Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport Across Cell Membrane
Transport Across Cell Membrane
Uploaded by
Shannen NaraceOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transport Across Cell Membrane
Transport Across Cell Membrane
Uploaded by
Shannen NaraceCopyright:
Available Formats
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
Transport Across Cell
Membrane
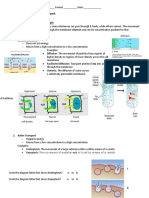
Cell membranes surround each cell and some organelles, such as the nucleus and
the Golgi body. They are comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and this acts as a
semipermeable barrier that regulates what enters and exits the cell or
organelle. This is highly important as this is how cells can obtain molecules such as
oxygen and remove waste products like urea.
There are two main ways in which molecules are transported across the cell
membrane:
Passive transport
Active transport
The main difference between these modes of transport is that active transport
requires energy in the form of ATP, but passive transport does not.
What are the passive transport methods?
Passive transport refers to transport across the cell membrane that does not require
energy from metabolic processes. Instead, this form of transport relies on the natural
kinetic energy of molecules and their random movement . There are three modes
of passive transport:
Simple diffusion
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 1/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Simple diffusion
Simple diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration
to a region of low concentration until an equilibrium is reached.
Example
Oxygen can freely diffuse through the cell membrane using this form of passive
transport.
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 2/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
Simple
diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the same as simple diffusion but this form of transport
uses membrane proteins, such as channel proteins and carrier proteins. Channel
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 3/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
proteins provide a hydrophilic channel for the passage of charged and polar
molecules, like ions. Meanwhile, carrier proteins change their conformational shape
for the transport of molecules.
Example
Glucose is an example of a molecule that is transported across the cell
membrane through facilitated diffusion.
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 4/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
Facilitated
diffusion
Osmosis
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 5/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of high water potential
to a region of lower water potential through a semipermeable membrane. This form
of transport looks very different between plant and animal cells as plant cells have
cell walls surrounding each cell. Cell walls allow plant cells to withstand water
flowing in. However, animal cells are more prone to cell bursting as they do not have
this added support.
The rate of osmosis can be increased if aquaporins are present in the cell
membrane. Aquaporins are membrane proteins that selectively transport water
molecules.
Example
The uptake of water by plant root hair cells is dependent on this form of passive
transport.
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 6/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
The diagram shows the movement of molecules through the cell membrane during
osmosis
What are the active transport methods?
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 7/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
Active transport is the transport of molecules across the cell membrane using carrier
proteins and energy from metabolic processes in the form of ATP. Carrier proteins
are membrane proteins that allow the passage of specific molecules across the cell
membrane. They are used in both facilitated diffusion and active transport. Carrier
proteins use ATP to change their conformational shape in active transport, allowing
a bound molecule to pass through the membrane. In facilitated diffusion, however,
ATP is not needed to change the shape of the carrier protein.
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 8/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
The diagram shows the movement of molecules in
active transport
Example
A process that relies on active transport is the uptake of mineral ions in plant
root hair cells. The type of carrier proteins involved is specific for mineral ions.
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 9/10
11/18/22, 1:32 PM Transport Across Cell Membrane
There are different modes of active transport, such as cotransport and bulk
transport.
Transport Across Cell
Membrane - Key takeaways
The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds each cell and
some organelles. It regulates what enters and exits the cell and organelles.
Passive transport does not require energy in the form of ATP. Passive
transport relies on the natural kinetic energy and random movement of
molecules.
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis are the forms of passive
transport.
Active transport across the cell membrane requires carrier proteins and
energy in the form of ATP.
There are different types of active transport, such as cotransport and bulk
transport.
Create the best notes with
StudySmarter.de
https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3782118/summary/25192721 10/10
You might also like
- Aqa Gcse Science Content BookDocument216 pagesAqa Gcse Science Content BookVincentBauzaNo ratings yet
- Dat Test Sample ItemsDocument67 pagesDat Test Sample ItemsKickHannaNo ratings yet
- Cell DiffusionDocument11 pagesCell DiffusionShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Cueva-Cell TransportDocument15 pagesCueva-Cell TransportCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- Cell Surface MembraneDocument3 pagesCell Surface Membraneb111broomNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Theory 2Document18 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory 2ao868598No ratings yet
- Prelim Session 3 Cellular Transport MembraneDocument33 pagesPrelim Session 3 Cellular Transport MembraneAnxi XiNo ratings yet
- Group 4 G12 STEM Sept.30 General Biology Transport Mechanism in CellDocument38 pagesGroup 4 G12 STEM Sept.30 General Biology Transport Mechanism in CellAnime AddictNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectDocument53 pagesSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Exchange With The Environment Ch4.1 7th PDF (Information Obtained From Holt Science and Technology: Life Science. Austin: Holt Rinehart & Winston, 2007. Print.)Document18 pagesExchange With The Environment Ch4.1 7th PDF (Information Obtained From Holt Science and Technology: Life Science. Austin: Holt Rinehart & Winston, 2007. Print.)thegedusNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport - Module-3.09272021Document3 pagesCell Transport - Module-3.09272021Deps CesiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportDocument11 pagesMODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportBrandon James SevillaNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument6 pagesTransport MechanismJessie Katrisha Tayag100% (2)
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Visual6 1 CellTransport-PassiveDocument21 pagesVisual6 1 CellTransport-PassiveLouise AndreiNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active TransportDocument3 pagesPassive and Active TransportEdelweiss AnwarNo ratings yet
- 2structure and Functions of Cell MembraneDocument19 pages2structure and Functions of Cell MembraneedriansamaNo ratings yet
- 2.cell Membrane Physiology and TransportDocument88 pages2.cell Membrane Physiology and Transport234820No ratings yet
- Active Vesicular TransportDocument14 pagesActive Vesicular Transportsarah abarcaNo ratings yet
- GENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument22 pagesGENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsJiro SamontañezNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 2 HoshmandDocument15 pagesCell Biology 2 HoshmandHoshmand HershNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Transportronsta86No ratings yet
- GUIDED READING & Video Notes - Cell Membrane & TransportDocument4 pagesGUIDED READING & Video Notes - Cell Membrane & TransportMs. BainNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Cell Exchange of Materials Tissues Tonicity 2021Document72 pagesTopic 2 - Cell Exchange of Materials Tissues Tonicity 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument3 pagesTransport MechanismsAdrian AbitanNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument16 pagesActive TransportShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Theory - StructureDocument32 pagesBasic Cell Theory - StructureRuby SamarNo ratings yet
- Lab SHT Act-1 - Santos - Yzai (DMD 2y2-2)Document3 pagesLab SHT Act-1 - Santos - Yzai (DMD 2y2-2)Miguel Yancy AverillaNo ratings yet
- LAB SHT #2 - Cell TransportDocument3 pagesLAB SHT #2 - Cell TransportMiguel Yancy AverillaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and TransportDocument31 pagesCell Membrane and Transportmary balansagNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Chap. 05+Document47 pagesGeneral Biology - Chap. 05+정서진No ratings yet
- Topic 1.4: Membrane Transport: Key FactsDocument2 pagesTopic 1.4: Membrane Transport: Key FactsArvinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1Document9 pagesChapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1VeiliLookNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Cell Membranes and Transport PMTDocument3 pages1.3. Cell Membranes and Transport PMTJamesNo ratings yet
- 2 Struc Func of A Mammalian CellDocument82 pages2 Struc Func of A Mammalian Cellchochojk36No ratings yet
- Histology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsDocument48 pagesHistology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsZmeu CristinaNo ratings yet
- Cell 1Document48 pagesCell 1Mihai ChirniciniiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manualvocality.duettoqw603100% (40)
- Fluid Mosaic Model !Document6 pagesFluid Mosaic Model !dbsarah11No ratings yet
- Physiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Document5 pagesPhysiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Man Dejelo100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6karyo eseymNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport (Module 3)Document20 pagesMembrane Transport (Module 3)Aldine MabulacNo ratings yet
- Cellular ProcessesssssssssssssDocument10 pagesCellular ProcessesssssssssssssJay Soledad ManganaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7Document14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7JewelNo ratings yet
- 03CellMembrane Oct 2014Document41 pages03CellMembrane Oct 2014USA EMAILNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Transport MechanismDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Transport MechanismMervin GapasinNo ratings yet
- MODULE 12 - GB1 (Cell Transport)Document8 pagesMODULE 12 - GB1 (Cell Transport)NATHANIEL CORTEZNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions ManualLeslieBuchanannjfy100% (54)
- 6-Transport Molecules Across Cell MembraneDocument16 pages6-Transport Molecules Across Cell MembraneMary Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Membrane Structure: Ane Austin Lynn N. Rebancos Bsed-Science 3ADocument9 pagesAssignment For Membrane Structure: Ane Austin Lynn N. Rebancos Bsed-Science 3Ajane austin lynn rebancosNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes Topic 4 CIE Biology A LevelDocument3 pagesSummary Notes Topic 4 CIE Biology A LevelZirimenya JoelNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeMega CyclopsNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab Group 1Document23 pagesBiochem Lab Group 1Charmaine Angela BautistaNo ratings yet
- Module 10 ACTDocument5 pagesModule 10 ACTLeighNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism 1Document21 pagesTransport Mechanism 1Lovely PeñaredondoNo ratings yet
- A Level Key Words Topic 2 Cells and MembranesDocument4 pagesA Level Key Words Topic 2 Cells and MembranesAlice VitelliNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell Membranes-1Document7 pagesTransport Across Cell Membranes-1Ifeoma JulietNo ratings yet
- Light-Dependent ReactionDocument6 pagesLight-Dependent ReactionShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Rate of PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesRate of PhotosynthesisShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic PigmentsDocument7 pagesPhotosynthetic PigmentsShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Light-Independent ReactionDocument6 pagesLight-Independent ReactionShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument11 pagesOsmosisShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesisShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Cell DiffusionDocument11 pagesCell DiffusionShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane StructureDocument19 pagesCell Membrane StructureShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument16 pagesActive TransportShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Biology P.D Lab Report InfoDocument3 pagesBiology P.D Lab Report InfoShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- English B - Prose 2018 ResponseDocument2 pagesEnglish B - Prose 2018 ResponseShannen Narace100% (1)
- English - Argumentative Essay - Covid19 Vaccine 19-02-21Document2 pagesEnglish - Argumentative Essay - Covid19 Vaccine 19-02-21Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- English B - Tempest Past Paper QuestionDocument2 pagesEnglish B - Tempest Past Paper QuestionShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Multiple Choice Answers PresentationDocument6 pagesChemistry - Multiple Choice Answers PresentationShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- English - Narrative EssayDocument1 pageEnglish - Narrative EssayShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous LeavesDocument8 pagesMonocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous LeavesShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- English B - Coursework Test F5T2. 03-03-21Document2 pagesEnglish B - Coursework Test F5T2. 03-03-21Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- English - Notice, Agenda & MinutesDocument3 pagesEnglish - Notice, Agenda & MinutesShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Geography - Industries-The Pitch LakeDocument6 pagesGeography - Industries-The Pitch LakeShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- English - Argumentative Essay - Juvenile DelinquenceDocument2 pagesEnglish - Argumentative Essay - Juvenile DelinquenceShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- The Pitch Lake New 1 - Powerpoint Presentation - Geography - 09-11-20Document13 pagesThe Pitch Lake New 1 - Powerpoint Presentation - Geography - 09-11-20Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Biology - The Eye (Cateracts)Document5 pagesBiology - The Eye (Cateracts)Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- English: NAME: Shannen Narace FORM: 5-4 TEACHER: Mrs. PhillipDocument1 pageEnglish: NAME: Shannen Narace FORM: 5-4 TEACHER: Mrs. PhillipShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Water ProjectDocument17 pagesChemistry - Water ProjectShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- January 2017 ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesJanuary 2017 ElectrochemistryShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Biology - Project On Human ImpactDocument15 pagesBiology - Project On Human ImpactShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Biology - The Eye (Glaucoma)Document8 pagesBiology - The Eye (Glaucoma)Shannen Narace100% (2)
- Open and Closed System in EcologyDocument37 pagesOpen and Closed System in EcologyPhoebie Gael AsisNo ratings yet
- Quiz Bowl Review Grade 7 2ND QDocument51 pagesQuiz Bowl Review Grade 7 2ND QAnonymous SpjVHfNpqNo ratings yet
- Teaching Pack: Cambridge International AS & A Level Biology 9700Document32 pagesTeaching Pack: Cambridge International AS & A Level Biology 9700Dashania GregoryNo ratings yet
- 5090 Workshop 2024 by Miss Iram HabibDocument39 pages5090 Workshop 2024 by Miss Iram Habibmalikrayan76No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2.2Document8 pagesWorksheet 2.2izazuanNo ratings yet
- Ready-To-Print-Diagnostic-Exam LETDocument6 pagesReady-To-Print-Diagnostic-Exam LETjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- Bio 103-L1Document24 pagesBio 103-L1Nahid Sagar 1812889042No ratings yet
- DNA Extraction Grade 9 5Document3 pagesDNA Extraction Grade 9 5spike manNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is Like Army CampDocument1 pageA Cell Is Like Army CampOli Memerit0% (1)
- Oxygen Ontents - Reading - ExcerptDocument23 pagesOxygen Ontents - Reading - ExcerptBabli Lovely Nicky100% (1)
- Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman Centre For Foundation Studies Fhsc1214 Fundamentals of Cell Biology Tutorial 6 Cell Biology and Basic Histology IDocument3 pagesUniversiti Tunku Abdul Rahman Centre For Foundation Studies Fhsc1214 Fundamentals of Cell Biology Tutorial 6 Cell Biology and Basic Histology IEngNo ratings yet
- B1.1 Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesB1.1 Knowledge OrganisermtauhidNo ratings yet
- DHA General 03/03/2021: c-90-120 DaysDocument6 pagesDHA General 03/03/2021: c-90-120 DaysMONFOLA100% (1)
- Content Review PacketDocument9 pagesContent Review Packetapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Living Things Other Than Plants and AnimalsDocument5 pagesLiving Things Other Than Plants and AnimalsMariel Niña Erasmo100% (2)
- I Am Joe's Cell: by J.D. Ratcliff From Reader's Digest December 1973Document5 pagesI Am Joe's Cell: by J.D. Ratcliff From Reader's Digest December 1973klfyuioashNo ratings yet
- Biology Igcse Questions and Answers Paper 4Document96 pagesBiology Igcse Questions and Answers Paper 4nermeenNo ratings yet
- DP1 BioSL - Topic 1 - Revision WorksheetDocument19 pagesDP1 BioSL - Topic 1 - Revision WorksheetlesedimamareganeNo ratings yet
- Workbook of BiochemDocument22 pagesWorkbook of BiochemMedStudent MedStudentNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument2 pagesProkaryotic CellFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument5 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionIRDINA ADLIN BINTI FIRDAUS MoeNo ratings yet
- Full Download pdf of Guyton & Hall Physiology Review (Guyton Physiology) 4th Edition John E. Hall Phd - eBook PDF all chapterDocument69 pagesFull Download pdf of Guyton & Hall Physiology Review (Guyton Physiology) 4th Edition John E. Hall Phd - eBook PDF all chapterichuunjoober100% (4)
- Bacteria and Archaea Are Classified As Prokaryotes ( Pro Before Karyon - Nucleus)Document2 pagesBacteria and Archaea Are Classified As Prokaryotes ( Pro Before Karyon - Nucleus)Sekar AyuNo ratings yet
- Zoology IntroductionDocument52 pagesZoology IntroductionJessieNo ratings yet
- CELLMOL Long Exam 02 PDFDocument18 pagesCELLMOL Long Exam 02 PDFcalliemozartNo ratings yet
- Journal of Infection and Public HealthDocument6 pagesJournal of Infection and Public HealthungureanucameliaNo ratings yet
- Genetic CentreDocument37 pagesGenetic CentreProf. Madhavan100% (3)
- Miniseries Illustrating The Machinery of LifeDocument8 pagesMiniseries Illustrating The Machinery of LifeJason ParsonsNo ratings yet