Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Task
Task
Uploaded by
Anjali PatelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Task
Task
Uploaded by
Anjali PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2.
Generally, software requirements specifications (SRSs) describe what the software will do and how it
will perform. Furthermore, it defines what functionality the product must have to satisfy the
requirements of all stakeholders (business and users).
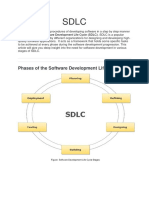
Q3. SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) is a framework defining the activities carried out during a
software development cycle. The SDLC model consists of six phases. 1. Requirement: In this phase, all
the requirements are collected from the customer/client. They are provided in a document called
Business requirements specification (BRS) and System requirement specification (SRS). All the details are
discussed with the customer/client in detail. 2. Design: It has two steps: ❖ High-level design (HLD): It
describes the architecture of software products. ❖ Low-level design (LLD): It describes how each and
every feature in the product should work and every component. 3. Implementation: ❖ This is the
longest phase. ❖ This phase consists of the Front end + Middleware + Back-end. ❖ In front-end:
Development of coding is done even SEO settings are done. ❖ In Middleware: They connect both the
front end and back end. ❖ In the back-end, a database is created. 4. Testing: Testing is carried out to
verify the entire system. The aim of the tester is to find out the gaps and defects within the system and
also to check whether the system is running according to the requirement of the customer/client. 5.
Deployment: After successful testing, the product is delivered/deployed to the client, and even clients
are trained on how to use the product. 6. Maintenance: Once the product has been delivered to the
client a task of maintenance starts as when the client will come up with an error the issue should be
fixed from time to time.
Q4. ● The term project refers to a temporary undertaking by a company or organization (such as the
creation of a new product, service, or result). ● The concept of a program refers to a collection of
projects that have similar or related goals, and which are managed and coordinated as a group instead
of independently ● Portfolios are collections of related and unrelated programs and/or projects within
the same organization Q5 Difficult stakeholders are those stakeholders who could disrupt or even bring
an end to a project unless you manage them carefully. They might not be open and forthcoming in their
communications, or they may only offer negative feedback. Some stakeholders may be frustrated at the
progress of the project or may not seem to be very engaged in the work. Here are some strategies to
manage these stakeholders: 1. Identify your stakeholders 2. Categorize and prioritize them 3. Stay calm
4. Listen carefully 5. Understand their motivation 6. Be objective 7. Respond quickly to issues 8. Be firm,
if necessar
You might also like
- Microsoft PL-900 Exam - Questions and Answers - CertLibrary - Com-Pg1Document11 pagesMicrosoft PL-900 Exam - Questions and Answers - CertLibrary - Com-Pg1Radu Lucian Mihai0% (1)
- Agile ModelDocument5 pagesAgile ModelRaghavendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Software AssignmentDocument22 pagesSoftware AssignmentNitin CoolNo ratings yet
- Airline Information System-Evolution & TrendsDocument37 pagesAirline Information System-Evolution & Trendsdyutimanganguly100% (1)
- Product ManagementDocument9 pagesProduct ManagementKu RatheeshNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document10 pagesLab 2Chauhan AkanshaNo ratings yet
- CT091 0 M SydmDocument25 pagesCT091 0 M SydmDipesh GurungNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument57 pagesSDLCKai BeeNo ratings yet
- Contact Me To Get Fully Solved Smu Assignments/Project/Synopsis/Exam Guide PaperDocument10 pagesContact Me To Get Fully Solved Smu Assignments/Project/Synopsis/Exam Guide PaperMrinal KalitaNo ratings yet
- Se NotesDocument4 pagesSe NotesYashavanth B ANo ratings yet
- BA Learning MaterialDocument212 pagesBA Learning MaterialSai VenkatNo ratings yet
- Agile SDLCDocument28 pagesAgile SDLCkartiknamburiNo ratings yet
- SDLCunit 1Document7 pagesSDLCunit 1Divyadeep SinghNo ratings yet
- -朴维- PARVEZ MOHAMMAD SHARIAR - Homework3Document5 pages-朴维- PARVEZ MOHAMMAD SHARIAR - Homework3Shariar Parvez TonmoyNo ratings yet
- SDLC ModelsDocument43 pagesSDLC ModelsdbedadaNo ratings yet
- Christine Mae Cion - ASYNCHRONOUS ACTIVITY NO 1Document3 pagesChristine Mae Cion - ASYNCHRONOUS ACTIVITY NO 1Christine Mae CionNo ratings yet
- Se Bava!Document9 pagesSe Bava!Mr.CrazybeanNo ratings yet
- DSDLC ModelsDocument26 pagesDSDLC ModelsAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life: Cycle (SDLC)Document34 pagesSoftware Development Life: Cycle (SDLC)JohnNo ratings yet
- What Is Software Economics?Document10 pagesWhat Is Software Economics?Abdul Raheem MemonNo ratings yet
- NB: Should Include Transport, Any Catering and AccommodationsDocument6 pagesNB: Should Include Transport, Any Catering and AccommodationsSarange AnneNo ratings yet
- The Discipline of Product ManagementDocument10 pagesThe Discipline of Product ManagementGodofredo O̲̲̅̅f̲̲̅̅i̲̲̅̅c̲̲̅̅i̲̲̅̅a̲̲̅̅l̲̲̅̅'̲̲̅̅F̲̲̅̅b̲̲̅̅No ratings yet
- Software Project Management Software Project Management Software Project Management Software Project ManagementDocument67 pagesSoftware Project Management Software Project Management Software Project Management Software Project ManagementSaumya SwapnesawrNo ratings yet
- UdayDocument19 pagesUdayRAJNo ratings yet
- Software Engineer NotesDocument15 pagesSoftware Engineer NotesISMAIL SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- Management of Time Uncertainty in AgileDocument12 pagesManagement of Time Uncertainty in AgileijseaNo ratings yet
- Devops Unit 1Document57 pagesDevops Unit 1vivekNo ratings yet
- PM Unit 1Document15 pagesPM Unit 1haashboi5100% (1)
- Software Life CycleDocument15 pagesSoftware Life CycleJaiNo ratings yet
- Process ModelDocument4 pagesProcess ModelParvathi GoudNo ratings yet
- Testing ReportDocument36 pagesTesting Reportmakkenahemanth5No ratings yet
- Agile ModelDocument6 pagesAgile ModelNDDHSADNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3.1 Software Development Life Cycle EditDocument10 pagesWorksheet 3.1 Software Development Life Cycle EditOscarinho OrtizNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 08 Project Management NoteDocument5 pagesChapter - 08 Project Management NoteGolam MostofaNo ratings yet
- SPM IntroDocument43 pagesSPM IntroRamya Nandakumar100% (1)
- Overview of Software Project Planning and Step Wise Software Project PlanningDocument32 pagesOverview of Software Project Planning and Step Wise Software Project PlanningANIRUDH B K 19BIT0348No ratings yet
- Se ch1Document55 pagesSe ch1mubarek muhammedNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument12 pagesAssignmentOsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Computer Science ProjectDocument28 pagesComputer Science ProjectNandish.DNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis in A Agile Software Project Management NotebookDocument6 pagesBusiness Analysis in A Agile Software Project Management NotebookreverieNo ratings yet
- International Agile Product Owner Foundation - Study GuideDocument42 pagesInternational Agile Product Owner Foundation - Study GuideAjay KUmar100% (1)
- Modern Academy: Department of Manufacturing Engineering and Production TechnologyDocument22 pagesModern Academy: Department of Manufacturing Engineering and Production TechnologybassemNo ratings yet
- R20 IT 4-1 - DevOps - UNIT - 1Document23 pagesR20 IT 4-1 - DevOps - UNIT - 1Bitra Venugopal100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1.exerciseDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 1.exerciseBalamurugan Balahaisnin100% (1)
- Untitled DocumentDocument9 pagesUntitled DocumentamyNo ratings yet
- ITPM Task ADocument16 pagesITPM Task Ajumaboyevabarno80No ratings yet
- Software Engineering Ch-2Document16 pagesSoftware Engineering Ch-2om chavanNo ratings yet
- Project Management ProjectDocument4 pagesProject Management Projectbacchusw90No ratings yet
- Chapter IV - Software Development Life CycleDocument94 pagesChapter IV - Software Development Life Cyclelloyd yusoresNo ratings yet
- Prince2 ThemesDocument3 pagesPrince2 Themesshiva_1912-1No ratings yet
- Manufa Midterm (Arayata)Document9 pagesManufa Midterm (Arayata)Menchie Ella Diezmos GunoNo ratings yet
- Prince2 Themes EbookDocument16 pagesPrince2 Themes EbookRupoNo ratings yet
- PM Chapter-7Document4 pagesPM Chapter-7GolamSarwarNo ratings yet
- Agile Project ManagementDocument7 pagesAgile Project ManagementMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- IT Technical best practices: How to Reduce Agile cycle time with reusable code?From EverandIT Technical best practices: How to Reduce Agile cycle time with reusable code?No ratings yet
- Independencia de América - Fuentes para Su Estudio, Catálogo de Documentos Conservados en El Archivo General de Indias de Sevilla Vol. 1 (Digital Version)Document473 pagesIndependencia de América - Fuentes para Su Estudio, Catálogo de Documentos Conservados en El Archivo General de Indias de Sevilla Vol. 1 (Digital Version)Viviana PiciuloNo ratings yet
- Status Profile Creation and Assignment To An Order Type in SAP PPDocument7 pagesStatus Profile Creation and Assignment To An Order Type in SAP PPHemant UNICHEMLLPNo ratings yet
- Panel Data Models Stata Program and Output PDFDocument8 pagesPanel Data Models Stata Program and Output PDFcrinix7265No ratings yet
- Lynn Htet Aung - Current Topics PaperDocument3 pagesLynn Htet Aung - Current Topics PaperLeo ChangesnamealotNo ratings yet
- Helmut Leitner Patterns LectureDocument1 pageHelmut Leitner Patterns LectureSergiu Dumulesc DemeanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Messages and Memorandums: Instructor Only VersionDocument39 pagesElectronic Messages and Memorandums: Instructor Only VersionPuyatnako100% (1)
- O-RAN WG4 IOT 0-v04 00Document122 pagesO-RAN WG4 IOT 0-v04 00mahyar777No ratings yet
- Sony Kv28,32fq75 Chassis Ae-5aDocument108 pagesSony Kv28,32fq75 Chassis Ae-5asistemsistemNo ratings yet
- Free Download A Beginners Guide To Watercolor Painting Step by Step Lessons For Portraits Landscapes and Still Lifes Includes 16 Practice Postcards Takako Y Miyoshi Full Chapter PDFDocument52 pagesFree Download A Beginners Guide To Watercolor Painting Step by Step Lessons For Portraits Landscapes and Still Lifes Includes 16 Practice Postcards Takako Y Miyoshi Full Chapter PDFisabel.fernandez806100% (23)
- Valhallaroom - New Reverb Mode Lv-426Document1 pageValhallaroom - New Reverb Mode Lv-426aaaaNo ratings yet
- Poster - Dept of MathDocument1 pagePoster - Dept of MathDrSenthilkumar R DharmalingamNo ratings yet
- Learning Processing: A Beginner's Guide To Programming Images, Animation, and InteractionDocument10 pagesLearning Processing: A Beginner's Guide To Programming Images, Animation, and Interactionabas004100% (1)
- E23CSEU1043 Sneha Assignment 7Document7 pagesE23CSEU1043 Sneha Assignment 7chipichipichapachapa2121No ratings yet
- Insite Register MapDocument571 pagesInsite Register Mapyago matiolliNo ratings yet
- Flash Support 081010Document9 pagesFlash Support 081010Dario Sebastian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Business Architecture Basics: Presentation To The Metropolitan State University 2016-01-19Document97 pagesBusiness Architecture Basics: Presentation To The Metropolitan State University 2016-01-19VinayKarthikBSNo ratings yet
- Molly Mcgregors ResumeDocument1 pageMolly Mcgregors Resumeapi-248127956No ratings yet
- HESHBON Wheel Balancer: Installation/Operation & Maintenance ManualDocument54 pagesHESHBON Wheel Balancer: Installation/Operation & Maintenance ManualanoNo ratings yet
- Design Patterns CDF PDFDocument13 pagesDesign Patterns CDF PDFRajesh KannaNo ratings yet
- Agile A Managers GuideDocument48 pagesAgile A Managers GuideDwaipayan MojumderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1 - 1.8 QuizDocument2 pagesChapter 1.1 - 1.8 Quizspeterlee6253No ratings yet
- Pentium Vs 604eDocument1 pagePentium Vs 604escriNo ratings yet
- Project Charter Form TemplateDocument5 pagesProject Charter Form TemplatensadnanNo ratings yet
- Using Oracle Database Cloud Service 1 PDFDocument388 pagesUsing Oracle Database Cloud Service 1 PDFKuldeep PariharNo ratings yet
- Distributed MutexDocument24 pagesDistributed MutexmukiNo ratings yet
- Veritas Volume Replicator 5.x For Solaris - COURSE DESCRIPTIONDocument2 pagesVeritas Volume Replicator 5.x For Solaris - COURSE DESCRIPTIONPascal LouisNo ratings yet
- Financial Management For IT ServicesDocument10 pagesFinancial Management For IT ServicesAmeen MtNo ratings yet
- InteliCharger 65 - 24 AF DatasheetDocument3 pagesInteliCharger 65 - 24 AF Datasheetjean sanchezNo ratings yet