Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
Uploaded by
DeepakCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 11 Sensing The Environment PDFDocument12 pages11 Sensing The Environment PDFTAi Man Chan100% (4)
- Study Questions Special SensesDocument37 pagesStudy Questions Special SensesSurajit Bhattacharjee93% (15)
- Review Manual Dost Sei Scholarship ExampdfDocument40 pagesReview Manual Dost Sei Scholarship ExampdfJose BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Special SensesDocument4 pagesQuiz - Special SensesGlydenne Glaire Poncardas Gayam100% (1)
- LEC M3.3 BlockADocument8 pagesLEC M3.3 BlockASieg100% (1)
- Final Doc 1 PDFDocument20 pagesFinal Doc 1 PDFDev ROYNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansDocument19 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansParardha DharNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument8 pagesSense OrgansKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- Biology Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesBiology Sense OrgansasdasdNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test Lesson 4Document3 pagesAnatomy Test Lesson 4Mary Rose BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs - Work SheetDocument11 pagesSense Organs - Work SheetVarshni NateshmariNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument74 pagesHuman EyeAditi MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Exercise 15Document22 pagesUnit 8 Exercise 15Andrei AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Special Senses TestDocument47 pagesSpecial Senses TestNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- 02 - Human Eye and Colourful World - X - SSMDocument33 pages02 - Human Eye and Colourful World - X - SSMDøomNo ratings yet
- Write The Name of Each Numbered Part On The Corresponding Line of The Answer SheetDocument5 pagesWrite The Name of Each Numbered Part On The Corresponding Line of The Answer Sheetsilva, april joy c.No ratings yet
- MCQS On EyeDocument71 pagesMCQS On EyeFareed KhanNo ratings yet
- Biology of Humans Concepts Applications and Issues 5Th Edition Goodenough Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesBiology of Humans Concepts Applications and Issues 5Th Edition Goodenough Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbridget.price734100% (15)
- Sense Organs PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organs PDFTanzila SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Skull and Orbital Cavity Anatomy QuestionsDocument9 pagesSkull and Orbital Cavity Anatomy QuestionsAnon AnonNo ratings yet
- Eye Dissection Report Write Up 2014Document8 pagesEye Dissection Report Write Up 2014api-351895935No ratings yet
- The Ear and The Eye Topic Test With PermissionsDocument12 pagesThe Ear and The Eye Topic Test With Permissionsphenyommolawa561No ratings yet
- OpthamologyDocument12 pagesOpthamologyRayyanNo ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument95 pagesOphthalmologyB34-YvesJethro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Bit Bank Ix - ClassDocument3 pagesSense Organs: Bit Bank Ix - ClassSurya RaoNo ratings yet
- Scan Jan 29, 2021Document25 pagesScan Jan 29, 2021sheinarkarbo2020No ratings yet
- 4.1 Answers: RememberingDocument24 pages4.1 Answers: RememberingDanny TNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in LS2Document3 pagesSummative Test in LS2Riza Joy Nalix SolayaoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesNervous System and Sense OrgansSudeep MandalNo ratings yet
- Healthy Eyes and Ears Unit 16Document4 pagesHealthy Eyes and Ears Unit 16CARMIN INES GOMEZ RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 2Document235 pagesOphthalmology 2yididiyagirma30No ratings yet
- RSPL/1: CBSE Pariksha-2014 AnswersDocument8 pagesRSPL/1: CBSE Pariksha-2014 Answersprof_ktNo ratings yet
- Grand Test 166.. 2019 PDFDocument116 pagesGrand Test 166.. 2019 PDFPandey AyushNo ratings yet
- Assuit - MCQs (NeDocument84 pagesAssuit - MCQs (NeMax TraderNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Document72 pagesLakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Aishwaria MurthyNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document5 pagesModule 6Aya AbdelgaleelNo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 5 - Science - Sample Paper MSDocument10 pagesScience - Grade 5 - Science - Sample Paper MSAmita BarjtiyaNo ratings yet
- Dho Health Science Updated 8th Edition Simmers Test BankDocument9 pagesDho Health Science Updated 8th Edition Simmers Test Bankjosephrodriguez04121993gbm100% (30)
- Hukogman Eye Back ExerciseDocument7 pagesHukogman Eye Back ExerciseAbhay Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- PM291 ErrataDocument10 pagesPM291 ErrataServal GideonNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteDocument29 pagesSense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteAnkit SubediNo ratings yet
- 15 Detecting EnvironmentDocument106 pages15 Detecting EnvironmenttoperissaNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz: Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology: Nursing Test Bank NCLEX Practice QuestionsDocument32 pagesPractice Quiz: Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology: Nursing Test Bank NCLEX Practice QuestionsLelah Faye VidalNo ratings yet
- 1 Parts and Function of Eye WsDocument2 pages1 Parts and Function of Eye Wsaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs NewDocument14 pagesSense Organs NewSubham KalwarNo ratings yet
- Ujian Bab 1 Form 3: Stimuli and ResponsesDocument2 pagesUjian Bab 1 Form 3: Stimuli and Responsesalya sophiaNo ratings yet
- Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics SchoolDocument6 pagesMethodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics SchoolAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - WS - X-24-25Document4 pagesNervous System - WS - X-24-25shnc1801No ratings yet
- Science Worksheet - Light: Q1: Choose The Correct OptionDocument2 pagesScience Worksheet - Light: Q1: Choose The Correct OptionSarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Human Eye WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Eye Worksheetcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- Biophy ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiophy ReviewerMikhaelaNo ratings yet
- OPHTHALMOLOGYDocument69 pagesOPHTHALMOLOGYcollinsmagNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Neuro Sense OrgansDocument25 pagesMedsurg Neuro Sense Organsj UNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Basis Dentistry 4th Liebgott Test BankDocument5 pagesAnatomical Basis Dentistry 4th Liebgott Test BankfahedqNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument25 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourful WorldjituNo ratings yet
- EN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytDocument18 pagesEN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- OPAL MCQs & SEQsDocument39 pagesOPAL MCQs & SEQsanilNo ratings yet
- Special Senses OutlineDocument10 pagesSpecial Senses OutlinePIOZRNo ratings yet
- 21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersDocument6 pages21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersGuru SrinivaasNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Final ExamDocument7 pagesStudy Guide - Final ExamRichard LaRouechNo ratings yet
- 2.BLock E Sloved Proff 2020Document26 pages2.BLock E Sloved Proff 2020mghassan45No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Solutions For Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 - MetallurgyDocument33 pagesICSE Selina Solutions For Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 - MetallurgyDeepakNo ratings yet
- Blue-J: ICSE Class - 10Document186 pagesBlue-J: ICSE Class - 10DeepakNo ratings yet
- Indian Maps Labelling ICSE Geogarphy Class 10Document5 pagesIndian Maps Labelling ICSE Geogarphy Class 10DeepakNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledDeepakNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pagesMiddle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Dr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media TreatmentDocument54 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis Media TreatmentPrateek VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Anatomy and Physiology: AuditionDocument16 pagesOverview of The Anatomy and Physiology: AuditionEm Hernandez AranaNo ratings yet
- Ms Drills 3Document10 pagesMs Drills 3Karen Mae Santiago AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Easy Peasy EardrumsDocument52 pagesEasy Peasy EardrumsUCD GEMNo ratings yet
- ADULT HEALTH NURSING-2 INCLUDING GERIATRIC NURSING (Syllabus)Document4 pagesADULT HEALTH NURSING-2 INCLUDING GERIATRIC NURSING (Syllabus)Abhishek NaharNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment: Assessment Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal FindingsDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment: Assessment Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal FindingsJosal SinonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NOTESDocument3 pagesChapter - 2 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NOTESShri ShriNo ratings yet
- Foto Acoustic EmitionDocument83 pagesFoto Acoustic EmitionAlok kumarNo ratings yet
- Plants ScreamDocument27 pagesPlants ScreamМария ПавловаNo ratings yet
- VertigoDocument3 pagesVertigoGirishNo ratings yet
- Dr. Huma Fatima AliDocument24 pagesDr. Huma Fatima AliNouman Umar100% (1)
- The Floppiness of The Bunny EarsDocument1 pageThe Floppiness of The Bunny EarsxSymbyotyKxNo ratings yet
- Sensorineuralsystem MAY152023Document94 pagesSensorineuralsystem MAY152023Edmalyn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- All Histology Semester 2 QuizzesDocument21 pagesAll Histology Semester 2 QuizzesBarwdi ZenNo ratings yet
- Module Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesModule Nervous SystemMan Gal7No ratings yet
- AL Biology 1989 Paper 1 MarkingDocument12 pagesAL Biology 1989 Paper 1 Markingapi-3860987No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: External EarDocument73 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: External Earvidge5No ratings yet
- n82 - Procedure For Aural ToiletDocument2 pagesn82 - Procedure For Aural ToiletDaniel Tanri Rannu100% (1)
- The Audiogram Workbook Nonorganic Hearing Loss Cases - MedOne, ThiemeDocument10 pagesThe Audiogram Workbook Nonorganic Hearing Loss Cases - MedOne, ThiemeLara AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansMelanie GialogoNo ratings yet
- Mastoidectomy: Surgical Techniques: Key PointsDocument14 pagesMastoidectomy: Surgical Techniques: Key PointsMichel Dayanna Serrano TasconNo ratings yet
- 267 Impulses Serving Pain Sensation in The Left Foot Are RelayedDocument12 pages267 Impulses Serving Pain Sensation in The Left Foot Are RelayedNathanNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma of The Ear CanalDocument9 pagesCholesteatoma of The Ear CanalWanda DamayantiNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For A Neuropsychiatric ExamDocument29 pagesHow To Prepare For A Neuropsychiatric ExamEricNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument19 pagesThe Human EarNicole maderaziNo ratings yet
- Eng 341 Course Material PDFDocument185 pagesEng 341 Course Material PDFSergio LamusNo ratings yet
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
Uploaded by
DeepakOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
Uploaded by
DeepakCopyright:
Available Formats
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Class 10
Science (Biology)
Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
A. Multiple Choice Type
(Select the most appropriate option in each case)
1.Which part of the eye is grafted in a needy patient from a donated eye?
a. Conjunctiva
b. Cornea
c. Choroid
d. Ciliary muscles
Ans: (b.) Cornea
2. Which part of our ear is shaped like a snail shell?
a. Semicircular canals
b. Cochlea
c. Stapes
d. Eustachian Tube
Ans: (b.) Cochlea
3. The three parts of the human ear contributing to hearing are
a. Cochlea, ear ossicles and tympanum
b. Semicircular canals, utriculus and sacculus
c. Eustachian tube, tympanum and utriculus
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 1
d. Perilymph, ear ossicles and semicircular canals
Ans: (a.) Cochlea, ear ossicles and tympanum
4. The region in the eye where the rods and cones are located is the
a. Retina
b. Cornea
c. Choroid
d. Sclera
Ans: (a.) retina
B. Very Short Answer Type
1. Name the following:
a) The photosensitive pigment present in the rods of the retina
Ans: Rhodopsin
b) The part which equalizes the air pressure in the middle and external ear
Ans: Equalizer tube
c) The ear ossicle attached to the tympanum
Ans: Malleus, incus, and stapes
d) The tube which connects the cavity of the middle ear with the throat
Ans: Eustachian tube
e) The part of the eye responsible for its shape
Ans: Ciliary body
f) The nerves which transmit impulse from ear to the brain.
Ans: Auditory nerves
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 2
g) The photoreceptors found in the retina of the eye.
Ans: Rods and cones
h) The eye defect caused due to shortening of the eye ball from front to back.
Ans: Hypermetropia
2. Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable
word/ words for the fourth place.
a) Cones: Iodopsin: Rods: ____________
Ans: Rhodopsin
b) Sound: Eardrum: Dynamic balance: ____________
Ans: Semicircular canals
3. Which one or more of the expressions in column II are appropriate for the
items listed in column I? Rewrite the correct matching pairs:
Column I Column II
(i) The blind spot (a) Colour of the eye
(ii) The yellow spot (b) Shape of the eye
(iii) Ciliary muscles (c) Amount of light entering the eye
(iv) Iris (d) Maximum sensory cells
(v) Pupil (e) No sensory cells
Ans:
Column I Column II
(i) The blind spot (e) No sensory cells
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 3
(ii) The yellow spot (d) Maximum sensory cells
(iii) Ciliary muscles (b) Shape of the eye
(iv) Iris (a) Colour of the eye
(v) Pupil (c) Amount of light entering the eye
C. Short Answer Type questions
1. State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F). If false, correct it
by changing one single word.
a) Deafness is caused due to rupturing of pinna
Ans: False, Deafness is caused due to rupturing of tympanum.
b) Semicircular canals are concerned with static (positional) balance.
Ans: True.
2. Where are the following located? State their main functions:
a. Yellow Spot
Ans: On the horizontal axis of the eyeball, the yellow spot is virtually in the centre at
the back of the eye. It's the brightest part of your vision, as well as your colour vision.
b. Lacrimal Gland
Ans: The upper sideward portion of the eye orbit contains the lacrimal glands. They
discharge the secretion in the form of tears, that act as a lubricant, antibacterial, and
even clean the eyes of dust particles.
c. Organ of Corti
Ans: The Organ of Corti is located in the middle of the cochlear canal. It assists with
hearing.
d. Semicircular canal
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 4
Ans: In the inner ear, semicircular canals can be found. These aid in maintaining the
body's dynamic homeostasis.
e. Oval Window
Ans: The oval window is in the center of the ear. It aids in the vibration of the fluid in
the cochlear canals.
f. Utriculus
Ans: The inner ear contains the utriculus. It connects the cochlea to the semi-circular
canals. It also aids in regulating the body's static balance.
3. Given below are two sets (a) and (b) of five parts in each. Rewrite them in the
correct sequence.
a. Cochlea, tympanum, auditory canal, ear ossicles, oval window
Ans: Auditory canal, tympanum, ear ossicles, oval window, cochlea
b. Conjuctiva, retina, cornea, optic nerve, lens
Ans: Conjunctiva, cornea, lens, retina, optic nerve
4. Given below are certain structures. Write against them their special functional
activity.
a. Cochlea
Ans: The Cochlea includes the Corti organ, which includes hearing sensory cells.
They use the auditory nerve to send sound signals to the brain.
b. Auditory nerve
Ans: This is the major nerve that originates from the sensory cells in the cochlea.
Sound impulses travel from the inner ear to the brain by this nerve.
c. Retina
Ans: The retina is the light-sensitive innermost layer of the eye. The image of an
object perceived by the eyes is formed by the retina.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 5
d. Choroid
Ans: The choroid is the eyeball's main vascular layer. The eye receives nutrients from
choroid.
e. Sacculus
Ans: It is a component of the inner ear's semicircular canals. It contains sensory cells
known as macula, that aid in the body's static balance while it is in a stationary
position.
5. Complete the following table by filling in the blank spaces.
Structure Function
1. (i) Transfers impulse from inner ear to brain
2. (ii) Help to change the focal length of the eye lens
3. (iii) Dynamic equilibrium
Ans:
Structure Function
1. Auditory Nerve (i) Transfers impulse from inner ear to brain
2. Ciliary Muscle (ii) Help to change the focal length of the eye lens
3. Semicircular Canals (iii) Dynamic equilibrium
6. Name the following:
a. Two Pigments of the sensory cells
Ans: Rhodopsin and iodopsin.
b. Two types of adaptations
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 6
Ans: Dark adaptation and light adaptation.
c. Two kinds of accommodations
Ans: Distant vision accommodation and near vision accommodation.
d. Three layers of the eyeball
Ans: Sclera, choroid and retina.
7. Name the eye defects caused due to each of the following:
Cause Eye Defect
(a) Lens turns opaque
(b) Uneven curvature of the cornea
(c) Deficiency of Vitamin A
(d) Lens loses its flexibility
(e) Eye ball lengthens from front to back
(f) Lens becomes too flat
Ans:
Cause Eye Defect
(a) Lens turns opaque Cataract
(b) Uneven curvature of the cornea Astigmatism
(c) Deficiency of Vitamin A Night Blindness
(d) Lens loses its flexibility Presbyopia
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 7
(e) Eyeball lengthens from front to back Myopia
(f) Lens becomes too flat Hyperopia
D. Descriptive Type
1. Define the following terms:
(a) Conjunctiva:
Ans: The conjunctiva is a thin connective membrane that surrounds the surface of the
eyeball (bulbar conjunctiva) and reflects back to form the eyelid's inner layer
(palpebral conjunctiva). At the limbus, in which the sclera touches the cornea, this
tissue is firmly attached to the sclera. The conjunctiva contains the auxiliary lacrimal
glands (Krause and Wolfring), as well as goblet cells, which are responsible for
maintaining the eye moist.
(b) Macula Lutea:
Ans: The macula, also known as the macula lutea, is an oval-shaped pigmented area at
the centre of the human and animal retinas. The umbo, foveal avascular zone, foveola,
fovea, parafovea, and perifovea areas of the macula in humans have a diameter of
roughly 5.5 mm (0.22 in) and are subdivided into the foveola, umbo, fovea, foveal
avascular zone, parafovea, and perifovea areas.
(c) Adaptation:
Ans: The ability of the retina of the eye to adjust to different levels of light is known
as adaptation.
(d) Ampulla:
Ans: When the body is in motion, the ampulla is the inflated broad section of each
semicircular canal that includes sensory cells called cristae that aid in dynamic
equilibrium or dynamic balance.
2. Differentiate between members of each of the following pairs with reference to
what is given in brackets.
a) Myopia and hyperopia (Cause of the defect)
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 8
Ans:
Myopia Hyperopia
Myopia is produced by thecurvature Hyperopia is caused by the eyeball
of the lens or the lengthening of the shortening or a lens that is overly
eyeball. flat.
b) Rods and cones (Sensitivity)
Ans:
Rods Cones
Rods are light-sensitive. The cones are color sensitive.
c) Semi-circular canal and cochlea (Senses perceived)
Ans:
Semi-circular canal Cochlea
When the body is in motion, the Cochlea is sensitive to sound for
semicircular canal aids in dynamic hearing.
balance.
d) Rod and cone cells (Pigment)
Ans:
Rod Cells Cone Cells
Rod cells have rhodopsin. Cone cells have iodopsin.
e) Dynamic balance and static balance (Definition)
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 9
Ans:
Dynamic balance Static balance
Dynamic balance refers to the
The equilibrium that is maintained
body's ability to retain its
when the body is stationary is
equilibrium while rotating or
known as static balance.
spinning.
3. Give reason:
A. Sometimes medicines dropped into the eye come into the nose and even the
throat.
Ans: As the nasolacrimal duct directs the secretion into the nasal cavity, drugs spilled
into the eyes can often end up in the nose and throat.
B. Three small bones of ear ossicles are advantageous as compared to one single
bone for hearing.
Ans: The vibrations received by the tympanum are transmitted and amplified by three
little bones in the ear called ossicles. The vibrations received by the tympanum would
not be increased if these were substituted by a single bone. As a result, three tiny
ossicles of the ear are preferable than a single bone for hearing.
C. Blind spot is considered as 'area of no vision'.
Ans: Since there are no sensory cells in the blind spot, it is referred to as a 'region of
no vision,' and no picture striking it can be detected.
4. Answer the following:
(a) What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? Name the muscles of
the eye responsible for the same.
Ans: The power of accommodation refers to the ability to focus the eye at various
distances. The ciliary muscles are in charge of accommodation power.
(b) Mention the characteristics of the image that falls on the retina of the eye.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 10
Ans: The Characteristics of the image that gets formed on the retina is inverted and
real.
5. Describe the mechanism of focusing the image of a distant object in your eye
when you raise your head after reading a book.
Ans: While reading a book, the lens tends to become more convex or rounded because
of the contraction of ciliary muscles and that is why the book is usually read from a
short distance. When we elevate our heads to look at something far away, the ciliary
muscles relax in order to increase the tension on the suspensory ligament, allowing the
lens to stretch. We can focus on distant objects because of the shift in lens curvature.
6. By closing the eyes and gently pressing them with your palms, you may see
some specs of brilliant light. How do you get this sensation while there is no light
entering your eyes?
Ans: When we look at a bright object and thereafter close our eyes, the light
impression lasts only a few seconds. This is referred to as the persistence image or the
following image. It just lasts a tenth of a second. As a result, we can see some brilliant
light specks by closing your eyes on firmly touching them with our palms.
7. Name the three ear ossicles. How do they contribute in the mechanism of
hearing?
Ans: Malleus (hammer), Incus (anvil), and Stapes (stirr up) are the three ear ossicles.
The outer ear is where hearing begins. Sound waves, or vibrations, travel through the
external auditory canal and hit the eardrum when a sound is made outside the outer ear
(tympanic membrane). Vibrations are felt in the eardrum. The vibrations are
subsequently transmitted to the ossicles, which are three small bones in the middle ear.
The sound is amplified by the ossicles. They transmit sound waves to the inner ear,
where they are received by the fluid-filled hearing organ (cochlea).Sound waves are
transformed to electrical impulses when they reach the inner ear. These impulses are
sent to the brain via the auditory nerve. These electrical impulses are then translated
into sound by the brain.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 11
E. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
1. With reference to the functioning of the eye, answer the questions that follow:
a. What is the shape of the lens during (1) near vision (2) distant?
Ans: Shape of the lens:
Near vision - flattened
Distant - rounded or more convex
b. Name the two structures in the eye responsible for bringing about the change
in the shape of the lens.
Ans: Ciliary muscles and suspensory ligament are the two structures in the eye
responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of the lens.
c. Name the cells of the retina and their respective pigments which get activated
(1) in the dark and (2) in the light.
Ans: The cells of the retina and their respective pigments which get activated:
In the dark: Cells - rod cells, Pigment - rhodopsin
In the light: Cells - cone cells, Pigment - iodopsin
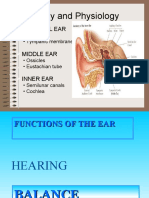
2. With reference to the human ear, answer the questions that follow:
a. Give the technical term for the structure found in the inner ear.
Ans: The inner ear is made up of tubes and channels known as the Labyrinth, which is
made up of two structures: the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth.
b. Name the part of the ear associated with (1) static balance (2) hearing (3)
dynamic balance.
Ans: The malleus, incus, and stapes are three ossicles (or small bones) in the middle
ear that are connected in a chain-like way. They are collectively known as Ear
ossicles.
c. Name the nerve, which transmits messages from the ear to the brain.
Ans: Auditory nerve transmits messages from the ear to the brain.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 12
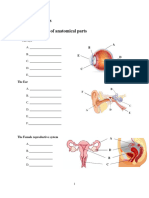
3. The figure given below refers to the vertical section of the eye of a mammal.
Study the figure carefully and answer the following questions.
(a) Label the guidelines shown as 1 to 10.
Ans: 1 - Aqueous chamber,
2 - Lens,
3 - Iris,
4 - Cornea,
5 - Conjunctiva,
6 - Sclera,
7 - Choroid,
8 - Retina,
9 - Yellow spot,
10 - Optic nerve (Blind spot)
(b) Write one important role of parts shown as 3 and 7.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 13
Ans: Part 3- It shows the Iris. Iris has radial and circular muscles that dilate and
constrict the pupil, respectively.
Part 7- It shows Choroid. It's the eyeball's central layer, which is densely packed with
blood vessels and feeds the eye.
(c) Write one structural difference between the parts shown as 9 and 10.
Ans:
Part 9- Yellow spot Part 10 - Optic nerve
It carries sensory cells and
It carries no sensory cells.
especially the cone cells.
(d) Mention one functional difference between the parts shown as 6 and 8.
Ans:
Part 6 - Sclera Part 8 - Retina
Sclera is responsible for giving Retina is responsible for acting as
shape to the eyeball. screen to form image of an object.
4. Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same
and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the defect shown in the diagram.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 14
Ans: Myopia is the defect shown in the diagram.
(b) Give two possible reasons for this defect.
Ans: The two possible reasons for this defect are:-
(i) The lens of the eye becomes convex or curved.
(ii) The eyeball's depth is excessive, i.e. the eyeball is stretched from front to rear.
(c) Name the parts labeled 1 to 4.
Ans: Part 1 - vitreous humour,
Part 2 - blind spot,
Part 3-lens,
Part 4-pupil.
(d) Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
Ans: Concave lens the type used to correct this eye defect.
(e) Draw a labeled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified
using the lens named above.
Ans:
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 15
5. The figure below is the sectional view of a part of the skull showing a sense
organ:
(i) Name the sense organ.
Ans: Ear
(ii) What are the parts labeled 'm', 'i' and 's'? What do these parts constitute
collectively?
Ans: m - malleus,
i - incus and
s - stapes
These are collectively called ear ossicles.
(iii) What do you call the part shown in the form of a spiral? What is its function?
Ans: Cochlea. Vibrations in the hair of the sense cells in the cochlea transfer the
hearing impulse to the brain through the auditory nerve.
(iv) Name the part labeled 'tm'. What is its function?
Ans: Membrane of the tympanic cavity. In the process of hearing, it vibrates and then
sets the ear ossicles vibrating.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 16
6. Given below is a diagram of a part of the human ear. Study the same and
answer the questions that follow:
(i) Give the collective biological term for Malleus, Incus and Stapes.
Ans: Ear ossicles is the collective biological term for Malleus, Incus and stapes.
(ii) Name the parts labeled A, B and C in the diagram.
Ans: A - Cochlea,
B - Semicircular canals,
C - Ear ossicles.
(iii) State the functions of the parts labeled 'A' and 'B'.
Ans: Part A- The cochlea aids in the transmission of impulses from the auditory nerve
to the brain.
Part B- The body's dynamic balance is maintained via semicircular canals.
(iv) Name the audio receptor region present in the part labeled 'A'.
Ans: Organ of Corti is the audio receptor region present in the part labeled 'A'.
7. Draw a labeled diagram of the inner ear. Name the part of the inner ear that is
responsible for static balance in human beings.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 17
Ans:
Utriculus and Sacculus are responsible for maintaining static balance in human beings.
8. Have a look at the posture of this woman who is reading a book and answer the
questions which follow:
(a) What problem is she facing? Name the problem.
Ans: Myopia is the problem that she is facing.
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 18
(b) What are the two conditions shown in sections A and B of the eye as
applicable to her?
Ans: A-Normal eye, B-Myopia
(c) What kind of looking glasses she needs?
Ans: Here, concave-lens looking glasses are required.
9. The figure given below shows the principal parts of a human ear. Study the
diagram and answer the following questions.
(a) Label the parts 1 to 8.
Ans: 1 - External ear (pinna),
2 - Ear drum (tympanum),
3 - Auditory canal,
4 - Malleus,
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 19
5 - Semicircular canals,
6 - Cochlea,
7 - Auditory nerve,
8 - Eustachian tube.
(b) State the role of parts 6, 7 and 8.
Ans: The role of:
Part 6 (Cochlea) - Cochlea is responsible for carrying the sensory cells for hearing.
Part 7 (Auditory nerve) - Auditory Nerve is responsible for transmitting the impulse of
hearing to the brain.
Part 8 (Eustachian tube) - Eustachian tube is responsible for equalizing air pressure on
both the sides of the tympanum.
(c) Why is it harmful to use a sharp object to remove ear wax? Mention the
number and name of the part involved.
Ans: Using a sharp tool to remove ear wax is dangerous since it can rupture the ear
drum. The part involved is part 2 - Ear drum (tympanum).
Class X Biology www.vedantu.com 20
You might also like
- 11 Sensing The Environment PDFDocument12 pages11 Sensing The Environment PDFTAi Man Chan100% (4)
- Study Questions Special SensesDocument37 pagesStudy Questions Special SensesSurajit Bhattacharjee93% (15)
- Review Manual Dost Sei Scholarship ExampdfDocument40 pagesReview Manual Dost Sei Scholarship ExampdfJose BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Special SensesDocument4 pagesQuiz - Special SensesGlydenne Glaire Poncardas Gayam100% (1)
- LEC M3.3 BlockADocument8 pagesLEC M3.3 BlockASieg100% (1)
- Final Doc 1 PDFDocument20 pagesFinal Doc 1 PDFDev ROYNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansDocument19 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Sense OrgansParardha DharNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument8 pagesSense OrgansKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- Biology Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesBiology Sense OrgansasdasdNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test Lesson 4Document3 pagesAnatomy Test Lesson 4Mary Rose BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs - Work SheetDocument11 pagesSense Organs - Work SheetVarshni NateshmariNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument74 pagesHuman EyeAditi MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Exercise 15Document22 pagesUnit 8 Exercise 15Andrei AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Special Senses TestDocument47 pagesSpecial Senses TestNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- 02 - Human Eye and Colourful World - X - SSMDocument33 pages02 - Human Eye and Colourful World - X - SSMDøomNo ratings yet
- Write The Name of Each Numbered Part On The Corresponding Line of The Answer SheetDocument5 pagesWrite The Name of Each Numbered Part On The Corresponding Line of The Answer Sheetsilva, april joy c.No ratings yet
- MCQS On EyeDocument71 pagesMCQS On EyeFareed KhanNo ratings yet
- Biology of Humans Concepts Applications and Issues 5Th Edition Goodenough Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesBiology of Humans Concepts Applications and Issues 5Th Edition Goodenough Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbridget.price734100% (15)
- Sense Organs PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organs PDFTanzila SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Skull and Orbital Cavity Anatomy QuestionsDocument9 pagesSkull and Orbital Cavity Anatomy QuestionsAnon AnonNo ratings yet
- Eye Dissection Report Write Up 2014Document8 pagesEye Dissection Report Write Up 2014api-351895935No ratings yet
- The Ear and The Eye Topic Test With PermissionsDocument12 pagesThe Ear and The Eye Topic Test With Permissionsphenyommolawa561No ratings yet
- OpthamologyDocument12 pagesOpthamologyRayyanNo ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument95 pagesOphthalmologyB34-YvesJethro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Bit Bank Ix - ClassDocument3 pagesSense Organs: Bit Bank Ix - ClassSurya RaoNo ratings yet
- Scan Jan 29, 2021Document25 pagesScan Jan 29, 2021sheinarkarbo2020No ratings yet
- 4.1 Answers: RememberingDocument24 pages4.1 Answers: RememberingDanny TNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in LS2Document3 pagesSummative Test in LS2Riza Joy Nalix SolayaoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesNervous System and Sense OrgansSudeep MandalNo ratings yet
- Healthy Eyes and Ears Unit 16Document4 pagesHealthy Eyes and Ears Unit 16CARMIN INES GOMEZ RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 2Document235 pagesOphthalmology 2yididiyagirma30No ratings yet
- RSPL/1: CBSE Pariksha-2014 AnswersDocument8 pagesRSPL/1: CBSE Pariksha-2014 Answersprof_ktNo ratings yet
- Grand Test 166.. 2019 PDFDocument116 pagesGrand Test 166.. 2019 PDFPandey AyushNo ratings yet
- Assuit - MCQs (NeDocument84 pagesAssuit - MCQs (NeMax TraderNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Document72 pagesLakhmir Singh Class 10 Solutions Physics Chapter 6Aishwaria MurthyNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document5 pagesModule 6Aya AbdelgaleelNo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 5 - Science - Sample Paper MSDocument10 pagesScience - Grade 5 - Science - Sample Paper MSAmita BarjtiyaNo ratings yet
- Dho Health Science Updated 8th Edition Simmers Test BankDocument9 pagesDho Health Science Updated 8th Edition Simmers Test Bankjosephrodriguez04121993gbm100% (30)
- Hukogman Eye Back ExerciseDocument7 pagesHukogman Eye Back ExerciseAbhay Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- PM291 ErrataDocument10 pagesPM291 ErrataServal GideonNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteDocument29 pagesSense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteAnkit SubediNo ratings yet
- 15 Detecting EnvironmentDocument106 pages15 Detecting EnvironmenttoperissaNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz: Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology: Nursing Test Bank NCLEX Practice QuestionsDocument32 pagesPractice Quiz: Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology: Nursing Test Bank NCLEX Practice QuestionsLelah Faye VidalNo ratings yet
- 1 Parts and Function of Eye WsDocument2 pages1 Parts and Function of Eye Wsaastha dograNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs NewDocument14 pagesSense Organs NewSubham KalwarNo ratings yet
- Ujian Bab 1 Form 3: Stimuli and ResponsesDocument2 pagesUjian Bab 1 Form 3: Stimuli and Responsesalya sophiaNo ratings yet
- Methodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics SchoolDocument6 pagesMethodical Instruction For The 1st Year Students of The General Medicine and Pediatrics SchoolAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - WS - X-24-25Document4 pagesNervous System - WS - X-24-25shnc1801No ratings yet
- Science Worksheet - Light: Q1: Choose The Correct OptionDocument2 pagesScience Worksheet - Light: Q1: Choose The Correct OptionSarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Human Eye WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Eye Worksheetcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- Biophy ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiophy ReviewerMikhaelaNo ratings yet
- OPHTHALMOLOGYDocument69 pagesOPHTHALMOLOGYcollinsmagNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Neuro Sense OrgansDocument25 pagesMedsurg Neuro Sense Organsj UNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Basis Dentistry 4th Liebgott Test BankDocument5 pagesAnatomical Basis Dentistry 4th Liebgott Test BankfahedqNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument25 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourful WorldjituNo ratings yet
- EN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytDocument18 pagesEN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- OPAL MCQs & SEQsDocument39 pagesOPAL MCQs & SEQsanilNo ratings yet
- Special Senses OutlineDocument10 pagesSpecial Senses OutlinePIOZRNo ratings yet
- 21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersDocument6 pages21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersGuru SrinivaasNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Final ExamDocument7 pagesStudy Guide - Final ExamRichard LaRouechNo ratings yet
- 2.BLock E Sloved Proff 2020Document26 pages2.BLock E Sloved Proff 2020mghassan45No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Solutions For Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 - MetallurgyDocument33 pagesICSE Selina Solutions For Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 7 - MetallurgyDeepakNo ratings yet
- Blue-J: ICSE Class - 10Document186 pagesBlue-J: ICSE Class - 10DeepakNo ratings yet
- Indian Maps Labelling ICSE Geogarphy Class 10Document5 pagesIndian Maps Labelling ICSE Geogarphy Class 10DeepakNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledDeepakNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pagesMiddle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Dr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media TreatmentDocument54 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis Media TreatmentPrateek VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Anatomy and Physiology: AuditionDocument16 pagesOverview of The Anatomy and Physiology: AuditionEm Hernandez AranaNo ratings yet
- Ms Drills 3Document10 pagesMs Drills 3Karen Mae Santiago AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Easy Peasy EardrumsDocument52 pagesEasy Peasy EardrumsUCD GEMNo ratings yet
- ADULT HEALTH NURSING-2 INCLUDING GERIATRIC NURSING (Syllabus)Document4 pagesADULT HEALTH NURSING-2 INCLUDING GERIATRIC NURSING (Syllabus)Abhishek NaharNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment: Assessment Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal FindingsDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment: Assessment Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal FindingsJosal SinonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NOTESDocument3 pagesChapter - 2 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NOTESShri ShriNo ratings yet
- Foto Acoustic EmitionDocument83 pagesFoto Acoustic EmitionAlok kumarNo ratings yet
- Plants ScreamDocument27 pagesPlants ScreamМария ПавловаNo ratings yet
- VertigoDocument3 pagesVertigoGirishNo ratings yet
- Dr. Huma Fatima AliDocument24 pagesDr. Huma Fatima AliNouman Umar100% (1)
- The Floppiness of The Bunny EarsDocument1 pageThe Floppiness of The Bunny EarsxSymbyotyKxNo ratings yet
- Sensorineuralsystem MAY152023Document94 pagesSensorineuralsystem MAY152023Edmalyn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- All Histology Semester 2 QuizzesDocument21 pagesAll Histology Semester 2 QuizzesBarwdi ZenNo ratings yet
- Module Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesModule Nervous SystemMan Gal7No ratings yet
- AL Biology 1989 Paper 1 MarkingDocument12 pagesAL Biology 1989 Paper 1 Markingapi-3860987No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: External EarDocument73 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: External Earvidge5No ratings yet
- n82 - Procedure For Aural ToiletDocument2 pagesn82 - Procedure For Aural ToiletDaniel Tanri Rannu100% (1)
- The Audiogram Workbook Nonorganic Hearing Loss Cases - MedOne, ThiemeDocument10 pagesThe Audiogram Workbook Nonorganic Hearing Loss Cases - MedOne, ThiemeLara AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansMelanie GialogoNo ratings yet
- Mastoidectomy: Surgical Techniques: Key PointsDocument14 pagesMastoidectomy: Surgical Techniques: Key PointsMichel Dayanna Serrano TasconNo ratings yet
- 267 Impulses Serving Pain Sensation in The Left Foot Are RelayedDocument12 pages267 Impulses Serving Pain Sensation in The Left Foot Are RelayedNathanNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma of The Ear CanalDocument9 pagesCholesteatoma of The Ear CanalWanda DamayantiNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For A Neuropsychiatric ExamDocument29 pagesHow To Prepare For A Neuropsychiatric ExamEricNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument19 pagesThe Human EarNicole maderaziNo ratings yet
- Eng 341 Course Material PDFDocument185 pagesEng 341 Course Material PDFSergio LamusNo ratings yet