Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 67-4 - Commonly Used Antiemetics
Table 67-4 - Commonly Used Antiemetics
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table 67-4 - Commonly Used Antiemetics
Table 67-4 - Commonly Used Antiemetics
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićCopyright:
Available Formats
CURRENT Diagnosis &Treatment: Family Medicine, 5e >Hospice &Palliative Medicine
Jeannette E. South-Paul, Samuel C. Matheny, Evelyn L. Lewis+
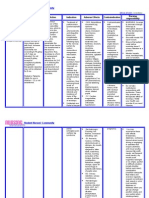
Table 67–4.Commonly used antiemetics.
Drug Receptor Activity/Effect Common Indication Dosage/Route Side Effects
0.5–4 mg PO or SC or IV every 6
Haloperidol D2 Opioid-induced N/V EPS, QTc prolongation
hours (Q6h)
Opioid-induced N/V, delayed gastric 5–20 mg PO or SC or IV before meals EPS, esophageal spasm, colic in
Metoclopramide Peripheral D2
emptying and at bedtime complete bowel obstruction
Opioid-induced N/V, N/V of unknown 5–10 mg PO or IV Q6h or 25 mg PR
Prochlorperazine D2 EPS and sedation
etiology Q6h
Dry mouth, blurred vision, ileus,
1.5 mg transdermal patch every 3
Scopolamine Ach, H1 Vestibular dysfunction urinary retention, and confusion; patch
days
starts being effective after 24 hours
Chemotherapy- or radiation 4–8 mg PO as pill or dissolvable tablet
Ondansetron 5-HT3 Headache, fatigue, constipation
therapy–induced N/V or IV every 4–8 hours
Increased intracranial pressure, 4–8 mg every morning or BID, PO (pill
Dexamethasone Decreases intracranial pressure Agitation, insomnia, hyperglycemia
capsular stretch or liquid) or IV
Lorazepam GABA receptor Anticipatory N/V 0.5–2 mg PO or IV every 4–6 hours Sedation, confusion, delirium
125 mg PO on day 1, 80 mg PO on Somnolence, fatigue, may reduce
Aprepitant NK1 Severe chemotherapy-induced N/V
days 2–3 warfarin levels
BID, twice per day; EPS, extrapyramidal symptoms; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; IV, intravenous; N/V, nausea/vomiting; PO, per mouth; PR, per rectum; SC, subcutaneous.
Date of download: 12/27/22 from AccessMedicine: accessmedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Psychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Document841 pagesPsychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Dragutin Petrić100% (1)
- Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Document555 pagesClinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin Petrić100% (1)
- LabetalolDocument3 pagesLabetalolTri Purma Sari50% (2)
- Drug Study SertralineDocument5 pagesDrug Study SertralineJose Luis Hernandez50% (2)
- Drug Study HaloperidolDocument2 pagesDrug Study HaloperidolRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument2 pagesFentanylKatie McPeek63% (8)
- 4 SeizuresDocument11 pages4 SeizuresApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesValproic Acid Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Psychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyDocument4 pagesPsychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- 9 PropofolDocument2 pages9 PropofolAbdelhafiz Susmiran100% (3)
- Valproic Acid Drug Study PDFDocument4 pagesValproic Acid Drug Study PDFLiza Marie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Breathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetDocument8 pagesBreathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Propofol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPropofol Drug StudyAngelica shane Navarro100% (2)
- Drug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGpretty_mary100% (4)
- Perphenazine Drug StudyDocument4 pagesPerphenazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockDocument1 pageAdult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- NursingCrib Com LevodopaDocument3 pagesNursingCrib Com LevodopaSubendu BarikNo ratings yet
- LevodopaDocument3 pagesLevodopaderic50% (2)
- Part2 Drug AnalysisDocument15 pagesPart2 Drug Analysisghian carloNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument4 pagesOlanzapineJaica Jane BunadoNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin DRUGSTUDYDocument3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDYEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Dosage & RouteDocument1 pageDosage & RoutepiasolNo ratings yet
- PRN Medications: Indications & UseDocument23 pagesPRN Medications: Indications & Usedis_is_me100% (1)
- Pharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsDocument7 pagesPharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- (Pharmacology) Antispasmodic DrugsDocument11 pages(Pharmacology) Antispasmodic Drugsairon jakeNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine.1 3Document1 pageHydralazine.1 3SNo ratings yet
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateRomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- AbilifyDocument2 pagesAbilifyWendy SimsNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac IVDocument3 pagesKetorolac IVEli Thy IgopNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductDocument3 pagesMyasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DonepezilDocument2 pagesDonepezilAmberNo ratings yet
- Ad Handout StudentDocument3 pagesAd Handout Studentapi-588254706No ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument25 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSCheetahboi Shopee100% (4)
- GROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoDocument5 pagesGROUP 2: Azuelo, Cano Pacheco, Inoc, Pareja, TejanoJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument10 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBenzodiazepines Drug Studyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Intro To PsychopharmacologyDocument8 pagesIntro To Psychopharmacologyprettykiran7No ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University College of Nursing: Psychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyDocument2 pagesCebu Normal University College of Nursing: Psychotropic Drug Study in Psychiatry As A Nursing SpecialtyJvWoodzNo ratings yet
- Clorazepate 3.75 MG Classification Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesClorazepate 3.75 MG Classification Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesAirah Ramos PacquingNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsDocument16 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: La Salle UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: La Salle UniversityJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study TramadolLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- TRAMADOLDocument9 pagesTRAMADOLheluNo ratings yet
- LorazepamDocument3 pagesLorazepamgovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- GenericDocument1 pageGenericmcarter402No ratings yet
- Fluphenazine Hydrochloride Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFluphenazine Hydrochloride Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- RisperidoneDocument4 pagesRisperidoneJay Lemuel BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- LortabDocument2 pagesLortabKatie McPeek100% (1)
- 8 Propofol Drug StudyDocument4 pages8 Propofol Drug Studyshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- Home Care Team Visit With Nurse Asmaa, Physiotherapist Maria and Dietician KhuludDocument10 pagesHome Care Team Visit With Nurse Asmaa, Physiotherapist Maria and Dietician KhuludAnonymous T4oP0BEvNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Drug Study FurosemideDocument3 pagesDrug Study FurosemideLouie Danielle Segarra100% (1)
- BisoprololDocument2 pagesBisoprololNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- PSYC - Medication TemplateDocument15 pagesPSYC - Medication TemplateM Henry100% (1)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- THPDocument3 pagesTHPtonmoyNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Psychiatry - A Case-Based Textbook, 2e (Mar 30, 2024) - (3031478010) - (Springer) (Ana Hategan, James A. Bourgeois Etc.) (Z-Library)Document939 pagesGeriatric Psychiatry - A Case-Based Textbook, 2e (Mar 30, 2024) - (3031478010) - (Springer) (Ana Hategan, James A. Bourgeois Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument216 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- PsihijatrijaDocument223 pagesPsihijatrijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 8Document1 page8Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- EtikaDocument218 pagesEtikaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Etika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Document238 pagesEtika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument1 pageŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument3 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Textbook of PsychiatryDocument3 pagesTextbook of PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Agitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDocument2 pagesAgitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDocument1 pageDrug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Kurs Pozitivne Filozofije Auguste ConteDocument152 pagesKurs Pozitivne Filozofije Auguste ConteDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Gender PsychiatryDocument12 pagesGender PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Selected Root Causes of Moral DistressDocument1 pageSelected Root Causes of Moral DistressDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Faze Liječenja Velikog Depresivnog PoremećajaDocument2 pagesFaze Liječenja Velikog Depresivnog PoremećajaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- FDADocument2 pagesFDADragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Liječenje Depresije Naknadni PosjetiDocument3 pagesLiječenje Depresije Naknadni PosjetiDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Stablo Odlučivanja Kako Odrediti Je Li Osoba Prikladna Za Liječenje Usmjereno Na PonašanjeDocument2 pagesStablo Odlučivanja Kako Odrediti Je Li Osoba Prikladna Za Liječenje Usmjereno Na PonašanjeDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 7Document24 pages7Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Stablo Odlučivanja StepDocument3 pagesStablo Odlučivanja StepDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 6Document34 pages6Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Morphine Hydrochloride: Drugs Name Medicinal Forms, DosesDocument2 pagesMorphine Hydrochloride: Drugs Name Medicinal Forms, Dosesanon_840648043No ratings yet
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsK1K5KNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydrocodoneDocument1 pageDrug Study HydrocodoneYlrenne DyNo ratings yet
- Toxicology of Drugs of Abuse: Robert Paul S. Lim, RPHDocument71 pagesToxicology of Drugs of Abuse: Robert Paul S. Lim, RPHƉarwin Lopez ObelNo ratings yet
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs in Black Patients With HypertensionDocument9 pagesACE Inhibitors and ARBs in Black Patients With HypertensionMarisol Estefany FarfanNo ratings yet
- Limits of Chemicals in Dosage FormDocument206 pagesLimits of Chemicals in Dosage FormNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Co CrystallizationDocument6 pagesCo Crystallizationshah777No ratings yet
- BPT Question BankDocument10 pagesBPT Question BankRoydenPTNo ratings yet
- M.I. (Losartan) Drug Study)Document2 pagesM.I. (Losartan) Drug Study)Angelica Marie MacaslingNo ratings yet
- Sedation With "Non-Sedating" Antihistamines: Four Prescription-Event Monitoring Studies in General PracticeDocument9 pagesSedation With "Non-Sedating" Antihistamines: Four Prescription-Event Monitoring Studies in General PracticeDan StratulatNo ratings yet
- Practice Guidelines: ACOG Guidelines On Psychiatric Medication Use During Pregnancy and Lactation - American Family PhysicianDocument4 pagesPractice Guidelines: ACOG Guidelines On Psychiatric Medication Use During Pregnancy and Lactation - American Family PhysicianKim Villeneuve100% (1)
- Dapa HF TrialDocument36 pagesDapa HF Trialvarshith kumarNo ratings yet
- Active IngredientDocument18 pagesActive IngredientHima Bindu ValluriNo ratings yet
- IVTDocument71 pagesIVTIrene Soriano BayubayNo ratings yet
- Medication Calculation: Dosage and ConversionsDocument3 pagesMedication Calculation: Dosage and ConversionsKaren Ruste Villaluna-AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Vere Labs: VL-Delta 8 THC Cartridge 1Document1 pageVere Labs: VL-Delta 8 THC Cartridge 1Michael WalkerNo ratings yet
- DS PNSSDocument4 pagesDS PNSSKathryne May JinonNo ratings yet
- Common OB DrugsDocument4 pagesCommon OB Drugstempraboy100% (5)
- Perez Et Al 1991Document5 pagesPerez Et Al 1991Reza Rahman 15No ratings yet
- Antiinflam Sedative, Anesthetics KwesDocument10 pagesAntiinflam Sedative, Anesthetics KwesRyka Gumangan DumangengNo ratings yet
- FormularyDocument5 pagesFormularyMichelle WongNo ratings yet
- Shivansh Pande Clinical Pharmacist Apollo Hospitals, Jubilee Hills, HyderabadDocument12 pagesShivansh Pande Clinical Pharmacist Apollo Hospitals, Jubilee Hills, HyderabadshivanshpandeNo ratings yet
- Kayexalate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKayexalate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- Cerebyx JJJDocument10 pagesCerebyx JJJFaya WidyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Aclasta (MIMS)Document2 pagesAclasta (MIMS)setiajie82No ratings yet
- Gazette 2022-03-15 Price Revision of 60 Varieties of Medicinal DrugsDocument10 pagesGazette 2022-03-15 Price Revision of 60 Varieties of Medicinal DrugsAda Derana100% (1)
- Pharmaceutics Is The Discipline of Pharmacy That Deals With The Process of Turning ADocument6 pagesPharmaceutics Is The Discipline of Pharmacy That Deals With The Process of Turning ANGMC Clinical TrialNo ratings yet
- Drug and Substance Abuse Prevention and ControlDocument28 pagesDrug and Substance Abuse Prevention and ControlKarlyn RamosNo ratings yet
- mcq ثانيDocument4 pagesmcq ثانيمحمدأميندماج100% (1)