Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Notes
Bio Notes
Uploaded by
Ishita KamraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Notes
Bio Notes
Uploaded by
Ishita KamraCopyright:
Available Formats
Osmosis:- The net diffusion of free water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a
region with a low solute concentration to a region with high solute concentration
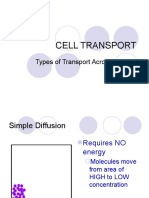
Simple Diffusion:- The passive net movement of a substance from a region with high concentration
to a region with low concentration
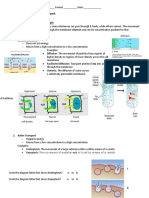
Facilitated Diffusion:- The passive movement of molecules across a membrane down a concentration
gradient via a specific channel or carrier protein. Does not require energy. Carrier Protein – change
shape to help a molecule through a membrane
Transmembrane proteins – channel proteins and carrier proteins
Active Transport – The movement of materials across a membrane against their concentration
gradient, via a specific carrier protein. Requires the cell to spend ATP energy
Bulk transport:- involves the movement of materials, too large to pass through a carrier or channel
protein, in membrane-bound vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane. Two kinds of bulk transport,
endocytosis(molecules enter the cell) – the cell furrows, or “invaginates” to surround a particle and
engulf it within a vacuole and exocytosis(molecules exit the cell) – process by which large molecules
or particles are exported by a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the cell membrane.
Phagocytosis – solid is engulfed (‘cell eating’)
Pinocytosis – fluid is engulfed (‘cell drinking’)
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpDocument67 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpSilver CypressNo ratings yet
- CMBCH 8Document2 pagesCMBCH 8Kyle PeñarroyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Cell Transport ReviewerDocument9 pagesCell Transport ReviewerNa LuNo ratings yet
- Facilitated Diffusion: + + 2+ - 3 SmallDocument2 pagesFacilitated Diffusion: + + 2+ - 3 SmallKyle PeñarroyoNo ratings yet
- Cell ExchangesDocument28 pagesCell ExchangesBenzerari ManaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportshammmssNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell TransportationDocument3 pages2 Cell TransportationxNo ratings yet
- Passiv TransportDocument12 pagesPassiv TransportsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument6 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membraneshekinah656No ratings yet
- Transport Across Membranes FinalDocument77 pagesTransport Across Membranes FinalLorraine Eve Abila100% (1)
- Transport MechanismDocument28 pagesTransport MechanismRenz Marian LazanasNo ratings yet
- San Pedro College: Senior High School DepartmentDocument54 pagesSan Pedro College: Senior High School DepartmentKrisha Diane FunaNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument18 pagesCell TransportCallista FeliciaNo ratings yet
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- L9 Cellular TransportDocument2 pagesL9 Cellular TransportStephanie SyNo ratings yet
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDocument15 pagesCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Document 8Document8 pagesDocument 8Tiana PolackNo ratings yet
- Transport Mecha Wps OfficeDocument9 pagesTransport Mecha Wps Officeailynancheta90No ratings yet
- Types of Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument26 pagesTypes of Transport Across The Cell MembraneAsad ShalmaniNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument4 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellshillskimberly24No ratings yet
- Movements Across Cell MembraneDocument30 pagesMovements Across Cell Membraneعلیزہ نعیمNo ratings yet
- 2 5 Transport MechanismDocument25 pages2 5 Transport Mechanismıamnıkolaı 4100% (1)
- TransportDocument65 pagesTransportsiddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture: Diffusion: Movement of Particles From A Region of Higher Concentration To A Region of LowDocument5 pagesThe Big Picture: Diffusion: Movement of Particles From A Region of Higher Concentration To A Region of LowNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport.Document2 pagesMembrane Transport.Adeaga ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive TransportDocument23 pagesActive and Passive TransportSai SridharNo ratings yet
- ACTIVE TRANSPORT Vs PASSIVE TRANSPORTDocument6 pagesACTIVE TRANSPORT Vs PASSIVE TRANSPORTfelixnellyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Membrane TransportDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Membrane Transportapi-302118206No ratings yet
- Cell Maintain A BalanceDocument26 pagesCell Maintain A BalanceAchRudiNNo ratings yet
- Membrane - FunctionDocument4 pagesMembrane - Functionphuong anhNo ratings yet
- Membrane - FunctionDocument4 pagesMembrane - Functionphuong anhNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport and HomeostasisDocument2 pagesCell Transport and Homeostasishomamunfat100% (1)
- Active TransportDocument11 pagesActive TransportDARLENE JANE MAYNESNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Transport of SubstancesDocument25 pages1.1 Transport of SubstancesRayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Bio QuizDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Bio QuizMafalda SeabraNo ratings yet
- Membrane TransportDocument4 pagesMembrane TransportNiharika GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocument24 pagesCell Membrane Transport NotesJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- CH5 Membrane TraffickingDocument48 pagesCH5 Membrane TraffickingAhmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its FunctionDocument26 pagesCell and Its FunctionMarielle MatunogNo ratings yet
- The Permeability of The Plasma MembraneDocument32 pagesThe Permeability of The Plasma Membranenozel77No ratings yet
- L-3 Cell Mech. of Transport PDFDocument33 pagesL-3 Cell Mech. of Transport PDFdemaNo ratings yet
- Membran: Kusumo Hariyadi Blok 3Document10 pagesMembran: Kusumo Hariyadi Blok 3YUFFANo ratings yet
- MF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2Document33 pagesMF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Assignment-2Document14 pagesIntegrated Science Assignment-2giganiga3132No ratings yet
- Transport MembraneDocument2 pagesTransport Membranesna240839No ratings yet
- CellularTransport MATSAPUMEDocument37 pagesCellularTransport MATSAPUMEPanyapat SrisawatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesLesson 1 (Reviewer)Faith Angela VillasfirNo ratings yet
- 1 4Document10 pages1 4nevio.wirtgenNo ratings yet
- Cellular Processes FoldableDocument1 pageCellular Processes FoldableCameo SlaybaughNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANDocument15 pagesCell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANchfalgueraNo ratings yet
- Active Transport: Zed Malenab Kurt Sebastian MagbooDocument16 pagesActive Transport: Zed Malenab Kurt Sebastian MagbooZed MalenabNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument20 pagesTransport Across Cell Membrane安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Cueva-Cell TransportDocument15 pagesCueva-Cell TransportCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- Transport Membrane (Lengkap)Document53 pagesTransport Membrane (Lengkap)Isma Suss LolaloadingNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument2 pagesDiffusionfillymassangaNo ratings yet
- Saul of TarsusDocument3 pagesSaul of TarsusIshita KamraNo ratings yet
- Notes On PaulDocument1 pageNotes On PaulIshita KamraNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument7 pagesBio NotesIshita KamraNo ratings yet
- Related Text FireDocument5 pagesRelated Text FireIshita KamraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIshita KamraNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument3 pagesChem NotesIshita KamraNo ratings yet