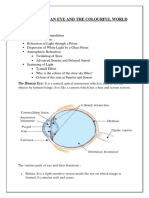
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 viewsDocScanner 10 Feb 2023 15-21
DocScanner 10 Feb 2023 15-21
Uploaded by
Ishi SCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- HW Worksheet 21 CH 5 SolutionDocument6 pagesHW Worksheet 21 CH 5 SolutionIshi SNo ratings yet
- HW Worksheet 25 CH 10 SolutionDocument11 pagesHW Worksheet 25 CH 10 SolutionIshi SNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (1) Science Class: X 2022-23 Date of SubmissionDocument3 pagesWorksheet (1) Science Class: X 2022-23 Date of SubmissionIshi SNo ratings yet
- Ch.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheDocument17 pagesCh.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheIshi SNo ratings yet
- HWDocument7 pagesHWIshi SNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Science Class: X 2022-23 Date: Ch. 15 - Our EnvironmentDocument2 pagesWorksheet Science Class: X 2022-23 Date: Ch. 15 - Our EnvironmentIshi SNo ratings yet
- Section A This Section Comprises of 20 Questions of ONE Mark Each Choose The Right Option To Make The Following Statements CorrectDocument6 pagesSection A This Section Comprises of 20 Questions of ONE Mark Each Choose The Right Option To Make The Following Statements CorrectIshi SNo ratings yet
- Wa0028Document31 pagesWa0028Ishi SNo ratings yet
- Maths QuestionsDocument6 pagesMaths QuestionsIshi SNo ratings yet
DocScanner 10 Feb 2023 15-21
DocScanner 10 Feb 2023 15-21
Uploaded by
Ishi S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views15 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views15 pagesDocScanner 10 Feb 2023 15-21
DocScanner 10 Feb 2023 15-21
Uploaded by
Ishi SCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 15
CEOS,
ation hs Feces (a), (2),
(©) and (a, Choos
¢
eg = ;
any of light travelling in air fats gt ANd wTite the correct
(a) go into the water without a liquely on the surf tee
MFO ts pant nee OF alm pond, He sil
(a deviate away from the normal
(o deviate towards the n
(g turn back on is original paxh
(™ diameter of the reflecting surfac c
Surface of 5
(@ aperture
(o radius of curvature
Pherical mirror is called its
(b) focal length
choose the incorrect statement (4) none of these
ia) The height of the object ist
principal axis. ‘aken to be
The height of the i
Ne a pale be taken as positive for bot!
i) Anegative sign in the v; ‘ r both vi as
da A postive sign in pie walue ofthe magnification indicates ie re
value of the magnifies cae that te images real
oan aagnification indica aa
{. Ifthe magnification of a lens has a positive siwieees aa
@) real the image i
a inverted () virtual and erect
(d) none of these
Positive as the
as the object is usually placed above the
‘An object is placed at the centre of i
a leaeaan of curvature of a concave mirror. The distance between the
(0) equal tof (0) greater than f but less than 3f
(0 equal to 2f- (@) greater than 2f
6, Ifthe magnification of a lens has a negative value, the image is
(®) virtual
(@) real and inverted
(@) none of these
(© erect
Ree
The focal length, f = “5 is valid
t not for concave mirror.
ror
(a) for convex mirror bu
() for concave mirror but not for convex ™
(0 for both convex and concave mirrors.
ror nor for concave mirror
screen by using
he distance between
(é) neither for convex mi
‘a concave mirror. The focal
© The; ;
The image of the distant objec
length of the mirror can be det
(@) the object and the mirror
®) the object and the screen
(} the mirror and the screen
(@) the mirror and the screen
Which of the following ean make @ P™
incident on it?
{) Concave mirror as well as conve
‘oncave lens
0° to each other
ve lens
is obtained on
fermined by measuring t
pject andl the sereen
ar between the ol
when Light from a p
fig
source is
as well as tha
rallel beam ©
x lens
e Convex mirror as well as ¢
() Tro plane mirrors placed at 9
) Concave mirror as well as Con
10, i :
0. Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form a real image
° tha,
n
tual object?
(a) When the object is kept at a distance equal to its radius of cu
1 its focal length
(b) When object is kept at a distance less th;
(c) When object
(A) When object is kept at a distance greater than its radius of curvature
15 cm in front of a concave mirror, Whe
© of the object?
laced between the focus and centre of curvature
11. Rays from Sun converge at a point
be placed so that size of its image is equal to the
(@) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(©) between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
12. Which one of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light in
shown in figure?
5
@ A
@ q Bi
©
A &
@
4 5
81 Science-X: Term-1
Fe shoul
cident on a |
INCERT Exe
oh
hier,
ens ay
pla)
Py
f the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of cides ae
diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident
‘on a conca
viel a
15. Near as shown im Figure?
[NCERT Exemplar}
(a)
-* -
c F P
a @
14. You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media a ray of
light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most? INCERT Exemplar|
(a) Kerosene () Water
(©) Mustard oil (d) Glycerine
15. A child is standing in front ‘of a magic mirror, He finds the i {his head bigger, the
middle portion of his body to he of same size and that of the legs smaller, Which of the
raraaing is the order of combinations for them nirror from the top? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Plane, convex and concave
(b) Convex, concave and plane
{e) Concave, plane and convex
(@) Convex, plane and concave
16. Two lenses of power +2.50 D and -3.75 D are combined to form a
Jength in em will be
(@) 40 (b) 40 (d) -80
17. Aman runs towards the plan mirror at 2. ms", The relative speed of his image with respect
to him will be
(@ ams" () 4m? (©) 8s" W@ oust
4, An object is placed 20 cm in front of a plane mirror, The mirror | imoved 2 em towards the
cone of the original and final images seen the mirror is
“object. The distance between the p
(a) 2cm W4cm (© 10cm (dy 22cm
Light-Reflection and Refraction |109
19,
20.
21.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
of incidence of 30°, is req
OR placed at rightangles ty,
the gt
Aray jkes a plane mirror PQ at an angle
the aaa Se ged then \Pjkes a second plane mirror
mirror. The angle of reflection at the second mirrors
(a) 30° (b) A5° (0) 60 , - 0
Which position of the a magnified virtual image, 1a coneaye 9
focal length 15 cm is being used? _ i,
@) 10cm (b) 206m (©) 80cm wb) 85m
magnifica 44. The object is placed
(d) 90
cot will product
A concave mirror product
(@) Atthe focus
(b) Between focus and centre of curvature
(©) Between focus and pole
(4) Beyond the centre of curvature
Two big mirrors A and Bare fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at such a gig,
from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in both the ‘ors. When the”
starts walking towards the mirrors, he finds that the face in mirror 4 9".
increasing but that in mirror B remains the same
(@) Mirror A is concave and mirror B is convex
(b) Mirror A is plane and mirror B is concave
(©) Mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
(4) Mirror A is convex and mirror B is concave
ht is travelling in a direction perpendicular to the boundary of a parallel ¢,
A goes
A ray of
slab. The ray of light
(a) Is refracted towards the normal (0) Is refracted away from the normal
(0) Is reflected along the same path
A ray of light passes from a medium X to another medium Y. No refraction of light occur
the ray of light hits the boundary of medium Y at an angle of
(@) 120° (6) 90° (©) 45° @o
A lens of focal length 12 cm forms an erect image, three times the size of the object. Tb
distance between the object and image is,
(a) 8cm (0) 16 cm
If an object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens, the image formed is slightly smaller th»
the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 19 cm from the lens, the image formed!
slightly larger than the object. The approximate focal length of the lens is
(©) 10cm () Sem
(@ Does not get refracted
(©) 24cm (@) 36 cm
(a) 20cm (6) 18cm
‘A student does the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing throus)
rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence, He can get a correct measure of
ii ed in figure
angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by following the labelling ind
\
A 4
@Dd
(B) (c)
@c
@A
a student traces the path of a ray of Fight
P
through a rectangular slab,
For measuring the angle of incidence, he mu: iti
in the figure ¢, he must position the protractor in the manner shown,
@a ; ® in . oc mp
gg, A student traces path of a ray of light passing th a .
A stage talus of angle of incidence (2) namely SE ene eas
oP incident ray by a dotted Tine and measur et i .
extended incident ray and the emergent = es the perpendicular distance ‘I’ between the
og
He will observe that
(a) T keeps on increasing with increase in angle of incidence
(@) ‘T keeps on decreasing with increase in angle of incidence
(0) ‘remains the same for all three angles of incidence
(@) ‘Vis the maximum for Zi = 45° and is less than this value for i = 0° and Zi = 60°.
30. Focal length of plane mirror is
(a) Avinfinity () Zero
(© Negative (d) None of these
31. Image formed by plane mirror
(@ Real and erect () Real and inverted
(© Virtual and erect (d) Virtual and inverted
32, Aconcave mirror gives real, inverted and same size image if the object is placed
(@ AF (6) Atinfinity (ac (d) Beyond C
33. In opti a . ae
7 te, a lect whi has higher refractive index is called
[ (© Opteaty rarer (6) Optically eer (e) optical density (d) Refractive index
@ as forms a real, point sized image at focus, the object is placed
eee @) Between Fand 2F (¢) Acinfinity (@) ACE
init of power of lens is
(@) Metre
SE Therap tea enters (o) Dioptre @s
0c urate of a mirror is 20cm the focal length is
©) 10cm (c) 40cm (@d) Sem
9%) Light-Reflection and Refraction 111
38.
39.
40.
41.
42,
43.
44,
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
e mirror. The distang,
eh
An object is placed at a distance of 0.25 m in front of a plan .
the object and image will be ° oy
(a) 0.25 m () 1.0m (0.5m @ 0.125 m
zero reflection angle is
‘The angle of incidence for a ray of light having 70°
(a) 0° (b) 30° (©) 45
al image?
ich of the following can produce a re
(0) Concave lens (@) Convex mirro,
(d) 90°
For a real object, whi
(a) Plane mirror (b) Concave mirror
a small cavity?
used by a dentist to examine
Which of the following mirror is
(a) Convex mirror () Plane mirror
(©) Concave mirror (d) Combination of convex and concave py,
i
An object at a distance of + 15 cm is slowly moved towards the pole of a convex Mirto, '
image will get "Th
(a) shortened and real () enlarged and real
(©) enlarged and virtual (@) diminished and virtual
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. Its focal length in air and water diffe,
(a) 15 (6) 20 (© 30 @0 4
A concave ‘ror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of object, Forth
virtual position of image, the position of object will be at
(a) 25cm (b) 40 cm (c) 10cm (d) At infinity
inverted and of the same size as that of 4
The image formed by concave mirror is real, i
object. The position of object should be
(b) at the centre of curvature
(a) at the focus
(c) between focus and centre of curvature (d) beyond centre of curvature
The nature of the image formed by concave mirror when the object is placed between
focus (F) and centre of curvature (C) of the mirror observed by us is
(@) real, inverted and diminished (b) virtual, erect and smaller in size
(©) real, inverted and enlarged
The nature of image formed by a convex mirror when the object distance from the mirror
less than the distance between pole and focal point (F) of the mirror would be
(@) virtual, upright and enlarged
(@ real, inverted and diminished in size
(6) real, inverted and enlarged in size
(0) virtual, upright and diminished in size
(@ virtual, upright and enlarged in size
The angle of incidence i and angle of refraction r are equal in a transparent slab when
value of j is
@o (b) 45°
(c) 90° (d) depend on the material of the slab
The refractive index of transparent medium is greater than one because
(a) Speed of light in vacuum < speed of light in transparent medium
(b) Speed of light in vacuum > speed of light in transparent medium
(0 Speed flight in vacuum = speed of light in transparent medium
(d) Frequency of light wave changes when it moves from rarer to denser medium sas!
You are given three media A, B and C of refractive index 1.33, 1.65 and 1.46- The med
which the light will travel fastest is ene?
(b) B
oe (@) equal in all he
(aya
30
uY
53
54.
56.
57.
ight from the Sun falling on
a) contre of curvature lens will con,
: verge
(o) radius of curvature 0) focus et 2 Point called
A divergent lens will produce © optical ceny
re
(a) always real image
(¢) both real and virtual image (aay viral image
when an object moves closer to convex | (d) none of these
lens, s
(a) avay from the lens
() towards the lens
d formed hy it
the image formed
() first towards and then away from the lens
(@ first away and then towards the lens
When object moves closer to a concave lens, the i
(a) away from the lens on the same side of objec nee
() towards the lens
(@ away from the lens on the other side of lens
(@) first towards and then away from the lens
‘A magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the object i
(@F (®) between F and oF a
(0 2F @ (a) and (b) both
|A.10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror ‘A5 mm long image of
the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is
[NCERT Exemplar]
@ -30cm (b) - 20cm
(@ -40.em (@) - 60cm
Refractive index of the
[NCERT Exemplar]
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B-
medium B relative to medium A is
2
:
; oles
Beams of light are incident through the h
Beams emerge out of box through the holes Geile
B tispectively as shown in the figure: Whie
following could be inside the DO oper Exe plarl
(@ Arectangular glass slab
(b) A convex lens .
(@) Aconcave lens
(@) A prism
ion 113
Light-Reflection and Refract
58. A beam of light is inci re holes on side A and emerges out of the ho!
light is incident through the holes on si ge Qf thi
le 0,
other face of t! x: wn it igure. Which of the following could be
f the box as shown in the figure. Which of Mowing insia
si
th
le the batt
1 Weber
(a) Concave lens
() Rectangular glass slab
(©) Prism
(d) Convex lens
59. Which of the following statements is/are true? (NCERT Exempl;
a
(a) A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m on
(6) A convex lens has -4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(©) Aconcave lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(@) A concave lens has ~ 4 dioptre having a focal length 0.25 m
60. Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles INCERT Exemplar]
61.
62.
63.
(a) is less than one
(b) is more than one
(c) is equal to one
(d) can be more than o
‘A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using
[NCERT Exemplar]
1 Jess than one depending upon the position of the object in front ofit
(a) aconcave mirror
(b) a convex mirror
(©) a plane mirror
(d) both concave as well as plane mirror
In torches, search lights and headlights o!
(a) between the pole and the focus of the reflector
(b) very near to the focus of the reflector
nd centre of curvature of the reflector
f vehicles the bulb is placed [NCERT Exemplar]
(0) between the focus a
(d) at the centre of curvature of the reflector aries
The laws of reflection hold good for INCE!
(a) plane mirror only
(0) concave mirror only
(©) convex mirror only
(d) all mirrors irrespective of their shape
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
n-
phe path of a ray of li
(le gour students are sree coming f
Tek Cand
m1,
-
Passi
Da eassing thro
in figure, Wong
Fectangy
me cpanel la
lab traced hy
INCERE Feemplar|
oN
x
)
con
@A OB
In which of the following,
and point sized?
(a) Concave mirror only
() Convex mirror only
(o Convex lens only
(@) Concave mirror
When light falls on a smo
(a) is reflected in the same
(o) is scattered
Jmage formed by reflectio
direction
the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly dit
convex mirror, concave lens 27
oth polished surfaces most oft
sa from a plane mirroe is
o \
@c wp
[NCERT Exemplar
.d convex lens.
(b) is reflected in different directions
(@ is refracted nto the second median
al and erect
(o) real and inverted @ vi ‘
(0) real and erect (@) virtual and inverted
et vill
yn the focus, the re rected ray Wi
ae (uy be parallel? the principal axis
Ifan incident ray P@
(a) pass through the
(0) retrace its path
Focal length of a concave
(a) negative
(@) depends on the position °
2D, what is i
pole
mirror is
f object
If the power of a lens is —
@ +50cm
() 50cm
When the object is placed betwee? fand 2
(a) ak
(©) beyond 2f
@ pas through ihe centre oF curvatane
postive
a) depen sosition oF se
2
js on the F
cat length?
w 100m
qw toe"
vex Hens e formed is
9 0) the imag
o
a2
@ petwee™ oandf
ion and Refraction 115
Light-Reflect!
72.
79.
80.
81.
82.
83.
84.
If the image is formed in front of the mirror, then the image distance will be
(@) positive or negative depending on the size of the object
() neither positive nor negative
(© positive
(@) negative
¢ medium to a denser medium. While
ce it
A ray of light is tr 4, from
denser medium at the point of i
(@ goes sv
(©) bends away from the normal (d) does not c
de
ight into the second medi
(h) bends towards the normat
ter at all
Monochromatic light of frequency 5 x 10! Hz travelling in vacuum enters 4 py,
refractive index 1.5. Its wavelength in the medium is in
(a) 5000 4 (6) 4000 A (0) 5500 A (d) GO00.A
‘Two thin lenses, one of focal length +60 cm and the other of focal length -20 cm as,
contact. Their combined focal length is hep
(@ ~30cm () + 30cm (= 15cm (@) + 30cm
When light travels from one medium to other whose refractive index is different, the
of the given will change? ahi
(@) Wavelength and velocity () Frequency and wavelength
(© Frequency and wavelength (d) Frequency, wavelength and velocity
The number of images observable between two parallel mirrors is
@2 (4 (6 (d) Infinity
£ = 1/2 is valid
(a) For convex mirrors but not for concave mirrors
() For concave mirrors but not for convex mirrors
(©) For both convex and concave mirrors
@ Neither for convex mirrors nor for concave mirrors
A hole is made in a convex lens, then
(a) A hole appears in the image (®) Image size decreases
(©) Image intensity decreases (@) No change
Which of the given is not true of an image formed by a plane mirror ?
@ Icis erect () Itis virtual
(0) Ivis diminished (@) Itis at the same distance as the object
contact. The focal length of
‘Iwo lenses of power +3 and -1 dioptres are placed
combined lens is
(@) 100 cm () 25 cm (©) 50cm @ 30.3.cm
‘The focal length of a concave mirror is 50 cm. To obtain an inverted image two times thes
of the object, the object should be placed at
(@) 50 cm (b) 63 cm (©) 72cm (d) 75cm
The focal length of lens depends on
(@) The radii of curvature of its surfaces
(0) The refractive index of its material
(©) The refractive index of the medium surrounding
@ Alll of these factors
A parallel beam of light is incident on a converging lens parallel
move away from the lens on the other side on its principal axis, th
() Continuously increases
(d) First increases and then decreases
to its principal axis: 5"
intensity of light
(a) Remains constant
(c) Continuously decreases
VL Taem 1
8
86
87.
88.
89.
90.
ol.
92.
93.
94.
ing a +
using a convex lens, a clear image of
tear images can be received on this candle Name
seree
(a) Alange number
|. How many of
(b) Only one more “
(@) None of the
water. How w
Increases
@ its power change ?
(6) Remain unchanged
(0) Decreases
({) Increases for red colour and dec
es for blue colour
which of the given can produce a virtual image larger in size th
la ize than the object ?
Concave lens
ee () Convex
{@) Convex concave lens ae jens
‘atens has a power of +0.5D. Itis eae
fay Aconeave lens of lea Iength 5m (BA convex lens of fora
P ex lens of focal lengt
(0) Aconvex Jens of focal length 5 m (d) Aconcave lens of fo ie i am
A diverging lens will produce ocal length 2 m
(@) Always. virtual image (b) Real or virtual image
(¢) Always real image (d) None of these °
Refractive index
(a) Depends on the wavelength of light used
(vy Is actual property of the substance
(c) Depends on the angle of incidence
(@ None of these
Which of the given is NOT paired correctly?
(a) Solar furnace-concave mirror (b) Rear -view mirror-convex mirror
(© Magnifying glass -convex lens
In order to obtain a magnification of
(a) None of these
0.6 (minus 0.6) with a concave mirror, the object must
be placed
(a) At the focus (0) Between pole and focus
(©) Between focus and ce Beyond the centre of curvature
Which statement is true fo [CBSE Question Bank]
(a) The angle of incidence
(6) The sum of angle of in
(0 The reflected light is less bri
(@ The beams of incident light a
‘The image shows reflection of lig
ntre of curvature @
«the reflection of light?
and reflection are equal-
cidence and reflection is a
ght than the incident lights
ges at uneg
Jays greater than 90°.
angles.
fter reflection diver
Jht on a mirror,
Incident ‘ Reflected
ray
ray
“es Ue
Reflecting surface
Light-Reflection and Refraction t
Based on the image, what can be inferred?
[CBsE Question py,
(@) The angle between incident ray and normal is greater than the angle between Moray
the reflected ray. a
(© The incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence and the refleceq
lie in the same plan “al
(©) The incident ray,
plane.
athe point of reflection do not le on gy
ne,
angle between nor,
‘al ang
(@) The angle between incident ray and normal is smaller t
the reflected ray.
the
95. The image shows the path of
lent rays to a concave mirror.
Object
Where would the reflected rays meet for the image formation to take place?
(a) Between Fand 0 (6) Beyond C
(©) Between C and F (d) Behind the mirror
96. An object is placed near a concave mirror at a distance of one-fourth the radius of curvature
of the concave mirror. Which ray diagram shows the incident rays, reflected rays, and the
Position and nature of the image formed? [CBSE Question Bani}
@
[CBSE Question Bank
©
object
ne irror when at
97. Which image represents the path of incident and reflected ray from a convex mirror when
object is placed at infinity? [CBSE Question Ba
(@)
Incident ray Reflected ray
Object
atininity
1 | Science-X: Term-1
object
atinfinity
o Incidentray _—_—Rfected ray
object
atinfinity
Convex
mitror
@ incdentray Reflected roy
Onject
atinfinty
gg, A student studies that convex mirror always forms virtual image irrespective of its position.
What causes the convex mirror (0 always form a virtual image? [CBSE Question Bank]
(a) Because the reflected ray never intersect,
(@) Because the incident ray traces its path back along the principal axis
(0) Because the incident ray ofa convex mirror gets absorbed in the mirror.
(a) Because the reflected ray converses ata single point.
99, A student conducts an activity using # concave mirror with focal length
the object 15 em from the mirror ing ae is the image likely 0 form?
(@) Av6.cmin front of the mirror
() At 6 cm behind the mirror
(0) At 30 cm behind the mirror
(d) At 30 cm in front of the mirror
100. Rekha placed a juice bottle at 2 distance
focal length of 20 cm. Where is the image
(a) Ata distance of 10 cm in front of the mirror
() At focus in front of the mirror
ee “ science of 10 cm behind the mirror
01. Sunil ocdtts en sai aa object of height 10 cm anda convex mirror of focal length
cm. He placed the object aa ance of 20cm in front of the Taal
height of the image produced?
@ ~5em )5.cm_ i
h of 10 cm. He placed
{CBSE Question Bank]
fof 20 em in front of a conver ror whieh has 9
Tikely to form? [CBSE Question Bank]
(len
Light-Reflection and Refraction 119
com al
102. ‘The image shows the path of light travelling through
103.
104.
105.
106.
107.
ha glass slab.
4 ™
Mostom 1
[CBSE Question ey,
What causes the ray of light to deviate from its orig
(a) Change in the temperature of the air
(®) Change in the amount of light
(©) Change in the direction of wind flow
(@ Change in the density of the medium
A student studies that speed of light in air is 300000 km/sec whereas that of speed ina glassy,
is about 197000 km/ sec. What causes the difference in speed of light in these two media?
[CBSE Question Ban
() Difference in amount of light
(@) Difference in density
(@) Difference in temperature
(©) Difference in direction of wind flow
‘The speed of light in air is 3 x 10° ms", whereas that of the speed of light in water is 225.
10° ms“, What is the refractive index of water with respect to air? [CBSE Question Bani
(@ 2.64 @1 (©) 1.32 @ 0.75
height 10 cm and a concave lens with oc!
ans. Can the image
[CBSE Question Bart]
Rahul conducts an experiment using an object of
length 20 cm. The object is placed at a distance of 25 cm from the le
formed on a screen?
(a) Yes, as the image formed will be real.
(0) No, as the image formed will be inverted.
(©) No, as the image formed will be virtual.
(a) Yes, as the image formed will be erect.
‘A student conducts an experiment using a convex lens of focal length
of height 15 cm. He placed the object at 25 em from the lens. Can the
h 20 cm and an objet
image be formed 0"
[CBSE Question Bos!
screen?
(a) Yes, because a real image will be formed.
(b) Yes, because an erect image will be formed.
(©) No, because an inverted image will be formed.
(d) No, because a virtual image will be formed.
Rakhi conducts an experiment to produce an image of an object on a screen
at 20 cm from the lens. She uses a convex lens of focal length 15 em for the expe
which is ph"
sriment-
‘Where should she place the object in order to produce the sharpest
(6) 8 cm in front of the lens
(a) 20 cm in front of the lens
(@) 60 cm in front of the lens
(©) 15 cmin front of the lens
491 Science-X: Term-1
of an object is produced on a screen which
vhic
mage : x
anima duced is about 3 times the si h is al
ie ate pro e size of the abject, What OM Using a eon
ai by
(0) -12em He size the ahjer The
wre Om gl ten
a ight 10 cm is placed in fi Ye ak
pject of height ©" front of a convex le . aw
(e pets placed at a distance of 36 cm in front ofthelens if having focal length of
i ates tragnified? + How many times ig thelnec, The
0 i Age libely
ties (b) 3 times (0) Atimes hy erin reat
. . times
nt conducts an experiment using a convex lens, Hi .
yt student cr of the lens and observed that the image is Fae Places the object ata distance of
go cm i 0 5 med at a distance of 3 s
What is the power of the lens? i" 0 cm behind
the lens: . [CBSE Question Rank|
(a) 0.005 dioptre (b) 50 dioptre (©) 5 dioptre (d) 0.05 dioptee
swers
ae 2, (a) 3. (0) 4. 0) 5. 6@ 70 8a
@ wo WO 2 BO WWM 1
3 20. (a) 2. (0) 22, (0) 2B. id) 2h)
|
|
|
lene 0 19. ()
Lr Z 0 me 8) BO) SB BLO BU
Et 34. © 35. (c) 36. (b) 37. (0) 38. (a) 39. (6) 40-0)
a0 0 HO BO 46. 47 @) 48.00
‘ 51. (b) 52. (a) 53. (b) 54. (d) 55. (b) 56. (a)
61. (6) 62. (6) 63. (d) G4. Ob)
@ 70. mo Be
@ 7% @ 8.10
87. (b) 88. ())
49.(@) 50. @)
sa) 58. @)
67.6) 68 @)
ares @ me me ie e
(0
ay eae pa 95. (0) 96. (2)
. (d) 93. (a) 94. (b) ;
u@ & a Oey mee woo
)
59. (a) 60. (@)
73.0) 74 0) 15.
gi.) 82 @)
89. (a) 90. (a)
98. (a) 99 @
106. (a) 107. @) 109. @)
110. (0)
108. (€)
—’
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- HW Worksheet 21 CH 5 SolutionDocument6 pagesHW Worksheet 21 CH 5 SolutionIshi SNo ratings yet
- HW Worksheet 25 CH 10 SolutionDocument11 pagesHW Worksheet 25 CH 10 SolutionIshi SNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (1) Science Class: X 2022-23 Date of SubmissionDocument3 pagesWorksheet (1) Science Class: X 2022-23 Date of SubmissionIshi SNo ratings yet
- Ch.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheDocument17 pagesCh.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheIshi SNo ratings yet
- HWDocument7 pagesHWIshi SNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Science Class: X 2022-23 Date: Ch. 15 - Our EnvironmentDocument2 pagesWorksheet Science Class: X 2022-23 Date: Ch. 15 - Our EnvironmentIshi SNo ratings yet
- Section A This Section Comprises of 20 Questions of ONE Mark Each Choose The Right Option To Make The Following Statements CorrectDocument6 pagesSection A This Section Comprises of 20 Questions of ONE Mark Each Choose The Right Option To Make The Following Statements CorrectIshi SNo ratings yet
- Wa0028Document31 pagesWa0028Ishi SNo ratings yet
- Maths QuestionsDocument6 pagesMaths QuestionsIshi SNo ratings yet