Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Manureet SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ebook Ebook PDF Planning Local Economic Development Theory and Practice 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Planning Local Economic Development Theory and Practice 6th Edition PDFsteven.cornell545100% (41)
- Energy Loss in Pipe and FittingsDocument10 pagesEnergy Loss in Pipe and FittingsMuhd Fadhil Nazer25% (4)
- Penawaran Pekerjaan Fire Fighting (Upah + Material)Document3 pagesPenawaran Pekerjaan Fire Fighting (Upah + Material)vixer ndi89% (9)
- Faussette On Wilson Darwin CathedralDocument13 pagesFaussette On Wilson Darwin CathedralDavid Enrique De La Dolorosa Chi BritoNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChemical BondRohan lallNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- G2 NSE1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesG2 NSE1 ReviewerjohnmilesvillaranteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocument7 pagesThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- VBT MotDocument23 pagesVBT Motskyanan592No ratings yet
- W) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXDocument10 pagesW) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXSav OliNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10th Chemistry NotesRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Week # 8 Chemcial BondingDocument3 pagesWeek # 8 Chemcial BondingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding.Document2 pagesChemical Bonding.shadnawazkhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingJonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesMd TaaseenNo ratings yet
- LoloDocument6 pagesLoloapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsjoeldpenosNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument19 pagesChemistry37 CM3Vijayalaxmi KambleNo ratings yet
- Science March 14Document1 pageScience March 14josefbonifacioleeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond and Its TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond and Its TypesKhan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- 06 ANSWERS SummaryDocument1 page06 ANSWERS SummaryJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Bondingahmad batataNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentalishbajaved159No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- S9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesS9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingMark Kevin Cagande EscletoNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesCH 3 Chemical BondingbatazaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3-Chemical Bonds and Functional GroupsDocument64 pagesLecture-3-Chemical Bonds and Functional GroupsWiza MulengaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: What Is An Ionic or Covalent Bond?Document2 pagesCovalent Bonding: What Is An Ionic or Covalent Bond?M3xobNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 1105Document51 pagesChemical Bond 1105Abid HasanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Chemical Bonds - DummiesDocument2 pages4 Types of Chemical Bonds - DummiesMarta HalimNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument8 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsdanNo ratings yet
- CH 3, ChemDocument6 pagesCH 3, ChemAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2mehrunnisaqaisar111No ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument69 pagesChemical Bondingirenerielo19No ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- 7.1 7.2Document2 pages7.1 7.2noora.rami48No ratings yet
- Lewis Structure Shows A Representation of A Bond Between Atoms of A Molecule Also WithDocument4 pagesLewis Structure Shows A Representation of A Bond Between Atoms of A Molecule Also WithRen ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Types of Chemical BondingDocument32 pagesChapter - 4 Types of Chemical BondingMadhur ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesChemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionsgibbsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistryzaryabfaraz314No ratings yet
- Notes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesNotes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesCovalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartArcelie Alberca EscasinasNo ratings yet
- CB 1Document4 pagesCB 1Mahmudur Rahman27No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsDocument68 pagesChemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsRalph RebugioNo ratings yet
- Properties of BondsDocument36 pagesProperties of BondsPaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Atkins Chemical Principles The Quest For InsightDocument6 pagesChapter 2, Atkins Chemical Principles The Quest For InsightericthecmhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypeDocument8 pagesChemical Bond TypeShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
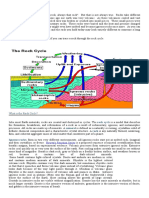
- The Rock CycleDocument3 pagesThe Rock CycleRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- 04.00 ExerciseDocument3 pages04.00 ExerciseecorobNo ratings yet
- Effective Utilization of Various Industrial Wastes in Concrete For Rigid Pavement Construction - A Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesEffective Utilization of Various Industrial Wastes in Concrete For Rigid Pavement Construction - A Literature ReviewIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Fabricated From 3D Printed Silica PreformsDocument8 pagesOptical Fiber Fabricated From 3D Printed Silica PreformsMahmudur Rahman RashaNo ratings yet
- Ad360 Port and System RequirementsDocument8 pagesAd360 Port and System RequirementsjrosariocabreraNo ratings yet
- ASi BUSDocument1 pageASi BUSLuis AguilarNo ratings yet
- C O / C - S,, Y V: /Itdversions/19.3.0.1/Itdstart - Aspx?Svc 3F50C3C0-1874-400E-Af3A-5036E 79Dec9FDocument201 pagesC O / C - S,, Y V: /Itdversions/19.3.0.1/Itdstart - Aspx?Svc 3F50C3C0-1874-400E-Af3A-5036E 79Dec9FharshiniNo ratings yet
- Speak Now 1 Class Audio ScriptDocument43 pagesSpeak Now 1 Class Audio ScriptNguyễn Đăng KhoaNo ratings yet
- MJPRU Exam SchemeDocument9 pagesMJPRU Exam SchemePrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- WattsBox Insulated Enclosures Specification SheetDocument4 pagesWattsBox Insulated Enclosures Specification SheetWattsNo ratings yet
- Rutherford 9322 Data SheetDocument2 pagesRutherford 9322 Data SheetJMAC SupplyNo ratings yet
- ME2403-Power Plant EngineeringDocument5 pagesME2403-Power Plant EngineeringkrishnabrNo ratings yet
- Schistura ThavoneiDocument9 pagesSchistura ThavoneiSubhadra LaimayumNo ratings yet
- 1732 - Square BarDocument6 pages1732 - Square BarDxFxNo ratings yet
- ASME SA240 304 (S30400) Stainless Steel Plate - A516Gr70 - S355J2 - SA516GR70 - A516 Grade 70 - SA516 Grade 70 - A572GR50 Steel Plate PDFDocument7 pagesASME SA240 304 (S30400) Stainless Steel Plate - A516Gr70 - S355J2 - SA516GR70 - A516 Grade 70 - SA516 Grade 70 - A572GR50 Steel Plate PDFJA KNo ratings yet
- A Diamond Will Not Dissolve in AcidDocument3 pagesA Diamond Will Not Dissolve in AcidangelNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions SolutionsDocument12 pagesSec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions Solutionsjiajing shenNo ratings yet
- AravindDocument6 pagesAravindyuvi7003No ratings yet
- Ijfmpvol 12no 3jul-Sep2019Document116 pagesIjfmpvol 12no 3jul-Sep2019Grnitrv 22No ratings yet
- Additional Maths Revision NotesDocument87 pagesAdditional Maths Revision NotesSamson YauNo ratings yet
- Il'tq FTWN: On Deworming Administr, Ation and Management Followng Deworming (Aefd)Document12 pagesIl'tq FTWN: On Deworming Administr, Ation and Management Followng Deworming (Aefd)Kristina Ruth Marie V. MoyaNo ratings yet
- The Heychris DramaDocument14 pagesThe Heychris DramaAnnNo ratings yet
- BIO 361 Syllabus 2014Document3 pagesBIO 361 Syllabus 2014jyahn14No ratings yet
- Module 4 System and Product IntroductionDocument125 pagesModule 4 System and Product Introductionrodrigue ntchounkeuNo ratings yet
- Mech CD 300Document1 pageMech CD 300Aya EzzNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete GeotechDocument10 pagesTEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete Geotechfaraeiin57No ratings yet
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Manureet SinghOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Manureet SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
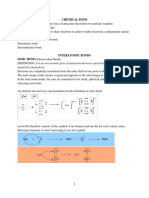
A chemical Bond is thus defined as the force of attraction that holds various constituents like atoms,
ions etc. together. The three main types of bonds that are formed are:
Ionic or electrovalent bonds
Covalent bonds
Co-ordinate covalent or dative bonds
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is the force of attraction between atoms that leads to the formation of chemical
compounds. The bond occurs because of,electrostatic force of attraction between atoms of opposite
charges, and through the sharing of electrons (in covalent bonds).
Atoms lose, gain or share electrons to attain octet configuration and stability. The force of attraction is
the result of the behavior of outermost or valence electrons. Based on this force, different types of
bonds are formed giving to rise to different properties in compounds.
The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably leading to the formation of either strong or primary
bonds and weak or secondary bonds.
Strong bonds include ionic or electrovalent bonds, covalent bonds and co-ordinate covalent or dative
bonds.
Weak bonds include dipole-dipole interaction and hydrogen bonds.
The three main types of atomic bonds are:
Ionic Bonds: They are formed because of non-directional interatomic forces and electron transfer. They
give structures of high coordination and there is electrical conductivity at low temperatures.
Covalent Bonds: They are formed because of localised (directional) large interatomic forces and electron
sharing. They help form structures of low coordination and low conductivity at low temperature (for
pure crystals).
Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron between atoms. Ionic bonds occur between
metals (electron donors) and non-metals (electron acceptors) because of the electrostatic force of
attraction between positive and negative ions.
Ionic or electrovalent bonds are formed under the conditions of low ionization energy, high electron
affinity.
Why does ionic bonding occur?
It occurs in metals because metals have few valence electrons and metals tend to lose electrons to
attain octet configuration and achieve noble gas configuration.
It occurs in nonmetals since non-metals readily accept electrons to achieve noble gas configuration.
Characteristics of ionic bonds:
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
They are dense because their crystalline forms contain crystal lattices of tightly packed molecules.
Their crystalline forms are always soluble in water.
Crystals cannot conduct electricity in the solid state.
The chemical bond generates two oppositely charged ions.
Metals lose electrons to become a positively charged cations while non-metals accept those electrons to
become a negatively charged anions.
Covalent
There are certain compounds in which bonds are formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons
between them. Each of these atoms contributes one electron and both the electrons (in pair) jointly
orbit the nuclei. This produces a bond between the two atoms, known as the covalent bond.
In covalent bonds, electrons are not transferred from one atom to another, but a pair of electrons is
shared by two atoms.
A variant of the covalent bond is the co-ordinate bond, where the shared electrons are supplied by the
same atom.
Covalent bond
Covalent bonds are formed between two or more atoms when they share electrons. They are normally
formed between atoms of similar electronegativity and may occur between atoms of same or of
different kind.
Example: Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen share 1, 2 and 3 electrons respectively, with similar atoms to form
molecules. Carbon and hydrogen share electrons to form hydrocarbons.
Covalent bonds can be polar or non-polar. The more the difference in electronegativity, the more is the
polar nature of the molecule.
Polar covalent bonds are formed between atoms with difference in electronegativity, for example,
water and hydrogen chloride.
Covalent bonds are of three types: single covalent bonds, double covalent bonds and triple covalent
bonds.
Conditions for the formation of a covalent bond:
Both atoms should have four or more electrons in their outermost shells (non-metals with exceptions
being H, Be, B, Al, etc.).
Both the atoms should have high electronegativity, electron affinity and ionisation energy.
The electronegativity difference between the combining atoms should be either zero or negligible.
Co-ordinate Bond or Dative Bond
A coordinate covalent bond also known as a dative bond or coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond
in which the two-shared electrons are supplied by the same atom.
It is formed by two atoms sharing a pair of electrons where one of the atoms has a lone pair of
electrons. The electrons are attracted to both the nuclei. The atom which supplies both the electrons is
called donor and the other atom is called acceptor.
Example:
Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons of which three are used for bonding with hydrogen to form ammonia.
Nitrogen in ammonia thus has one lone pair of electrons left.
When ammonia combines with a hydrogen ion it forms ammonium ion. Nitrogen is the donor and
hydrogen is the acceptor.
You might also like
- Ebook Ebook PDF Planning Local Economic Development Theory and Practice 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Planning Local Economic Development Theory and Practice 6th Edition PDFsteven.cornell545100% (41)
- Energy Loss in Pipe and FittingsDocument10 pagesEnergy Loss in Pipe and FittingsMuhd Fadhil Nazer25% (4)
- Penawaran Pekerjaan Fire Fighting (Upah + Material)Document3 pagesPenawaran Pekerjaan Fire Fighting (Upah + Material)vixer ndi89% (9)
- Faussette On Wilson Darwin CathedralDocument13 pagesFaussette On Wilson Darwin CathedralDavid Enrique De La Dolorosa Chi BritoNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChemical BondRohan lallNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- G2 NSE1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesG2 NSE1 ReviewerjohnmilesvillaranteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocument7 pagesThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- VBT MotDocument23 pagesVBT Motskyanan592No ratings yet
- W) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXDocument10 pagesW) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXSav OliNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10th Chemistry NotesRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Week # 8 Chemcial BondingDocument3 pagesWeek # 8 Chemcial BondingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding.Document2 pagesChemical Bonding.shadnawazkhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingJonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesMd TaaseenNo ratings yet
- LoloDocument6 pagesLoloapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsjoeldpenosNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument19 pagesChemistry37 CM3Vijayalaxmi KambleNo ratings yet
- Science March 14Document1 pageScience March 14josefbonifacioleeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond and Its TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond and Its TypesKhan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- 06 ANSWERS SummaryDocument1 page06 ANSWERS SummaryJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Bondingahmad batataNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentalishbajaved159No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- S9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesS9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingMark Kevin Cagande EscletoNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesCH 3 Chemical BondingbatazaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3-Chemical Bonds and Functional GroupsDocument64 pagesLecture-3-Chemical Bonds and Functional GroupsWiza MulengaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: What Is An Ionic or Covalent Bond?Document2 pagesCovalent Bonding: What Is An Ionic or Covalent Bond?M3xobNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 1105Document51 pagesChemical Bond 1105Abid HasanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Chemical Bonds - DummiesDocument2 pages4 Types of Chemical Bonds - DummiesMarta HalimNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument8 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsdanNo ratings yet
- CH 3, ChemDocument6 pagesCH 3, ChemAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2mehrunnisaqaisar111No ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument69 pagesChemical Bondingirenerielo19No ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- 7.1 7.2Document2 pages7.1 7.2noora.rami48No ratings yet
- Lewis Structure Shows A Representation of A Bond Between Atoms of A Molecule Also WithDocument4 pagesLewis Structure Shows A Representation of A Bond Between Atoms of A Molecule Also WithRen ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Types of Chemical BondingDocument32 pagesChapter - 4 Types of Chemical BondingMadhur ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesChemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionsgibbsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistryzaryabfaraz314No ratings yet
- Notes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesNotes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesCovalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartArcelie Alberca EscasinasNo ratings yet
- CB 1Document4 pagesCB 1Mahmudur Rahman27No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsDocument68 pagesChemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsRalph RebugioNo ratings yet
- Properties of BondsDocument36 pagesProperties of BondsPaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Atkins Chemical Principles The Quest For InsightDocument6 pagesChapter 2, Atkins Chemical Principles The Quest For InsightericthecmhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypeDocument8 pagesChemical Bond TypeShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument3 pagesThe Rock CycleRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- 04.00 ExerciseDocument3 pages04.00 ExerciseecorobNo ratings yet
- Effective Utilization of Various Industrial Wastes in Concrete For Rigid Pavement Construction - A Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesEffective Utilization of Various Industrial Wastes in Concrete For Rigid Pavement Construction - A Literature ReviewIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Fabricated From 3D Printed Silica PreformsDocument8 pagesOptical Fiber Fabricated From 3D Printed Silica PreformsMahmudur Rahman RashaNo ratings yet
- Ad360 Port and System RequirementsDocument8 pagesAd360 Port and System RequirementsjrosariocabreraNo ratings yet
- ASi BUSDocument1 pageASi BUSLuis AguilarNo ratings yet
- C O / C - S,, Y V: /Itdversions/19.3.0.1/Itdstart - Aspx?Svc 3F50C3C0-1874-400E-Af3A-5036E 79Dec9FDocument201 pagesC O / C - S,, Y V: /Itdversions/19.3.0.1/Itdstart - Aspx?Svc 3F50C3C0-1874-400E-Af3A-5036E 79Dec9FharshiniNo ratings yet
- Speak Now 1 Class Audio ScriptDocument43 pagesSpeak Now 1 Class Audio ScriptNguyễn Đăng KhoaNo ratings yet
- MJPRU Exam SchemeDocument9 pagesMJPRU Exam SchemePrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- WattsBox Insulated Enclosures Specification SheetDocument4 pagesWattsBox Insulated Enclosures Specification SheetWattsNo ratings yet
- Rutherford 9322 Data SheetDocument2 pagesRutherford 9322 Data SheetJMAC SupplyNo ratings yet
- ME2403-Power Plant EngineeringDocument5 pagesME2403-Power Plant EngineeringkrishnabrNo ratings yet
- Schistura ThavoneiDocument9 pagesSchistura ThavoneiSubhadra LaimayumNo ratings yet
- 1732 - Square BarDocument6 pages1732 - Square BarDxFxNo ratings yet
- ASME SA240 304 (S30400) Stainless Steel Plate - A516Gr70 - S355J2 - SA516GR70 - A516 Grade 70 - SA516 Grade 70 - A572GR50 Steel Plate PDFDocument7 pagesASME SA240 304 (S30400) Stainless Steel Plate - A516Gr70 - S355J2 - SA516GR70 - A516 Grade 70 - SA516 Grade 70 - A572GR50 Steel Plate PDFJA KNo ratings yet
- A Diamond Will Not Dissolve in AcidDocument3 pagesA Diamond Will Not Dissolve in AcidangelNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions SolutionsDocument12 pagesSec 3 Graphs Challenging Questions Solutionsjiajing shenNo ratings yet
- AravindDocument6 pagesAravindyuvi7003No ratings yet
- Ijfmpvol 12no 3jul-Sep2019Document116 pagesIjfmpvol 12no 3jul-Sep2019Grnitrv 22No ratings yet
- Additional Maths Revision NotesDocument87 pagesAdditional Maths Revision NotesSamson YauNo ratings yet
- Il'tq FTWN: On Deworming Administr, Ation and Management Followng Deworming (Aefd)Document12 pagesIl'tq FTWN: On Deworming Administr, Ation and Management Followng Deworming (Aefd)Kristina Ruth Marie V. MoyaNo ratings yet
- The Heychris DramaDocument14 pagesThe Heychris DramaAnnNo ratings yet
- BIO 361 Syllabus 2014Document3 pagesBIO 361 Syllabus 2014jyahn14No ratings yet
- Module 4 System and Product IntroductionDocument125 pagesModule 4 System and Product Introductionrodrigue ntchounkeuNo ratings yet
- Mech CD 300Document1 pageMech CD 300Aya EzzNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete GeotechDocument10 pagesTEST 1 - Answer Scheme - Complete Geotechfaraeiin57No ratings yet