarcaya OntiverosNo ratings yet
- (Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrDocument378 pages(Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrGustavo Sá MottaNo ratings yet
- SGLT2 Inhibitors and Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefit: A State-Of-The-Art ReviewDocument10 pagesSGLT2 Inhibitors and Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefit: A State-Of-The-Art ReviewLucian SiriteanuNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument26 pagesAnatomyAvinashNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat B. Ingg KLS 9 2022-2023Document6 pagesSoal Pat B. Ingg KLS 9 2022-2023Muhammad Khanif FurqonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Notes On Endocrine DrugsDocument2 pagesPharmacology: Notes On Endocrine DrugsByron ChuNo ratings yet
- Made By:: Khloud A.elbasetDocument30 pagesMade By:: Khloud A.elbasetMunachande KanondoNo ratings yet
- +I$ GT G$: Ila +reggseragiagiggDocument7 pages+I$ GT G$: Ila +reggseragiagiggDorisjuarsa SmsNo ratings yet
- Desmoid Tumor PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDesmoid Tumor Pathophysiologyjo_annamae4413No ratings yet
- Fins of FishesDocument12 pagesFins of Fishesrano khanNo ratings yet
- FOR5Document7 pagesFOR5Nacyl LanceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson Frank100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1bDocument15 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1bNormal Fan100% (1)
- Protos, Meaning of The First Rank' or of PrimeDocument16 pagesProtos, Meaning of The First Rank' or of Primepinkish7_preciousNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Stress and Sport PerformanceDocument6 pagesOxidative Stress and Sport PerformanceFatur Sang Ahli WarNo ratings yet
- KU - Lesson 4A - DRUGS USED IN ANAEMIADocument60 pagesKU - Lesson 4A - DRUGS USED IN ANAEMIAchristine gisembaNo ratings yet
- Biology EOC Review Answers Goal 2Document5 pagesBiology EOC Review Answers Goal 2wbvnpp8hzzNo ratings yet
- Sleeping Habits: HH Mahanidhi SwamiDocument3 pagesSleeping Habits: HH Mahanidhi SwamiJeevanNo ratings yet
- The Anticoagulant Activity of Pineapple (Ananas Comosus) Core Extract in Human Blood Samples Full ChapterDocument40 pagesThe Anticoagulant Activity of Pineapple (Ananas Comosus) Core Extract in Human Blood Samples Full Chaptertfb31058No ratings yet
- Urine FormationDocument14 pagesUrine FormationWaziri MbarukuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OSPE Revision (Team WRK) PDFDocument15 pagesAnatomy OSPE Revision (Team WRK) PDFAbdi Ñãśìr Møhàmèď ŚàĺàhNo ratings yet
- Blood Gases and Acid-Base BalanceDocument11 pagesBlood Gases and Acid-Base BalanceREMAN ALINGASANo ratings yet
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument4 pagesErythrocyte Sedimentation RateCarlos LemosNo ratings yet
- Surgical Approaches To The Forearm: Robert Strauch MDDocument18 pagesSurgical Approaches To The Forearm: Robert Strauch MDMichael John TedjajuwanaNo ratings yet
- Phinma - University of PangasinanDocument2 pagesPhinma - University of PangasinanRonnie De Vera IINo ratings yet
- My Power Subliminals DescriptionsDocument13 pagesMy Power Subliminals DescriptionsAayansh RihaanNo ratings yet
Formulas
Formulas
Uploaded by
Nujhat TabassumOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas
Formulas
Uploaded by
Nujhat TabassumCopyright:
Available Formats
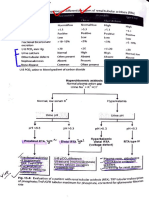
Appencdices B69
APPENDIX u: IMPORTANT FORMULAE
Estimated glomerular x height (cm) n g no managenenit
Altration rate (GFR) Sserum creatininef(mg/dl)
serum creainina chronic kidney disease
where k- 043
Serum anion gap Na' (Cl+HCO,) Normal value 6-12 mEq/l
Urine anion gap Na +K-C Index of urinary NH,' excretion
Plasma osmolality ucose Normal 280-285 mOsrm/kg
2(Na") Approrimnates twice plasrna Na
BUN blood urea nitrogen, mg/dl
Free water deficit Total body water x[(sodium Total body water = 0.6 m (kg)
concentration/140) 1 )
Plasma volume 0.065 x weight (kg) x ( - Approximately 30-40 ml/kg
hematocrit)
Urinary potassidm Urine K7 (urine K' + urine Na") Value >0.6 (60%) suggests
index nypovolemia
Transtubular UrineK xplasma osmolality Reflects aldosterone mediated
1staiksecretion. Normal <2.5
potassium gradient Plasma K"x urine osmolality
(TTKG) during hypokalemia;>7 in
nyperkalemia
Fractional excretion Urine Na' x plasma creatinine <1% in volume
contraction with
ppropriate renal Na' retentionn
of sodium Plasmà
Na xurine creainine
Calcium correction for 08x (4.0-patient albumin)+
Serum calcium
hypoalbuminemia
Infusate Na": Concentration of Na
Change in sodium
Infusate Na"-serum Na in fluid intused
Total body
i infusion o water +1)
Age + 2) x 30 mL Infants:Capacity= 7 * weight (kg)
Expected bladder
capacity (2-12 years
Ordge
*The fractional excretion of any substance can be calculated similarly
Appenciices 569
APPENDIX ll: IMPORTANT FORMULAE
Formula Remarks
Staging and nanagement of
Estimated glomerular
fhltration rate (GFR)
GFR kxheight (cm)
serum creatinine (mg/dl) chronic kidney disease
where k =0.43
Serum anion gap Na -(Cl+ HCO,) Normal value 6-12 mEq/l
Urine anion gap Na+K'-Cl Index of urinary NH, excretion
Plasma osmolality 2 (Na") +0N glucose Normal 280-285 mOsm/kg
2.8 8 Approximates twice plasma Na
BUN blood urea nitrogen, mg/dL
Free water deficit Total body water x [(sodium Total body water = 0.6 x wt (kg)
concentration/140) -1]
weight (kg) x (1- Approximately 30-40 mL/kg
Plasma volume 0.065 x
hematocrit)
Urinary potassiumn Urine K/ (urine K*+ urine Na) Value >0.6 (60%) suggests
index hypovolemia
Transtubular Reflects aldosterone mediated
Urine K x plasma osmolality distal K* secretion. Normal <2.5
potassium gradient Plasma Kx urine osmolality
(IKG) during hypokalemia;>7 in
hyperkalemia
<1% in volume cóntraction with
Fractional excretion
Urine Nax plasma creatinine appropriate renal Na" retention
of sodium* Plasma Na' x urine creatinine
Calcium correction for 0.8 x (4.0 patient albumin)+
serum calcium
hypoalbuminemia
Infusate Na': Concentration of Na"
Change in sodium Infusate Na" -serum Na")
concentration in fluid infused
(Total body water + 1)
following infusion of
1L solution
(Age+2) x 30 mL Infants: Capacity = 7 x weight (kg)
Expected bladder
capacity (2-12 years
Oage)
The fractional excretion of any substance can be calculated similariy
You might also like
- Nephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyDocument64 pagesNephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyMohammed Risq100% (2)
- Nephrology FormulasDocument3 pagesNephrology FormulasM Patel0% (1)
- Disorders of SodiumDocument38 pagesDisorders of SodiumMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Children's Purification CourseDocument160 pagesChildren's Purification Coursemujtabatm1662100% (1)
- Pediatric NotesDocument45 pagesPediatric NoteskkkssbbNo ratings yet
- Dripselec ImbalancesDocument46 pagesDripselec ImbalancesJennicaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Haerani Rasyid FK Unhas 2016Document46 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Haerani Rasyid FK Unhas 2016Ana Yusriana AzzahraNo ratings yet
- 1-Must Be Withen Normal Body Temperature 2-Must Be Clear, Strile, No Turbidity &no P.P.T 3-Must Be Injected Slowly I/VDocument3 pages1-Must Be Withen Normal Body Temperature 2-Must Be Clear, Strile, No Turbidity &no P.P.T 3-Must Be Injected Slowly I/VMorad ImadNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes SummaryDocument23 pagesElectrolytes SummaryDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- RCPCH TAS Renal Anatomy and Physiology Patrick DaviesDocument25 pagesRCPCH TAS Renal Anatomy and Physiology Patrick DaviesWaleed abdul hayeeNo ratings yet
- Nephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyDocument64 pagesNephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafyrazan moneerNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Renal SystemDocument30 pagesFunctions of The Renal SystemBlessing ChirwaNo ratings yet
- Nursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2Document6 pagesNursing 75 Fluid and Electrolyte Exam 2chubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Urine FormationDocument49 pagesUrine FormationMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Fluid - Electrolytes Cram SheetDocument20 pagesFluid - Electrolytes Cram SheetMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Water Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticDocument3 pagesWater Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticMark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument42 pagesAcute Kidney InjurysushmaNo ratings yet
- Biohemija Bubrega2011Document94 pagesBiohemija Bubrega2011Dejan Todorovic100% (1)
- ELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Document3 pagesELECTROLYTES (Na & K)Alondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan Pada AnakDocument48 pagesTerapi Cairan Pada AnakAstri Novia RizqiNo ratings yet
- DKA in AdultsDocument1 pageDKA in AdultsAhmed AdelNo ratings yet
- Fluid & Electrolytes Cram SheetDocument20 pagesFluid & Electrolytes Cram SheetTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- MS - Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesMS - Fluids and ElectrolytesJOHN LOYD CASTILLONo ratings yet
- ADA Management Adults DKA - UpToDateDocument1 pageADA Management Adults DKA - UpToDatewaldirNo ratings yet
- W2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Document6 pagesW2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Syximsh FPNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan Dalam Praktek Sehari-Hari Oleh DR - Sumara Niman, SP - AnDocument49 pagesTerapi Cairan Dalam Praktek Sehari-Hari Oleh DR - Sumara Niman, SP - AnRiony GusbaniansyahNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument84 pagesRenal PhysiologyFauzan HafizNo ratings yet
- Clinical MicroDocument9 pagesClinical Microbelle navalNo ratings yet
- Intern Survival GuideDocument12 pagesIntern Survival GuideHunter RossNo ratings yet
- Kidney Dysfunction: Copotoiu SmaDocument44 pagesKidney Dysfunction: Copotoiu SmaAdriana VillarrealNo ratings yet
- D - Water and Electrolyte Balance of KidneyDocument6 pagesD - Water and Electrolyte Balance of KidneyNav ThiranNo ratings yet
- LS607 Module 7 Renal PhysiologyDocument24 pagesLS607 Module 7 Renal PhysiologyasmaaalmesaifriNo ratings yet
- Creatinine EstimationDocument16 pagesCreatinine Estimationishapriyadarshini2004No ratings yet
- EarDocument11 pagesEarakku.rajvanshi86No ratings yet
- AKI, CKD SummaryDocument4 pagesAKI, CKD SummaryMuathNo ratings yet
- The Patient With Hypokalemia or HyperkalemiaDocument5 pagesThe Patient With Hypokalemia or HyperkalemiaJennifer MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Balance Cairan Final.Document41 pagesBalance Cairan Final.Niqko Bayu PrakarsaNo ratings yet
- EPALS DKA Flowchart Jan 23 V4Document1 pageEPALS DKA Flowchart Jan 23 V4Miguel BaiaNo ratings yet
- Urine Electrolytes PDFDocument26 pagesUrine Electrolytes PDFNyomanGinaHennyKristiantiNo ratings yet
- Resuscitare Sepsis RezidentiDocument51 pagesResuscitare Sepsis RezidentiMihai PopescuNo ratings yet
- 2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityDocument16 pages2 Fluid and Electrolyte AbnormalityGoez Aditya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- CirrhosisDocument2 pagesCirrhosisKaja MatovinovicNo ratings yet
- 3.3 KidneyDocument54 pages3.3 KidneySurvin KandhariNo ratings yet
- Aki - CKDDocument51 pagesAki - CKDAyu Luh Ratri WeningNo ratings yet
- Biokimia KardioDocument98 pagesBiokimia KardioirmaNo ratings yet
- DKACalculatorDocument1 pageDKACalculatorRitch BassNo ratings yet
- Kdigo Criteria For Aki: (Pick Highest Stage) : Stage 1: Inc in Serum CreatinineDocument3 pagesKdigo Criteria For Aki: (Pick Highest Stage) : Stage 1: Inc in Serum CreatinineJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument36 pagesUrinalysisMarl EstradaNo ratings yet
- CC1 LAB Creatinine PDFDocument34 pagesCC1 LAB Creatinine PDFAlan Daniel EspañaNo ratings yet
- ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY. 2016m UNISMUHDocument26 pagesACUTE KIDNEY INJURY. 2016m UNISMUHWhulandary DyaswaraNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument32 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryPremKumar ShamugamNo ratings yet
- NA 01 - Renal PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesNA 01 - Renal PathophysiologyMaggie CacieNo ratings yet
- 11.0 Acute Kidney InjuryDocument26 pages11.0 Acute Kidney InjuryHeny KsNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Urine Production. Urine Composition in Health and Pathologies. Biochemistry of Water and Salts TurnoverDocument73 pagesMechanism of Urine Production. Urine Composition in Health and Pathologies. Biochemistry of Water and Salts TurnoverRAJA RAJANNo ratings yet
- Sia DH FinalDocument26 pagesSia DH FinalJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- GA4420 00 - Creatinine Enzymatic - 0Document2 pagesGA4420 00 - Creatinine Enzymatic - 0Abdalrhman FarajNo ratings yet
- Di, Siadh, CSW Tabel PerbedaanDocument17 pagesDi, Siadh, CSW Tabel PerbedaanMichael Tambunan100% (1)
- Urinary Stones: Medical and Surgical ManagementFrom EverandUrinary Stones: Medical and Surgical ManagementMichael GrassoNo ratings yet
- How To Collect Anterior Nasal Specimen For COVID 19Document2 pagesHow To Collect Anterior Nasal Specimen For COVID 19Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 18 Feb 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 15 Jan 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 15 Jan 2023Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Drug Dose Pediatrics NephrologyDocument16 pagesDrug Dose Pediatrics NephrologyNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Vvimp: Investigationsto Differentiate Ypes of Renal (Rta)Document1 pageVvimp: Investigationsto Differentiate Ypes of Renal (Rta)Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Editor Deputy EditorDocument1 pageEditor Deputy EditorNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum: Kidney International (2023) 103, 798Document1 pageCorrigendum: Kidney International (2023) 103, 798Nujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment of ReviewersDocument7 pagesAcknowledgment of ReviewersNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- 2.5 EnzymesDocument42 pages2.5 EnzymesHelena GlanvilleNo ratings yet
- B5M2Q1 CompilationDocument22 pagesB5M2Q1 CompilationMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Soalan BK1 Finalyre15Document12 pagesSoalan BK1 Finalyre15hanafizaNo ratings yet
- cc2861 PDFDocument6 pagescc2861 PDFArturo Eduardo Huarcaya OntiverosNo ratings yet
- (Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrDocument378 pages(Dahlem Workshop Reports Life Sciences Research Report 20) T. a. Sears (Auth.), T. a. Sears (Eds.) - Neuronal-glial Cell Interrelationships_ Report of the Dahlem Workshop on Neuronal-glial Cell InterrGustavo Sá MottaNo ratings yet
- SGLT2 Inhibitors and Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefit: A State-Of-The-Art ReviewDocument10 pagesSGLT2 Inhibitors and Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefit: A State-Of-The-Art ReviewLucian SiriteanuNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument26 pagesAnatomyAvinashNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat B. Ingg KLS 9 2022-2023Document6 pagesSoal Pat B. Ingg KLS 9 2022-2023Muhammad Khanif FurqonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Notes On Endocrine DrugsDocument2 pagesPharmacology: Notes On Endocrine DrugsByron ChuNo ratings yet
- Made By:: Khloud A.elbasetDocument30 pagesMade By:: Khloud A.elbasetMunachande KanondoNo ratings yet
- +I$ GT G$: Ila +reggseragiagiggDocument7 pages+I$ GT G$: Ila +reggseragiagiggDorisjuarsa SmsNo ratings yet
- Desmoid Tumor PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDesmoid Tumor Pathophysiologyjo_annamae4413No ratings yet
- Fins of FishesDocument12 pagesFins of Fishesrano khanNo ratings yet
- FOR5Document7 pagesFOR5Nacyl LanceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson Frank100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1bDocument15 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1bNormal Fan100% (1)
- Protos, Meaning of The First Rank' or of PrimeDocument16 pagesProtos, Meaning of The First Rank' or of Primepinkish7_preciousNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Stress and Sport PerformanceDocument6 pagesOxidative Stress and Sport PerformanceFatur Sang Ahli WarNo ratings yet
- KU - Lesson 4A - DRUGS USED IN ANAEMIADocument60 pagesKU - Lesson 4A - DRUGS USED IN ANAEMIAchristine gisembaNo ratings yet
- Biology EOC Review Answers Goal 2Document5 pagesBiology EOC Review Answers Goal 2wbvnpp8hzzNo ratings yet
- Sleeping Habits: HH Mahanidhi SwamiDocument3 pagesSleeping Habits: HH Mahanidhi SwamiJeevanNo ratings yet
- The Anticoagulant Activity of Pineapple (Ananas Comosus) Core Extract in Human Blood Samples Full ChapterDocument40 pagesThe Anticoagulant Activity of Pineapple (Ananas Comosus) Core Extract in Human Blood Samples Full Chaptertfb31058No ratings yet
- Urine FormationDocument14 pagesUrine FormationWaziri MbarukuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OSPE Revision (Team WRK) PDFDocument15 pagesAnatomy OSPE Revision (Team WRK) PDFAbdi Ñãśìr Møhàmèď ŚàĺàhNo ratings yet
- Blood Gases and Acid-Base BalanceDocument11 pagesBlood Gases and Acid-Base BalanceREMAN ALINGASANo ratings yet
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument4 pagesErythrocyte Sedimentation RateCarlos LemosNo ratings yet
- Surgical Approaches To The Forearm: Robert Strauch MDDocument18 pagesSurgical Approaches To The Forearm: Robert Strauch MDMichael John TedjajuwanaNo ratings yet
- Phinma - University of PangasinanDocument2 pagesPhinma - University of PangasinanRonnie De Vera IINo ratings yet
- My Power Subliminals DescriptionsDocument13 pagesMy Power Subliminals DescriptionsAayansh RihaanNo ratings yet