Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Questions For CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
Important Questions For CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Nikhil KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Class 9 - Maths - Introduction To Euclids GeometryDocument11 pagesClass 9 - Maths - Introduction To Euclids GeometryVOYAGER K100% (1)
- CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes Important Questions 2022-23Document14 pagesCBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes Important Questions 2022-23BharathiNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral SDocument5 pagesQuadrilateral SNesimovic SanelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Elucids GeometryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Elucids GeometryM SreehithaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Week 1 GEOMETRYDocument8 pagesQuarter 3 Week 1 GEOMETRYsineNo ratings yet
- 6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical IdeasDocument20 pages6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical Ideasvaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- Workshop 1: I. Quadrilaterals Ii. OverviewDocument10 pagesWorkshop 1: I. Quadrilaterals Ii. OverviewRonieta VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Perpendiculars Can'T Be Drawn UsingDocument7 pagesEngineering Graphics Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Perpendiculars Can'T Be Drawn UsingNiranjan BankarNo ratings yet
- MLP CH 4 - Basic Geometrical Ideas (3) - 1Document3 pagesMLP CH 4 - Basic Geometrical Ideas (3) - 1KS GAMERNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3Document14 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3NidaNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document54 pagesBinder 1BharathiNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - SAT Mathematics Sample Paper 10Document4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - SAT Mathematics Sample Paper 10RuchiNo ratings yet
- Math 8 4th Exam FINALDocument2 pagesMath 8 4th Exam FINALlovely mae ponciaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper No.3 - Mathematics Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 InstructionsDocument7 pagesSample Question Paper No.3 - Mathematics Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 Instructionskan PadmasreeNo ratings yet
- 4th Periodical Test in Mathematics 7Document4 pages4th Periodical Test in Mathematics 7Ian Johnlyn FreyraNo ratings yet
- Quarter Assessment in Mathematics 7: Mother Guaini School, IncDocument4 pagesQuarter Assessment in Mathematics 7: Mother Guaini School, IncJanGianVillarealNo ratings yet
- Geometry Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesGeometry Practice QuestionsYsabela BernardoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document2 pagesActivity 3Jhunred AycochoNo ratings yet
- 7 Iranian Geometry Olympiad: Contest Problems With SolutionsDocument50 pages7 Iranian Geometry Olympiad: Contest Problems With SolutionsX MIPA 325Muhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz - Math 9 Q3Document4 pagesLong Quiz - Math 9 Q3Nicole Asilum100% (1)
- GR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Document18 pagesGR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Desmond SmithNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Math ExamVinson AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Math G9 HowsDocument4 pagesMath G9 Howstae hyungNo ratings yet
- 8.1 23 Marks From 23 Questions: EquilateralDocument8 pages8.1 23 Marks From 23 Questions: Equilateralchan aldwinNo ratings yet
- Unit Test: Grade 9 MathematicsDocument3 pagesUnit Test: Grade 9 MathematicsEmelyn V. CudapasNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 12 & 13 شرحDocument95 pagesMath Unit 12 & 13 شرحMohamed SaidNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestVaneza Joy LargoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2021 Set 1Document11 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2021 Set 1Manicks VelanNo ratings yet
- Maths X FA4Document5 pagesMaths X FA4BGTM 1988No ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 SummativeDocument3 pagesMathematics 4 SummativeCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-MathsDocument13 pagesChapter 5-MathsChitturi SushanthNo ratings yet
- 9th Annual Exam Regular Set-2Document8 pages9th Annual Exam Regular Set-2auditpartyutNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Document15 pagesUNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Celina MarraNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesDocument3 pagesThird Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesJeo HuminisNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1578879152579Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1578879152579Klay Stephen Juarez100% (1)
- Math9 Q3 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver1.0Document41 pagesMath9 Q3 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver1.0Ann HurbodaNo ratings yet
- Quiz BeeDocument33 pagesQuiz BeePhoebe Imee ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 4Document3 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 4neetuagarwal766No ratings yet
- Quadrilateral Worksheet For Class 9Document1 pageQuadrilateral Worksheet For Class 9Suman joonNo ratings yet
- Fourth Grading Exam 2019Document27 pagesFourth Grading Exam 2019Querubee Donato DiolulaNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry Part 1 To Part 6Document99 pagesPlane Geometry Part 1 To Part 6Eunice Miranda100% (1)
- Class 6-Maths-WORKSHEET ON BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEASDocument3 pagesClass 6-Maths-WORKSHEET ON BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEASveeresh punjaniNo ratings yet
- Class-IX Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Document2 pagesClass-IX Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Apex Institute0% (1)
- Unit 4 GeometryDocument5 pagesUnit 4 GeometryAzista PharmaNo ratings yet
- Maths 9th Full3Document9 pagesMaths 9th Full3SanjayNo ratings yet
- General Direction: Read and Analyze The Items Below and Circle The Letters of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesGeneral Direction: Read and Analyze The Items Below and Circle The Letters of The Correct AnswerAldrin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Geometry STD 9 Maharashtra SSCDocument20 pagesGeometry STD 9 Maharashtra SSCHrishikesh Kodmur50% (2)
- 10th Maths English Medium Kolar GLANCE QuestionsDocument21 pages10th Maths English Medium Kolar GLANCE Questionskusuma mNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following Questions Dealing With Quadrilaterals.: Which Statements Describe The Properties of A ?Document7 pagesAnswer The Following Questions Dealing With Quadrilaterals.: Which Statements Describe The Properties of A ?Leila GagapNo ratings yet
- 4th Pre Finals MATH IIIDocument2 pages4th Pre Finals MATH IIIAhn DohNo ratings yet
- Sanskriti School Maths SmartskillsDocument61 pagesSanskriti School Maths SmartskillsManomay GhoshalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Examination Grade 9Document5 pages2nd Quarter Examination Grade 9Jerryco GarciaNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q4 Wk3 Module 3Document18 pagesMath8 Q4 Wk3 Module 3delgadomanilyn487No ratings yet
- Math8 - Summative Test - Modules1-2Document4 pagesMath8 - Summative Test - Modules1-2noahannemillanNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration UNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Document15 pagesSolid Mensuration UNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Joshua ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Geometry (PJ)Document317 pagesGeometry (PJ)sarma e.mNo ratings yet
- 5 - Q2 MathDocument19 pages5 - Q2 MathmtchqnlNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 12Document9 pagesRD Sharma Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 12sohamNo ratings yet
- Peace EducationDocument4 pagesPeace EducationKWEKWE ANo ratings yet
- Brevini ADB3E01CM Valve DatasheetDocument7 pagesBrevini ADB3E01CM Valve Datasheetdoganoglu.t40No ratings yet
- "Put Out Into The Deep": A Reflection On John Paul II's Apostolic Letter Novo Millennio IneunteDocument13 pages"Put Out Into The Deep": A Reflection On John Paul II's Apostolic Letter Novo Millennio IneunteTimothy HerrmanNo ratings yet
- DLL Iwrbs Week 6Document5 pagesDLL Iwrbs Week 6Errol Lariza100% (2)
- R20ut2905eg0100 RSK TFT App Board SchematicDocument4 pagesR20ut2905eg0100 RSK TFT App Board SchematicZeeshan AslamNo ratings yet
- How To Produce Your Book With Scribus.: Make The Front MatterDocument3 pagesHow To Produce Your Book With Scribus.: Make The Front MattersudyNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Reading With ChildrenDocument34 pagesThe Importance of Reading With ChildrenFarah Allaik 1No ratings yet
- Mid 185 - Sid 254 - Fmi 9Document3 pagesMid 185 - Sid 254 - Fmi 9AkbarNo ratings yet
- Accessories Andrew PDFDocument64 pagesAccessories Andrew PDFaralsoNo ratings yet
- Focus Group Discussion Questionnaire (24.01.2022)Document4 pagesFocus Group Discussion Questionnaire (24.01.2022)Mohammed EcoNo ratings yet
- Reed-Merrill and Greville Methods: Abridged Life TableDocument1 pageReed-Merrill and Greville Methods: Abridged Life TableYogesh RanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5K57 TRAN THI MINH NGOCNo ratings yet
- Engleza Curs + Exam ExamplesDocument92 pagesEngleza Curs + Exam ExamplessebiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General BackgroundDocument14 pages1.1 General BackgroundChris TanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Alcohol Abuse in KenyaDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Alcohol Abuse in Kenyagw0ttn7j100% (1)
- Roch Company Profile UpdatedDocument38 pagesRoch Company Profile UpdatedjmvengineerconsNo ratings yet
- OCLC Top 1000 Books Complete List - 2005 - With CoversDocument191 pagesOCLC Top 1000 Books Complete List - 2005 - With CoversmtwdrmNo ratings yet
- Cristiano Ronaldo: By:Jamal&KelvinDocument9 pagesCristiano Ronaldo: By:Jamal&KelvinmaligujamalNo ratings yet
- Banking Assessment 10Document10 pagesBanking Assessment 10AMARJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Q3 - ARTS8 - LAS2 - MELC2 From Capiz To RO 12921 Pages DeletedDocument9 pagesQ3 - ARTS8 - LAS2 - MELC2 From Capiz To RO 12921 Pages DeletedJohn Rey Manolo BaylosisNo ratings yet
- MWX FFDDEDocument6 pagesMWX FFDDEAlfin RizqiadiNo ratings yet
- The Path To An Exceptional Candidate ExperienceDocument7 pagesThe Path To An Exceptional Candidate ExperienceGeorgia BWNo ratings yet
- 2 - Maths Activity Mats Pack 1 - Lower AbilityDocument12 pages2 - Maths Activity Mats Pack 1 - Lower AbilityShamini SandrakasanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Procedure Abbreviations: The Abbreviations in Table Are Common in Written Chemical ProceduresDocument4 pages1.1 Procedure Abbreviations: The Abbreviations in Table Are Common in Written Chemical ProceduresascensionNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument58 pagesStress ManagementDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- A Model For Evaluating IT Security Investments: by Huseyin Cavusoglu, Birendra Mishra, and Srinivasan RaghunathanDocument7 pagesA Model For Evaluating IT Security Investments: by Huseyin Cavusoglu, Birendra Mishra, and Srinivasan RaghunathanMonish MohanNo ratings yet
- Class A3A1Document20 pagesClass A3A1SalimNo ratings yet
- List of Recent Sponsored Research ProjectsDocument8 pagesList of Recent Sponsored Research ProjectsHhuNo ratings yet
- Scientix4 New Ambassadors T&C-Feb-23Document4 pagesScientix4 New Ambassadors T&C-Feb-23dada_dadyNo ratings yet
- Timcard 12 IDocument5 pagesTimcard 12 Ifaizan.kareemNo ratings yet
Important Questions For CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
Important Questions For CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Nikhil KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Questions For CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
Important Questions For CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
Uploaded by
Nikhil KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Questions for Class 6
Mathematics
Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas
Very Short Answer Type 1 Mark
1. A line segment has no length. Say True or False.
Ans: False. (As a line segment has two fixed points. It has a finite length.)
2. The line AB is same as that of line BA . Say true or false.
Ans: True. (Since line AB and BA are two different methods of writing it.)
3. A _____ has only one end point.
Ans: Ray. (A ray has only one fixed point.)
4. _____ lines can be drawn passing through two given points.
Ans: One. (Only one line can be drawn from two fixed points.)
5. Choose the false statement.
(a) Line PQ is same as that of line QP
(b) Ray PQ is same as ray QP
(c) Line segment PQ is same as the line segment QP
(d) None of these
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 1
Ans: Option (b) is false. (As ray PQ has its fixed point at P and ray QP has its
fixed point at Q.)
6. Quadrilateral is a polygon formed by _____ line segments.
Ans: Four. (A quadrilateral consists of 4 sides.)
7. Curve in which starting point and ending points does not meet is called
_____curve.
Ans: Open. (In an open curve the starting and ending points do meet each other.)
8. All radii of circle are equal. Say True or False.
Ans: True. (As the distance between the centre and the circumference is constant.)
9. Diameter of a circle 2 ____
Ans: Radius. (Diameter is two times the radius.)
10. _____ is the largest chord.
Ans: Diameter.(A chord is a line which has both its end in the circumference.
Diameter is the longest chord as it passes through centre.)
11. A _____ of a circle is a line segment at the one end point in centre and
other end point on circumference.
Ans: Radius (It is the distance between the centre and the circumference.)
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 2
Short Answer Type Questions 2 Marks
1. Identify and Name the line segments and rays.
Ans:
Line segments (it has two fixed points)
EF , EH , BE
Rays (it has only one fixed point)
BA, BC, ED, HG, HI
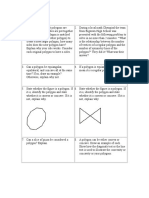
2. Which of the following are polygons?
(a)
(b)
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 3
(c)
(d)
Ans: Simple closed curve are known as polygons, i.e., a closed figure of straight
lines which do not overlaps itself. Therefore, (b) and (d) are polygons.
3. Explain concentric circles with diagram.
Ans: A collection of circles that has same centre but different radius are called
concentric circles.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 4
Short Answer Type Questions 3 Mark
1. Define curves. Write its different types with example.
Ans: When the line segment is not straight then those lines are said to be curved
lines.
Types of curves:
(a) Open curve: When the starting point and ending point do not meet one another,
it is said to be open curve.
(b) Closed curve: When the starting point and ending point meet one another, it is
said to be closed curve.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 5
2. Name the vertex and arms of PQR in the figure.
Ans: Vertex is a point from which two or more line arises,
Here point Q is the vertex.
Rays that make up the angle are said to be arms/sides of angle,
Here QP, QR are the sides.
3. Define the following w.r.t to circle with figures.
(a) chord of a circle
(b) secant of a circle
Ans:
(a) Chord – A line segment whose both fixed points lie in the circumference.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 6
(b) Secant of a circle – A line that passes through the circle. It intersects the
circumference of the circle at two points.
Long Answer Type Questions 4 Marks
1. Define the following:
(a) Intersecting lines
Ans: Two lines that cross one another at a point are called intersecting lines.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 7
(b) Parallel lines
Ans: When two or more lines are always equidistant from one another, i.e., they
never intersect one another. Such lines are said to be parallel.
(c) Concurrent lines
Ans: When two or more line passes through a same point, those lines are said to be
concurrent lines. Point of intersection of all the lines is said to be point of
concurrence.
Here, point P is the point of concurrence.
(d) Collinear points
Ans: If two or more lines lie on the same lie then such points are said to be
collinear points.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 8
2. Match the following:
Column I Column II
Triangle 4 sides
Quadrilateral 8 sides
Heptagon 3 sides
Pentagon 5 sides
Octagon 10 sides
Hexagon 6 sides
7 sides
Ans: The correct match is:
Column I Column II
Triangle 3 sides
Quadrilateral 4 sides
Heptagon 7 sides
Pentagon 5 sides
Octagon 8 sides
Hexagon 6 sides
3. In the given figure, list the points which
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 9
(a) are interior of AOB
Ans: Interior of AOB = point Y, point M, point N
(b) are exterior of AOB
Ans: Exterior of AOB = point X, point Z
(c) lie on AOB
Ans: Lie on AOB = point A, point B, point O
4. In the given triangle name the following
(a) side opposite to Z
Ans: side XY is opposite to Z
(b) side opposite to vertex Y
Ans: side XZ is opposite to vertex Y
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 10
(c) angle opposite to side YZ
Ans: X is opposite to side YZ
(d) vertex opposite to side XZ
Ans: Y vertex is opposite to side XZ
Long Answer Type Questions 6 Marks
1. Define the following:
(a) Circumference of circle
Ans: Length of the boundary of a circle is called its circumference.
(b) Segments of circle
Ans: When a chord divides a circle in two parts. Then the area in between chord
and the arc are called segments of circle.
The types of segments are:
(i) major segment
(ii) minor segment
(c) Semicircle
Ans: When a circle is divided by the diameter it is known as semi-circle.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 11
(d) Sector of a circle
Ans: Area covered by an arc and two radius of a circle.
Two types of sectors:
(i) major sector
(ii) minor sector
2. Say True or False
(a) Two lines are parallel if they do not meet, even when produced.
Ans: True
(b) Two parallel lines are everywhere the same distance apart.
Ans: True
(c) If two line segments do not intersect, they are parallel.
Ans: True
(d) If two rays do not intersect, they are parallel.
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 12
Ans: True
(e) A line between two parallel lines is always perpendicular to each other.
Ans: True
Class VI Maths www.vedantu.com 13
You might also like
- Class 9 - Maths - Introduction To Euclids GeometryDocument11 pagesClass 9 - Maths - Introduction To Euclids GeometryVOYAGER K100% (1)
- CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes Important Questions 2022-23Document14 pagesCBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes Important Questions 2022-23BharathiNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral SDocument5 pagesQuadrilateral SNesimovic SanelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Elucids GeometryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Elucids GeometryM SreehithaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Week 1 GEOMETRYDocument8 pagesQuarter 3 Week 1 GEOMETRYsineNo ratings yet
- 6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical IdeasDocument20 pages6th - Maths - Basic Geometrical Ideasvaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- Workshop 1: I. Quadrilaterals Ii. OverviewDocument10 pagesWorkshop 1: I. Quadrilaterals Ii. OverviewRonieta VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Perpendiculars Can'T Be Drawn UsingDocument7 pagesEngineering Graphics Mcqs (Set-1) : 1. Perpendiculars Can'T Be Drawn UsingNiranjan BankarNo ratings yet
- MLP CH 4 - Basic Geometrical Ideas (3) - 1Document3 pagesMLP CH 4 - Basic Geometrical Ideas (3) - 1KS GAMERNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3Document14 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 3NidaNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document54 pagesBinder 1BharathiNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - SAT Mathematics Sample Paper 10Document4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - SAT Mathematics Sample Paper 10RuchiNo ratings yet
- Math 8 4th Exam FINALDocument2 pagesMath 8 4th Exam FINALlovely mae ponciaNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper No.3 - Mathematics Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 InstructionsDocument7 pagesSample Question Paper No.3 - Mathematics Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 Instructionskan PadmasreeNo ratings yet
- 4th Periodical Test in Mathematics 7Document4 pages4th Periodical Test in Mathematics 7Ian Johnlyn FreyraNo ratings yet
- Quarter Assessment in Mathematics 7: Mother Guaini School, IncDocument4 pagesQuarter Assessment in Mathematics 7: Mother Guaini School, IncJanGianVillarealNo ratings yet
- Geometry Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesGeometry Practice QuestionsYsabela BernardoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document2 pagesActivity 3Jhunred AycochoNo ratings yet
- 7 Iranian Geometry Olympiad: Contest Problems With SolutionsDocument50 pages7 Iranian Geometry Olympiad: Contest Problems With SolutionsX MIPA 325Muhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz - Math 9 Q3Document4 pagesLong Quiz - Math 9 Q3Nicole Asilum100% (1)
- GR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Document18 pagesGR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Desmond SmithNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Math ExamVinson AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Math G9 HowsDocument4 pagesMath G9 Howstae hyungNo ratings yet
- 8.1 23 Marks From 23 Questions: EquilateralDocument8 pages8.1 23 Marks From 23 Questions: Equilateralchan aldwinNo ratings yet
- Unit Test: Grade 9 MathematicsDocument3 pagesUnit Test: Grade 9 MathematicsEmelyn V. CudapasNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 12 & 13 شرحDocument95 pagesMath Unit 12 & 13 شرحMohamed SaidNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestVaneza Joy LargoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2021 Set 1Document11 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2021 Set 1Manicks VelanNo ratings yet
- Maths X FA4Document5 pagesMaths X FA4BGTM 1988No ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 SummativeDocument3 pagesMathematics 4 SummativeCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-MathsDocument13 pagesChapter 5-MathsChitturi SushanthNo ratings yet
- 9th Annual Exam Regular Set-2Document8 pages9th Annual Exam Regular Set-2auditpartyutNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Document15 pagesUNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Celina MarraNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesDocument3 pagesThird Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesJeo HuminisNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1578879152579Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1578879152579Klay Stephen Juarez100% (1)
- Math9 Q3 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver1.0Document41 pagesMath9 Q3 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver1.0Ann HurbodaNo ratings yet
- Quiz BeeDocument33 pagesQuiz BeePhoebe Imee ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 4Document3 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 4neetuagarwal766No ratings yet
- Quadrilateral Worksheet For Class 9Document1 pageQuadrilateral Worksheet For Class 9Suman joonNo ratings yet
- Fourth Grading Exam 2019Document27 pagesFourth Grading Exam 2019Querubee Donato DiolulaNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry Part 1 To Part 6Document99 pagesPlane Geometry Part 1 To Part 6Eunice Miranda100% (1)
- Class 6-Maths-WORKSHEET ON BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEASDocument3 pagesClass 6-Maths-WORKSHEET ON BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEASveeresh punjaniNo ratings yet
- Class-IX Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Document2 pagesClass-IX Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Apex Institute0% (1)
- Unit 4 GeometryDocument5 pagesUnit 4 GeometryAzista PharmaNo ratings yet
- Maths 9th Full3Document9 pagesMaths 9th Full3SanjayNo ratings yet
- General Direction: Read and Analyze The Items Below and Circle The Letters of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesGeneral Direction: Read and Analyze The Items Below and Circle The Letters of The Correct AnswerAldrin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Geometry STD 9 Maharashtra SSCDocument20 pagesGeometry STD 9 Maharashtra SSCHrishikesh Kodmur50% (2)
- 10th Maths English Medium Kolar GLANCE QuestionsDocument21 pages10th Maths English Medium Kolar GLANCE Questionskusuma mNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following Questions Dealing With Quadrilaterals.: Which Statements Describe The Properties of A ?Document7 pagesAnswer The Following Questions Dealing With Quadrilaterals.: Which Statements Describe The Properties of A ?Leila GagapNo ratings yet
- 4th Pre Finals MATH IIIDocument2 pages4th Pre Finals MATH IIIAhn DohNo ratings yet
- Sanskriti School Maths SmartskillsDocument61 pagesSanskriti School Maths SmartskillsManomay GhoshalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Examination Grade 9Document5 pages2nd Quarter Examination Grade 9Jerryco GarciaNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q4 Wk3 Module 3Document18 pagesMath8 Q4 Wk3 Module 3delgadomanilyn487No ratings yet
- Math8 - Summative Test - Modules1-2Document4 pagesMath8 - Summative Test - Modules1-2noahannemillanNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration UNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Document15 pagesSolid Mensuration UNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Joshua ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Geometry (PJ)Document317 pagesGeometry (PJ)sarma e.mNo ratings yet
- 5 - Q2 MathDocument19 pages5 - Q2 MathmtchqnlNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 12Document9 pagesRD Sharma Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 12sohamNo ratings yet
- Peace EducationDocument4 pagesPeace EducationKWEKWE ANo ratings yet
- Brevini ADB3E01CM Valve DatasheetDocument7 pagesBrevini ADB3E01CM Valve Datasheetdoganoglu.t40No ratings yet
- "Put Out Into The Deep": A Reflection On John Paul II's Apostolic Letter Novo Millennio IneunteDocument13 pages"Put Out Into The Deep": A Reflection On John Paul II's Apostolic Letter Novo Millennio IneunteTimothy HerrmanNo ratings yet
- DLL Iwrbs Week 6Document5 pagesDLL Iwrbs Week 6Errol Lariza100% (2)
- R20ut2905eg0100 RSK TFT App Board SchematicDocument4 pagesR20ut2905eg0100 RSK TFT App Board SchematicZeeshan AslamNo ratings yet
- How To Produce Your Book With Scribus.: Make The Front MatterDocument3 pagesHow To Produce Your Book With Scribus.: Make The Front MattersudyNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Reading With ChildrenDocument34 pagesThe Importance of Reading With ChildrenFarah Allaik 1No ratings yet
- Mid 185 - Sid 254 - Fmi 9Document3 pagesMid 185 - Sid 254 - Fmi 9AkbarNo ratings yet
- Accessories Andrew PDFDocument64 pagesAccessories Andrew PDFaralsoNo ratings yet
- Focus Group Discussion Questionnaire (24.01.2022)Document4 pagesFocus Group Discussion Questionnaire (24.01.2022)Mohammed EcoNo ratings yet
- Reed-Merrill and Greville Methods: Abridged Life TableDocument1 pageReed-Merrill and Greville Methods: Abridged Life TableYogesh RanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5K57 TRAN THI MINH NGOCNo ratings yet
- Engleza Curs + Exam ExamplesDocument92 pagesEngleza Curs + Exam ExamplessebiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General BackgroundDocument14 pages1.1 General BackgroundChris TanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Alcohol Abuse in KenyaDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Alcohol Abuse in Kenyagw0ttn7j100% (1)
- Roch Company Profile UpdatedDocument38 pagesRoch Company Profile UpdatedjmvengineerconsNo ratings yet
- OCLC Top 1000 Books Complete List - 2005 - With CoversDocument191 pagesOCLC Top 1000 Books Complete List - 2005 - With CoversmtwdrmNo ratings yet
- Cristiano Ronaldo: By:Jamal&KelvinDocument9 pagesCristiano Ronaldo: By:Jamal&KelvinmaligujamalNo ratings yet
- Banking Assessment 10Document10 pagesBanking Assessment 10AMARJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Q3 - ARTS8 - LAS2 - MELC2 From Capiz To RO 12921 Pages DeletedDocument9 pagesQ3 - ARTS8 - LAS2 - MELC2 From Capiz To RO 12921 Pages DeletedJohn Rey Manolo BaylosisNo ratings yet
- MWX FFDDEDocument6 pagesMWX FFDDEAlfin RizqiadiNo ratings yet
- The Path To An Exceptional Candidate ExperienceDocument7 pagesThe Path To An Exceptional Candidate ExperienceGeorgia BWNo ratings yet
- 2 - Maths Activity Mats Pack 1 - Lower AbilityDocument12 pages2 - Maths Activity Mats Pack 1 - Lower AbilityShamini SandrakasanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Procedure Abbreviations: The Abbreviations in Table Are Common in Written Chemical ProceduresDocument4 pages1.1 Procedure Abbreviations: The Abbreviations in Table Are Common in Written Chemical ProceduresascensionNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument58 pagesStress ManagementDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- A Model For Evaluating IT Security Investments: by Huseyin Cavusoglu, Birendra Mishra, and Srinivasan RaghunathanDocument7 pagesA Model For Evaluating IT Security Investments: by Huseyin Cavusoglu, Birendra Mishra, and Srinivasan RaghunathanMonish MohanNo ratings yet
- Class A3A1Document20 pagesClass A3A1SalimNo ratings yet
- List of Recent Sponsored Research ProjectsDocument8 pagesList of Recent Sponsored Research ProjectsHhuNo ratings yet
- Scientix4 New Ambassadors T&C-Feb-23Document4 pagesScientix4 New Ambassadors T&C-Feb-23dada_dadyNo ratings yet
- Timcard 12 IDocument5 pagesTimcard 12 Ifaizan.kareemNo ratings yet