Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsAudit Engagement
Audit Engagement
Uploaded by
vaishnav v kunnathThe document discusses an audit engagement and the audit process. It explains that an audit engagement refers to the audit that an auditor performs, which includes initially accepting the audit offer and outlining their understanding of the purpose of the audit. It also discusses developing an audit program, which is a detailed plan of how the audit will be performed and specifies procedures. The document also mentions audit working papers, audit notebooks, audit risks, obtaining sufficient audit evidence, and submitting an audit report at the conclusion of the audit. Additionally, it covers internal check and internal audit, including internal control questionnaires, surprise checks, cut-off procedures, and examination in depth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Audit Objectives Procedures Evidences and DocumentationDocument35 pagesAudit Objectives Procedures Evidences and Documentationrietzhel22100% (3)
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning and Risk Assessment New SlidesDocument38 pagesAudit Planning and Risk Assessment New SlidesAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is The General Objective of Planning For An Audit?Document6 pagesWhat Is The General Objective of Planning For An Audit?Chris JacksonNo ratings yet
- 5-IS & IT Audit (Process of Auditing IS)Document19 pages5-IS & IT Audit (Process of Auditing IS)Madhu khan100% (1)
- Unit II Company Audit and VouchingDocument36 pagesUnit II Company Audit and VouchingMuskan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Discussion QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 Discussion QuestionsJuliana ChengNo ratings yet
- Audit Procedure-5Document4 pagesAudit Procedure-5yashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6DonNo ratings yet
- 7 Major Phases On AuditDocument4 pages7 Major Phases On AuditvinceNo ratings yet
- Principles of Auditing Lecture 5Document4 pagesPrinciples of Auditing Lecture 5Isaac PortelliNo ratings yet
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument4 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlFritzie Ann ZartigaNo ratings yet
- Audting Chapter4Document12 pagesAudting Chapter4Getachew JoriyeNo ratings yet
- Essay On AuditingDocument7 pagesEssay On AuditingAndy Rdz0% (1)
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument38 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlMaria Paz GanotNo ratings yet
- Audit EvidenceDocument18 pagesAudit EvidenceTigRao UlyMel100% (1)
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument37 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlMaria Paz GanotNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance Part 2Document28 pagesAudit and Assurance Part 2ALEKSBANDANo ratings yet
- Chap.3 Audit Plannng, Working Paper and Internal Control-1Document10 pagesChap.3 Audit Plannng, Working Paper and Internal Control-1Himanshu MoreNo ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument26 pagesAudit PlanningDev PipilNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 5 Audit TechniquesDocument9 pagesChapter No. 5 Audit TechniquesAnnam InayatNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlDocument27 pagesInternal ControlChristianNo ratings yet
- Ignou MS04Document3 pagesIgnou MS04Safiya HashimNo ratings yet
- Alan Fernandes (AUDIT EVIDENCE TO AUDIT REPORTING)Document28 pagesAlan Fernandes (AUDIT EVIDENCE TO AUDIT REPORTING)Alan FernandesNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6: in An Effective Manner. Planning Consists of A Number of Elements. However, They Could Be Summarized AsDocument10 pagesChapter-6: in An Effective Manner. Planning Consists of A Number of Elements. However, They Could Be Summarized AsNasir RifatNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 (Short Notes)Document4 pagesChapter - 2 (Short Notes)Aakansha SinghNo ratings yet
- PA603 - Audit ApproachDocument75 pagesPA603 - Audit ApproachnikazidaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Chapter-5Document29 pagesAuditing Chapter-5jamila mufazzalNo ratings yet
- Auditing IntroductionDocument29 pagesAuditing Introductionnvenu7434No ratings yet
- Unit VI Performing Substantive TestDocument29 pagesUnit VI Performing Substantive TestMark GerwinNo ratings yet
- Audit BudgetDocument7 pagesAudit Budgetlacasandile.danicaNo ratings yet
- Audit ProcessDocument2 pagesAudit Processrajahmati_28No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Audit ProcessDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Audit ProcessGokul.S 20BCP0010No ratings yet
- Audit ProceduresDocument4 pagesAudit Procedureschristien tshikaNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning TechniquesDocument12 pagesAudit Planning TechniquesRahul KadamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6BảoNgọcNo ratings yet
- Auditing Planning Chapt 3Document8 pagesAuditing Planning Chapt 3bhumika aggarwalNo ratings yet
- CompilationDocument95 pagesCompilationAnwar BogabongNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Handout RectifiedDocument11 pagesGroup 1 Handout RectifiedNe BzNo ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument4 pagesAudit PlanningLoo Bee YeokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Audit Testing and Audit Sampling - To Be PrintDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Audit Testing and Audit Sampling - To Be PrintsteveiamidNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Audit - CGDocument70 pagesUnit 2-Audit - CGRalfNo ratings yet
- Section 404 Audits of Internal Control and Control RiskDocument36 pagesSection 404 Audits of Internal Control and Control RiskAbdifatah Abdilahi100% (2)
- Consideration of Internal Control - NotesDocument6 pagesConsideration of Internal Control - NotesLovenia M. FerrerNo ratings yet
- Is Audit Report - Chapter 7Document18 pagesIs Audit Report - Chapter 7Mary Grace Caguioa AgasNo ratings yet
- Fairfield Institute of Management and Technology Audit Principles, Procedures and TechniquesDocument9 pagesFairfield Institute of Management and Technology Audit Principles, Procedures and TechniquesStar BoyNo ratings yet
- Audit in Nursing Management and AdministrationDocument31 pagesAudit in Nursing Management and Administrationbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument2 pagesAudit PlanningMarconni B. AndresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Completing The IT AuditDocument21 pagesLecture 8 Completing The IT Auditbarbie robertsNo ratings yet
- Auditing ReportDocument47 pagesAuditing ReportNoj WerdnaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Audit IDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 4 Audit IDanisaraNo ratings yet
- .Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument39 pages.Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary Activitiespamelajanmea2018No ratings yet
- Bat 13 Final Grading Ass.Document5 pagesBat 13 Final Grading Ass.JadeNo ratings yet
- Auditing One 04 For ClassDocument22 pagesAuditing One 04 For ClassRObel demisNo ratings yet
- Audit 4Document14 pagesAudit 4Nikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Auditing 1Document4 pagesAssignment Auditing 1Nootan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Practical AuditingDocument21 pagesPractical Auditing6008 G. DhayanithiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Internal Control and Fraud and ErrorDocument6 pagesOverview of Internal Control and Fraud and ErrorbabyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Organization of Working Papers on Operational AuditsFrom EverandGuidelines for Organization of Working Papers on Operational AuditsNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsFrom EverandThe Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsNo ratings yet
Audit Engagement
Audit Engagement
Uploaded by
vaishnav v kunnath0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesThe document discusses an audit engagement and the audit process. It explains that an audit engagement refers to the audit that an auditor performs, which includes initially accepting the audit offer and outlining their understanding of the purpose of the audit. It also discusses developing an audit program, which is a detailed plan of how the audit will be performed and specifies procedures. The document also mentions audit working papers, audit notebooks, audit risks, obtaining sufficient audit evidence, and submitting an audit report at the conclusion of the audit. Additionally, it covers internal check and internal audit, including internal control questionnaires, surprise checks, cut-off procedures, and examination in depth.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses an audit engagement and the audit process. It explains that an audit engagement refers to the audit that an auditor performs, which includes initially accepting the audit offer and outlining their understanding of the purpose of the audit. It also discusses developing an audit program, which is a detailed plan of how the audit will be performed and specifies procedures. The document also mentions audit working papers, audit notebooks, audit risks, obtaining sufficient audit evidence, and submitting an audit report at the conclusion of the audit. Additionally, it covers internal check and internal audit, including internal control questionnaires, surprise checks, cut-off procedures, and examination in depth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesAudit Engagement
Audit Engagement
Uploaded by
vaishnav v kunnathThe document discusses an audit engagement and the audit process. It explains that an audit engagement refers to the audit that an auditor performs, which includes initially accepting the audit offer and outlining their understanding of the purpose of the audit. It also discusses developing an audit program, which is a detailed plan of how the audit will be performed and specifies procedures. The document also mentions audit working papers, audit notebooks, audit risks, obtaining sufficient audit evidence, and submitting an audit report at the conclusion of the audit. Additionally, it covers internal check and internal audit, including internal control questionnaires, surprise checks, cut-off procedures, and examination in depth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Audit Engagement
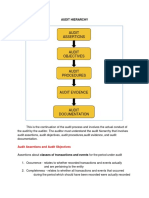
Refers to audit that auditor performs.
Initial stage of audit where he accepts offer and tells about his
understanding of what the purpose of audit is, etc.
Audit programme - Detailed plan of how the audit is to be
performed, specifying the procedures to be followed
Written plan containing exact details with regard to conduct of
a particular audit, serves as guide in arranging and distributing
audit work.
Audit working papers- record of planning and execution, retain
it for each year, current years is current working papers, WP
related to more than 1 year are kept separately as permanent
WP.
Audit note book – a bound book, large variety matters
observed during course of audit are recorded, permanent
record, great evidential tool.
Audit Risk – inherent ( suspectibility of a acc bal or class of
transactions ) control ( risk that misstatements could occur in
account balance ) detection ( risk that an auditor’s substantive
procedures will not detect misstatements )
Audit evidence – Auditor come across various assertions,
Evaluate all of it and express his opinion, evaluation can be
made in light of facts and these facts and reasons are audit
evidence.
He must obtain sufficient audit evidence.
Audit report – preliminary work audit, conduct of actual audit,
conclusion of audit which means submission of audit report.
Internal Check And Internal Audit
Internal Check = Number of steps in acc transactions like
posting recording etc, involves various no of staffs, thus
continuous internal audit is carried on by staff itself =, work of
1 indiv is checked by the other staff, it is valuable part of
internal control.
Internal control questionnaires = evaluation of internal check
system is of great concern both to the auditor as well as
internal auditor, due to limitation of time he has to decide the
extent of in depth audit of many areas, particularly checking
and verification of routine aspects of FS.
Surprise Check- All audit procedures are applied not in general
routine, but are spontaneous in nature and are performed
without prior notice, ( features of it = spontaneous, random
selection of items, helps assure maintenance of up to date acc,
performed in situations facing weak internal controls.)
Cut off procedures – periods usually coincide with calendar
months lead to need for specific demarcation between
transactions forming part of 1 period from those included in
the following period, cut off procedures are adopted to
allocate revenues and costs to the proper accounting period.
Examination in depth = fixation of mac tolerable error,
selecting a few transactions, verification of those selected
transactions.
Internal control = comprises all the method and procedures
adopted to assist in achieving objectives of efficient conduct of
business, ensure adherence to management policies,
safeguarding assets, etc.
Internal audit = independent appraisal activity within the
organisation for review of financial accounting and other
operations done as a ba sis of service to the management.
You might also like
- Audit Objectives Procedures Evidences and DocumentationDocument35 pagesAudit Objectives Procedures Evidences and Documentationrietzhel22100% (3)
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning and Risk Assessment New SlidesDocument38 pagesAudit Planning and Risk Assessment New SlidesAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is The General Objective of Planning For An Audit?Document6 pagesWhat Is The General Objective of Planning For An Audit?Chris JacksonNo ratings yet
- 5-IS & IT Audit (Process of Auditing IS)Document19 pages5-IS & IT Audit (Process of Auditing IS)Madhu khan100% (1)
- Unit II Company Audit and VouchingDocument36 pagesUnit II Company Audit and VouchingMuskan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Discussion QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 Discussion QuestionsJuliana ChengNo ratings yet
- Audit Procedure-5Document4 pagesAudit Procedure-5yashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6DonNo ratings yet
- 7 Major Phases On AuditDocument4 pages7 Major Phases On AuditvinceNo ratings yet
- Principles of Auditing Lecture 5Document4 pagesPrinciples of Auditing Lecture 5Isaac PortelliNo ratings yet
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument4 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlFritzie Ann ZartigaNo ratings yet
- Audting Chapter4Document12 pagesAudting Chapter4Getachew JoriyeNo ratings yet
- Essay On AuditingDocument7 pagesEssay On AuditingAndy Rdz0% (1)
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument38 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlMaria Paz GanotNo ratings yet
- Audit EvidenceDocument18 pagesAudit EvidenceTigRao UlyMel100% (1)
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument37 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlMaria Paz GanotNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance Part 2Document28 pagesAudit and Assurance Part 2ALEKSBANDANo ratings yet
- Chap.3 Audit Plannng, Working Paper and Internal Control-1Document10 pagesChap.3 Audit Plannng, Working Paper and Internal Control-1Himanshu MoreNo ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument26 pagesAudit PlanningDev PipilNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 5 Audit TechniquesDocument9 pagesChapter No. 5 Audit TechniquesAnnam InayatNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlDocument27 pagesInternal ControlChristianNo ratings yet
- Ignou MS04Document3 pagesIgnou MS04Safiya HashimNo ratings yet
- Alan Fernandes (AUDIT EVIDENCE TO AUDIT REPORTING)Document28 pagesAlan Fernandes (AUDIT EVIDENCE TO AUDIT REPORTING)Alan FernandesNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6: in An Effective Manner. Planning Consists of A Number of Elements. However, They Could Be Summarized AsDocument10 pagesChapter-6: in An Effective Manner. Planning Consists of A Number of Elements. However, They Could Be Summarized AsNasir RifatNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 (Short Notes)Document4 pagesChapter - 2 (Short Notes)Aakansha SinghNo ratings yet
- PA603 - Audit ApproachDocument75 pagesPA603 - Audit ApproachnikazidaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Chapter-5Document29 pagesAuditing Chapter-5jamila mufazzalNo ratings yet
- Auditing IntroductionDocument29 pagesAuditing Introductionnvenu7434No ratings yet
- Unit VI Performing Substantive TestDocument29 pagesUnit VI Performing Substantive TestMark GerwinNo ratings yet
- Audit BudgetDocument7 pagesAudit Budgetlacasandile.danicaNo ratings yet
- Audit ProcessDocument2 pagesAudit Processrajahmati_28No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Audit ProcessDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Audit ProcessGokul.S 20BCP0010No ratings yet
- Audit ProceduresDocument4 pagesAudit Procedureschristien tshikaNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning TechniquesDocument12 pagesAudit Planning TechniquesRahul KadamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6BảoNgọcNo ratings yet
- Auditing Planning Chapt 3Document8 pagesAuditing Planning Chapt 3bhumika aggarwalNo ratings yet
- CompilationDocument95 pagesCompilationAnwar BogabongNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Handout RectifiedDocument11 pagesGroup 1 Handout RectifiedNe BzNo ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument4 pagesAudit PlanningLoo Bee YeokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Audit Testing and Audit Sampling - To Be PrintDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Audit Testing and Audit Sampling - To Be PrintsteveiamidNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Audit - CGDocument70 pagesUnit 2-Audit - CGRalfNo ratings yet
- Section 404 Audits of Internal Control and Control RiskDocument36 pagesSection 404 Audits of Internal Control and Control RiskAbdifatah Abdilahi100% (2)
- Consideration of Internal Control - NotesDocument6 pagesConsideration of Internal Control - NotesLovenia M. FerrerNo ratings yet
- Is Audit Report - Chapter 7Document18 pagesIs Audit Report - Chapter 7Mary Grace Caguioa AgasNo ratings yet
- Fairfield Institute of Management and Technology Audit Principles, Procedures and TechniquesDocument9 pagesFairfield Institute of Management and Technology Audit Principles, Procedures and TechniquesStar BoyNo ratings yet
- Audit in Nursing Management and AdministrationDocument31 pagesAudit in Nursing Management and Administrationbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument2 pagesAudit PlanningMarconni B. AndresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Completing The IT AuditDocument21 pagesLecture 8 Completing The IT Auditbarbie robertsNo ratings yet
- Auditing ReportDocument47 pagesAuditing ReportNoj WerdnaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Audit IDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 4 Audit IDanisaraNo ratings yet
- .Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument39 pages.Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary Activitiespamelajanmea2018No ratings yet
- Bat 13 Final Grading Ass.Document5 pagesBat 13 Final Grading Ass.JadeNo ratings yet
- Auditing One 04 For ClassDocument22 pagesAuditing One 04 For ClassRObel demisNo ratings yet
- Audit 4Document14 pagesAudit 4Nikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Auditing 1Document4 pagesAssignment Auditing 1Nootan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Practical AuditingDocument21 pagesPractical Auditing6008 G. DhayanithiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Internal Control and Fraud and ErrorDocument6 pagesOverview of Internal Control and Fraud and ErrorbabyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Organization of Working Papers on Operational AuditsFrom EverandGuidelines for Organization of Working Papers on Operational AuditsNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsFrom EverandThe Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsNo ratings yet