Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Fizik Tingkatan 5 Jawapan
Modul Fizik Tingkatan 5 Jawapan
Uploaded by
Nureen ZuhairahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul Fizik Tingkatan 5 Jawapan
Modul Fizik Tingkatan 5 Jawapan
Uploaded by
Nureen ZuhairahCopyright:
Available Formats
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
MODUL • FIZIK TINGKATAN 5
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
JAWAPAN / ANSWERS
1 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
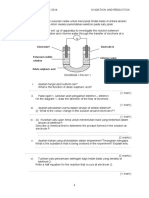
Unit DAYA DAN GERAKAN II Kaedah I / Method I Kaedah I / Method I
1 FORCE AND MOTION II Pertimbangkan jisim 4 kg sahaja Pertimbangkan jisim 3 kg sahaja
(gerak ke bawah) (gerak ke bawah)
1.1 Consider only the 4 kg mass Consider only the 3 kg mass
Contoh / Example (moving downwards) (moving downwards)
40 N – T = m1a 30 N – T = ma
2 12 N – 5 N = 7 N; Arah ke kanan / To the right
40 N – T = (4 kg)(1.43 m s–2) 30 N – T = (3 kg)(4 m s–2)
3 Daya paduan, F / Resultant force, F
∴ T = 34.28 N ∴ T = 30 N – 12 N
= 500 N + 200 N
= 18 N
= 700 N ke kanan / to the right Kaedah II / Method II
4 Daya paduan, F / Resultant force, F Pertimbangkan jisim 3 kg sahaja Kaedah II / Method II
= 500 N – 200 N (gerak ke atas) Pertimbangkan jisim 4 kg sahaja
= 300 N ke kanan / to the right Consider only the 3 kg mass (gerak ke atas)
(moving upwards) Consider only the 4 kg mass
Latihan / Exercises T – 30 N = m2a (moving upwards)
1 1 cm : 1 N T = 30 N + (3 kg)(1.43 m s–2) T – 2 N = ma
T = 34.29 N ∴ T = 2 N + (4 kg)(4 m s–2)
(a)
.0
N = 2 N + 16 N
0
=1 = 18 N
an
du ce
a pa t for
y n
6N Da sulta
Re Latihan / Exercises
1 (a) Berat budak / Mass of the boy
37°
= W
8N = mg
10 N pada sudut 37° dengan daya 8 N = 50 kg × 10 m s–2
10 N at angle of 37° with the 8 N force = 500 N
(b) (i) R = W = 500 N
(b)
(ii) R – mg = ma
R = 500 N + (50 kg)(2 m s–2)
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
=1
5.6
N
= 600 N
uan e
ap
ad
forc (iii) mg – R = ma
Day ultant
8N
Res R = 500 N – (50 kg)(2 m s–2)
= 400 N
(iv) R – mg = ma
Tetapi a = 0 (kerana halaju malar)
10 N but a = 0 (because constant velocity)
15.6 N pada sudut 27° dengan daya 10 N ∴ R = mg = 500 N
15.6 N at an angle of 27° with the 10 N force 2 (a) (i) F = ma
(c) 3 0 N = [(2 + 3) kg][a]
a = 6 m s–2
.0 N
(ii) dari gerakan troli
t fo n = 5
rce
from the motion of the trolley
ult dua
Res a pa
5N
an
T = ma
y
Da
= (2 kg)(6 m s–2)
5N = 12 N
atau dari gerakan jisim 3 kg
5.1 N pada sudut 60° dengan daya 5 N or from the motion of the 3 kg-mass
5.1 N at an angle of 60° with 5 N force 30 N – T = ma
2 2 cm : 1 N 30 N – T = (3 kg)(6 m s–2)
Daya T = 30 N – 18 N
padu
an / R
esult
ant fo
= 12 N
2N rce =
6 .2 N (b) (i) 30 N – 10 N = (3 + 2) kg × a
120°
16° 20 N = 5 kg × a
5N a = 4 m s–2
6.25 N pada sudut 16° dengan daya 5 N (ii) dari gerakan troli
6.25 N at an angle of 16° with 5 N force from the motion of the trolley
T – 10 N = ma
B Takal / Pulley T – 10 N = (2 kg)(4 m s–2)
T = 8 N + 10 N
F = 40 N – 30 N = 10 N F = 30 N – 2 N = 28 N = 18 N
atau dari gerakan jisim 3 kg
m = 4 kg + 3 kg = 7 kg m = 4 kg + 3 kg = 7 kg or from the motion of the 3 kg-mass
F = ma 30 N – T = m1 a
F = ma, ∴28 N = (7 kg)(a)
30 N – T = (3 kg)(4 m s–2)
10 N 28 N
a= = 1.43 m s–2 a= = 4 m s–2 T = 30 N – 12 N
7 kg 7 kg
= 18 N
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 2
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
1.2 1.3
Contoh / Example Contoh keadaan yang melibatkan daya keseimbangan daya
Fx Example of conditions that involve forces in equilibrium
1 (b) = sin 70°
75 N 2
∴ Fx = 75 N sin 70° = 70.48 N
30º
Fy
= kos / cos 70° T2
75 N
∴ Fy = 75 N kos / cos 70° = 25.65 N
5 cm
Fx (20 N)
(c) = sin 40°
5N
∴ Fx = 5 N sin 40° = 3.21 N
T1
Fy
= kos / cos 40° 30º
5N
∴ Fy = 5 N kos / cos 40° = 3.83 N
Fx
(d) = kos / cos 60° 3 R
6N
θ θ
∴ Fx = 6 N kos / cos 60° = 3.0 N
Fy
= sin 60° T T
6N
∴ Fy = 6 N sin 60° = 5.20 N
Latihan / Exercises
Latihan / Exercises
1 Daya geseran / Friction force, FR
Fx = mg sin θ
1 (a) = kos / cos 60°
6N = 5 × 10 × sin 15°
∴ Fx = 6 N kos / cos 60° = 3.0 N = 50 × 0.2588
(b) F = ma = 12.9 N
3N F(normal) = mg kos / cos θ
a = = 1.5 m s–2
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
2 kg = 5 × 10 × kos / cos 15°
2 (a) = 50 × 0.9659
F = 5 000 N = 48.3 N
Fy
60° 2 (a)
Fx 40°
Fx Berat
(b) = kos / cos 60° T Weight
5 000 N 3.0 N
∴ Fx = 5 000 N kos / cos 60° = 2 500 N
Fy
= sin 60°
5 000 N F
∴ Fy = 5 000 N sin 60° = 4 330 N
Perhatian / Note:
3 (a) Arah bagi tiga daya itu adalah berkitar.
F = 100 N
Fy The directions of the three forces are cyclic.
55° (b) Dari segi tiga di atas, / From the triangle above,
Fx
T
= tan 40°
Fx 3.0 N
(b) = kos / cos 55°
100 N F = 3.0 N tan 40°
∴ Fx = 100 N kos / cos 55° = 57.36 N = 2.52 N
Fy (c) Dari segi tiga di atas, / From the triangle above,
= sin 55°
100 N 3.0 N
= kos / cos 40°
∴ Fy = 100 N sin 55° = 81.92 N T
4 (a) Berat budak, W / Weight of boy, W = 400 N 3.0 N
T =
Wc = mg sin θ kos / cos 40°
Daya,Wc / Force, Wc = 3.92 N
= 400 N sin 30º 3 Pecahkan daya kepada komponen
= 200 N Split the force into component
(b) Daya paduan / Resultant force (a) Bagi komponen mendatar:
= 200 + (–120) For horizontal component:
= 80 N T sin θ = 25 sin 45°
(c) F = ma T sin θ = 17.68......①
F = (40 kg)a
(40 kg)a = 80 N
80 N
a =
40 kg
= 2 m s–2
3 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Bagi komponen mengufuk: / For vertical component:
1 Pemanjangan spring, x berkadar langsung
T kos / cos θ + 25 kos / cos 45° = 35
dengan daya, F
T kos / cos θ = 35 – 25 kos / cos 45°
Extension of the spring, x is directly
T kos / cos θ = 17.32......②
proportional to the force, F
T sin θ 17.68
① ÷ ②: = Pemanjangan spring / Extension of spring
T kos / cos θ 17.32 2
Daya / Force
tan θ = 1.021 Perbincangan
3 Jika spring diregangkan dengan berat yang
θ = 45.6° Discussion
berlebihan, ia mungkin tidak akan kembali
ke panjang asal kerana telah melebihi had
25 N
kenyal.
45°
If the spring is stretched by too large weight,
it might not return to its original length due
35 N
to its exceeding its elastic limit.
Faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi kekenyalan
25 kos / cos 45°
Factors that affect elasticity
Kurang kenyal / Less elastic
25 sin 45°
35 N Lebih kenyal / More elastic
Kurang kenyal / Less elastic
(b) Gantikan / Substitute θ Lebih kenyal / More elastic
= 45.6° ke dalam persamaan ① / into equation ①
Kurang kenyal / Less elastic
T sin 45.6° = 17.68
17.68 Lebih kenyal / More elastic
T =
sin 45.6°
T = 24.7 N
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Ketegangan pada tali B / Tension in rope B = 24.7 N Latihan / Exercises
1 (a) 20 g → 7 cm – 5 cm = 2 cm
1.4 40 g → 4 cm
(b) 20 g menghasilkan pemanjangan 2 cm
kembali ke panjang dan bentuk asal 20 g gives an extension of 2 cm
return to its original length and shape ∴ 60 g → pemanjangan / extension 6 cm
∴ panjang spring dengan beban 60 g = 5 cm + 6 cm = 11 cm
kedudukan asalnya / original positions length of spring with 60 g load = 5 cm + 6 cm = 11 cm
2 (a) x = 13 cm – 10 cm = 3 cm
Daya tolakan antara molekul / Repulsive intermolecular forces
F 6N
k = = = 2 N cm–1
Daya tarikan antara molekul / Attractive intermolecular forces x 3 cm
(b) (i) 6 N → 3 cm
12 N → 6 cm
Eksperimen / Experiment Jumlah panjang / Total length
= 10 cm + 10 cm + 6 cm + 6 cm = 32 cm
Pemboleh ubah F 12 N
dimanipulasi Daya / Berat / Jisim (ii) k = = = 1 N cm–1
x 12 cm
Manipulated Force / Weight / Mass (c) (i) 4 N → 1 cm
variable 12 N → 3 cm
Pemboleh ubah Jumlah panjang / Total length
bergerak balas Pemanjangan spring = 10 cm + 3 cm = 13 cm
Responding Extension of a spring 12 N
(ii) k = = 4 N cm–1
variable 3 cm
3 (a) A: 10 g → 2 cm B: 10 g → 4 cm
Pemboleh ubah 20 g → 4 cm 20 g → 8 cm
Diameter spring / Ketebalan spring
dimalarkan Jumlah pemanjangan / Total extension
Diameter of the spring / Thickness of the spring
Fixed variable = 4 cm + 8 cm = 12 cm
(b) 10 g → 1 cm 50 g → 5 cm
Pemanjangan sistem / Extension in the system = 5 cm
(c) Sistem B / System B : 10 g → 2 cm
∴ 40 g → 8 cm
A : 10 g → 2 cm
∴ 40 g → 8 cm
∴ Pemanjangan sistem / Extension in the system
= 8 cm + 8 cm = 16 cm
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 4
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
1 (b) (i)
4 E = Fx
2 30º T
1
= × (0.02 kg × 10 m s–2) × 0.03 m W
2
= 0.003 J
30º T
1
5 E = Fx
2
1 250
= (20 N) (0.4 m) (ii) = kos / cos 30°
2 T
= 4.0 J T = 289 N
1 2 (c) 1. Sudut antara tali dan palang yang lebih besar untuk
6 (a) E = kx
2 mengurangkan tegangan tali.
1 Bigger angle between the rope and the bar to reduce
= (200 N m–1) (0.04 m)2
2 the tension on the rope.
= 0.16 J 2. Tali yang kurang kenyal supaya tidak berayun.
1 Lower elasticity rope so that no swinging.
(b) mv2 = 0.16 J
2
2 × 0.16 J
v2 = = 32 m2 s–2
0.01 kg Unit TEKANAN
v = 5.66 m s–1 2 PRESSURE
Perhatian / Note:
J Nm F
= 1 P =
kg kg A
(kg m s–2)(m) 160 N
= =
kg 0.2 m2
= m2 s–2 = 800 N m–2
F
2 (a) PMaksimum =
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE AMinimum
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions mg
=
AMinimum
1 A 2 C 3 A 4 B 5 B 6 B
0.5 kg × 10 m s–2
7 D 8 D 9 A 10 A =
(0.05 × 0.10) m2
Soalan Struktur / Structure Question = 1 000 N m–2
F
1 (a) (i) x berkadar langsung dengan W, asalkan had kenyal (b) PMinimum =
AMaksimum
tidak dilebihi.
mg
x is directly proportional to W, provided the elastic =
AMaksimum
limit is not exceeded.
(ii) Hukum Hooke / Hooke’s Law 0.5 kg × 10 m s–2
=
(0.2 × 0.10) m2
(b) Pemanjangan, x / cm
Extension, x / cm = 250 N m–2
mg
7 3 P =
A
6
60 kg × 10 m s–2
5 2 × 104 Pa =
A
4 (60 × 10) N
berslot A = (Perhatian / Note:
ght 3 2 × 104 Pa 1 Pa = 1 N m–2)
2 = 3.0 × 10–2 m2
1
0
Berat, W / N 2.1
Weight, W / N
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Eksperimen A / Experiment A
10 N Inferens / Inference
(c) k = = 250 N m–1
0.04 m Tekanan dalam cecair bergantung kepada kedalamannya.
1 The pressure of the liquid depends on its depth.
(d) E = Fx
2
Hipotesis / Hypothesis
1 Apabila kedalaman cecair bertambah, tekanannya juga bertambah.
= (10 N) (0.04 m)
2 When the depth of the liquid increases, its pressure also increases.
= 0.2 J
2 (a) Kuantiti jirim / Amount of matter Tujuan / Aim
Untuk menyiasat hubungan antara tekanan sesuatu cecair dengan
kedalamannya.
To investigate the relationship between the pressure of a liquid and
its depth.
5 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Pemboleh ubah / Variables 2 P = ρgh
Kedalaman cecair / Depth of liquid = (1.36 × 104 kg m–3)(10 m s–2)(0.8 – 0.2) m
Tekanan cecair / Pressure of liquid = 8.16 × 104 Pa / 8.16 kPa
Ketumpatan cecair / Density of liquid 3 P = ρgh
= (1 000 kg m–3) (10 m s–2) (5 m)
Susunan radas / Arrangement of the apparatus
Tiub getah = 50 000 Pa / 50 kPa
Rubber tube
Bekas Pembaris meter Aplikasi tekanan dalam cecair
Container Metre rule Applications of pressure in liquids
(d) • tekanan / pressure
y Kaki retort • tekanan atmosfera + ρgH / atmospheric pressure + ρgH
Corong tisel h Retort stand
Thistle funnel • tinggi / higher
Kepingan getah Manometer
Rubber sheet Manometer 2.2
Cecair
Liquid Aktiviti untuk menunjukkan kewujudan tekanan atmosfera
Activities to show the existence of atmospheric pressure
Prosedur / Procedure
1 Radas disusun seperti dalam rajah. • lebih besar / greater • berkurang / decreases
The apparatus is set up as shown in the diagram.
2 Bekas diisi dengan cecair.
Latihan / Exercises
A container is filled with a liquid.
3 Satu corong tisel dipasang pada manometer. 1 P = hρg
A thistle funnel is attached to the manometer. = (0.76 m) × (1.36 × 104 kg m–3) × (10 m s–2)
4 Mulut corong tisel diturunkan secara mencancang ke dalam = 1.03 × 105 Pa
cecair sehingga kedalaman, h = 10 cm. 2 Tekanan gas X / Pressure of gas X
The mouth of thistle funnel is lowered vertically into the liquid = (76 cm Hg) – (40 cm Hg)
until the depth, h = 10 cm. = 36 cm Hg
5 Perbezaan paras air di dalam manometer, y direkodkan. 3 (a) 75 cm
The different of water level in manometer, y is recorded. (b) (i) 75 cm
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
6 Langkah 4 dan 5 diulang untuk kedalaman, h = 20 cm, 30 cm, (ii) 75 cm
40 cm dan 50 cm. (c) (i) P = hρg
Steps 4 and 5 are repeated for the depths of h = 20 cm, 30 cm, = (0.75 m) × (1.36 × 104 kg m–3) × (10 m s–2)
40 cm and 50 cm. = 1.02 × 105 Pa
(ii) Tekanan atmosfera merkuri = Tekanan atmosfera air
Menganalisis data / Analysing data Atmospheric pressure of mercury
y (cm) = Atmospheric pressure of water
Pm = Pa
hmρmg = haρag
∴ 1.02 × 105 Pa = (ha) × (1 × 103 kg m–3) × (10 m s–2)
∴ ha = 10.2 m
(iii) Tekanan / Pressure
h (cm)
= (10.2 + 0.40) m = 10.6 m
0
(tekanan meningkat, jadi panjang h meningkat)
Eksperimen B / Experiment B (pressure increases, so the length of h increases)
4 Jumlah tekanan / Total pressure
Inferens / Inference
= Kedalaman ikan dari paras air + tekanan atmosfera
Tekanan dalam cecair bergantung kepada ketumpatan cecair.
Depth of fish from the water surface + atmospheric pressure
The pressure of liquid depends on the density of liquid.
= 3 m + 10 m
Hipotesis / Hypothesis = 13 m
Apabila ketumpatan cecair bertambah, tekanannya juga bertambah.
When the density of liquid increases, its pressure also increases. 2.3
Tujuan / Aim Latihan / Exercises
Untuk menyiasat hubungan di antara tekanan sesuatu cecair dengan 1 (a) Pgas = Patm + h cm Hg
ketumpatannnya. = 76 cm Hg + 15 cm Hg
To investigate the relationship between the pressure of liquid and its = 91 cm Hg
density. (b) Pgas = hρg
= (0.91 m) × (1.36 × 104 kg m–3) × (10 m s–2)
Pemboleh ubah / Variables = 1.24 × 105 Pa
Ketumpatan cecair / Density of liquid 2 (a) Tekanan di titik B / Pressure at point B
Tekanan cecair / Pressure of liquid = Tekanan atmosfera + Tekanan disebabkan jalur AB
Kedalaman / Depth Atmospheric pressure + Pressure due to column AB
= 76 cm Hg + 8 cm Hg
Latihan / Exercises = 84 cm Hg
1 P = ρgh = (0.84 m)(1.32 × 104 kg m–3)(10 N kg–1)
= (1 150 kg m–3) (10 m s–2) (40 m) = 110 880 N m–2
= 460 000 Pa / 460 kPa = 1.11 × 105 Pa
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 6
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Tekanan di titik C = Tekanan di titik B (pada sama paras) Kapal selam / Submarine
Pressure at point C = Pressure at point B (at the same level) Kapal selam tenggelam / Submarine sinks
= 82 cm Hg • lebih besar / larger
= 1.11 × 105 Pa • tenggelam / sink
(b) Tekanan bekalan gas / Pressure of gas supply Kapal selam timbul semula / Submarine rise up
= Tekanan pada titik C / Pressure at point C • lebih kecil / smaller
= 82 cm Hg • timbul semula / rise up
= 1.11 × 105 Pa
(c) Ketinggian jalur merkuri tidak berubah kerana tekanan Ciri-ciri kapal selam: / Characteristics of a submarine:
tidak bergantung pada saiz tiub manometer. (b) menahan / withstand
The height of the mercury column does not change because (c) tenggelam; terapung / sink; float
the pressure is independent of the size of the manometer (d) memantau / observe
tube. (e) pernafasan / respiration
2.4 Belon udara panas / Hot air balloons
Latihan / Exercises • daya apungan; berat belon / buoyant force; weight of the balloon
F1 F2 Ciri-ciri belon udara panas: / Characteristics of hot air balloons:
1 =
A1 A2 (a) lebih besar / bigger
F1 2 500 N (b) lebih besar / bigger
=
50 cm2 20 m2 (d) mengurangkan / reduce
2 500 N (e) rintangan udara / air resistance
F1 = 50 cm2 ×
20 × 104 cm2
= 0.625 N Hidrometer / Hydrometer
F1 F2 • terapung ke atas / float upright
2 =
A1 A2 • sensitif / sensitive
250 N F • lebih dalam / more
=
5 cm2 200 cm2
F = 10 000 N Ciri-ciri sebuah hidrometer: / Characteristics of a hydrometer:
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
3 (a) tekanan yang dipindahkan / the pressure transmitted, (b) kecil / small
20 N (d) terkakis / corrode
P = = 4 000 N m–2
0.005 m2
Latihan / Exercises
mg
(b) P = 1 (a) Daya keapungan / Buoyant force, FB
A2
jisim / mass × 10 m s–2 = berat di udara – berat ketara
4 000 N m = –2
weight in the air – apparent weight
0.1 m2
∴ jisim / mass = 40 kg = 65 N – 30 N
= 35 N
(b) Berat air yang disesarkan / Weight of water displaced
2.5
= daya apungan / buoyant force
Menghubungkaitkan daya apungan dengan berat air yang = 35 N
disesarkan dan isi padu air yang disesarkan (c) Daya keapungan / Buoyant force,
Relate buoyant force to the weight of the water displaced and FB = ρVg
volume of the water displaced 35 N = (1 000 kg m–3)(V)(10 m s–2)
(c) bertambah / increases
35 N
(d) bersamaan / equal V =
(1 000 kg m–3 × 10 m s–2)
= 0.0035 m3
Daya apungan dan keapungan / Buoyant force and flotation
Blok tenggelam sepenuhnya, maka isi padu blok = isi padu
(a) =
air yang disesarkan = 0.0035 m3
(b) <
The block is completely submerged, so volume of the block
(c) >
= volume of water displaced = 0.0035 m3
2 (a) (i) Jumlah berat yang bertindak pada bola pantai X >
Sesebuah kapal akan tenggelam lebih dalam ke dalam air jika
Jumlah berat yang bertindak pada bola pantai Y
berat yang lebih diletakkan di dalamnya.
Total weight acting on the beach ball X > Total weight
The hull of the ship will sink deeper in the water if extra weight is
acting on the beach ball Y
put into it.
(ii) Isi padu air laut yang disesarkan oleh bola pantai X >
• bertambah; bertambah / increases; increases
Isi padu air laut yang disesarkan oleh bola pantai Y
• bertambah / increases
Volume of sea water displaced by the beach ball X >
• besar / larger
Volume of sea water displaced by the beach ball Y
(iii) Berat air laut yang disesarkan oleh bola pantai X >
Peranan simbol Plimsoll pada kapal laut
Berat air yang disesarkan oleh bola pantai Y
The purpose of Plimsoll symbol on a ship
Weight of sea water displaced by the beach ball X >
(a) streamline / Streamlined
Weight of sea water displaced by the beach ball Y
(b) tinggi / high
(iv) Daya apungan yang bertindak ke atas bola pantai X >
(c) stabil / stable
Daya apungan yang bertindak ke atas bola pantai Y
(d) daya apung yang besar / high buoyant force
7 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Buoyant force acting on the beach ball X > Buoyant As the speed of air flow decreases, the air pressure
force acting on the beach ball Y increases OR vice versa
(v) Ketumpatan air laut adalah sama atau tidak berubah (c) Prinsip Bernoulli / Bernoulli’s principle
Density of sea water is same or unchanged (d) • Kapal terbang bergerak dengan laju yang tinggi.
(b) (i) Daya apungan / Buoyant force Aeroplane moves with high velocity.
(ii) Prinsip Archimedes / Archimedes’ principle • Bahagian atas sayap kapal terbang: Udara lebih laju,
(c) (i) Semakin bertambah isi padu air laut yang disesarkan, tekanan lebih rendah.
semakin bertambah daya apungan ATAU sebaliknya Upper part of the wings: air flow is faster, pressure is
As the volume of sea water displaced increases, the lower.
buoyant force increases OR vice versa • Bahagian bawah sayap kapal terbang: Udara kurang laju,
(ii) Semakin bertambah berat air laut disesarkan, semakin tekanan lebih tinggi.
bertambah daya apungan ATAU sebaliknya Lower part of the wings: air flow is slower, pressure is
As the weight of sea water displaced increases, the higher.
buoyant force increases OR vice versa • Perbezaan tekanan menolak sayap kapal terbang ke atas.
(d) (i) Isi padu air disesarkan / Berat air disesarkan Difference of pressure pushes the wings upwards.
Volume of water displaced / Weight of water displaced • Daya angkat > Berat kapal terbang.
(ii) Daya apungan / Buoyant force Lift > Weight of the aeroplane.
(iii) Ketumpatan air laut / Density of sea water • Luas permukaan sayap: lebih besar, menghasilkan daya
angkat lebih besar
2.6 Large wing’s surface area: larger, resulting in greater
Aktiviti / Activity 1 lifting power
(c) bertambah / increases
(d) lebih tinggi / higher
(e) daya paduan / resultant force Unit ELEKTRIK
Aktiviti / Activity 2
3 ELECTRICITY
(c) bertambah / increases 3.1
(d) perbezaan / difference
Medan elektrik / Electric field
(e) mendekati / closer
3 cas positif / positive charges
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Aktiviti / Activity 3 4 magnitud; arah / magnitude; direction
(2) • rendah / lowest
(3) • paling rendah / lowest Corak Medan Elektrik / Electric Field Pattern
Aktiviti / Activity 4
(c) rendah / decreases
(d) tinggi / higher
(e) Daya paduan / resultant force
Penunu Bunsen / Bunsen burner
(c) atmosfera / Atmospheric
(d) tekanan / pressure
(e) gas bahan api / fuel gas
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
1 A 2 D 3 C 4 D 5 A 6 D Latihan / Exercises
7 D 8 A 9 C 10 C 11 C
1 (a) Kerana minyak zaitun merupakan bahan penebat yang baik
Soalan Struktur / Structure Question Because olive oil is a good insulator.
(b) Membentuk garisan corak yang menghubungkan antara
1 (a) (i) Bacaan tolok Bourdon A > bacaan tolok Bourdon B elektrod positif dan elektrod negatif.
Reading of Bourdon gauge A > Reading of Bourdon Form a pattern lines connecting the positive and negative
gauge B electrodes.
(ii) Tekanan udara di X > tekanan udara di Y (c) Kekuatan medan elektrik meningkat.
Air pressure at X > Air pressure at Y The strength of the electric field increases.
(iii) Diameter tiub kaca di X > diameter tiub kaca di Y
Diameter of glass tube at X > Diameter of glass tube Latihan / Exercises
at Y
(iv) Tinggi paras air di X < tinggi paras air di Y 1 ammeter; bersiri / ammeter; series
Height of water level at X < Height of water level at Y 2 voltmeter; selari / voltmeter; parallel
(v) Perbezaan tekanan di X < perbezaan tekanan di Y 3 (a) Cas / Charge, Q = It
Difference of pressure at X < Difference of pressure at = 8.0 A × (50 × 60 s)
Y = 8.0 C s–1 × 3 000 s
(vi) Laju aliran udara di X < laju aliran udara di Y = 24 000 C
Speed of air flow at X < Speed of air flow at Y (b) Beza keupayaan / Potential difference,
(b) Semakin berkurang laju aliran udara, semakin bertambah E 5.76 × 106 J
V = = = 240 V
tekanan udara ATAU sebaliknya Q 24 000 C
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 8
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
4 Diberi / Given V = 6 V, Q = 40 C 2 (a) VXZ = IRXZ
Kerja dilakukan / Work done, E = VQ 1 1 1
= 6 V × 40 C = +
RYZ 8 Ω 8 Ω
J
= 6 × 40 C 1 2
C =
= 240 J RYZ 8 Ω
∴ RYZ = 4 Ω
3.2 ∴ RXZ = RXY + RYZ
Hukum ohm / Ohm’s law
=8Ω+4Ω
• berkadar terus / directly proportional = 12 Ω
V 20 V
Konduktor bukan Ohm / Non-ohmic conductors ∴ I = = = 1.67 A
RXZ 12 Ω
• tidak mematuhi / not obey (b) VXZ = IXZRXZ
Latihan / Exercises 1 1 1
= +
RYZ 2 Ω 2 Ω
1 V = IR
1.00 = 0.40 (R) 1 2
=
1.00 RYZ 2 Ω
R =
0.40 ∴ RYZ = 1 Ω
= 2.5 Ω ∴ RXZ = RXY + RYZ
Nilai y / Value of y
=8Ω+1Ω
V = IR = 9 Ω
y = (0.70)(2.5) VXZ 4.5 V
∴ IXZ = = = 0.5 A
y = 1.75 V RXZ 9Ω
Nilai x / Value of x
I2 2Ω
V = IR
A
2.25 = x(2.5) I R2
x = 0.9 A Y 2Ω Z
2 V = IR
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
12 = 2(R) I3
R3
R = 6 Ω I = I2 + I3
3 P mempunyai rintangan yang lebih besar dari Q. Dari bahagian litar yang merentasi YZ,
P has a bigger resistance than Q. From the section of the circuit across YZ,
∴ Kecerunan P lebih tinggi daripada Q. I = IXZ = 0.5 A
Gradient of P is higher than Q. Tetapi / But
I2 = I3
2 sama / same 3 sama / same (Kerana / Because, R2 = R3)
3 berkadar langsung 6 masih akan / still be able ∴ 2I2 = I
directly proportional 2I2 = 0.5 A
6 tidak / would not I2 = 0.25 A
∴ Bacaan ammeter / Ammeter reading = 0.25 A
Latihan / Exercises Dari bahagian litar yang merentasi XY,
1 (a) RPQ = 20 Ω + 10 Ω + 5 Ω = 35 Ω From the section of the circuit across XY,
VXY 3.0 V
1 1 1 1 3 I2 = = = 0.5 A
(b) = + + = 6Ω 6Ω
RPQ 8 Ω 8 Ω 8 Ω 8 Ω ∴ Bacaan ammeter / Ammeter reading = 0.25 A
8Ω
∴ RPQ = = 2.67 Ω
3 Teknik Menjawab [Format Kertas 2 : Perbandingan]
1 1 1 2 Answering Technique [Paper 2 Format : Comparison]
(c) = + =
RYQ 8 Ω 8 Ω 8 Ω (a)
∴ RYQ = 4 Ω
Rajah (a) / Diagram (a) Rajah (b) / Diagram (b)
∴ RYQ = 10 Ω + 20 Ω + RYQ
= 10 Ω + 20 Ω + 4 Ω Selari / Parallel Bersiri / Series
= 34 Ω
1 1 1 1 Malap / Dim
(d) = + +
RPQ 16 Ω 8 Ω 8 Ω Kurang / Less Lebih / More
1 1+2+2 5
= = Lebih / More
RPQ 16 Ω 16 Ω
16 Ω (b) (i) Mentol pada sambungan selari menghasilkan rintangan
∴ RPQ =
5 berkesan yang lebih kecil ATAU Mentol pada sambungan
= 3.2 Ω bersiri menghasilkan rintangan berkesan yang lebih besar.
Bulbs in parallel connection produces a lower effective
resistance OR Bulbs in series connection produces a
greater effective resistance.
9 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
(ii) Semakin berkurang rintangan berkesan, semakin bertambah
1 Litar dihidupkan. 1 Dengan
jumlah arus di dalam litar.
The circuit is menggunakan
As the effective resistance decreases, amount of current in
switched on. pembaris meter,
the circuit increases.
2 Reostat dilaraskan ukur panjang wayar
sehingga ammeter konduktor,
Faktor yang mempengaruhi rintangan dawai
memberikan ℓ = 20.0 cm.
Factors that affect the resistance of wire
bacaan 0.2 A. By using a meter
bertambah berkurang rendah Bacaan voltmeter ruler, measure
increases decreases low dicatatkan. the length of the
The rheostat is conductor,
adjusted until the ℓ = 20.0 cm.
Eksperimen / Experiment ammeter gives a 2 Litar dihidupkan.
reading of 0.2 A. The circuit is
Beza keupayaan yang Rintangan pada The reading of switched on.
merentasi konduktor konduktor logam the voltmeter is 3 Bacaan voltmeter
logam bergantung bergantung kepada recorded. dan bacaan ammeter
kepada arus yang panjang wayar. 3 Eksperimen diulangi dicatatkan.
mengalir melalui The resistance of metal dengan nilai arus The readings of
Inferens konduktor logam. conductor depends on yang berbeza, the voltmeter
Inference The potential the length of the wire. I = 0.3 A, 0.4 A, and ammeter are
difference across a 0.5 A, 0.6 A dan recorded.
Prosedur
metal conductor 0.7 A dengan 4 Rintangan
Procedure
depends on the current melaraskan reostat. dikira dengan
flowing through the The experiment menggunakan
metal conductor. is repeated with rumus, R = V / I
different values of The resistance is
Beza keupayaan yang Rintangan pada current, I = 0.3 A, calculated using the
merentasi konduktor konduktor logam 0.4 A, 0.5 A, 0.6 A formula, R = V / I
logam meningkat meningkat apabila
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
and 0.7 A by 5 Eksperimen
apabila arus yang panjang dawai adjusting the diulangi dengan
mengalir melalui meningkat. rheostat. menggunakan
konduktor logam The resistance of metal panjang wayar yang
Hipotesis meningkat. conductor increases as berbeza,
Hypothesis The potential the length of wire ℓ = 40.0 cm,
difference across a increases. 60.0 cm, 80.0 cm
metal conductor dan 100.0 cm.
increases as the The experiment
current flowing is repeated with
through the metal different lengths of
conductor increases. the wire,
ℓ = 40.0 cm,
Untuk mengkaji Untuk mengkaji
60.0 cm, 80.0 cm
hubungan antara beza hubungan antara
and 100.0 cm.
keupayaan, V, dan rintangan dan panjang
arus, I, dalam konduktor logam.
Menjadualkan ℓ / cm 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 100.0
konduktor logam. To investigate the
Tujuan data I / A 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 I/A
To investigate the relationship between
Aim Tabulation of V/V V/V
relationship between the resistance and the
data R/Ω
the potential length of a metal
difference, V, and conductor. Beza keupayaan, Rintangan,
current, I, in a metal Menganalisis
Potential difference, V / V Resistance, R / Ω
conductor. data
Analysis of the
Arus / Current Panjang konduktor
data Arus, Panjang,
Beza keupayaan logam 0 Current,
I /A
0 Length,
ℓ / cm
Potential difference Length of the metal
Suhu wayar conductor
Pemboleh ubah Temperature of wire Beza keupayaan
Variables Potential difference
Suhu wayar, luas
keratan rentas
Temperature of wire,
cross-sectional area
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 10
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Eksperimen / Experiment
1 Litar elektrik 1 Litar elektrik
disusun seperti yang disusun seperti yang
Luas keratan rentas Jenis bahan dawai
ditunjukkan. ditunjukkan.
dawai mempengaruhi mempengaruhi
The electric circuit is The electric circuit is
Inferens rintangannya. rintangannya.
set up as shown. set up as shown.
Inference Cross- sectional area of The type of material
2 Dawai konstantan 2 Dawai nikrom 50 cm
wire affect its wire affect its
dengan luas keratan disambung merentasi
resistance. resistance.
rentas 0.02 mm2 terminal P dan Q.
Apabila luas keratan Apabila jenis bahan disambung merentasi 50 cm nichrome wire
rentas bertambah, dawai berubah, terminal P dan Q. is connected across
rintangannya rintangannya turut Constantan wire the terminal P and
Hipotesis berkurang. berubah. with cross-sectional Q.
Hypothesis When the cross- When the type of area of 0.02 mm2 is 3 Suis dihidupkan dan
sectional area of wire material of the wire connected across the reostat dilaraskan
increases, its resistance changes, its resistance terminal P and Q. sehingga bacaan
decreases. also changes. 3 Suis dihidupkan dan ammeter ialah 0.5 A.
reostat dilaraskan Bacaan voltmeter
Untuk mengkaji Untuk mengkaji sehingga bacaan direkodkan.
hubungan antara luas hubungan antara jenis ammeter ialah The switch is on
keratan rentas dawai bahan dawai dan 0.5 A. Rekod bacaan and the rheostat is
dan rintangannya. rintangannya. voltmeter. adjusted until the
Tujuan
To investigate the To investigate the The switch is turned reading of ammeter
Aim Prosedur
relationship between relationship between on and the rheostat is 0.5 A. The
the cross-sectional area the type of material of Procedure
is adjusted until the voltmeter reading is
of wire and its the wire and its reading of ammeter recorded.
resistance. resistance. is 0.5 A. The 4 Langkah 2 dan 3
voltmeter reading is diulang dengan
Luas keratan rentas Jenis bahan dawai
recorded. menggunakan dawai
dawai, A Type of material of the
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
4 Langkah 2 dan 3 konstantan 50 cm
Cross-sectional of wire, wire
diulang dengan dan dawai kuprum
A Rintangan, R
menggunakan dawai 50 cm.
Pemboleh ubah Rintangan, R Resistance, R
konstantan dengan Step 2 and 3 are
Variables Resistance, R Ketebalan, panjang
luas keratan rentas repeated by using
Panjang, jenis dawai dawai dan suhu dawai
0.04 mm2, 0.06 mm2, 50 cm constantan
dan suhu dawai Thickness, length of the
0.08 mm2, 0.10 mm2. wire and 50 cm
Length, type and wire and temperature
Step 2 and 3 are copper wire.
temperature of wire of the wire
repeated by using 5 Semua keputusan
Dawai konstantan 50 cm dawai nikrom, constantan wire of direkodkan.
sepanjang 30 cm 50 cm dawai cross-sectional area All the results are
dengan luas keratan konstantan, 50 cm 0.04 mm2, 0.06 mm2, recorded.
rentas 0.02 mm2, dawai kuprum, 0.08 mm2, 0.10 mm2.
0.04 mm2, 0.06 mm2, ammeter, voltmeter, 5 Semua keputusan
0.08 mm2, 0.10 mm2, dawai penyambung, sel direkodkan.
ammeter, voltmeter, kering, suis dan reostat. All the results are
Senarai radas recorded.
dawai penyambung, sel 50 cm nichrome wire,
dan bahan
kering, suis dan reostat. 50 cm constantan wire,
List of R (Ω) V (V)
Constantan wire of 50 cm copper wire,
apparatus Menganalisis Nikrom
length 30 cm with ammeter, voltmeter, Nichrome
and materials data Konstantan
cross-sectional area of connecting wires, dry Constantan
0.02 mm2, 0.04 mm2, cells, a switch and Analysis of the
Kuprum
0.06 mm2, 0.08 mm2, rheostat. data Copper
0.10 mm2, ammeter, 0 A (mm2) 0 I (A)
voltmeter, connecting
wires, dry cells, a Latihan / Exercises
switch and rheostat.
1 A = 0.01 cm2 = 0.01 × 10–6 m2
pℓ (1.724 × 10–6 Ω m)(100 m)
R = =
A (0.01 × 10–6 m2)
R = 1.724 × 10 Ω 4
2 A = 0.05 cm2 = 0.05 × 10–6 m2
pℓ
R =
A
ρ(50 m)
0.5 Ω =
0.05 × 10–6 m2
ρ = 5 × 10–10 Ω
11 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
3.3
Menjadualkan Arus melalui sel, I / A
Perbandingan antara daya gerak elektrik dan beza keupayaan data Current flowing through cell, I / A
0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
Comparison between electromotive force and potential difference Tabulation of Beza keupayaan merentasi sel, V / V
Potential difference across cell, V / V
data
• terbuka; daya gerak elektrik • kecil / smaller
(d.g.e) V/V
Menganalisis
open; electromotive force
data
(e.m.f.)
Analysis of the
• 1.5 V
data 0 I /A
• haba / heat
• kurang / less Pengiraan Apabila / When I = 0 A,
rintangan V = Ԑ (dalam Volt / in Volt)
kecerunan / gradient
dalam Kecerunan graf / Gradient of the graph = – r
V = –rI + Ԑ Calculation of ∴ r = – kecerunan graf (dalam Ω)
internal – gradient of the graph (in Ω)
Eksperimen / Experiment resistance
Apabila arus, I meningkat, pengurangan tenaga Latihan / Exercises
semakin bertambah dan menyebabkan beza
1 (a) Ԑ = 1.5 V
Hipotesis keupayaan, V, menurun.
(b) Ԑ = V + Ir
Hypothesis When the current, I, increases, the energy being
1.5 V = 1.35 V + (0.3 A)r
dissipated increases and causes the potential
(0.3 A)r = (1.5 – 1.35)V
difference, V, to decrease.
0.15 V
r = = 0.5 Ω
Arus yang mengalir melalui sel, I 0.3 A
Current flowing through the cell, I (c) V = IR
Pemboleh ubah
Beza keupayaan merentasi sel, V 1.35 V = (0.3 A)R
Variables
Potential difference across the cell, V 1.35 V
R = = 4.5 Ω
Suhu wayar / Temperature of wire 0.3 A
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
2 Diberi / Given Ԑ = 1.5 V, V = 1.0 V, R = 5 Ω
Senarai radas Sel kering, suis, voltmeter, ammeter, reostat dan
V 1.0 V
dan bahan wayar penyambung Arus / Current, I = = = 0.2 A
R 5A
List of Dry cell, switch, voltmeter, ammeter, rheostat
Ԑ = V + Ir
apparatus and connecting wires
1.5 V = 1.0 V + (0.2 A)r
and materials
(1.5 – 1.0) V
r = = 2.5 Ω
Suis / Switch 0.2 A
3 Apabila nilai I = 0, didapati V = Ԑ.
Susunan radas When the value of I = 0, V = Ԑ is obtained.
Reostat
Arrangement of V Sel kering
Rheostat
Daripada graf, Ԑ = 3.0 V
Dry cell
apparatus From the graph, Ԑ = 3.0 V
R Maka, rintangan dalam, r (kecerunan graf)
A Hence, the internal resistance, r (gradient of graph)
Ԑ – V (3.0 – 1.7) V
r = = = 1.76 Ω
1 Litar elektrik disediakan seperti dalam rajah. I 0.74 A
The electric circuit is set up as shown in 4 Apabila akumulator disambungkan kepada perintang 2 Ω,
diagram. When the accumulator is connected to the 2 Ω resistor,
2 Suis ditutup dan bacaan ammeter, I = 0.2 A Ԑ = V + Ir
dan voltmeter, V dicatatkan dengan = IR + Ir
melaraskan reostat. = (4 A)(2 Ω) + (4 A)r
The switch is closed and the reading of Ԑ = 8 V + (4 A)r ———(i)
Prosedur
the ammeter, I = 0.2 A and voltmeter, V is Apabila akumulator disambungkan kepada perintang 3 Ω,
Procedure
recorded by adjusting the rheostat. When the accumulator is connected to the 3 Ω resistor,
3 Eksperimen diulangi dengan nilai I yang Ԑ = V + Ir = IR + Ir
berbeza iaitu I = 0.3 A, 0.4 A, 0.5 A, 0.6 A = (3 A)(3 Ω) + (3 A)r
dengan melaraskan reostat. Ԑ = 9 V + (3 A)r ———(ii)
The experiment is repeated with different Persamaan (i) = Persamaan (ii), / Equation (i) = Equation (ii),
values of I = 0.3 A, 0.4 A, 0.5 A, 0.6 A, by 8 V + (4 A)r = 9 V + (3 A)r
adjusting the rheostat. (1 A)r = 1 V
1V
r =
1A
∴ r = 1 Ω
Dari (i), / From (i),
Ԑ = 8 V + (4 A)(1 Ω) = 12 V
∴ e.m.f. = 12 V
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 12
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
5 (a) (i) Apabila I meningkat, V berkurang. 3 (a) P = VI
When I increases, V decreases. 3 000 W = (240 V)I
V/V 3 000 W
I = = 12.5 A
240 V
1.5
(b) P = VI = (IR)I
P = I2 R
1.0 3 000 W = (12.5 A)2R
3 000 W
R = = 19.2 Ω
(c)(i)
156.25 A2
0.5
Mengira kos tenaga elektrik
I/A Calculating the cost of electrial energy
0
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
(ii) Berdasarkan ekstrapolasi pada graf, apabila Pemanas air / Water heater 2 × 1 kW × 60 j = 120 kWj
Based on extrapolation of the graph, when
I = 0.0 A, V = 1.5 V Lampu / Lamps 6 × 0.04 kW × 200 j = 48 kWj
(iii) Daya gerak elektrik, Ԑ
Pengisar makanan / Food blender 1 × 0.06 kW × 30 j = 1.8 kWj
Electromotive force, Ԑ
(1.5 – 1.0) V Kipas angin / Fan 5 × 0.06 kW × 100 j = 30 kWj
(b) r = –m = = 0.5 Ω
(0 – 1.0) A
(c) (i) Daripada graf, apabila / From the graph, when Jumlah penggunaan elektrik
I = 0.8 A, V = 1.1 V Total electricity consumption
1.1 V = 739.8 kWj / kWh
(ii) r = = 1.38 Ω
0.8 A
Untuk 200 kWj yang pertama:
(d) Betulkan ralat sifar bagi voltmeter dan ammeter
For the first 200 kWh:
Correct zero errors in the voltmeter and ammeter
200 × 0.2180 = RM43.60
atau / or
Bayaran bil untuk bulan
Elakkan ralat paralaks semasa mengambil bacaan voltmeter Untuk 100 kWj yang berikutnya: Ogos 2020:
dan ammeter
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
For the next 100 kWh: Bill payment for month of
Avoid parallax errors when taking the voltmeter and 100 × 0.3340 = RM33.40 August 2020:
ammeter readings
Untuk 300 kWj yang berikutnya: RM43.60 + RM33.40 +
For the next 300 kWh: RM134.06 + RM76.33
3.4 = RM287.39
300 × 0.5160 = RM154.80
Formula
E = Pt Untuk 300 kWj yang berikutnya:
P = VI For the next 300 kWh:
139.8 × 0.5460 = RM76.33
Tenaga elektrik / Electrical energy
• tenaga bunyi / sound energy
Kecekapan peralatan elektrik / Efficiency of electrical appliances
1 (a) Einput = VIt
Latihan / Exercises
= 12 V × 5.0 A × 2.5 s
1 Diberi / Given V = 240 V, I = 5 A, t = 10 × 60 s = 150 J
E = Pt (b) Eoutput = Tenaga keupayaan graviti
= (VI)t Potential gravitational energy
= 240 V × 5 A × (10 × 60 s) = mgh
= 720 000 J = 2 kg × 10 m s–2 × 3 m
2 Pertama, kira rintangan berkesan RXY = 60 J
Firstly, calculate the effective resistance, RXY 150 J
1 1 1 (c) ∴ Pinput = = 60 W
= + 2.5 s
RXY 2Ω 6Ω 60 J
1 4 Poutput = = 24 W
= 2.5 s
RXY 6Ω ∴ Kecekapan motor / Efficiency of the motor
6Ω POutput
∴ RXY = = 1.5 Ω = × 100%
4 PInput
∴ RWZ = 8 Ω + 1.5 Ω + 2.5 Ω = 12 Ω 24 W
= × 100%
Dari / From 60 W
V = IR = 40%
V 24 V
I= = =2A Latihan / Exercises
RWZ 12 Ω
Kemudian, gunakan rumus tenaga elektrik 1 Kuasainput / Powerinput = Pinput = 3 000 W
Then, using the formula of electrical energy Eoutput = mcθ
E = VIt = 24 V × 2 A × (5 × 60 s) = 14 400 J = 0.5 kg × 4 200 J kg–1ºC–1 × (100 – 20)ºC
= 168 000 J
13 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
∴ Kuasaoutput / Poweroutput = Poutput LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
168 000 J Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
=
90 s 1 D 2 C 3 A 4 A 5 C 6 D
= 1866.67 W 7 B 8 B 9 D 10 B
Kecekapan cerek elektrik / The efficiency of the kettle
POutput Soalan Struktur / Structure Question
= × 100%
PInput 1 (a) Apabila beza keupayaan yang dibekalkan ialah 6 V, kuasa
1866.67 W yang dihasilkan ialah 12 W.
= × 100%
3 000 W When the voltage supplied is 6 V, the power produced is
= 62.22% 12 W.
2 (a) Tenaga elektrik ditukarkan ke tenaga keupayaan graviti (b) Bersiri / Series
Electrical energy is changed to gravitational potential Selari / Parallel
energy (c) Voltan untuk setiap mentol dalam Rajah (b) lebih daripada
(b) (i) Eoutput = mgh Rajah (a). Jumlah rintangan dalam Rajah (b) kurang
= 0.8 kg × 10 m s–2 × 1.5 m daripada Rajah (a). Arus mengalir dalam setiap mentol
= 12 J dalam Rajah (b) lebih daripada Rajah (a).
(ii) Einput = VIt Voltage for each bulb in Diagram (b) is more than
= 5.0 V × 1.2 A × 4.0 s Diagram (a). The total resistance in Diagram (b) is less
= 24 J than Diagram (a). Current flow in each bulb in Diagram (b)
12 J
(iii) Kecekapan / Efficiency = × 100% = 50% is more than that in Diagram (a).
24 J
(c) (i) Bertambah / Increases (d) (i) R1 = 4 Ω + 4 Ω + 4 Ω = 12 Ω
(ii) Bertambah / Increases V 6.0 V
3 Diberi / Given, F = mg = 60 N I = = = 0.5 A
R 12 Ω
Jika tenaga elektrik digunakan = tenaga keupayaan graviti yang 1 1 1 1 3
diperoleh (ii) = + + = ,
R 4Ω 4Ω 4Ω 4Ω
Since electrical energy used = gravitational potential energy
4Ω
gained RT = = 1.33 Ω
3
VIt = mgh
V 6.0 V
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
mgh IT = = = 4.5 A
I = RT 1.33 Ω
Vt
Arus mengalir dalam setiap mentol
60 N × 2 m
= Current flow in each bulb
12 V × 4 s
4.5
= 2.5 A = = 1.5 A
3
4 [1 kWj = 1 unit tenaga elektrik]
(e) (i) Rajah (b) / Diagram (b)
[1 kWh = 1 unit of electrical energy]
(ii) • Jika satu daripada mentol terbakar, mentol yang lain
Jumlah tenaga yang digunakan
masih berfungsi.
= 0.8 kW × 8 j × 30 = 192 kWj
If one bulb blow, another bulb can still function.
Oleh itu, kos elektrik yang digunakan
• Rintangan berkesan kurang // lebih banyak arus
RM0.22
= 192 unit × = RM42.24 mengalir.
unit
Less effective resistance // more current flow.
Total energy used = 0.8 kW × 8 j × 30 = 192 kWh
Hence, the cost of using electricity Teknik Menjawab [Format Kertas 2 : Bahagian B]
RM0.22 Answering Technique [Paper 2 Format : Part B]
= 192 units × = RM42.24
unit
5 60% daripada tenaga elektrik = tenaga cahaya Kekonduksian yang lebih baik Boleh mengalirkan arus
60% of the electrical energy = light energy Good conductivity Can conduct current
60 % × E = tenaga cahaya / light energy
60
× Pt = tenaga cahaya / light energy
100 Nikrom Rintangan lebih tinggi
6 Nichrome Higher resistance
× 40 W × (7 × 60 s) = tenaga cahaya / light energy
10
Oleh itu, tenaga cahaya / Hence, light energy
= 10 080 J
Lebih kecil Rintangan lebih tinggi
6 Ei = Pt = 3 000 W × 90 s = 270 000 J
Smaller Higher resistance
Eo = mcθ
= 0.5 kg × 4 200 J kg–1 °C–1 × (100 – 20)°C
= 168 000 J
Eo Lebih panjang Rintangan lebih tinggi
Efficiency = × 100 Longer Higher resistance
Ei
168 000 J
= × 100
270 000 J
= 62.22% Lebih banyak Rintangan lebih tinggi
More Higher resistance
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 14
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Latihan / Exercises
Unit KEELEKTROMAGNETAN
1 (a)
4 ELECTROMAGNETISM
4.1 U/N S/S
Latihan / Exercises
F
(b) F
U/N S/S
2 Dengan menggunakan peraturan tangan kiri Fleming: D
By using Fleming’s left-hand rule: D
3 Dengan menggunakan peraturan tangan kiri Fleming: C
By using Fleming’s left-hand rule: C
4 Dengan menggunakan peraturan tangan kiri Fleming: A
By using Fleming’s left-hand rule: A
5 Dengan menggunakan peraturan tangan kiri Fleming: A
By using Fleming’s left-hand rule: A
Eksperimen / Experiment
Magnitud daya pada Magnitud daya pada
konduktor pembawa konduktor pembawa
U/N S/S arus dalam medan arus dalam medan
magnet bergantung magnet bergantung
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
kepada magnitud arus kepada kekuatan
yang mengalir. medan magnet yang
The magnitude of the kekal.
Inferens
force on a current- The magnitude of a
Wayar lurus / Straight wire Inference
carrying conductor in force on a current-
(c) arus di tengah / the current in the middle a magnetic field carrying conductor in
depends on the a magnetic field
Elektromagnet / Electromagnet magnitude of the depends on the
(a) elektromagnet / electromagnet current. strength of the
(c) (ii) Bilangan lilitan / Number of turns permanent magnetic
(iii) Jenis teras besi / Type of iron core field.
(iv) Bentuk teras besi / The shape of the iron core
Magnitud daya pada Magnitud daya pada
Kekuatan medan magnet bertambah dengan: konduktor yang konduktor yang
The strength of the magnetic field is increased by: membawa arus dalam membawa arus dalam
(ii) menambahkan / increasing medan magnet medan magnet
bertambah (ditentukan bertambah (ditentukan
Latihan / Exercises oleh jarak gerakan oleh jarak gerakan
wayar kuprum pendek) wayar kuprum pendek)
(a) Sama / Same Sama / Same apabila magnitud arus apabila kekuatan
yang mengalir medan magnet
Sama / Same Sama / Same bertambah (ditentukan bertambah (ditentukan
oleh magnitud beza oleh bilangan magnet).
Banyak / More Kurang / Less
keupayaan, V). The magnitude of the
Hipotesis
Lebih rapat / Closer Kurang rapat / Less closer The magnitude of the force on a current-
Hypothesis
force on a current- carrying conductor in
Lebih kuat / Stronger Kurang kuat / Less stronger carrying conductor in a magnetic field
a magnetic field (indicated by the
(b) Bilangan lilitan gegelung dawai semakin bertambah, kekuatan (indicated by the distance of movement
medan magnet di sekeliling dawai semakin bertambah. distance of movement of short copper wire)
As the number of turns of wire coil increases, the strength of of short copper wire) increases as the
magnetic field around the wire increases. increases as the strength of the
(c) Elektromagnet / Electromagnet magnitude of the magnetic field
(d) (i) Bilangan lilitan gegelung dawai current increases increases (indicated by
Number of turns of wire coil (indicated by the number of
(ii) Kekuatan medan elektromagnet / Strength of electromagnet magnitude of potential magnets).
(iii) Arus elektrik / Current difference, V).
15 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Magnitud beza Bilangan magnet Bilangan Jarak gerakan
keupayaan, V. magnadur magnet wayar, L (cm)
Number of Distance of
Magnitude of the Number of magnadur magnets movement, L (cm)
potential difference, V. magnets 1 pasang
Beza Jarak gerakan
Jarak gerakan wayar Jarak gerakan wayar keupayaan wayar magnet
1 pair of
kuprum pendek, L. kuprum pendek, L Potential Distance of
Pemboleh ubah difference, movement, magnet
Distance of movement Distance of movement Penjadualan
Variables V/V L / cm 2 pasang
of short copper wire, L. of short copper wire, L data 1.5 magnet
Kekuatan medan Magnitud beza Tabulation of 2 pairs of
2.0 magnet
magnet kekal keupayaan, V data 2.5 3 pasang
The strength of the Magnitude of potential 3.0 magnet
permanent magnetic difference, V 3.5
3 pairs of
magnet
field
4 pasang
magnet
1 Voltan bekalan 1 Radas disediakan 4 pairs of
kuasa a.t. yang seperti yang magnet
digunakan ditunjukan pada
dicatatkan; rajah. Jarak gerakan,
Distance of movement,
Jarak gerakan,
Distance of movement,
V = 1.5 V. The apparatus is set Menganalisis L / cm L / cm
Bekalan kuasa a.t. up as shown in the data
dihidupkan. diagram. Analysis of the Beza
Bilangan
pasang
The voltage of the 2 Dua magnet data
keupayaan,
Potential
magnet
0 0 Number of
d.c. power supply magnadur difference, pair of
V/V magnets
used is recorded; diletakkan pada
V = 1.5 V. The d.c. dening besi
power supply is berbentuk U dengan Motor arus terus / Direct current motor
switched on. kutub bertentangan
2 Jarak gerakan wayar menghadap satu Penerangan (e) inersia / inertia
kuprum pendek di sama lain. Explanation (f) • menambahkan / increasing
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
atas wayar kuprum Two magnadur • menambahkan / increasing
tebal diukur dengan magnets are placed
pembaris = L. on the U-shaped Latihan / Exercises
The distance of iron yoke with
movement of short opposite poles 1 D 2 D 3 A 4 A 5 C
copper wire on the facing each other.
thick copper wire is 3 Bekalan kuasa a.t Latihan / Exercises
Prosedur
measured by a ruler dihidupkan. Jarak
Procedure (a) Kurang / Less Lebih / More
= L. gerakan wayar
3 Eksperimen diulangi kuprum diukur
Kurang / Less Lebih / More
dengan bekalan beza dengan pembaris =
keupayaan, L. Kurang / Less Lebih / More
V = 2.0 V, 2.5 V, The d.c power
3.0 V dan 3.5 V. supply is switched (b) (i) Apabila arus elektrik yang mengalir melalui kabel semakin
The experiment on. The distance of bertambah, jisim besi buruk yang dinaikkan semakin
is repeated with movement of copper bertambah atau sebaliknya.
different voltages of wire is measured by As the current flowing through the cable increases, the mass
d.c. power supply, a ruler = L. of scrap metal lifted increases or vice versa.
V = 2.0 V, 2.5 V, 4 Eksperimen diulang (ii) Apabila arus elektrik yang mengalir melalui kabel semakin
3.0 V and 3.5 V. dengan menambah bertambah, kekuatan medan magnet yang terhasil semakin
1, 2, 3 dan 4 pasang bertambah atau sebaliknya.
magnet magnadur As the current flowing through the cable increases, the
pada dening besi strength of magnetic field produced increases or vice versa.
berbentuk U. (c) Elektromagnet / Electromagnet
Experiment is (d) (i) Arus elektrik / Current
repeated with 1, (ii) Kekuatan medan elektromagnet
2, 3 and 4 pairs of Strength of electromagnet field
magnadur magnets (iii) Bilangan lilitan gegelung dawai pada teras besi lembut
on the U-shaped The number of turns of wire coil on the soft iron core
iron yoke.
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 16
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
4.2
Menambahkan kadar pemotongan fluks
Gerakan relatif untuk menghasilkan arus teraruh Lebih banyak
magnet
Relative motion to produce induce currents More
To increase the cutting rate of magnetic flux
(a) pegun / stationary Lebih besar Rintangan lebih kecil
(b) wayar / solenoid Larger Smaller resistance
wire / solenoid
(d) berbeza / different Kuprum Rintangan lebih kecil
Copper Smaller resistance
(b) reostat R / rheostat R
Menambahkan kadar pemotongan fluks
Mengayunkan / Oscillating Lebih kecil
magnet
Smaller
To increase the cutting rate of magnetic
Penjana Arus Terus Penjana Arus Ulang-alik Perbandingan antara Penjana Arus Terus dan Penjana Arus
D.C. Generator A.C. Generator Ulang Alik
Differences between Direct Current Generator and Alternating
(a) arus aruhan (b) garis medan magnet Current Generator
induced current magnetic field lines satu arah yang tetap / one fixed direction
(b) maksimum / maximum (c) menegak / vertical
(f) terus / direct (f) ulang-alik / alternating 4.3
Teknik Menjawab [Format Kertas 2 : Perbandingan] Struktur • gegelung primer / primary coil
Answering Technique [Paper 2 Format : Comparison] Structure • gegelung sekunder / secondary coil
(a)
Prinsip kerja • arus ulang-alik / alternating current
Rajah (a) / Diagram (a) Rajah (b) / Diagram (b) Working • arus aruhan / induced current
principle
Lebih laju / Higher speed Kurang laju / Lower speed
Ciri-ciri Beza keupayaan sekunder
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Lebih besar / Larger Lebih kecil / Smaller Characteristics Secondary potential difference
Lebih cerah / Brighter Kurang cerah / Dimmer
JENIS TRANSFORMER (Klasifikasi)
(b) (i) Semakin bertambah laju kayuhan basikal, semakin cerah TYPES OF TRANSFORMERS (Classifying)
nyalaan mentol.
As the cycling speed of bike increases, the bulb lights up
brighter. Gegelung
primer
Gegelung
sekunder Gegelung Gegelung
(ii) Apabila kadar pemotongan fluks magnet oleh gegelung Primary coil Secondary coil primer
Primary coil
sekunder
Secondary coil
dawai dinamo semakin bertambah, arus elektrik yang
terhasil semakin bertambah. VP VS
VP VS
As the cutting rate of magnetic flux by the coil wire of
dynamo increases, the current produced increases.
(c) (i) Aruhan elektromagnet / Electromagnetic induction
(ii) Hukum Lenz / Lenz’s law
VS > VP
Teknik Menjawab [Format Kertas 2 : Kefahaman / Esei Pendek]
Answering Technique [Paper 2 Format : Comprehension / Short
Essay]
NS > NP NS < NP
1 • Magnet kekal diputarkan.
The permanent magnet is rotated.
• Fluks magnet dipotong oleh gegelung dawai secara gerakan
relatif.
The magnetic flux is cut by the coil wire through the relative
motion.
• Arus aruhan terhasil melalui aruhan elektromagnet.
Faktor yang mempengaruhi kecekapan transformer dan cara
The induced current produced through the electromagnetic
untuk meningkatkan kecekapannya
induction.
Factors that affect the efficiency of a transformer and ways to
• Tenaga kinetik → Tenaga elektrik → Tenaga cahaya
improve the efficiency
Kinetic energy → Electric energy → Light energy
• tebal / thick • haba / heat
2 Lebih kuat Menghasilkan arus yang lebih besar
Stronger Produce larger induced current Teras berlamina haba
Laminated core heat
Mudah dimagnet dan mudah dinyah-
Besi lembut magnetkan
Soft iron Easier to be magnetised and easier to be
demagnetised fluks magnet / magnetic flux
17 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Penghantaran Tenaga Elektrik / Transmission of Electricity (b) Vs = 12 V, Ps = 48 W
(i) ulang-alik / alternating Ps 48 W
(ii) arus kecil / small current \ Is = = = 4.0 A
Vs 12 V
(iii) menurunkan / lower
(c) Kuasa output / Output power = 48 W
Kecekapan / Efficiency
(i) tenaga haba • injak naik (i) kuprum Poutput
heat energy step-up Copper = × 100%
Pinput
(iii) (a) • dikurangkan (i) tinggi
mengurangkan reduced high 48 W
= × 100%
reducing Ip Vp
(vii) berkadar 48 W
songsang = × 100%
0.3 A × 240 V
inversely = 66.67%
proportional
5 (a) Hitungkan nilai arus dalam kabel, I
Latihan / Exercises Calculate value of current in the cable, I
1 Diberi / Given Kuasa dihantar melalui kabel, P = VI
Ns= 250 lilitan / turns, The power transmitted by the cable, P = VI
Np= 50 lilitan / turns, 40 × 103 W = 5 000 V × I
Vp = 12 V 40 × 103 W
Ns Vs I = =8A
= 5 000 V
Np Vp
Maka, kuasa yang hilang disebabkan rintangan,
Ns Vs So, the power loss due to the resistance,
Vs =
Vp P = I 2R
250 lilitan / turns × 12 V = (8 A)2 × 8 Ω
=
50 lilitan / turns = 512 W
= 60 V (b) P = VI
2 Diberi / Given: V = 12 V, Vp= 240 V, Np = 500 lilitan / turns 40 × 103 W = (20 × 103) V × I
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Ns Vs 40 × 103 W
= I = =2A
Np Vp 20 × 103 V
Ns 12 V Maka, kuasa yang hilang disebabkan rintangan,
=
500 lilitan / turns 240 V So, the power loss due to the resistance,
12 V × 500 lilitan / turns P = I 2R
Ns =
240 V = (2 A)2 × 8 Ω
= 25 lilitan / turns = 32 W
3 Diberi / Given: 6 (a) Hitungkan nilai arus dalam kabel, I
Vp = 240 V, Poutput = 90 W, Vs = 30 V Calculate value of current in the cable, I
(a) Poutput = Is Vs
Kuasa dihantar melalui kabel, P = VI
90 W = Is × 30 V The power transmitted by the cable, P = VI
90 W 80 × 106 W = (80 × 103 V) × I
Is =
30 V 80 × 106 W
Is = 3 A I = = 1 000 A
80 × 103 V
(b) Ip Vp = Is Vs
Oleh itu, kuasa hilang akibat rintangan,
Ip × 240 V = 3 A × 30 V So, the power loss due to the resistance
3 A × 30 V P = I 2R
Ip = = 0.375 A
240 V = (1 000 A)2 × 5 Ω
atau / or = 5 × 106 W
Kuasa input = Kuasa output / Input power = Output power (b) Peratus kuasa hilang / Percentage of power loss
Jadi, / Therefore, 5 × 106 W
Ip Vp = 90 W = × 100% = 6.25%
80 × 106 W
90 W (c) Tenaga dihantar = Kuasa dibekal – Kuasa hilang
∴ Ip =
240 V Power transmitted = Power supply – Power loss
Ip = 0.375 A = (80 × 106 W) – (5 × 106 W)
4 Diberi / Given: = 75 × 106 W
Vp = 240 V, Ns = 200 lilitan / turns, Vs = 12 V, Ip = 0.3 A Kecekapan / So, efficiency
Ns Vs 75 × 106 W
(a) = = × 100% = 93.75%
Np Vp 80 × 106 W
200 lilitan / turns 12 V (d) Pengurangan voltan / Voltage drop
=
Np
240 V = IR
240 V × 200 lilitan / turns = 1 000 A × 5 Ω
Np = = 5 000 V
12 V
Np = 4 000 lilitan / turns
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 18
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE Unit ELEKTRONIK
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
5 ELECTRONICS
1 B 2 B 3 B 4 B 5 D 6 C
7 C 8 C 9 D 10 B 11 D 5.1
Jenis Pergerakan Sinar Katod dalam Tiub Sinar Katod
Soalan Struktur / Structure Question Types of Motion of Cathode Rays in a Cathode Ray Tube
1 (a) Transformer injak turun.
Step-down transformer. Pecutan seragam / Uniform acceleration
NS VS Halaju seragam / Uniform velocity
(b) (i) =
NP VP
VS
NS = × NP
VP (a) garis lurus / straight line
12 V
= × 1 200 lilitan / turns • kesan berpendarfluor; tenaga cahaya
240 V
fluorescence; light energy
= 60 lilitan / turns
(ii) Kuasa output / Output power = 40 W medan magnet / magnetic field
∴ Kuasa input / Input power
= 40 W
(Untuk transformer unggul / For ideal transformer) (b) garis lurus / straight line
∴ PP = 40 W, VP = 240 V
negatif / negatively
PP = VP IP
PP negatif / negatively
∴ IP =
VP
40 W Ciri-ciri Sinar Katod / The Characteristic of Cathode Rays
=
240 V
= 0.1667 A
= 0.17 A
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
(c) Diod. / Diode.
2 (a) Lebih besar / Larger Lebih kecil / Smaller negatif
Negatively
Lebih kecil / Smaller Lebih besar / Larger
(148.15 A) (166.67 A)
Sama / Same Sama / Same medan elektrik; medan magnet
electric field; magnetic field
Lebih kecil / Smaller Lebih besar / Larger
(20 MW – 18 MW = 2 MW) (20 MW – 15 MW = 5 MW)
Latihan / Exercises
Lebih besar / Larger Lebih kecil / Smaller 1 pancaran termion / thermionic emission
(18 MW) (15 MW) 2 B
3 Tenaga keupayaan elektrik / Electrical potential energy
Sama / Same Sama / Same
= Tenaga kinetik / Kinetic energy
Lebih cekap Kurang cekap 1
eV = mv 2
More efficient Less efficient 2
1
1.6 × 10 C × 7 × 10 V =
–19 3
× (9 × 10 –31 kg) × v 2
(b) (i) Semakin bertambah voltan pada kabel penghantaran, 2
semakin berkurang arus dalam kabel penghantaran (1.6 × 10–19 C)× (7 × 103 V)
As the voltage on the transmission cable increases, the v 2 =
(4.5 × 10–31 kg)
current in the transmission cable decreases v = 4.99 × 107 m s–1
(ii) Semakin berkurang arus dalam kabel penghantaran, 4 Tenaga keupayaan elektrik / Electrical potential energy
semakin berkurang kehilangan kuasa semasa = Tenaga kinetik / Kinetic energy
penghantaran eV = E
As the current in the transmission cable decreases, the (1.6 × 10–19 C) × (5 × 103 V) = E
loss of power during the transmission decreases E = 8.0 × 10–16 J
(iii) Semakin berkurang arus dalam kabel penghantaran, 5 E = eV
semakin bertambah kecekapan sistem penghantaran = (1.6 × 10 –19 C) × (20 × 103 V)
As the current transmission cable decreases, the = 32 × 10 –16 J
efficiency of transmission system increases = 3.2 × 10 –15 J
(c) (i) Arus dalam kabel, I
Current in the cable, I
(ii) Kehilangan kuasa, P
Loss of power, P
(iii) Rintangan kabel, R
Resistance of cable, R
19 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
5.2 produces a large collector current flow. The transistor
is switched on and the bulb lights up.
Semikonduktor jenis-n elektron bebas VP RP
(d) =
n-type semiconductor free electrons VXZ RP + RS
2.0 V 10 kΩ
Semikonduktor jenis-p lohong; majoriti ∴ =
6.0 V 10 kΩ + RS
p-type semiconductor holes; majority
∴ 10 kΩ + RS = 30 kΩ
∴ RS = 20 kΩ
Diod Semikonduktor / Semiconductor Diode 4 (a) (i) Termistor / Thermistor
Bagaimana (ii)
• lapisan susutan
simpang p-n depletion layer
berfungsi? • voltan simpang
How the p-n junction voltage
junction works?
(b) A: Tapak / Base
B: Pengumpul / Collector
Latihan / Exercises C: Pemancar / Emitter
1 rektifier / rectifier RX 4V
(c) (i) =
2 L ⇒ R ⇒ N 5 kΩ + RX 10 V
.
. . 10RX = 20 kΩ + 4RX
.
5.3 . . 10RX – 4RX = 20 kΩ
... 6RX = 20 kΩ
Cara sambungan • Transistor • positif ... RX = 3.33 kΩ
transistor di dalam dipincang ke positive 1 kΩ
(ii) VX = × 10 V = 1.67 V
litar depan (1 + 5) kΩ
The way of connection Transistor is VX < Vminimum
of transistor in circuit forward biased Oleh itu, mentol tidak menyala.
So, the bulb does not light up.
Arus-arus yang • berkadar • (i) dihidupkan
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
terlibat dalam operasi langsung switched on
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
transistor directly
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
The currents involved proportional
in the operation of 1 C 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 C 6 C
transistor 7 C 8 A
Soalan Struktur / Structure Question
Latihan / Exercises
1 (a) Diod ialah satu alat elektrik yang membenarkan arus
VP RP mengalir dalam satu arah sahaja.
1 =
VXZ RP + RS A diode is an electric device which allows current to flow in
2V 10 kΩ one direction only.
= (b) (i) Rajah (a) – anod pada diod disambungkan ke terminal
12 V 10 kΩ + RS
positif sel kering.
10 kΩ + RS = 60 kΩ
Rajah (b) – anod pada diod disambungkan ke terminal
RS = 50 kΩ
negatif sel kering.
2 Ie = Ib + Ic
Diagram (a) – anode of the diode is connected to
= 5 mA + 120 mA
positive terminal of dry cell.
= 125 mA
Diagram (b) – anode of diode is connected to the
3 (a) (i) Perintang peka cahaya (PPC)
negative terminal of dry cell.
Light-Dependent Resistor (LDR)
(ii) Mentol dalam Rajah (a) menyala, mentol dalam
(ii) Mengawal voltan tapak secara automatik.
Rajah (b) tidak menyala.
Automatically controls the base voltage.
Bulb in Diagram (a) lights up, bulb in Diagram (b)
(b) Mengawal dan mengehadkan arus tapak supaya transistor
does not light up.
tidak rosak.
(iii) Mentol tidak menyala apabila terminal positif diod
Control and limit the base current so that the transistor is
disambung kepada terminal negatif bateri // pincang
not damaged.
songsang.
(c) (i) Beza keupayaan merentasi VP meningkat
Mentol menyala apabila terminal positif diod
Potential difference across VP increases.
disambung kepada terminal positif bateri // pincang
(ii) Pada waktu malam, PPC mempunyai rintangan yang
depan.
sangat tinggi. Beza keupayaan merentasi PPC sangat
The bulb does not light up when the positive diode is
tinggi. Maka, voltan tapak adalah tinggi. Arus tapak
connected to negative terminal of battery // reversed
mengalir dan ini menyebabkan arus pengumpul yang
biased.
tinggi mengalir. Transistor dihidupkan dan mentol
The bulb light up when the positive diode is connected
menyala.
to positive terminal of battery // forward biased.
At night, the LDR has a very high resistance. The
potential difference across LDR is very high. Hence,
the base voltage is high. The base current flows and
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 20
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
2 • Semasa bercakap melalui mikrofon, arus berubah-ubah
Contoh siri reputan radioaktif
dihasilkan
Example of radioactive decay series
When speaking through the microphone, the varying current
is produced 234
Th → 234 234
91 Pa + –1 e Pa
0
90 91
• Mikrofon: tenaga bunyi → tenaga elektrik
Microphone: sound energy → electric energy
• Arus berubah-ubah melalui kapasitor C1 dan bercampur 234
dengan IB, maka berlaku pertambahan kecil dalam IB 92 U → 230
90 Th + 2 He
4 230
90 Th
The varying current passes through the capacitor C1 and adds 230
Th → 226
Ra + 42 He 226
Ra
90 88 88
with IB, causes the small increase in IB
• Apabila IB bertambah, Ic juga bertambah 3; 2
When IB increases, Ic also increases
• Berlaku amplifikasi arus Aktiviti / Activity
Current amplification occurs
Perbincangan: / Discussion:
• Pembesar suara: tenaga elektrik → tenaga bunyi
(c) belum mereput / not disintegrated
Speaker: electric energy → sound energy
(e) menurun / decreasing
3 Waktu malam / At night:
• Rintangan PPC bertambah / The resistance of LDR increases Kesimpulan: / Conclusion:
• VBE bertambah / VBE increases menurun / decreases
• IB bertambah / IB increases
• IC bertambah / IC increases Latihan / Exercises
• Transistor dihidupkan / The transistor is switched on 2 16 jam / hours 16 jam / hours 16 jam / hours 16 jam / hours
0.64 g 0.32 g 0.16 g 0.08 g 0.04 g
Waktu siang / Daytime:
• Rintangan PPC berkurang / The resistance of LDR decreases Masa yang diambil = 16 jam × 4 = 64 jam
• VBE berkurang / VBE decreases Time taken = 16 hours × 4 = 64 hours
• IB berkurang / IB decreases 3 256 → 128 → 64 → 32
• IC berkurang / IC decreases 3T 12 = 9 jam / hours
• Transistor dimatikan / The transistor is switched off T 12 = 3 jam / hours
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
4 (a) Semakin berkurang kadar reputan radioaktif, semakin
bertambah separuh hayat ATAU sebaliknya.
As the rate of radioactive decay decreases, the half-life
increases OR vice versa.
Unit FIZIK NUKLEAR
6 NUCLEAR PHYSICS (b) Lebih kecil / Smaller Lebih besar / Larger
6.1 Lebih rendah / Lower Lebih tinggi / Higher
4 mengorbit / orbiting
Lebih besar / Larger Lebih kecil / Smaller
8 nukleon / nucleons
13 neutral / neutral
Teknik Menjawab [Format Kertas 2 : Kefahaman / Esei Pendek]
Perbandingan antara 3 jenis sinaran radioaktif Answering Technique [Paper 2 Format : Comprehension / Short
The comparison between the three types of radioactive radiations Essay]
1
Jisim / Mass Besar / Large
Beta / Beta Kuasa penembusan sederhana.
Jenis cas Negatif Penetrating power is moderate.
Type of charge Negative
Tiub GM / GM tube Dapat mengesan sinar alfa, beta
Kelajuan dan gama secara berkesan.
Kelajuan cahaya Can detect alpha, beta and
Speed Speed of light gamma rays effectively.
Kuasa pengionan Tidak terlalu panjang dan tidak Supaya tumbuhan tidak dicemari
Tinggi
Power of terlalu pendek, mencukupi dengan bahan radioaktif untuk
High
ionisation untuk pelaksanaan kerja jangka masa yang terlalu lama.
pengesanan So that the plants are not
Kuasa penembusan Not too long and not too contaminated by radioactive
Sederhana
Power of short, enough time for the material for too long period.
Moderate
penetrating implementation of detecting
Boleh diberhentikan work
kertas aluminium
oleh Sederhana / Moderate Dapat menembusi dari bahagian
paper aluminium
Can be stopped by dalam tumbuhan ke luar dengan
kadar tertentu
Can penetrate from the inside to
the outside plant at certain rate
21 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Latihan / Exercises
Cecair / Liquid Boleh campur dan larut secara
seragam di dalam cecair badan 1 Cacat jisim / Mass defect = 0.02 u
tumbuhan. E = mc2
Can be uniformly mixed and = (0.02 × 1.66 × 10–27)kg × (3 × 108 m s–1)2
dissolved in the body fluids of = 2.99 × 10–12 J
plants. 2 E = mc2
= (0.00231 u × 1.7 × 10–27)kg × (3 × 108 m s–1)2
2 = 3.53 × 10–13 J
3 Cacat jisim / Mass defect
Gama / Gamma Tenaga tinggi dan boleh = Jisim / Mass
228
Th – (Jisim / Mass
224
Ra + Jisim / Mass 2 He)
4
90 88
membunuh sel kanser
High energy and can kill the = 228.028715 u – (224.020186 u + 4.002603 u)
cancer cells = 0.005926 u
E = mc2
Disasarkan secara tepat pada Untuk membunuh sel-sel kanser = (0.005926 × 1.66 × 10–27)kg × (3 × 108 m s–1)2
tempat yang dijangkit sel kanser sahaja dan tidak membunuh = 8.85 × 10–13 J
Targeted exactly (pin point) on sel-sel lain yang sihat 4 Cacat jisim / Mass defect
the part infected by cancer cells To kill the cancer cells only and = Jisim / Mass
235
U – (Jisim / Mass
231 4
Th + Jisim / Mass 2 He)
92 90
not kill other healthy cells
= 235.0439 u – (231.0363 u + 4.0026 u)
Mengikut darjah keseriusan Mencukupi untuk membunuh = 0.005 u
jangkitan sel-sel kanser sahaja = 0.005 × 1.66 × 10–27 kg
Based on the degree of severity Enough to kill cancer cells only = 8.3 × 10–30 kg
of the infection 5 (a) Pelakuran nukleus. / Nuclear fusion.
(b) E = mc2
Pendek / Short Mengelakkan pendedahan terlalu
= (3.341 × 10–29 kg)(3 × 108 m s–1)2
lama kepada sinar radioaktif = 3.01 × 10–12 J
Avoid prolonged exposure to 6 (a) a.m.u / u.j.a
radioactive rays = (235.04392 + 1.00867)u – [140.91963 + 92.92157 +
2(1.00867)]u
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
Lebih rendah / Lower Tidak terlalu banyak
= 0.19405 u
memusnahkan tisu-tisu yang
(b) E = mc2
sihat
= (0.19405 × 1.66 × 10–27)kg × (3 × 108 m s–1)2
Not destroy too much healthy
= 2.899 × 10–11 J
tissues
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE
Pembelahan nukleus dan pelakuran nukleus (Membanding & Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions
Membezakan)
1 A 2 A 3 A 4 B 5 C 6 D
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion (Comparing & Contrasting)
7 C 8 C 9 B 10 D 11 A
Soalan Struktur / Structure Question
1 (a) Atom unsur yang mempunyai nombor proton yang sama
tetapi nombor nukleon yang berbeza.
Atoms of elements which have same proton number, but
different nucleon number.
(b) (i) Daripada graf, separuh hayat isotop = 3.5 hari.
satu
neutron
satu nukleus yang From the graph, the half-life of the isotope = 3.5 days.
lebih berat
a neutron
a heavier nucleus (ii) % aktiviti
% activity
100
75
50
Contoh / Example
E
2 Kuasa / Power, P = 25
t
mc2 Masa/hari
=
t 0
5 10 15 20
Time/days
(0.5 × 10–3)kg × (3.0 × 108 m s–1)2 (c) (i) Tiub Geiger Muller
=
(0.05 × 10–6) s Geiger Muller tube
= 9 × 1020 W (ii) Bacaan latar belakang.
Background reading.
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 22
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
(iii) 562 – 20//19//21 = 542// 543// 541 bilangan / minit. 4 Kuasa output foton yang dipancarkan
562 – 20//19//21 = 542// 543// 541 counts/min. Output power of emitted photons
(iv) 5 cm P = 60% × 80.0 W
(v) 1 Pada 5 cm, bacaan daripada pengesan meningkat = 48.0 W
dengan cepat. c
P = nhf (Perhatikan, / Note that, f = )
At 5 cm, the reading from detector increase rapidly. λ
2 Dalam skala/bilangan yang besar, ia menunjukkan nhc
kewujudan zarah α. P =
λ
In large scale/ number, it shows the existing of (1.50 × 1020 s–1) × (6.63 × 10–34 J s) × (3.0 × 108 m s–1)
α-particles. 48.0 W =
λ
2 (a) Separuh hayat ialah masa yang diambil untuk jisim/aktiviti
λ = 6.22 × 10–7 m
radioisotop menjadi separuh daripada nilai jisim/aktiviti
= 622 nm
asalnya.
Half-life is the time taken for the mass/activity of
Latihan / Exercises
radioisotope to become half of its mass/activity.
(b) Untuk menjadi lebih stabil. / To become more stable. 1 E = hf
= 6.63 × 10–34 J s × 4.5 × 1014 s–1
(c) 140 140 140
400 g 200 g 100 g 50 g = 2.98 × 10–19 J
T 12 T 12 T 12 hc
2 Emaks / max =
Selepas 420 hari, jisim Polonium-210 yang masih aktif λ2
= 50 g. 6.63 × 10–34 J s × 3.0 × 108 m s–1
=
After 420 days, the mass of Polonium-210 that is still active 4.0 × 10–7 m
= 50 g. = 4.97 × 10–19 J
3 (a) Satu proses di mana suatu nukleus berat dipecahkan kepada hc
Emin =
dua nukleus yang hampir sama jisim. λ1
A process in which a heavy nucleus is split into two nuclei 6.63 × 10–34 J s × 3.0 × 108 m s–1
of almost equal mass. =
7.0 × 10–7 m
(b) Nukleus Uranium-236 dihentam oleh satu neutron. = 2.84 × 10–19 J
The nucleus of Uranium-236 is bombarded by a neutron. c
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
(c) (i) 3 3 P = nhf (Perhatikan, / Note that, f = )
λ
(ii) m = 0.18606 u nhc
= 0.18606 × 1.66 × 10–27 kg P =
λ
E = mc2 = 0.18606 u × 1.66 × 10–27 kg × (3 × 108 m s–1)2
n(6.63 × 10–34 J s × 3.0 × 108 m s–1)
= 2.780 × 10–11 J 100 W =
(400 × 10–9 m)
n = 2.01 × 10 foton s–1 / photons s–1
20
Unit FIZIK KUANTUM
7.2
7 QUANTUM PHYSICS
Ciri-ciri Kesan Fotoelektrik
7.1 Characteristics of Photoelectric Effect
Tokoh Fizik Teori Klasik • frekuensinya / frequency
Renowned Physicists Classical Theory melebihi / exceeds
Thomas Young • dwicelah cahaya / Double-Slits
J.J. Thompson • elektron / electrons
Albert Einstein • foton / photons
7.3
Contoh / Example
Nyatakan idea yang • berkadar terus
c dicetus oleh Einstein. directly proportional
2 P = nhf (Perhatikan, / Note that, f = )
λ Nyatakan idea yang
nhc dicetus oleh Einstein.
P =
λ State the idea that
n(6.63 × 10–34 J s × 3.0 × 108 m s–1) Einstein came up with.
100 W =
(4.7 × 10–7 m)
Apakah frekuensi minimum
n = 2.36 × 1020 foton s–1 / photons s–1
ambang, fo? Minimum
c
3 P = nhf (Perhatikan, / Note that, f = ) What is threshold
λ
frequency, fo?
nhc
P =
λ Apakah itu fungsi Tenaga minimum
(4.40 × 1019 s–1) × (6.63 × 10–34 J s) × (3.0 × 108 m s–1) kerja, W? Minimum energy
P = What is work function,
5.00 × 10–7 m
= 17.50 W W?
23 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
Latihan / Exercises (b) Pancaran fotoelektrik ialah pancaran fotoelektron dari
permukaan logam apabila cahaya dengan frekuensi yang
1 6.96 ×10–20 cukup tinggi meneranginya.
Photoelectric emission is the emission of photoelectrons
8.15 ×10–20 from a metal surface when light of sufficiently high
frequency illuminates it.
8.42 × 10–20
hc
(c) E =
9.01 × 10–20 λ
6.63 × 10–34 J s × 3.0 × 108 m s–1
=
2 W = hfo 3.65 × 10–7 m
= 6.63 × 10–34 J s × 1.23 × 1014 Hz = 5.45 × 10 J –19
= 8.15 × 10–20 J nhc
4 P =
3 hf = W + Kmaks / max λ
(6.63 × 10–34 J s)(7.41 × 1014 Hz) = (7.36 × 10–20 J) + Kmaks / max n(6.63 × 10–34 J s × 3.0 × 108 m s–1)
90 W =
Kmaks / max = 4.18 × 10–19 J 250 × 10–9 m
hc n = 1.13 × 1020 foton per saat / photons per second
4 E =
λ 5 (a) Frekuensi ambang ialah frekuensi minimum sinaran
1.243 × 103 eV nm elektromagnet tuju yang boleh mengeluarkan satu
E = = 2.07 eV fotoelektron daripada permukaan logam.
600 nm
1 Threshold frequency is the minimum frequency of the
mev2maks / max = 2.07 eV – 1.90 eV incident electromagnetic radiation that can emit a
2
= 0.17 eV photoelectron from a metal surface.
1 (b) (i) Fungsi kerja / Work function,
mev2maks / max = 0.17 eV × 1.60 × 10–19 J W = 2.0 × eV
2
= 2.0 × 1.60 × 10–19 J
1
mev2maks / max = 2.72 × 10–20 J = 3.2 × 10–19 J
2
(ii) W = hfo
2 × 2.72 × 10–20 J 3.2 × 10–19 J = (6.63 × 10–34 J s)fo
vmaks / max =
9.11 × 10–31 kg ∴ fo = 4.83 × 1014 Hz
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
= 2.44 × 105 m s–1 (iii) Dari / From c = f λ
c
Maka / Thus λmaks / max =
LATIHAN PENGUKUHAN / ENRICHMENT EXERCISE fo
Soalan Objektif / Objective Questions 3.0 × 108 m s1
=
4.83 × 1014 Hz
1 D 2 D 3 C 4 C 5 D 6 C
7 B = 6.21 × 10–7 m
6 (a) (i) Tenaga kinetik maksimum dari fotoelektron yang
Soalan Struktur / Structure Question dipancarkan tidak bergantung pada intensiti cahaya
tuju.
1 (a) frekuensi / frequency The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons
(b) berkuanta / quantised emitted does not depend on the intensity of the
(c) berkadar terus / directly proportional incident light.
(d) cahaya / light (ii) Fotoelektron hanya dapat dipancarkan jika frekuensi
(e) frekuensi / frequency cahaya tuju melebihi frekuensi ambang.
(f) fungsi kerja / work function Photoelectrons can only be emitted if the frequency of
(g) foton / photons the incident light exceeds the threshold frequency.
(h) foton / photon (b) Dari persamaan fotoelektrik Einstein
(i) momentum / momentum From Einstein’s photoelectric equation,
(j) bertambah / increases hf = W + Kmaks / max
2 (a) Tenaga satu foton, / Energy of a photon, Susun semula / Rearrange,
E = hf Kmaks / max = hf – W
hc hc
= = –W
λ λ
6.63 × 10–34 J s × 3.0 × 108 m s–1
=
7.0 × 10–7 m [
=
3.50 × 10–7 m ]
(6.63 × 10–34 J s)(3.0 × 108 m s–1)
–
= 2.84 × 10–19 J (2.30 × 1.60 × 10 J)
–19
h
(b) Momentum, p =
λ = 2.00 × 10–19 J
6.63 × 10–34 J s 1
= Kmaks / max = m v2
2 e maks / max
7.0 × 10–7 m
= 9.47 × 10–28 kg m s–1 1
mev2maks / max = 2.00 × 10–19 J
3 (a) Foton adalah satu paket tenaga elektromagnet yang 2
bergerak dengan halaju cahaya. 2 × (2.00 × 10–19 J)
v2maks / max =
A photon is a packet of electromagnetic energy which 9.11 × 10–31 kg
travels with the velocity of light. vmaks / max = 6.63 × 105 m s–1
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 24
MODUL • Fizik TINGKATAN 5
7 (a) Tenaga foton, / Photon energy,
E = hf
hc
=
λ
(6.63 × 10–34 J s)(3.0 × 108 m s–1)
=
4.30 × 10–7 m
= 4.62 × 10 J ........................................ (i)
–19
(b) Diberi / Given, λmaks / max = 650 nm
Ini bererti frekuensi adalah minimum, iaitu, frekuensi
ambang, fo.
This means that the frequency is minimum, that is threshold
frequency, fo.
Maka / Therefore, λmaks / max = λo
Fungsi kerja / Work function,
W = hfo
hc
=
λ
(6.63 × 10–34 J s)(3.0 × 108 m s–1)
=
6.50 × 10–7 m
= 3.06 × 10–19 J ........................................ (ii)
Maka dengan menggunakan persamaan (i) – persamaan (ii),
didapati
Therefore, by using equation (i) – equation (ii), we get
Tenaga maksimum fotoelektron
Maximum energy of photoelectrons,
Kmaks / max = hf – W
= (4.62 × 10–19 J) – (3.06 × 10–19 J)
= 1.56 × 10–19 J
JAWAPAN / ANSWER
25 © Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
You might also like
- ROGER J. OSBORNE and MARK M. COSGROVE PDFDocument14 pagesROGER J. OSBORNE and MARK M. COSGROVE PDFtatik prasetyoNo ratings yet
- Answer Modul Fizik T5 (Unit 1-3)Document14 pagesAnswer Modul Fizik T5 (Unit 1-3)Chong Wai Leong100% (1)
- Contoh Soalan Kimia Cikgu FanaDocument68 pagesContoh Soalan Kimia Cikgu FanaAimi Afrina08No ratings yet
- Latihan Bab 9 Biologi Tingkatan 4 KSSMDocument3 pagesLatihan Bab 9 Biologi Tingkatan 4 KSSMrouqi100% (1)
- BAB 13 Termokimia: ThermochemistryDocument43 pagesBAB 13 Termokimia: ThermochemistryJacqueline WongNo ratings yet
- Skema Halus Persamaan Kimia - PDFDocument9 pagesSkema Halus Persamaan Kimia - PDFIza MohdSabri50% (4)
- Chemquest 2018 c03 2018 p1 Jawapan PDFDocument2 pagesChemquest 2018 c03 2018 p1 Jawapan PDFNoorleha Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik F5 2023 (Answers)Document25 pagesModul Fizik F5 2023 (Answers)nyshahidaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Struktur Dan EseiDocument31 pagesSoalan Struktur Dan EseiShukor Sudin100% (1)
- 2022 Pahang - MPSM Chemistry K1 - K2 JawapanDocument14 pages2022 Pahang - MPSM Chemistry K1 - K2 JawapanCrystal GohNo ratings yet
- Selangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)Document17 pagesSelangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)SITI RAIHANI BINTI KAMSO MoeNo ratings yet
- Dn. BHD .: Konsep Mol, Formula Dan Persamaan KimiaDocument28 pagesDn. BHD .: Konsep Mol, Formula Dan Persamaan Kimialhmoo100% (1)
- Modul A - Fizik Tg4 - Jawapan LengkapDocument37 pagesModul A - Fizik Tg4 - Jawapan LengkapNUR MUHAMMAD FARIS BIN YUSAINI MoeNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Skema Bab 4 Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument30 pages2021 - Skema Bab 4 Jadual Berkala UnsurKishan Kumar100% (1)
- Jawapan Latihan Fizik T4 2021Document34 pagesJawapan Latihan Fizik T4 2021KHAIRINA NAZIHAH BINTI KAMARUL RIZAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Module Physics KSSM: JPN Melaka Modul Fizik KSSMDocument14 pagesModule Physics KSSM: JPN Melaka Modul Fizik KSSMMuhammad Qawiem100% (1)
- Mip 2023 Fizik - SkemaDocument27 pagesMip 2023 Fizik - SkemaIffah Nor SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Modul Bio Smart A+ K2 SPM 2023 - ExcellentDocument66 pagesModul Bio Smart A+ K2 SPM 2023 - Excellentdeannabatrisyia2405No ratings yet
- Soalan - Bab 5 Ting. 4Document29 pagesSoalan - Bab 5 Ting. 4mastor1969No ratings yet
- Jawapan Physics Pelangi Form 4Document63 pagesJawapan Physics Pelangi Form 4Cally ChewNo ratings yet
- Modul Biologi F4 (Answers) #Document33 pagesModul Biologi F4 (Answers) #irdina qistina100% (1)
- 02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4Document20 pages02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4ONG TEIK MING -100% (1)
- Kertas 2 Kimia Tingkatan 4 DwibahasaDocument17 pagesKertas 2 Kimia Tingkatan 4 DwibahasaIntan Nor Adila Mohammad100% (3)
- Paper 2 Form 4 2020Document28 pagesPaper 2 Form 4 2020Yusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- 2022 Selangor Chemistry K2 Set - 2 JawapanDocument14 pages2022 Selangor Chemistry K2 Set - 2 JawapanNuan Ting NgNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tambahan: JawapanDocument44 pagesMatematik Tambahan: JawapanNivehthaa Visvam100% (1)
- Jawapan Modul 21Document11 pagesJawapan Modul 21mdmema100% (2)
- Soalan KbatDocument3 pagesSoalan KbatnurulabrorNo ratings yet
- Skema Trial English Smka & Sabk K1 Set 2Document6 pagesSkema Trial English Smka & Sabk K1 Set 2Genius UnikNo ratings yet
- InersiaDocument3 pagesInersiaChel SonNo ratings yet
- ITEM BERFOKUS Fizik SPM 2022 JawapanDocument7 pagesITEM BERFOKUS Fizik SPM 2022 JawapanNur Ain Fitriah Mohamad KholibNo ratings yet
- Kimia JWP Bab 2Document25 pagesKimia JWP Bab 2CHA ZI YU MoeNo ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2Document22 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2PK ChunNo ratings yet
- Rajah 2.1 Menunjukkan Dua Tong Gas Yang Mengandungi Dua Jenis Hidrokarbon Yang Mempunyai Tiga Atom Karbon Per MolekulDocument6 pagesRajah 2.1 Menunjukkan Dua Tong Gas Yang Mengandungi Dua Jenis Hidrokarbon Yang Mempunyai Tiga Atom Karbon Per MolekulTai ZikingNo ratings yet
- Skema Kertas 2 KimiaDocument9 pagesSkema Kertas 2 KimiaariesNo ratings yet
- Dn. BHD .: Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument30 pagesDn. BHD .: Jadual Berkala UnsurlhmooNo ratings yet
- Set 1-Paper 2 (Soalan)Document20 pagesSet 1-Paper 2 (Soalan)NajwaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- JawapanBab3 PDFDocument32 pagesJawapanBab3 PDFMashithoh RosliNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Lembaran PBD: Bab 1: UbahanDocument13 pagesJawapan Lembaran PBD: Bab 1: UbahanLOVENNATH A/L RAVI MoeNo ratings yet
- Whole Book Answers-ChemistryDocument216 pagesWhole Book Answers-ChemistryZoe Siew100% (1)
- SKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewDocument8 pagesSKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewZulkefliNo ratings yet
- Kimia JWP Bab 3Document23 pagesKimia JWP Bab 3CHA ZI YU MoeNo ratings yet
- Seminar Skor A+ Chemistry SPM 2021 Chapter 1: Redox EquilibriumDocument23 pagesSeminar Skor A+ Chemistry SPM 2021 Chapter 1: Redox EquilibriumAtheerah ZaralynNo ratings yet
- Matematik K2 Ud3 2023Document33 pagesMatematik K2 Ud3 2023WONGYIMINGNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Modul SPM Excellent Selangor Matematik - 230617 - 174732Document44 pagesJawapan Modul SPM Excellent Selangor Matematik - 230617 - 174732ijanNo ratings yet
- Trial p2 Section C No-11Document4 pagesTrial p2 Section C No-11malaomar0% (1)
- 02-Physic F5 2018-WavesDocument44 pages02-Physic F5 2018-WavesSreedrann100% (4)
- Quadratic Function and EquationDocument16 pagesQuadratic Function and EquationAlia AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Soalan - Bab 7 Ting. 4Document11 pagesSoalan - Bab 7 Ting. 4kiaora4711No ratings yet
- Matematik Kertas 2 With Answer SchemeDocument48 pagesMatematik Kertas 2 With Answer SchemeelvivNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Topikal Kertas 1 Tingkatan 4Document16 pagesJawapan Topikal Kertas 1 Tingkatan 4qistinaunie07No ratings yet
- SPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 BerjawapanDocument18 pagesSPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar71% (7)
- SPM 4531 2007 Physics p2 BerjawapanDocument26 pagesSPM 4531 2007 Physics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar75% (4)
- Kertas Trial Matematik Perak K1&2 Set 2 + SkemaDocument54 pagesKertas Trial Matematik Perak K1&2 Set 2 + SkemaNUR BALQIS BINTI JAFAR MoeNo ratings yet
- 05 Jaw Lengkap GALUS MT Ting 5 Bab 5Document9 pages05 Jaw Lengkap GALUS MT Ting 5 Bab 5gunturean100% (1)
- Nilam Module F5 Biology AnswersDocument34 pagesNilam Module F5 Biology Answerskazin yuen kah zingNo ratings yet
- Physics TestDocument7 pagesPhysics TestManojNo ratings yet
- TorsiDocument14 pagesTorsiAndy SantosoNo ratings yet
- Data Hasil Praktikum Luas MomenDocument9 pagesData Hasil Praktikum Luas MomenRafif Aziz NurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Answer Tutorial 4Document3 pagesAnswer Tutorial 4Anas KamalNo ratings yet
- MC Web Mech2 9 2009 PDFDocument2 pagesMC Web Mech2 9 2009 PDFAshleyJaneFuentesNo ratings yet
- 6 SPM T4 CahayaDocument119 pages6 SPM T4 CahayaNureen ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- 1 SPM T5 Daya Dan Gerakan IiDocument64 pages1 SPM T5 Daya Dan Gerakan IiNureen ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- Poster BIODocument4 pagesPoster BIONureen ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseasesDocument2 pagesParkinson's DiseasesNureen ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- Earth and Space ExplorationDocument12 pagesEarth and Space ExplorationNureen ZuhairahNo ratings yet
- Tugas TermodinamikaDocument2 pagesTugas TermodinamikaJersey BengkuluNo ratings yet
- Absolute PressureDocument2 pagesAbsolute PressureAnonymous AyDvqgNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study On Steam Distillation and Hydro-Distillation Methods For Agarwood Oil ExtractionDocument4 pagesComparative Study On Steam Distillation and Hydro-Distillation Methods For Agarwood Oil ExtractionTrisna Bagus FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- SPE 18215 Flow Regimes in Vertical and Inclined Oil/Water Flow in PipesDocument8 pagesSPE 18215 Flow Regimes in Vertical and Inclined Oil/Water Flow in PipesPaola GamiñoNo ratings yet
- 2 - EPE Course Presentation v.0.0Document47 pages2 - EPE Course Presentation v.0.0Karim GaberNo ratings yet
- NG ProcessDocument5 pagesNG ProcesspanthaloorNo ratings yet
- Reservoir EngineeringDocument147 pagesReservoir Engineeringjohn ngandouNo ratings yet
- Triple Point Plot: Melting FreezingDocument16 pagesTriple Point Plot: Melting FreezingJorgeNo ratings yet
- 3 This Question Is About Pressure in A LiquidDocument1 page3 This Question Is About Pressure in A LiquidSalmuel SmithNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Set 5Document7 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Set 5MUSKAN PRNNo ratings yet
- Blackmer Autogas HandbookDocument32 pagesBlackmer Autogas HandbookMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- 2013 List of China's CBM Fields and CBM Bearing StructuresDocument2 pages2013 List of China's CBM Fields and CBM Bearing StructuresarapublicationNo ratings yet
- Psych RometryDocument6 pagesPsych Rometrypammy313No ratings yet
- Samsung R600a New Devl MarketingDocument18 pagesSamsung R600a New Devl MarketingAleksei EvchuNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument60 pagesIdeal Gas68zrvtr9bfNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.4 HeatDocument18 pagesLesson 4.4 HeatRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangesStates of Matter Answer KeyDocument1 pagePhase ChangesStates of Matter Answer KeyKristyne OliciaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Dry Gas Seal - SIEMENSDocument107 pagesDry Gas Seal - SIEMENSreguii100% (4)
- 1970 - Electrical and Optical Properties of Transition-Metal OxidesDocument10 pages1970 - Electrical and Optical Properties of Transition-Metal OxidesMohamed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Methods of MeasurementDocument6 pagesMethods of MeasurementShaho Abdulqader MohamedaliNo ratings yet
- Compro XL-S C F: Ompressor LuidDocument4 pagesCompro XL-S C F: Ompressor LuidJeremias UtreraNo ratings yet
- Diagrama GasesDocument7 pagesDiagrama GasesdelfingeliNo ratings yet
- Falling Film Evaporators WorkDocument9 pagesFalling Film Evaporators WorkWaiz Khan Waiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Practice QsMOD - Heating and Cooling Curve.1570522128Document8 pagesPractice QsMOD - Heating and Cooling Curve.1570522128Bryan DongNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My ExamsDocument1 page2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My Examsyichenlin111No ratings yet
- Classification of Polymer Based OnDocument4 pagesClassification of Polymer Based OnRobotrixNo ratings yet
- Mass Action Law:: in N-Type SemiconductorDocument10 pagesMass Action Law:: in N-Type Semiconductordheeraj rajNo ratings yet
- Dot and Cross PracticeDocument4 pagesDot and Cross PracticeDeez NutsNo ratings yet