Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology
Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology
Uploaded by
carlossaavedraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lechon Manok Business Planning Calculator - Final Version With Inventory - UpdatedDocument19 pagesLechon Manok Business Planning Calculator - Final Version With Inventory - UpdatedF Anton Nicolas50% (2)
- A Case Study On Starbucks: Delivering Customer ServiceDocument8 pagesA Case Study On Starbucks: Delivering Customer ServiceNHUNG LE THI QUYNHNo ratings yet
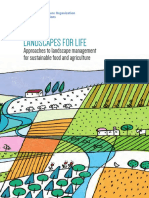
- Landscape For LifeDocument56 pagesLandscape For LifeCalendil LophianNo ratings yet
- Customer Value Propositions in Business Markets PDFDocument4 pagesCustomer Value Propositions in Business Markets PDFjaimequintoNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis On Ecommerce of JapanDocument2 pagesSWOT Analysis On Ecommerce of JapanTenzin Chogyel, BFound [Cohort2017 RTC]No ratings yet
- Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology ENGDocument1 pagePoster 13 Principles of Agroecology ENGTATIANA BUENO PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Implementing Conservation AgricultureDocument2 pagesImplementing Conservation AgricultureDomenico BevilacquaNo ratings yet
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2014Document12 pagesFAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2014Marcelo LouresNo ratings yet
- Pangniban Chapter 6 Quiz 1Document7 pagesPangniban Chapter 6 Quiz 1Lovely PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Reform ProposalDocument1 pageReform ProposalMichaela EsmeroNo ratings yet
- A Sus - Agric. An Introduction - Id.enDocument8 pagesA Sus - Agric. An Introduction - Id.ensecret angelNo ratings yet
- Armscaping: TO Nhance Iological OntrolDocument40 pagesArmscaping: TO Nhance Iological OntrolRex DufourNo ratings yet
- 2020 Food Security Standard FSS ENGDocument8 pages2020 Food Security Standard FSS ENGedwar tinocoNo ratings yet
- Manta Impact Assessment - Bahasa IndonesiaDocument1 pageManta Impact Assessment - Bahasa Indonesiaafwan shadriNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document5 pagesAssignment No.1Farrukh MuneerNo ratings yet
- Grade 8-Design Thinking WorksheetDocument4 pagesGrade 8-Design Thinking WorksheetKeshav Chaitan VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- Agro - Ecology The Virtuous Food Cycle: A Green Cooperative EconomyDocument1 pageAgro - Ecology The Virtuous Food Cycle: A Green Cooperative EconomyTyler DurdenNo ratings yet
- The Significance of Consumer's Awareness AboutDocument12 pagesThe Significance of Consumer's Awareness AboutNhud GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Agriculture: An Introduction: AttraDocument8 pagesSustainable Agriculture: An Introduction: AttraFiDe BlAckNo ratings yet
- Pillada Supplemental ScoresDocument14 pagesPillada Supplemental ScoresIIHC SMAW NC II LUCEÑA, ANGEL LANCE JERICHO A.No ratings yet
- Santos e Guarneiri - Social Indicators Short Supply ChainsDocument19 pagesSantos e Guarneiri - Social Indicators Short Supply ChainsIreneNo ratings yet
- Brochure Final - Updated - Million - Final For PrintDocument6 pagesBrochure Final - Updated - Million - Final For PrintVishnu ReddyNo ratings yet
- India's Rainfed Farming Variability and DiversityDocument4 pagesIndia's Rainfed Farming Variability and DiversityAshutosh LandeNo ratings yet
- Giannakas Yiannaka 2023 Food Fraud Causes Consequences and Deterrence StrategiesDocument23 pagesGiannakas Yiannaka 2023 Food Fraud Causes Consequences and Deterrence StrategiesJorge GarzaNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Principles of Integrated Farm SystemDocument6 pagesConcepts and Principles of Integrated Farm SystemIRISH BURGOSNo ratings yet
- Pillada Supplemental-ScoresDocument13 pagesPillada Supplemental-ScoresIIHC SMAW NC II LUCEÑA, ANGEL LANCE JERICHO A.No ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument1 pageMapa Conceptualmari peñaNo ratings yet
- Farming Systems: That Save and GrowDocument2 pagesFarming Systems: That Save and GrowNabhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 17312IIEDDocument4 pages17312IIEDmuhidinhawlet76No ratings yet
- Agriculture Week SaluteDocument16 pagesAgriculture Week SaluteThe Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Sustainability, ConceptsDocument19 pagesAgricultural Sustainability, Conceptswavin pe80No ratings yet
- Final 1Document19 pagesFinal 1SHOBHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Em PDFDocument17 pagesEm PDFMathiasrobby09No ratings yet
- Principles For Responsible Investment in Agriculture and Food SystemsDocument32 pagesPrinciples For Responsible Investment in Agriculture and Food SystemsAtos DiasNo ratings yet
- Pendahuluan Pertanian BerkelanjutanDocument89 pagesPendahuluan Pertanian BerkelanjutanMuhammad FadillahNo ratings yet
- Cs39 Triptico Minam Final RetiraDocument1 pageCs39 Triptico Minam Final RetiraLuis VillarNo ratings yet
- Giri Pragati ProgramDocument4 pagesGiri Pragati ProgramAksha RaviNo ratings yet
- Global Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel 09.07.05Document19 pagesGlobal Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel 09.07.05adelineo vlog ONo ratings yet
- Global Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel PDFDocument19 pagesGlobal Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel PDFPuneet KujurNo ratings yet
- PES Implementation in FarmDocument5 pagesPES Implementation in FarmManish NairNo ratings yet
- Commitment of SM Foundation Inc. On Livelihood Development: It's Effect To Its BenefactorDocument8 pagesCommitment of SM Foundation Inc. On Livelihood Development: It's Effect To Its BenefactorJomii SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Cotton Production of Cotton BAYER PDFDocument17 pagesSustainable Cotton Production of Cotton BAYER PDFSalil SheikhNo ratings yet
- Agrifood Booklet Series 2 Sustainable AgricultureDocument8 pagesAgrifood Booklet Series 2 Sustainable AgricultureSeyha L. AgriFoodNo ratings yet
- PlosOne Biotech Agriculture 2023Document14 pagesPlosOne Biotech Agriculture 2023Igor OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Media Campaign ProposalDocument3 pagesGroup 6 - Media Campaign ProposalAPRILLE ANN ORCULLO MALLARINo ratings yet
- PNAAP842Document152 pagesPNAAP842Aregawi TesfayNo ratings yet
- Syntropic Farming ReportDocument19 pagesSyntropic Farming Reportrobin.tensenNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Goals (2030 Agenda)Document1 pageSustainable Development Goals (2030 Agenda)dftiburcioNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Agritourism ExperiencesDocument15 pagesThe Influence of Agritourism Experienceszaratustra21No ratings yet
- Global Food and Drink Trends 2030Document28 pagesGlobal Food and Drink Trends 2030anzshinodaNo ratings yet
- 500 956 1 SMDocument14 pages500 956 1 SMstarkyNo ratings yet
- FAIRR 4 Labours of Regenerative Agriculture Report 2023Document40 pagesFAIRR 4 Labours of Regenerative Agriculture Report 2023abyssiniaglobalworldNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Compendium on Micronutrient Fertilisers in India Crop Response & Impact, Recent Advances and Industry TrendsFrom EverandCompendium on Micronutrient Fertilisers in India Crop Response & Impact, Recent Advances and Industry TrendsNo ratings yet
- 0113 - Busduct 630a - Offer Price - EmcoDocument1 page0113 - Busduct 630a - Offer Price - EmcoManish KumarNo ratings yet
- (TCF I-Great Infiniti Material) I-Great Infiniti Training SlidesDocument45 pages(TCF I-Great Infiniti Material) I-Great Infiniti Training Slidessu maiyahNo ratings yet
- Vision RX Lab Private Limited P-4, Kasba Industrial Estate, Phase - 1, Kolkata - 107Document1 pageVision RX Lab Private Limited P-4, Kasba Industrial Estate, Phase - 1, Kolkata - 107Pravin KhopadeNo ratings yet
- Name of Project: TUPAD DOLE Regional Office: VI Province: Negros Occidental Municipality: Pulupandan BarangayDocument16 pagesName of Project: TUPAD DOLE Regional Office: VI Province: Negros Occidental Municipality: Pulupandan BarangayMARYKNOL J. ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Kridha Logistics Pvt. Ltd. - Company ProfileDocument9 pagesKridha Logistics Pvt. Ltd. - Company ProfilePrateek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document32 pagesModule 2ElvisNo ratings yet
- Andris Ablazevics Baltech Ib GroglassDocument3 pagesAndris Ablazevics Baltech Ib GroglassAndris AblaNo ratings yet
- PROGRAM OF WORK N Bill of Materials Handwashing Facility SES 2022 UpdatedDocument2 pagesPROGRAM OF WORK N Bill of Materials Handwashing Facility SES 2022 UpdatedGeoff ReyNo ratings yet
- Mice Tourism Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Expand IccaDocument8 pagesMice Tourism Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Expand IccaAsiFAli100% (1)
- Brothers Anthony and Christopher Gaber Began Operations of Their ToolDocument1 pageBrothers Anthony and Christopher Gaber Began Operations of Their Toolhassan taimourNo ratings yet
- Frankfurt Modulhandbuch MIEEPDocument138 pagesFrankfurt Modulhandbuch MIEEPAlbi LikaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Itc LimitedDocument3 pagesCase Study of Itc LimitedMohanrajNo ratings yet
- Bus FinDocument2 pagesBus Fineidref ramosNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam - Mac 421Document5 pagesPrelim Exam - Mac 421Ezzz VeriNo ratings yet
- Practical 8: Visit A Bank/financial Institution To Enquire About Various Funding Schemes For Small Scale EnterpriseDocument4 pagesPractical 8: Visit A Bank/financial Institution To Enquire About Various Funding Schemes For Small Scale Enterprise02 - CM Ankita Adam83% (6)
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Venture Capital and Private EquityDocument79 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To Venture Capital and Private EquityerilNo ratings yet
- KA Corporate Filtered 12 Printed SANIYA ADocument28 pagesKA Corporate Filtered 12 Printed SANIYA AIrfan SheikNo ratings yet
- Facility Location and Layout - Numerical TechniquesDocument6 pagesFacility Location and Layout - Numerical TechniquesBanferbie NongrumNo ratings yet
- PasteDocument77 pagesPastealiasyt38No ratings yet
- Anup Engineering - NanoNivesh - ICICI DirectDocument8 pagesAnup Engineering - NanoNivesh - ICICI DirectAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Andrew Yule & Co. LTD: Board of DirectorsDocument8 pagesAndrew Yule & Co. LTD: Board of Directorsdarth vaderNo ratings yet
- Cross Docking PPT AVENGERSDocument13 pagesCross Docking PPT AVENGERSRei RacazaNo ratings yet
- EOB-Topic 1 - Sem 2 - 2023-24Document56 pagesEOB-Topic 1 - Sem 2 - 2023-24Makaylyn PetersenNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Profitability of Commercial Banks in BangladeshDocument12 pagesDeterminants of Profitability of Commercial Banks in BangladeshRatul HassanNo ratings yet
- Essential Drugs Frameworkagreementtender PDFDocument81 pagesEssential Drugs Frameworkagreementtender PDFIntegrated user03No ratings yet
- Pob NotesDocument122 pagesPob NotesFarel ThompsonNo ratings yet
Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology
Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology
Uploaded by
carlossaavedraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology
Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology
Uploaded by
carlossaavedraCopyright:
Available Formats
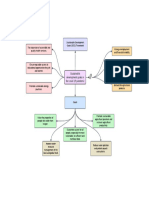
PARTICIPATION
Encourage social organization and greater
13
participation in decision-making by food
producers and consumers to support
decentralized governance and local adaptive
management of agricultural and food
TRANSFORMATIONAL
LEVEL 5 systems. LAND AND NATURAL
Build a new global food system based on
10
FAIRNESS
12 RESOURCE GOVERNANCE
FOOD SYSTEM
participation, localness, fairness and justice Recognize and support the needs and
Support dignified and robust interests of family farmers, smallholders
livelihoods for all actors engaged in and peasant food producers as sustainable
food systems, especially small-scale managers and guardians of natural and
food producers, based on fair trade, genetic resources.
fair employment and fair treatment
of intellectual property rights.
11
LEVEL 4
Reconnect consumers and producers
through the development of alternative
food networks
SOCIAL VALUES AND
DIETS CONNECTIVITY
9 CO-CREATION OF Ensure proximity and confidence
Build food systems based on the
between producers and
KNOWLEDGE
8
culture, identity, tradition, social
consumers through promotion of
and gender equity of local
Enhance co-creation and fair and short distribution
communities that provide healthy,
horizontal sharing of networks and by re-embedding
diversified, seasonally and
knowledge including local food systems into local
culturally appropriate diets.
and scientific innovation, economies.
LEVEL 3 especially through farmer-
1
Redesign agroecosystems to-farmer exchange.
AGROECOSYSTEM
ECONOMIC RECYCLING
7 6
DIVERSIFICATION SYNERGY Preferentially use local
renewable resources and
Diversify on-farm incomes by
Enhance positive ecological interaction, close as far as possible
ensuring small-scale farmers have
INCREMENTAL
synergy, integration, and resource cycles of nutrients
LEVEL2 greater financial independence and
complementarity amongst the elements and biomass.
value addition opportunities while
Substitute conventional inputs and of agroecosystems (plants, animals,
enabling them to respond to demand
trees, soil, water)
practices with agroecological alternatives from consumers.
ILLUSTRATIONS:DOROTTYA POÓR
BIODIVERSITY INPUT REDUCTION
LEVEL 1
Increase efficiency of input use and
5 Maintain and enhance diversity of
species, functional diversity and
genetic resources and maintain
biodiversity in the agroecosystem
Reduce or eliminate
dependency on purchased
inputs.
3
over time and space at field, farm
reduce use of costly, scarce or and landscape scales.
environmentally damaging inputs
SOIL HEALTH
4
Secure and enhance soil health and
functioning for improved plant
ANIMAL HEALTH growth, particularly by managing
Ensure animal health and organic matter and by enhancing soil
welfare. biological activity.
THE FIVE LEVELS OF TRANSITION TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE FOOD SYSTEMS AND THE RELATED 13 PRINCIPLES OF AGROECOLOGY
SOURCE: GLIESSMAN (2007) AND HLPE (2019)
You might also like
- Lechon Manok Business Planning Calculator - Final Version With Inventory - UpdatedDocument19 pagesLechon Manok Business Planning Calculator - Final Version With Inventory - UpdatedF Anton Nicolas50% (2)
- A Case Study On Starbucks: Delivering Customer ServiceDocument8 pagesA Case Study On Starbucks: Delivering Customer ServiceNHUNG LE THI QUYNHNo ratings yet
- Landscape For LifeDocument56 pagesLandscape For LifeCalendil LophianNo ratings yet
- Customer Value Propositions in Business Markets PDFDocument4 pagesCustomer Value Propositions in Business Markets PDFjaimequintoNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis On Ecommerce of JapanDocument2 pagesSWOT Analysis On Ecommerce of JapanTenzin Chogyel, BFound [Cohort2017 RTC]No ratings yet
- Poster 13 Principles of Agroecology ENGDocument1 pagePoster 13 Principles of Agroecology ENGTATIANA BUENO PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Implementing Conservation AgricultureDocument2 pagesImplementing Conservation AgricultureDomenico BevilacquaNo ratings yet
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2014Document12 pagesFAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2014Marcelo LouresNo ratings yet
- Pangniban Chapter 6 Quiz 1Document7 pagesPangniban Chapter 6 Quiz 1Lovely PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Reform ProposalDocument1 pageReform ProposalMichaela EsmeroNo ratings yet
- A Sus - Agric. An Introduction - Id.enDocument8 pagesA Sus - Agric. An Introduction - Id.ensecret angelNo ratings yet
- Armscaping: TO Nhance Iological OntrolDocument40 pagesArmscaping: TO Nhance Iological OntrolRex DufourNo ratings yet
- 2020 Food Security Standard FSS ENGDocument8 pages2020 Food Security Standard FSS ENGedwar tinocoNo ratings yet
- Manta Impact Assessment - Bahasa IndonesiaDocument1 pageManta Impact Assessment - Bahasa Indonesiaafwan shadriNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document5 pagesAssignment No.1Farrukh MuneerNo ratings yet
- Grade 8-Design Thinking WorksheetDocument4 pagesGrade 8-Design Thinking WorksheetKeshav Chaitan VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- Agro - Ecology The Virtuous Food Cycle: A Green Cooperative EconomyDocument1 pageAgro - Ecology The Virtuous Food Cycle: A Green Cooperative EconomyTyler DurdenNo ratings yet
- The Significance of Consumer's Awareness AboutDocument12 pagesThe Significance of Consumer's Awareness AboutNhud GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Agriculture: An Introduction: AttraDocument8 pagesSustainable Agriculture: An Introduction: AttraFiDe BlAckNo ratings yet
- Pillada Supplemental ScoresDocument14 pagesPillada Supplemental ScoresIIHC SMAW NC II LUCEÑA, ANGEL LANCE JERICHO A.No ratings yet
- Santos e Guarneiri - Social Indicators Short Supply ChainsDocument19 pagesSantos e Guarneiri - Social Indicators Short Supply ChainsIreneNo ratings yet
- Brochure Final - Updated - Million - Final For PrintDocument6 pagesBrochure Final - Updated - Million - Final For PrintVishnu ReddyNo ratings yet
- India's Rainfed Farming Variability and DiversityDocument4 pagesIndia's Rainfed Farming Variability and DiversityAshutosh LandeNo ratings yet
- Giannakas Yiannaka 2023 Food Fraud Causes Consequences and Deterrence StrategiesDocument23 pagesGiannakas Yiannaka 2023 Food Fraud Causes Consequences and Deterrence StrategiesJorge GarzaNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Principles of Integrated Farm SystemDocument6 pagesConcepts and Principles of Integrated Farm SystemIRISH BURGOSNo ratings yet
- Pillada Supplemental-ScoresDocument13 pagesPillada Supplemental-ScoresIIHC SMAW NC II LUCEÑA, ANGEL LANCE JERICHO A.No ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument1 pageMapa Conceptualmari peñaNo ratings yet
- Farming Systems: That Save and GrowDocument2 pagesFarming Systems: That Save and GrowNabhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 17312IIEDDocument4 pages17312IIEDmuhidinhawlet76No ratings yet
- Agriculture Week SaluteDocument16 pagesAgriculture Week SaluteThe Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Sustainability, ConceptsDocument19 pagesAgricultural Sustainability, Conceptswavin pe80No ratings yet
- Final 1Document19 pagesFinal 1SHOBHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Em PDFDocument17 pagesEm PDFMathiasrobby09No ratings yet
- Principles For Responsible Investment in Agriculture and Food SystemsDocument32 pagesPrinciples For Responsible Investment in Agriculture and Food SystemsAtos DiasNo ratings yet
- Pendahuluan Pertanian BerkelanjutanDocument89 pagesPendahuluan Pertanian BerkelanjutanMuhammad FadillahNo ratings yet
- Cs39 Triptico Minam Final RetiraDocument1 pageCs39 Triptico Minam Final RetiraLuis VillarNo ratings yet
- Giri Pragati ProgramDocument4 pagesGiri Pragati ProgramAksha RaviNo ratings yet
- Global Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel 09.07.05Document19 pagesGlobal Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel 09.07.05adelineo vlog ONo ratings yet
- Global Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel PDFDocument19 pagesGlobal Food Drink Trends 2019 Mintel PDFPuneet KujurNo ratings yet
- PES Implementation in FarmDocument5 pagesPES Implementation in FarmManish NairNo ratings yet
- Commitment of SM Foundation Inc. On Livelihood Development: It's Effect To Its BenefactorDocument8 pagesCommitment of SM Foundation Inc. On Livelihood Development: It's Effect To Its BenefactorJomii SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Cotton Production of Cotton BAYER PDFDocument17 pagesSustainable Cotton Production of Cotton BAYER PDFSalil SheikhNo ratings yet
- Agrifood Booklet Series 2 Sustainable AgricultureDocument8 pagesAgrifood Booklet Series 2 Sustainable AgricultureSeyha L. AgriFoodNo ratings yet
- PlosOne Biotech Agriculture 2023Document14 pagesPlosOne Biotech Agriculture 2023Igor OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Media Campaign ProposalDocument3 pagesGroup 6 - Media Campaign ProposalAPRILLE ANN ORCULLO MALLARINo ratings yet
- PNAAP842Document152 pagesPNAAP842Aregawi TesfayNo ratings yet
- Syntropic Farming ReportDocument19 pagesSyntropic Farming Reportrobin.tensenNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Goals (2030 Agenda)Document1 pageSustainable Development Goals (2030 Agenda)dftiburcioNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Agritourism ExperiencesDocument15 pagesThe Influence of Agritourism Experienceszaratustra21No ratings yet
- Global Food and Drink Trends 2030Document28 pagesGlobal Food and Drink Trends 2030anzshinodaNo ratings yet
- 500 956 1 SMDocument14 pages500 956 1 SMstarkyNo ratings yet
- FAIRR 4 Labours of Regenerative Agriculture Report 2023Document40 pagesFAIRR 4 Labours of Regenerative Agriculture Report 2023abyssiniaglobalworldNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsDocument14 pagesEffective Ways of Linking Relief and Rural Development: Oxfam's Experience of Implementing Programmes Using EU Food Facility FundsOxfamNo ratings yet
- Compendium on Micronutrient Fertilisers in India Crop Response & Impact, Recent Advances and Industry TrendsFrom EverandCompendium on Micronutrient Fertilisers in India Crop Response & Impact, Recent Advances and Industry TrendsNo ratings yet
- 0113 - Busduct 630a - Offer Price - EmcoDocument1 page0113 - Busduct 630a - Offer Price - EmcoManish KumarNo ratings yet
- (TCF I-Great Infiniti Material) I-Great Infiniti Training SlidesDocument45 pages(TCF I-Great Infiniti Material) I-Great Infiniti Training Slidessu maiyahNo ratings yet
- Vision RX Lab Private Limited P-4, Kasba Industrial Estate, Phase - 1, Kolkata - 107Document1 pageVision RX Lab Private Limited P-4, Kasba Industrial Estate, Phase - 1, Kolkata - 107Pravin KhopadeNo ratings yet
- Name of Project: TUPAD DOLE Regional Office: VI Province: Negros Occidental Municipality: Pulupandan BarangayDocument16 pagesName of Project: TUPAD DOLE Regional Office: VI Province: Negros Occidental Municipality: Pulupandan BarangayMARYKNOL J. ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Kridha Logistics Pvt. Ltd. - Company ProfileDocument9 pagesKridha Logistics Pvt. Ltd. - Company ProfilePrateek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document32 pagesModule 2ElvisNo ratings yet
- Andris Ablazevics Baltech Ib GroglassDocument3 pagesAndris Ablazevics Baltech Ib GroglassAndris AblaNo ratings yet
- PROGRAM OF WORK N Bill of Materials Handwashing Facility SES 2022 UpdatedDocument2 pagesPROGRAM OF WORK N Bill of Materials Handwashing Facility SES 2022 UpdatedGeoff ReyNo ratings yet
- Mice Tourism Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Expand IccaDocument8 pagesMice Tourism Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Expand IccaAsiFAli100% (1)
- Brothers Anthony and Christopher Gaber Began Operations of Their ToolDocument1 pageBrothers Anthony and Christopher Gaber Began Operations of Their Toolhassan taimourNo ratings yet
- Frankfurt Modulhandbuch MIEEPDocument138 pagesFrankfurt Modulhandbuch MIEEPAlbi LikaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Itc LimitedDocument3 pagesCase Study of Itc LimitedMohanrajNo ratings yet
- Bus FinDocument2 pagesBus Fineidref ramosNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam - Mac 421Document5 pagesPrelim Exam - Mac 421Ezzz VeriNo ratings yet
- Practical 8: Visit A Bank/financial Institution To Enquire About Various Funding Schemes For Small Scale EnterpriseDocument4 pagesPractical 8: Visit A Bank/financial Institution To Enquire About Various Funding Schemes For Small Scale Enterprise02 - CM Ankita Adam83% (6)
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Venture Capital and Private EquityDocument79 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To Venture Capital and Private EquityerilNo ratings yet
- KA Corporate Filtered 12 Printed SANIYA ADocument28 pagesKA Corporate Filtered 12 Printed SANIYA AIrfan SheikNo ratings yet
- Facility Location and Layout - Numerical TechniquesDocument6 pagesFacility Location and Layout - Numerical TechniquesBanferbie NongrumNo ratings yet
- PasteDocument77 pagesPastealiasyt38No ratings yet
- Anup Engineering - NanoNivesh - ICICI DirectDocument8 pagesAnup Engineering - NanoNivesh - ICICI DirectAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Andrew Yule & Co. LTD: Board of DirectorsDocument8 pagesAndrew Yule & Co. LTD: Board of Directorsdarth vaderNo ratings yet
- Cross Docking PPT AVENGERSDocument13 pagesCross Docking PPT AVENGERSRei RacazaNo ratings yet
- EOB-Topic 1 - Sem 2 - 2023-24Document56 pagesEOB-Topic 1 - Sem 2 - 2023-24Makaylyn PetersenNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Profitability of Commercial Banks in BangladeshDocument12 pagesDeterminants of Profitability of Commercial Banks in BangladeshRatul HassanNo ratings yet
- Essential Drugs Frameworkagreementtender PDFDocument81 pagesEssential Drugs Frameworkagreementtender PDFIntegrated user03No ratings yet
- Pob NotesDocument122 pagesPob NotesFarel ThompsonNo ratings yet