Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Philippine Popular Culture
Philippine Popular Culture
Uploaded by
christian Jay HorseradaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Philippine Popular Culture
Philippine Popular Culture
Uploaded by
christian Jay HorseradaCopyright:
Available Formats
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
PHILIPPINE POPULAR CULTURE
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Janice B. Sawe
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON NO.6 - COMPONENTS OF CULTURE-MATERIAL CULTURE AND
NON-MATERIAL CULTURE
● Pre-Spanish Period (cave, tree house, Nipa hut/Bahay
OUTLINE Kubo).
I. Components of Culture ● Spanish Period (Forts, Plaza, Churches, Government
A. Material Culture building or capitol, Bahay na bato or Stone House).
1. Art ● American Period (Chalet, two-storey house, bungalow
2. Architecture and Housing house, residential architecture).
3. Tools of Communication - We can learn a lot about the culture of a period by
4. Food looking at the material artifacts of that age. Indian art
B. Non-Material Culture and architecture are distinguished by their religious
1. Cognitive content, exquisite style and philosophical outlook. The
2. Normative artistic remains show their close connection with religion.
● Architecture of the Pre-Historic Period - In
North India, the Stone Age was followed by the
I. COMPONENTS OF CULTURE Copper Age, which was followed by the Iron Age.
But in South India, Stone Age was followed by the
Iron Age.
● Harappan Architecture - The discoveries of the
cities like Mohenjo Daro and Harappa show that
indus valley houses and the town planning show
that they had made much progress in
architecture. The public baths and public buildings
show that their architecture was characterized by
its utilitarianism.
● Architecture during Vedic Culture - Aryans
developed a new culture in North India around
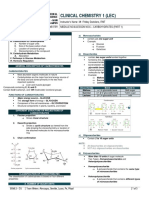
Figure 1. Components of Culture
2000 B.C. The great epics of Mahabharata and
Ramayana make reference to many places, royal
William Ogburn has given two forms of culture: courts, buildings and cities and a high degree of
A. Material Culture excellence in arts and architectural sense.
B. Non-Material Culture ● Buddhist Period - Not much progress in art and
architecture. Materials like the earth bamboo and
A. MATERIAL CULTURE wood were used for the purpose of construction.
A few buildings were made of stone.
All things that man has created, which are observed and ● Mauryan Period - Mauryan Empire made much
tangible are material artifacts. progress to art and architecture. Mauryan kings
→ Example: tools, table, chair etc. patronized many artists, architects, and
Elements of material culture in society can be observed engineers. Chandragupta had built a large and
through: beautiful wooden palace. King Ashoka built many
1. Art Stupas in honour of Lord Buddha.
- It refers to those forms of creative expression which ● Gupta Period - The Gupta era is regarded as the
are guided by aesthetic principles and which involve golden age in the history of ancient India. Art and
imagination, skill, and style. Every culture and society architecture entered its classical phase and a lot
has their own characteristic forms of art. For Example: of progress happened in architecture.
tea drinking is a form of art in Japan; calligraphy is a form ● Mughal-Maratha Period - The Indo-Islamic art of
of art in China and the Islamic Middle East. the earlier period was combined and there were
not many changes. To a certain extent, Persian
- Art is a universal aspect of human experience and influence was pre-dominant unto the end of the
there is no such known culture where art is not present. reign of Akbar after which Indian style dominated.
Art is not present. Art is a means by which people
express their values, perceptions of reality and the 3. Tools of Communication
identity of their culture. - There are different tools of communication used
by different communities. Some of them are:
2. Architecture and Housing I. Oral Culture - Communication here is generally
- The History and culture of the Philippines are reflected face-to-face and verbal.
in its architectural heritage. II. Writing - More than 5,000 years ago, the development
of alphabets took place independently in several places
Factors to consider in building a house: around the world. The medium used for carrying out this
form of communication was clay tablets by the
1. Setting (Geography) Sumerians, but Egyptians. Greeks, and Romans
2. Climate eventually made use of papyrus. Romans Later began to
3. Availability of resources use parchment. By A.D.100, the Chinese developed a
paper which was made from rags. Today, writing is no
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Tulio, Ipong, Montenegro, Flores 1 of 3
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
PHILIPPINE POPULAR CULTURE
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Janice B. Sawe
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON NO.6 - COMPONENTS OF CULTURE-MATERIAL CULTURE AND
NON-MATERIAL CULTURE
longer dependent on such rudimentary techniques and a broad and non-specific and norms are specific
variety of paper and writing materials are used. and definite.
III. Printing Press - This led to the spread of written ● Norms can be:
material and to mass communication being possible. ○ Prescriptive Norms - are those which
IV. Modern Communication Technologies - These prescribe or allow kinds of behavior to take
include newspapers, magazines, motion pictures, radio, place. Example: in college, you should study.
television and more recently the internet. ○ Proscriptive Norms - are those which prohibit
certain kinds of behavior. Example: murder and
4. Food crime are those acts which are forbidden by
- Food is also considered as a form of art in many society.
societies and cultures. ○ Cultural Norms - states how culture should
- In many cultures, it is seen as a tradition and traditional ideally followed, that is, how it actually should
recipes are handed down from one generation to the be. Example: one should always be honest.
next, from mother to daughter. The type of food eaten is ○ Statistical Norm - is the measure of the actual
also a part of culture. For Example: In China and India, conduct in the society. It is the ‘the actual
pigs are eaten and are seen as a source of protein but behaviour of a person in a given situation.’
religious tradition of Islam and Judaism forbid eating of Example: one shouldn’t break a traffic light -
pork. this is a norm =, but when one is in hurry and
one breaks it, then it is a statistical norm.
B. NON-MATERIAL CULTURE ● Norms include
1. Folkways: they are workable patterns
● This refers to various symbolic creation of man. It consists of accepted as appropriate but not insisted upon.
the intangible products of human society. Example: if you eat food with your hand, you
- For Example: values, norms, attitudes. won’t be punished. They are passed down from
● They are called Mentifacts. Both, material and non-material generation to generation either through
cultures are originally linked. deliberate or more imitation.
● Material culture emerges out of non-material culture. Material 2. Mores: they are morally and strongly
culture changes more frequently, whereas non-material sanctioned folkways regarded as important for
culture is slow to change. This gap between their paces of the survival of the group. Example: wearing
change is known as Culture Lag. clothes is a mores. Negative mores are called
- Example: Material aspect of Indian culture has taboos, which mean that something should not
changed a lot, in terms of technology and be done. Example: Incest- a sexual relation
lifestyle; whereas non-material aspects like relationship between father and daughter.
region and social values change slowly. 3. Customs: a custom is a long established
Elements of non-material culture in society can be observed usage or practice, gradually accepted as an
through: appropriate mode of behaviour. Customs are
sanctioned by group pressure. In traditional
A. Cognitive (Knowledge and Beliefs) societies the hold of customs is very strong.
a. Knowledge: All information about the material 4. Laws: Laws are codified norms or rules
world that can be objectively substantiated. It is enacted by those who exercise political power
the storage and recall of learned information. and are enforced through state machinery.
b. Beliefs: Ideas and speculation about the There is an element of force or compulsion in
physical, social and supernatural reality, not as law. They are needed in a modern, complex
easily supported by facts. They are cultural society to maintain social order. it is more
conventions that are concerned with true or formal as compared to the folkways, mores and
false assumptions, specific descriptions of the norms in the society.
nature of the universe and the place of human ● Different cultures manifest their non-material culture
begins in it. through:
B. Normative (Values and Norms) 1. Folklores: Folklores are an important part of
a. Values: They are a part of the cultural system many cultures, especially the primitive
and are inculcated into the psychological communities. In primitive communities, cultural
system through socialization and are transmission takes place through folklores.
instrumental in shaping and determining Folklores contain the philosophy of the people
behavior in groups and other social systems. of that society or culture. Most of the folklores
Example: Driving at high speed leads to have references made to the mutual relation of
accidents is a belief; driving should not exceed the people to their gods. Folklores help in
a certain limit is a value. socialization as they point out how different
b. Norms: These are usually derived from values. types of offences are punished by the
They are standards of behavior expected of supernatural powers. They also contain
individuals by their social groups and therefore descriptions about birds, beasts, trees and
norms supplement values. Values tend to be human beings etc.
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Tulio, Ipong, Montenegro, Flores 2 of 3
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
PHILIPPINE POPULAR CULTURE
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Janice B. Sawe
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON NO.6 - COMPONENTS OF CULTURE-MATERIAL CULTURE AND
NON-MATERIAL CULTURE
2. Myths: Myths owe their origin to belief and
ideals associated with leaders, patriots, national REVIEW QUESTIONS
heroes, institutions and individuals. They are
handed down from one generation to the next. 1. Define culture. Explain the components of culture.
They set examples and guide people in their 2. explain how housing and architecture are components of
life. Despite the fact that they are imaginative material culture.
and unrealistic, they are still very important. For 3. Explain the Cognitive and Normative elements of
Example: In India, myths have originated in non-material culture.
connection with Lord Krishna, Brishma, 4. Discuss how non-material culture manifest itself.
Tulsidas etc. Myths have functions in a society 5. Write short notes on:
like making the social-cultural reality stable, ● Legends
predictable and capable of being endured. They ● Tools and Communication
also maintain the relationship or link between ● Art
the past, present, and future. They also induce ● Norms
a feeling of security and ascertain the beliefs of
people.
3. Legends: They are a form of social myth which
REFERENCES
are based on some part of historical facts and
deal mainly with heroes and events, which are Rai, R., & Panna, K. (2009). Introduction to culture
related to the successes and failures in a group studies. Global Media.
society. Mostly the heroes are religious and the
events related to them, are of a divine
supra-social nature. For Example: In India ,
there are many legends attached to the life of
Lord Krishna.
● There are different types of
legends:
1. Religious Legends - Shri
Krishna, Sai Baba , etc.
2. Political Legends - Gandhi,
Abraham Lincoln.
3. Economic Legend - Karl
Marx.
4. Social Legend - Mother
Teresa.
● Legends evolve due to many reasons and they
are very important because they represent the
ideals and values in a society and they provide
an opportunity for the individual to acquaint
himself/herself with the culture of that society.
Legends are also important because they are
attached with the emotions, feelings and
assumptions of a particular society and culture.
4. Aesthetics: In every society, people express
themselves through different ways of creative
expression. These are guided by aesthetic
principles involving imagination. beauty, skill and
style. Example: Many cultures have a history of
appreciating music, poetry, forms of dance and
paintings.
Every Culture includes both material as well as
non material. Even though material culture
changes more frequently and drastically, as
compared to non material culture, without either
of them, no culture is complete.
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Tulio, Ipong, Montenegro, Flores 3 of 3
You might also like
- Test Bank For Human Sexuality in A World of Diversity 6th Canadian Edition RathusDocument29 pagesTest Bank For Human Sexuality in A World of Diversity 6th Canadian Edition RathusLorraine Holcombe100% (42)
- Ancient India and China (2600 B.C.-A.D. 550) : How Are Religion and Culture Connected?Document40 pagesAncient India and China (2600 B.C.-A.D. 550) : How Are Religion and Culture Connected?Lndyayo LndNo ratings yet
- Lit 101 Midterms CompiledDocument12 pagesLit 101 Midterms CompiledMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture ReviewerDocument6 pagesHistory of Architecture ReviewerJaymax the FirstNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture - III: Indus CivilizationDocument29 pagesHistory of Architecture - III: Indus Civilizationတမန္ေတာ္ တမန္ေတာ္No ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization: History of ArchitectureDocument22 pagesIndus Valley Civilization: History of ArchitectureTom JerryNo ratings yet
- Indian ArchitectureDocument14 pagesIndian ArchitectureJesseca AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Indian Architecture: ModuleDocument27 pagesIndian Architecture: ModuleAnuj PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Architectural Styles PDFDocument12 pagesArchitectural Styles PDFBKumrNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTUREDocument34 pagesARCHITECTUREShretima AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Ancient IndiaDocument40 pagesAncient IndiaKingston Maria InfantNo ratings yet
- HO4, iNDIADocument9 pagesHO4, iNDIAJRussell IgnacioNo ratings yet
- HOA Sanchez, KylaDocument21 pagesHOA Sanchez, KylaKYLA C SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Architecture of IndiaDocument60 pagesArchitecture of IndiaLaxmi MaradaNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture & The Built Environment - I Lecture-IDocument24 pagesHistory of Architecture & The Built Environment - I Lecture-IJoseph Carmelo Andres RagadiNo ratings yet
- Indian Architecture: With The Special Reference of Mughals: March 2018Document7 pagesIndian Architecture: With The Special Reference of Mughals: March 2018Abdullah Al Mamun PrantoNo ratings yet
- Indian Architecture: With The Special Reference of Mughals: March 2018Document7 pagesIndian Architecture: With The Special Reference of Mughals: March 2018Abdullah Al Mamun PrantoNo ratings yet
- Indian Architecture: With The Special Reference of Mughals: March 2018Document7 pagesIndian Architecture: With The Special Reference of Mughals: March 2018Abdullah Al Mamun PrantoNo ratings yet
- Indian Architecture With The Special Re Fference of MughalsDocument7 pagesIndian Architecture With The Special Re Fference of MughalsSudhan PaudelNo ratings yet
- 03-JULY-2021: The Hindu News Analysis - 3 July 2021 - Shankar IAS AcademyDocument16 pages03-JULY-2021: The Hindu News Analysis - 3 July 2021 - Shankar IAS Academyraorane.swati27No ratings yet
- Indian Architecture: With The Special Reference of MughalsDocument6 pagesIndian Architecture: With The Special Reference of MughalsSharmila NehalNo ratings yet
- Art & Culture Compilation Notes - PDF ONLYDocument127 pagesArt & Culture Compilation Notes - PDF ONLYndb01011978No ratings yet
- Indian Architecture LibreDocument27 pagesIndian Architecture LibreStephen.KNo ratings yet
- CavesDocument41 pagesCavesKrunal ShahNo ratings yet
- HOA - Indian Architecture InfluencesDocument5 pagesHOA - Indian Architecture InfluencesMike Vincent MejicoNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian ArchitectureDocument47 pagesAncient Indian ArchitectureKrishanNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5334837516639020371Document31 pagesInbound 5334837516639020371jhianespinola15No ratings yet
- Building Materials of Ancient Construction: Periods of Indian ArtDocument8 pagesBuilding Materials of Ancient Construction: Periods of Indian ArtMeeko MasangcapNo ratings yet
- Daily Current Affairs + PIB Summary (14 Jan 2023)Document13 pagesDaily Current Affairs + PIB Summary (14 Jan 2023)Paras DeolNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture II-1Document240 pagesHistory of Architecture II-1sashaNo ratings yet
- Architecture of IndiaDocument15 pagesArchitecture of IndiaMoon IightNo ratings yet
- Hoa JPT Module 5 - Generoso 2023Document55 pagesHoa JPT Module 5 - Generoso 2023Aprilyn Vanessa DegamoNo ratings yet
- Art & Culture 02 - Daily Class NotesDocument26 pagesArt & Culture 02 - Daily Class NotesLucky SharmaNo ratings yet
- Indian ArchitectureDocument14 pagesIndian ArchitectureVanshika SaiNo ratings yet
- Sharayu v. Dhavane - CBF-V - Colonial Architecture - PDFDocument21 pagesSharayu v. Dhavane - CBF-V - Colonial Architecture - PDFSharayu DhavaneNo ratings yet
- Ancient IndiaDocument115 pagesAncient Indiae.constructivesinghNo ratings yet
- History and Civics Revised Question Bank Class 09 2022 23Document46 pagesHistory and Civics Revised Question Bank Class 09 2022 23Ritwick SonkarNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Indian ArchitectureDocument33 pagesUnit-5 Indian Architecturejagmohan.jk11No ratings yet
- Indian ArchitectureDocument13 pagesIndian ArchitectureCliff Jason GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Indian ArchitectureDocument4 pagesIndian ArchitectureIvars GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Score: Answer Writing Workbook Answer Writing WorkbookDocument181 pagesScore: Answer Writing Workbook Answer Writing WorkbooktarunNo ratings yet
- History of Landscape Design in IndiaDocument23 pagesHistory of Landscape Design in IndiaNaba Neil BaruahNo ratings yet
- Ancient & Asian Architecture: Prepared and Delivered by Dr. Hazrina Haja Bava MohidinDocument46 pagesAncient & Asian Architecture: Prepared and Delivered by Dr. Hazrina Haja Bava MohidinTEO YIN JIA KM-Pelajar100% (1)
- ARCH 2201: Credit Hour: 2.0Document40 pagesARCH 2201: Credit Hour: 2.0Jubayet BariNo ratings yet
- HISTORY Ancient IndiaDocument18 pagesHISTORY Ancient Indiasandarbh12345No ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument11 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationerfan441790No ratings yet
- Cradles of Early Science - STSDocument6 pagesCradles of Early Science - STStyreseandrei1No ratings yet
- Sourcebook Aga Khan Deccan 22102021Document98 pagesSourcebook Aga Khan Deccan 22102021marius lazarNo ratings yet
- Indian Architectural AND Art Style: Arpit Kaur Keshav Sethi Namsit Narula ShipraDocument22 pagesIndian Architectural AND Art Style: Arpit Kaur Keshav Sethi Namsit Narula ShipraKeshav SethiNo ratings yet
- Day-1 SecureDocument8 pagesDay-1 Securefestivista.cessNo ratings yet
- 1.1 History of ArchitectureDocument26 pages1.1 History of ArchitectureJames Esguerra TuazonNo ratings yet
- Building Materials of Ancient ConstructiDocument8 pagesBuilding Materials of Ancient ConstructiAiman HashmiNo ratings yet
- Lesson-01 SST PDFDocument21 pagesLesson-01 SST PDFShivansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Architecture in IndiaDocument19 pagesArchitecture in IndiaSon Chaeyoung MinariNo ratings yet
- Culture - Evernote WebDocument20 pagesCulture - Evernote WebSahil Affriya YadavNo ratings yet
- Aalu Bhujiya Ki RecipeDocument87 pagesAalu Bhujiya Ki Recipesahurupesh52008No ratings yet
- Ancient India ArticleDocument6 pagesAncient India ArticleamypunkinNo ratings yet
- Indian Architecture (Buddhist and Hindu Period)From EverandIndian Architecture (Buddhist and Hindu Period)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Ancient India: A Captivating Guide to Ancient Indian History, Starting from the Beginning of the Indus Valley Civilization Through the Invasion of Alexander the Great to the Mauryan EmpireFrom EverandAncient India: A Captivating Guide to Ancient Indian History, Starting from the Beginning of the Indus Valley Civilization Through the Invasion of Alexander the Great to the Mauryan EmpireNo ratings yet
- Ancient India for Kids - Early Civilization and History | Ancient History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandAncient India for Kids - Early Civilization and History | Ancient History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1 (Lec)Document5 pagesClinical Chemistry 1 (Lec)christian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Histopathology Lab Lesson 2Document12 pagesHistopathology Lab Lesson 2christian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Pre-Analytical Factors and Gross Description: Histopathologic and Cytologic Techniques - LectureDocument28 pagesLesson 1: Pre-Analytical Factors and Gross Description: Histopathologic and Cytologic Techniques - Lecturechristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Decalcification - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath LecDocument2 pagesDecalcification - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath Lecchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Mls 410 Lec - Histopathologic and Cytologic Techniques: Infiltration, Embedding & SectioningDocument11 pagesMls 410 Lec - Histopathologic and Cytologic Techniques: Infiltration, Embedding & Sectioningchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesLesson 6 - Carbohydrateschristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Clearing - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath LecDocument2 pagesClearing - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath Lecchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALDocument19 pagesAsynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- RA 11166 and RA 7170Document16 pagesRA 11166 and RA 7170christian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Impregnation & Embedding - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath LecDocument5 pagesImpregnation & Embedding - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath Lecchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Dehydration - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath LecDocument2 pagesDehydration - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath Lecchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Amino AcidDocument10 pagesLesson 8 - Amino Acidchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Act. 5 - Appropriate Dehydration of Tissue SamplesDocument5 pagesAct. 5 - Appropriate Dehydration of Tissue Sampleschristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Act. 8 - Proper Method of Embedding Infiltrated TissuesDocument4 pagesAct. 8 - Proper Method of Embedding Infiltrated Tissueschristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Act. 6 - Correct Execution of Clearing TechniqueDocument4 pagesAct. 6 - Correct Execution of Clearing Techniquechristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- History of Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument6 pagesHistory of Medical Laboratory Sciencechristian Jay Horserada0% (1)
- Correspondence: Nature and ImportanceDocument45 pagesCorrespondence: Nature and Importancechristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- End of Quiz: GE 107 - Science, Technology, and Society - A11 Final Examination (Ge 107)Document5 pagesEnd of Quiz: GE 107 - Science, Technology, and Society - A11 Final Examination (Ge 107)christian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Final PurpDocument6 pagesFinal Purpchristian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Professional Ethics PPTDocument55 pagesProfessional Ethics PPTHanzla AfzalNo ratings yet
- The Role of Religion in EthicsDocument2 pagesThe Role of Religion in Ethicstine84394No ratings yet
- Peer Rel 01Document26 pagesPeer Rel 01One's2011No ratings yet
- AFIEFAH SULISTYOWATI - English Vers - SPIRITUAL CHARACTER BUILDING FOR TOURISM VOCATIONAL EDUCATIONDocument12 pagesAFIEFAH SULISTYOWATI - English Vers - SPIRITUAL CHARACTER BUILDING FOR TOURISM VOCATIONAL EDUCATIONAfie SulistyowatiNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 Syllabus 128 1Document9 pagesNSTP 1 Syllabus 128 1AYSA GENEVIERE O.LAPUZNo ratings yet
- Peer Influence On CheatingDocument3 pagesPeer Influence On CheatinglianjanebajaroNo ratings yet
- 7 - The Sociological Basis of MarketingDocument20 pages7 - The Sociological Basis of MarketingTamara RosenblumNo ratings yet
- Interstudia 31 - 2021Document289 pagesInterstudia 31 - 2021Angelica Helena MarinescuNo ratings yet
- 5 Eed 15 ModuleDocument24 pages5 Eed 15 ModuleNor-inNo ratings yet
- AGB Code of Conduct A4 Full BlueDocument3 pagesAGB Code of Conduct A4 Full BlueElvis PearceNo ratings yet
- Philippine College of Criminology: Course Module For Character Formation 1: Nationalism and Patriotism (CFLM 1)Document69 pagesPhilippine College of Criminology: Course Module For Character Formation 1: Nationalism and Patriotism (CFLM 1)Rhea Lynne DagatanNo ratings yet
- الثقافة التنظيمية كأحد العوامل المؤثرة على الأداء الوظيفيDocument20 pagesالثقافة التنظيمية كأحد العوامل المؤثرة على الأداء الوظيفيsaida.belmabediNo ratings yet
- Development Reading 1Document9 pagesDevelopment Reading 1Karen MolinaNo ratings yet
- Etymology of Ethics Activity 1 TenorioDocument3 pagesEtymology of Ethics Activity 1 TenorioJason PanganNo ratings yet
- Black (2008) Constructing and Contesting Legitimacy and Accountability in Polycentric Regulatory RegimesDocument28 pagesBlack (2008) Constructing and Contesting Legitimacy and Accountability in Polycentric Regulatory Regimesbaehaqi17No ratings yet
- EthicsDocument143 pagesEthicsJoyceees VillacruelNo ratings yet
- Professional Teachers (Secondary) 10-2022 Agri and Fishery ArtsDocument14 pagesProfessional Teachers (Secondary) 10-2022 Agri and Fishery ArtsPRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- Legal Basis of Values EducationDocument4 pagesLegal Basis of Values EducationAngel Mae PontilloNo ratings yet
- Ginny EricksonDocument7 pagesGinny Ericksonapi-640837803No ratings yet
- 09 - 00 - 30 - 18 - 12 - 2022 - Organisational Behavior by Anjali Mam NOTESDocument168 pages09 - 00 - 30 - 18 - 12 - 2022 - Organisational Behavior by Anjali Mam NOTESPapa DeltaNo ratings yet
- Answered Step-By-StepDocument5 pagesAnswered Step-By-Stepthamnguyen304No ratings yet
- SHS HUMSS UCSP Wk2 1-4Document4 pagesSHS HUMSS UCSP Wk2 1-4Jandeil GurreaNo ratings yet
- 8618 Assignment 1Document20 pages8618 Assignment 1Khan BabaNo ratings yet
- 1 - NUM1205 - An Introduction To Law and Ethics - SVDocument41 pages1 - NUM1205 - An Introduction To Law and Ethics - SVLuis Martin PunayNo ratings yet
- Bus Eth ch1Document13 pagesBus Eth ch1AN NesNo ratings yet
- Organizational Theory Design and Change 7th Edition Jones Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesOrganizational Theory Design and Change 7th Edition Jones Solutions Manualphongtuanfhep4u100% (27)
- Narrative ReportDocument9 pagesNarrative ReportJeah Kyla BeramoNo ratings yet
- Positive EnviromentsDocument34 pagesPositive EnviromentsWazeerullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Role of Religion in Shaping Filipino Family Values LPDocument4 pagesRole of Religion in Shaping Filipino Family Values LPkathiajanelumiguidNo ratings yet