Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resourceful Mock Examinations 2020: Physics
Resourceful Mock Examinations 2020: Physics
Uploaded by
Kawesa MustaphaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resourceful Mock Examinations 2020: Physics
Resourceful Mock Examinations 2020: Physics
Uploaded by
Kawesa MustaphaCopyright:
Available Formats
P510/2
PHYSICS
Paper 2
Nov, 2020
2½ hours
ST. MARYS’ KITENDE
Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education
RESOURCEFUL MOCK EXAMINATIONS 2020
PHYSICS
Paper 2
(Principal Subject)
2 hours 30 minutes
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
Answer only five questions, taking at least one question from each of the sections A, B,
Cand D, but not more than one question should be chosen from either section A or
section B.
Any additional question(s) answered will not be marked.
Mathematical tables and squared paper will be provided.
Non-programmable Silent Scientific Calculators may be used.
Assume where necessary:
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m s– 2
Specific heat capacity of water, = 4.20 × 103 J kg – 1 K – 1
Speed of light in Vacuum, c = 3.0 × 108m s – 1
Speed of sound in air, v = 3.40 × 102 m s – 1
Electroniccharge, e = 1.60 × 10 – 1 9 C
Electronic mass, me = 9.11 × 10 – 31 kg
Permeability of free space, µo = 4π × 10 – 7 H m – 1
Permittivity of free space,
ε0 = 8.85 ×10 – 1 2 F m– 1
1
The Constant, 4 πε 0 = 9.0 × 109 F– 1 m
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 1
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 2
SECTION A
1. (a) What is meant by the following terms?
(i) Monochromatic light. (1 mark)
(ii) Absolute refractive index of a material. (1 mark)
(b) (i) Define the term refracting edge of a triangular prism. (1 mark)
(ii) Describe an experiment to determine the refractive index of the
material of atriangular glass prism of known refracting angle
using a spectrometer. (6 marks)
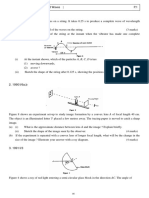
(c) A concave mirror of focal length 6.0 cm is arranged co-axially with a
concave lens of focal length 15.0 cm so that the distance between
them is 4.0 cm. A point object is placed 10.0 cm in front of the
concave lens and remote from the mirror as shown in figure 1.
(i) Determine the position of the final image formed after two
refractions by the concave lens and one reflection by the
concave mirror. (5 marks)
(ii) Sketch a ray diagram for the action in (i) above. (2 marks)
(d) (i) Draw a labelled diagram showing the essential parts of a
photographic camera. (2 marks)
(ii) Explain the role of the diaphragm in a photographic camera.
(2 marks)
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 3
2. (a) (i) Define the terms spherical and chromaticaberrations as applied to
lenses. (2 marks)
(ii) Explain how spherical and chromatic aberrations are minimized in
lenses. (4 marks)
(b) What is meant by the following terms?
(i) Accommodation of the eye. (1 mark)
(ii) Visual angle. (1 mark)
(c) (i) State two advantages and two disadvantagesof Galilean
telescopes over Astronomical telescopes. (4 marks)
(ii) An astronomical telescope has a distance of 100 cm between its
lenses and forms a final image of a distant object at infinity.
If the objective lens has a diameter of 10.0 cm and focal length
of 75.0 cm, determine the angular magnification of the
instrument and the size of the eye ring. (5 marks)
(d) Distinguish between compound microscopesand Astronomical
telescopes. (3 marks)
SECTION B
3. (a) (i) What are forced oscillations? (1 mark)
(ii) Give twoexample of forced oscillations. (2 marks)
(b) Define the terms as applied to piped instruments:
(i) Fundamental frequency. (1 mark)
(ii) Overtones. (1 mark)
(c) Two tuning forks of the same frequency of 512 Hz are sounded near
the open ends of two tubes of the same diameter but of different
lengths.
Tube A is closed at only one end while tube B is open at both ends. If
they both have the same end correction and are made to sound at
their first resonance:
(i) Determine the ratio of the length of tubeA to the length of tube
B. (3 marks)
(ii) Suppose the speed of sound in air is 330 m s and tube A has
–1
a length of 16.0cm, find the value of the end correction.
(3 marks)
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 4
(d) (i) What is Doppler effect? (1 mark)
(ii) An observer O moving along a straight road at a velocity u0
approaches a source of sound S moving in the opposite
direction at a velocity uS. Suppose f is the frequency of the
sound waves and V is the speed of sound waves in air, derive an
expression for the apparent frequency of waves received by the
observer. (3 marks)
(e) (i) What are beats? (1 mark)
(ii) Describe how a musical instrument can be tuned. (4 marks)
4. (a) (i) State Huygens’s principle. (1 mark)
(ii) Use Huygens’s principle to verify Snell’s law of refraction.
(4 marks)
(b) (i) What is optical path difference? (1 mark)
(ii) Explain how interference patterns are formed in Young’s double
slit experiment. (3 marks)
(c) Derive an expression for the fringe separation in Young’s double slit
experiment. (4 marks)
(d) Two optically thin, flat glass slides are separated at one end by a wire
of diameter 0.20 mm. At the other end, the slides touch each other,
giving the air between them a thickness ranging from 0 to 0.20 mm.
The plates are 15.0 cm long and are illuminated from above by light
of wave length 6.0 × 10 – 7 m.
(i) Use suitable well defined symbols to derive an expression for
the fringe separation observed in the air – wedge. (4 marks)
(ii) Determine the number of bright fringes seen in the reflected
light. (3 marks)
SECTION C
5. (a) (i) Define the termmagnetic flux density and state its unit.
(2 marks)
(ii) Write down the expression for the magnetic flux density at a
perpendicular distance, d, from a straight wire carrying a
current, I in free space. (1 mark)
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 5
(iii) Suppose a similar wire of the same length L, is placed parallel
to the first wire a distance, d from it and also carrying a current
I in opposite direction, derive an expression for the magnetic
force itt experiences. (4 marks)
(b) Figure 2 shows a simple device used to measure current, I, flowing
through each of the parallel wires QR and WY, each of length 9.81 cm
and separated by a distance of 4.0 mm. When I = 2.0 A, the wire
frame PQRS is made horizontal by weight Mg.
(i) Determine the value of mass M. (4 marks)
(ii) A third wire AB of the same length as QR and WY is placed
directly above WY and parallel to it at a distance y from WY
and is carrying a current of 3.0 A from right to left. Find
the value of y for which the resultant magnetic flux density
along wire WY is zero. (3 marks)
(c) State three structural adjustments necessary to convert a moving coil
galvanometer into a ballistic galvanometer. (3 marks)
(d) Explain the occurrence of hall voltage across opposite faces of a
conducting slab carrying current when placed across a magnetic
field. (3 marks)
6. (a) (i) State the laws of electromagnetic induction. (2 marks)
(ii) Use Lenz’s law and the conservation of energy to show that
when a straight conductor of length L, is moved across a
uniform magnetic field of flux density B, in a closed conducting
circuit at a terminal velocity v, an e.m.f, E = BLv is induced
across it. (4 marks)
(b) A uniform circular copper discof plane area Ais placed between the
poles of a large U shaped magnet with its plane normal to the field of flux
density B. The disc is then span about its axle at a frequency f.
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 6
(i) Derive an expression for the e.m.f. induced between the axle
and the rim the disc? (4 marks)
(ii) If the radius of the disc is 2.5 cm, the magnetic flux density in
the region of the disc is 0.84 T and the disc is rotated at 3000
revolutions per minute, what is the magnitude of the e.m.f.
generated across the disc? (4 marks)
(c) (i) What are Eddy currents? (2 marks)
(ii) With the aid of a labelled diagram, explainone industrial
application of Eddy currents. (4 marks)
7. (a) (i) Define peak value and root mean square value of alternating
current. (2 marks)
(ii) An alternating voltage V = 2.0 sin 120πt is connected across an
inductor of self-inductance 0.50 H. Determine the root mean
square current flowing through the inductor. (4 marks)
(b) (i) Describe the structure and mode of operation of a hot wire
ammeter. (5 marks)
(ii) State two advantages of a.c. meters over moving coil meters.
(2 marks)
(c) Figure 3 shows a 5.0 mH inductor and a 10.0 Ω connected in series
with a 6.0 V d.c. battery.
(i) Determine the voltage across the resistor immediately the
switch is just closed. (3 marks)
(ii) What will be the voltage across the 10.0 Ω resistor when the
switch has stayed closed for a much longer period of time.
(2 marks)
(iii) Explain the difference in the values of the results in (i) and (ii)
above. (2 marks)
SECTION D
8. (a) Distinguish between an electric field intensity and an electric
potential. (2 marks)
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 7
(b) Three point chargesP, Q and R of +5µC, – 4µC and + 25µC lie along
the + x direction in one straight line and in that respective order,
equidistant from one another 3.0 cm apart. A point, S, is 5.0 cm from
both P and R below the line PQR. Determine the resultant electric
field intensity at S. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Explain the term corona discharge? (3 marks)
(ii) Describe one industrial application of Corona discharge.
(6 marks)
(d) Briefly explain how anElectrophorus works. (3 marks)
9. (a) (i) What is a capacitor? (1 mark)
(ii) Give three industrial uses of a capacitor. (3 marks)
(b) (i) Derive an expression for the energy stored in a capacitor of
capacitance C, farads when connected to a d.c. source of e.m.f.
V, volts. (3 marks)
(ii) A 200 µF capacitor is connected across a 12.0 V battery and
allowed to charge fully. The capacitor is then disconnected from
the battery and instead connected to an electric heater
immersed in 1000 cm3 of water at room temperature. Assuming
no energy losses occur in the process, determine the
temperature change in the water. (4 marks)
(c) Describe how a calibrated gold leaf electroscope can be used to
investigate the effect of varying the effective area of overlapof a
capacitor on its capacitance. (5 marks)
(d) Figure 4 shows 1.0µF, 4.0µF, 5.0µF, 3.5 µF and 3.0 µF capacitors
arranged as shown and connected to a 12.0 V battery.
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 8
Determine the total charge stored in the network of the
capacitors. (4 marks)
10. (a) (i) Define the term temperature coefficient of resistanceof a
material. (1 mark)
(ii) Explain why conductors have a positive temperature coefficient
of resistance, while semi-conductors have a negative value of
temperature coefficient of resistance. (4 marks)
(b) (i) Derive a balance condition of a metre bridge. (3 marks)
(ii) Wires AB and PQ in figure 5 are each 100 cm long. Wire AB has
a resistance per cm of 0.40 Ωcm – 1 while PQ has a resistance per
cm of 0.50 Ω cm – 1. Switch K is closed and jockey J moved along
PQ until the Centre zero galvanometer G shows no deflection,
when AC = 60.0 cm and PJ = 35.0 cm.
Determine the resistance of resistor R. (4 marks)
(c) Explain the principle of operation of a slide wire potentiometer.
(3 marks)
(d) Describe how a potentiometer can be used to measure the resistance
of unknown value. (5 marks)
END
© 2020 P510/2 PHYSICS PAPER 2 RESOURCE MOCK EXAMINATIONS Page 9
You might also like
- Instrumens MCQsDocument9 pagesInstrumens MCQsAbdurrehman80% (25)
- Sky Observers Guide - Golden Guide PDFDocument164 pagesSky Observers Guide - Golden Guide PDFConifor100% (1)
- Humphrey 599 Autorefractor Manual: Read/DownloadDocument2 pagesHumphrey 599 Autorefractor Manual: Read/DownloadDaniel Rodriguez33% (6)
- Recent Advances in Surgical Technology PerioDocument45 pagesRecent Advances in Surgical Technology PerioFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- UACE Physics 2Document7 pagesUACE Physics 2zawayarobert45No ratings yet
- King'S College, Budo Physics Seminar - 15 JUNE, 2019 Paper 2 QuestionsDocument20 pagesKing'S College, Budo Physics Seminar - 15 JUNE, 2019 Paper 2 Questionsfahadsserubiri8No ratings yet
- P510/2 Physics Paper 2 Jul/ Aug 2018 3 Hours: Mukono Examination Council 2019Document7 pagesP510/2 Physics Paper 2 Jul/ Aug 2018 3 Hours: Mukono Examination Council 2019crazekeith256No ratings yet
- S.6 Physics Revision Questions - 2020Document83 pagesS.6 Physics Revision Questions - 2020Kizito JohnNo ratings yet
- UACE KCB MOCK Phy2 PDFDocument8 pagesUACE KCB MOCK Phy2 PDFTRIPPLE KAYZ UGNo ratings yet
- P510/2 Physics JULY 2012 Paper2Document8 pagesP510/2 Physics JULY 2012 Paper2Mutsyaba Victor JuniorNo ratings yet
- S.5 Phy P2Document8 pagesS.5 Phy P2kaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- S.6 Phy p2 Lubiri Test22Document7 pagesS.6 Phy p2 Lubiri Test22kayiwaabdulrahman1No ratings yet
- St. Joseph'S Ss Kakindu: Uace Resource Mock ExaminationsDocument10 pagesSt. Joseph'S Ss Kakindu: Uace Resource Mock ExaminationsAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Examination (2021-22) Class Xii: General InstructionsDocument3 pagesPre Board Examination (2021-22) Class Xii: General InstructionsRaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH-10,11,12,13Document12 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH-10,11,12,13sumitsagar2405No ratings yet
- PHYSICS P2 To Be Done On 26th MarchDocument7 pagesPHYSICS P2 To Be Done On 26th MarchsykehanscyphaNo ratings yet
- S6 Physics p2Document9 pagesS6 Physics p2Tumusiime osagyefo Johnbosco AdyeeriNo ratings yet
- Turkish Light Academy Uganda Advanced Certificate of EducationDocument6 pagesTurkish Light Academy Uganda Advanced Certificate of EducationMutsyaba Victor JuniorNo ratings yet
- Ch9-10 CBSE 2023Document4 pagesCh9-10 CBSE 2023tebor93898No ratings yet
- P510/2 Physics Paper 2Document6 pagesP510/2 Physics Paper 2Java JimmyNo ratings yet
- Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education: Physics Paper Two P510/2Document9 pagesUganda Advanced Certificate of Education: Physics Paper Two P510/2ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- Jif 212 - Final Exam 1516Document6 pagesJif 212 - Final Exam 1516Sharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Standard High School Zzana: P510/2 Physics Paper 2Document8 pagesStandard High School Zzana: P510/2 Physics Paper 2Kitone A Ndrew100% (1)
- Physics vst-1Document2 pagesPhysics vst-1Hemanta JenaNo ratings yet
- 15-04-2022 - SR Iit Star Batch-Ii& Co SC N120, Co Spark, Nipl Super-60 - Main Model Full Test (MFT-1) QP FinalDocument10 pages15-04-2022 - SR Iit Star Batch-Ii& Co SC N120, Co Spark, Nipl Super-60 - Main Model Full Test (MFT-1) QP FinalRani SaiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Term-Ii: (For CBSE Board) Class-Xii PhysicsDocument3 pagesPre-Term-Ii: (For CBSE Board) Class-Xii PhysicsBadAss GamingNo ratings yet
- Physics Seminar IIDocument9 pagesPhysics Seminar IImundu mustafaNo ratings yet
- Phy 2-2017Document4 pagesPhy 2-2017Eremu ThomasNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Physics Preboard Term 2 FinalDocument4 pagesCLASS XII Physics Preboard Term 2 FinalParth SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2022sem II - PHSH - CC4Document2 pages2022sem II - PHSH - CC4Řůpäm ŔøýNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22SUBHAM WORLDNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics B (For Non-Circuit Branches) : Category L T P Credit Year ofDocument10 pagesEngineering Physics B (For Non-Circuit Branches) : Category L T P Credit Year ofBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- S.6 Phy 2 Topical Questions - 011926Document31 pagesS.6 Phy 2 Topical Questions - 011926isaacssemakula90No ratings yet
- Xii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsDocument3 pagesXii Preboard Physics 2022 GsremsMaster GamingNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 5: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument15 pagesICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 5: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsArijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phys12sqp - 2Document3 pagesPhys12sqp - 2ShreeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 23 PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial 23 PDFtangkityeeNo ratings yet
- L-lIT-I/MME Date: 08/08/2016: Section - ADocument14 pagesL-lIT-I/MME Date: 08/08/2016: Section - ARefat Bin SultanNo ratings yet
- Hkcee Physics - Section 3 Waves - P.1Document34 pagesHkcee Physics - Section 3 Waves - P.1Y AdaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 M5 2023-24Document3 pagesPhysics Class 12 M5 2023-24Sonu6 SiddNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Phy P510-2 (1993-2012) .Document102 pagesQuestion Bank Phy P510-2 (1993-2012) .Tumusiime osagyefo Johnbosco Adyeeri100% (1)
- 861 Physics Paper 1 Sem II SpecimenDocument5 pages861 Physics Paper 1 Sem II SpecimenRahul DevNo ratings yet
- S.6 Physics Paper 2 Set 1 FebDocument6 pagesS.6 Physics Paper 2 Set 1 FebAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Scan 22 Feb 2022Document3 pagesScan 22 Feb 2022Aditya KavalanekarNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Paper 2 Littoral Mock 2021Document8 pagesPhysics Advanced Paper 2 Littoral Mock 2021olivier.tchuipetNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2022 YUHUAp 3 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2022 YUHUAp 3 QuestionASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeNo ratings yet
- Physics (OL1) (3rd) Dec2017Document1 pagePhysics (OL1) (3rd) Dec2017AmitNo ratings yet
- EN09 103 EnggDocument2 pagesEN09 103 EnggRanjith SomanNo ratings yet
- Uace Physics Paper 2007 GuideDocument21 pagesUace Physics Paper 2007 GuideSlater MarkNo ratings yet
- Phy-131.2 F6 MZUMBEDocument7 pagesPhy-131.2 F6 MZUMBENestory mahunjaNo ratings yet
- S5 Paper Ii Physics End of Term-YearDocument5 pagesS5 Paper Ii Physics End of Term-Yearlubangakene.francisNo ratings yet
- WAVE OPTICS Previous Year Question (1) Class 12 ImportantDocument4 pagesWAVE OPTICS Previous Year Question (1) Class 12 ImportantYatin KumarNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 ReviewDocument3 pagesExam 2 Reviewdhruv1117No ratings yet
- Worksheet LIGHT (REFRACTION) C-XDocument2 pagesWorksheet LIGHT (REFRACTION) C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Wave&acoustic 3rd Sem 2018Document4 pagesWave&acoustic 3rd Sem 2018Vishal TanwarNo ratings yet
- B.tech (Cse, Ai, Tcs DS, Ibm, I Nurture)Document128 pagesB.tech (Cse, Ai, Tcs DS, Ibm, I Nurture)ujjwalNo ratings yet
- Weekly Revesion Test No.3, 5mark QuesDocument4 pagesWeekly Revesion Test No.3, 5mark QuesGokul thennarasuNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocument11 pagesNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIKatto - Darling in the PianoNo ratings yet
- ELEC4610 Engineering Optics: Mid-Term ExaminationDocument3 pagesELEC4610 Engineering Optics: Mid-Term ExaminationJohn NgNo ratings yet
- Regional Mock Examination: 0780 PHYSICS 2Document8 pagesRegional Mock Examination: 0780 PHYSICS 2Achilles EgrcrNo ratings yet
- Means in The ExaminationDocument2 pagesMeans in The ExaminationSamar PratapNo ratings yet
- Isc Semester 2 Examination Specimen Question Paper Physics Paper 1 (Theory)Document5 pagesIsc Semester 2 Examination Specimen Question Paper Physics Paper 1 (Theory)marleyNo ratings yet
- Physics 1st YearDocument3 pagesPhysics 1st YearzzarghamNo ratings yet
- Lenses and RefractionDocument140 pagesLenses and RefractionElla Julienne EralinoNo ratings yet
- Salinan I - BAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS LINTAS MINATDocument15 pagesSalinan I - BAHASA DAN SASTRA INGGRIS LINTAS MINATAndi Randy Abu Asy-SyifaNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics 2 QuestionsDocument43 pagesA Level Physics 2 QuestionsTRIPPLE KAYZ UGNo ratings yet
- 04 - Positional AstronomyDocument19 pages04 - Positional AstronomySiddharth BhattNo ratings yet
- Compound MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCompound Microscopeaman100% (1)
- JWST 03 LightTelescopesDocument64 pagesJWST 03 LightTelescopesBrand FortnerNo ratings yet
- TELESCOPEDocument10 pagesTELESCOPEDevrajNo ratings yet
- Appendix A TestingDocument4 pagesAppendix A TestingStef Sc0% (1)
- Diaz - SC33 - Module 6 Vision and Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesDiaz - SC33 - Module 6 Vision and Optical InstrumentsJohn Rafael DiazNo ratings yet
- Telescope Design 1Document6 pagesTelescope Design 1JimNo ratings yet
- كتاب الانكليزي علميDocument99 pagesكتاب الانكليزي علميNada NadaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - Revision Test 5 - SolutionDocument34 pagesRay Optics - Revision Test 5 - SolutionAyesha MahboobNo ratings yet
- Endo Instruments - Copy 2Document119 pagesEndo Instruments - Copy 2Ju JuNo ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentsDocument2 pagesOptical InstrumentsJane PangilinanNo ratings yet
- SPINELLI & RIBEIRO, Historical Telescopes and Astronomy OutreachDocument6 pagesSPINELLI & RIBEIRO, Historical Telescopes and Astronomy OutreachAliceRibeirogeografaNo ratings yet
- Astronomy - Buying The Best Telescope - Sky & Telescope 1997Document7 pagesAstronomy - Buying The Best Telescope - Sky & Telescope 1997오상진No ratings yet
- 1996494754question Bank em Waves, Ray Optics & Wave OpticsDocument36 pages1996494754question Bank em Waves, Ray Optics & Wave OpticsAnkitNo ratings yet
- Binotron 27Document16 pagesBinotron 27aeroseb1No ratings yet
- Optical Instruments: Light: Mirrors & LensesDocument4 pagesOptical Instruments: Light: Mirrors & LensesJess Anthony Efondo100% (1)
- A Course in Low Vision Practice: P 5 - Magnification and MagnifiersDocument6 pagesA Course in Low Vision Practice: P 5 - Magnification and MagnifiersDanielle SangalangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Astronomy LectureDocument70 pagesChapter 5 Astronomy LectureAbdallah AlyNo ratings yet
- Astronomy - For.beginners.4th - Edition.2016 P2PDocument164 pagesAstronomy - For.beginners.4th - Edition.2016 P2Pcoco100% (3)
- Univeresity Physics Problems Chapter 34Document4 pagesUniveresity Physics Problems Chapter 34Antigoni KolisiatiNo ratings yet
- SpectroscopyOfDeepSpaceObjectsUsingHomemadeDobsonianTelescope by ConleyDitsworthJr Fall2004Document20 pagesSpectroscopyOfDeepSpaceObjectsUsingHomemadeDobsonianTelescope by ConleyDitsworthJr Fall2004neurolordNo ratings yet
- British Astronomical Association: JournalDocument68 pagesBritish Astronomical Association: JournalRonan NewmanNo ratings yet