Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ELECTROLYSIS
ELECTROLYSIS
Uploaded by
Jordan Daniel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageElectrolysis is the process of using electricity to decompose an electrolyte, which is an ionic substance in molten or aqueous state, into simpler substances. When an electric current is passed through an electrolyte, the ions move to the oppositely charged electrode where they gain or lose electrons to become neutral atoms, depositing as elements onto the electrodes. For electrolysis to occur, the ionic substance must be heated until molten to allow the ions to move freely through the solution when a power supply is connected to the electrodes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectrolysis is the process of using electricity to decompose an electrolyte, which is an ionic substance in molten or aqueous state, into simpler substances. When an electric current is passed through an electrolyte, the ions move to the oppositely charged electrode where they gain or lose electrons to become neutral atoms, depositing as elements onto the electrodes. For electrolysis to occur, the ionic substance must be heated until molten to allow the ions to move freely through the solution when a power supply is connected to the electrodes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageELECTROLYSIS
ELECTROLYSIS
Uploaded by
Jordan DanielElectrolysis is the process of using electricity to decompose an electrolyte, which is an ionic substance in molten or aqueous state, into simpler substances. When an electric current is passed through an electrolyte, the ions move to the oppositely charged electrode where they gain or lose electrons to become neutral atoms, depositing as elements onto the electrodes. For electrolysis to occur, the ionic substance must be heated until molten to allow the ions to move freely through the solution when a power supply is connected to the electrodes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
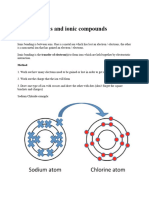
Electrolysis is the process of decomposing (breaking down) an ionic substance,
called an electrolyte, into simpler substances using electricity. The chemical
reaction of electrolysis occurs when an electric current is passed through a
solution containing ions (ions are charged atoms, they have more or less electrons
than protons which causes an imbalance, the overall charge can be negative or
positive).
For the electrolyte to conduct electricity, it must be:
An ionic compound
In molten or aqueous state
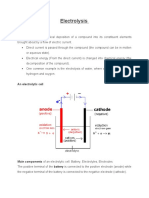
The process of Electrolysis: Electrolysis of an ionic substance
The ionic substance is heated until it melts.
The ions are able to move freely after the ionic substance is melted.
The power supply is connected and the electrodes are charged.
The ions move to the oppositely charged electrode (the negative electrons move to
the positive electrode, called the anode, and the positive electrons move to the
negative electrode, called the cathode).
The electrodes give/take electrons from the ions which makes the ions neutral.
The ions become atoms (because they are neutral) and are deposited onto the
electrode.
You might also like
- Solvation Ionic Compound SolventDocument1 pageSolvation Ionic Compound SolventSelina LeowNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Is The Chemical Deposition of A Compound Into Its Constituent ElementsDocument3 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Is The Chemical Deposition of A Compound Into Its Constituent ElementsEngrDebashisMallickNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis - NotesDocument3 pagesElectrolysis - NotesAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL EFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ,,,,,,,, Topic - ELECTROLYTEDocument5 pagesCHEMICAL EFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ,,,,,,,, Topic - ELECTROLYTESanjaya SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - ElectrolysisDocument41 pagesChapter I - ElectrolysisRodella ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Electrodes: Electrolysis and Redox ReactionDocument2 pagesElectrodes: Electrolysis and Redox Reactionvinod kumarNo ratings yet
- Electrodes: Electrolysis and Redox ReactionDocument2 pagesElectrodes: Electrolysis and Redox Reactionvinod kumarNo ratings yet
- U-3 (Electrochemistry) HandoutDocument6 pagesU-3 (Electrochemistry) HandoutbluejackbroNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesElectrolysisrayyankamran10No ratings yet
- IonizationDocument10 pagesIonizationInk TVNo ratings yet
- Chap 11: Electrolysis: ProcessDocument2 pagesChap 11: Electrolysis: ProcessAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Notes On ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesNotes On Electrolysiskhizermehmood2008No ratings yet
- Electrolysis NotesDocument19 pagesElectrolysis NotesXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document53 pagesUnit 7tesfayeNo ratings yet
- 02-Lecture-BE-Fundamentals ConectpsDocument14 pages02-Lecture-BE-Fundamentals ConectpsAdnan Hyder SoomroNo ratings yet
- Physics ResearchDocument4 pagesPhysics ResearchYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellDocument6 pagesElectrolytic CellJohn Israel R. CatedralNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument47 pagesChemical KineticsHabtamu mullu BiadgoNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument18 pagesElectrochemistryesotericgraphicapparelNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience ReviewerAzel RheadalNo ratings yet
- Ions and Ionic Compounds-NotesDocument3 pagesIons and Ionic Compounds-NotesKiran PandeyNo ratings yet
- Electrophysical Agent 1Document209 pagesElectrophysical Agent 1syammptNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic Chemistry Concepts - 6 - Spring 2022Document16 pagesIntroduction To Basic Chemistry Concepts - 6 - Spring 2022Malak RabieNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Revision NotesDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Revision NotesAnsh DhandiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Effect of CurrentDocument28 pagesChemical Effect of CurrentFatima SeharNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument8 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Notes On ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesNotes On ElectrolysisAnonymous FS4fOiNo ratings yet
- Creative TechnologiesDocument35 pagesCreative TechnologiesAivie PecasalesNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions, Electrolysis Set-Up Labeling Parts & Defining Terminologies - PILLADocument6 pagesGuide Questions, Electrolysis Set-Up Labeling Parts & Defining Terminologies - PILLAkloyidNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument7 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSISDocument5 pagesELECTROLYSISSereva Hosea BoeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry-12 2 11Document49 pagesElectrochemistry-12 2 11Vic VickyNo ratings yet
- The Transformation of Chemical Energy Into Electrical EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Transformation of Chemical Energy Into Electrical EnergyYasmin RokeyaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: AY20/21 S1Q1 - M5Document15 pagesElectrochemistry: AY20/21 S1Q1 - M5Menaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: ElectrologyDocument17 pagesElectrolysis: ElectrologyFrederic WustNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 9.ABakshDocument16 pagesChemistry Chapter 9.ABakshNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electrical Technology EditedDocument60 pagesIntro To Electrical Technology Editedmae OrgayaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Chemistry Note - SS 2Document50 pages2nd Term Chemistry Note - SS 2ebhojiayeemmanuel1No ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisSuci CahyantiNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2022-23Document18 pagesElectrolysis 2022-23Yasha RizviNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Conduction and Breakdown in GasesDocument58 pagesModule 2 - Conduction and Breakdown in GasesFah Rukh100% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocument1 pageElectrolysiszainab.fatima1150No ratings yet
- Report in Ia4Document22 pagesReport in Ia4CORONADO, EULENE MAYNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument1 pageElectrical EnergyBlack ThunderNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Chemical - Effect - of - Electric Current - classVIIIDocument15 pagesStudy Material - Chemical - Effect - of - Electric Current - classVIIIRajarshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04: Electrochemistry: Sheet-1Document35 pagesChapter 04: Electrochemistry: Sheet-1imtial kashemNo ratings yet
- Chem IGCSE 1 - Module 4Document4 pagesChem IGCSE 1 - Module 4carrisanicole2No ratings yet
- 3-Electrochemistry NotesDocument20 pages3-Electrochemistry NotesTech BusterNo ratings yet
- 8 - Chemical Effects of CurrentDocument4 pages8 - Chemical Effects of CurrentÁbìńàv GNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2: The Structure of The Atom Lesson 2.3 The Synthetic ElementsDocument7 pagesLesson 2.2: The Structure of The Atom Lesson 2.3 The Synthetic ElementsEa SyNo ratings yet
- Electricity 01 - Electric ChargeDocument16 pagesElectricity 01 - Electric ChargeAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- Corona DischargeDocument2 pagesCorona DischargeZia AteeqNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument8 pagesElectrolysisThanni AkanbiNo ratings yet
- Glossary: Sha Tin College Chemistry C5Document1 pageGlossary: Sha Tin College Chemistry C5jeniferNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Notes Igcse 9Document3 pagesElectrolysis Notes Igcse 9Advaith MasthipuramNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Ppt (New)Document43 pagesElectrolysis Ppt (New)Hidden NameNo ratings yet
- BT f5 Bab 6 DLP NniDocument43 pagesBT f5 Bab 6 DLP NniNURUL NADIAH BINTI IDRIS KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Current SolutionDocument12 pagesCurrent SolutionSwarnavo PramanikNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2015Document13 pagesElectrolysis 2015martinmbondjo062No ratings yet
- Unit 11 Electricity 9-1 GCSEDocument2 pagesUnit 11 Electricity 9-1 GCSEJordan DanielNo ratings yet
- 1CH0 2H Que 20211130Document32 pages1CH0 2H Que 20211130Jordan DanielNo ratings yet
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 (F) Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument32 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 (F) Edexcel Physics GCSEJordan DanielNo ratings yet
- Ict Past PaperDocument20 pagesIct Past PaperJordan DanielNo ratings yet