Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsRespi Chest Drainage
Respi Chest Drainage
Uploaded by
JAN FEDERICK BANTAYChest drainage systems are used to drain air or fluid from the pleural cavity through strategically positioned chest tubes. Chest tubes are connected to drainage systems to continuously drain fluid, blood, or air from the pleural cavity or to allow medication instillation. This restores normal intrapleural pressure and facilitates lung expansion. Proper maintenance of the closed drainage system and chest tube is important to prevent infection and maintain appropriate drainage and pressure in the pleural cavity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- DR Lal Path LabDocument2 pagesDR Lal Path LabRockey Singh0% (1)
- Lesson Plan On - Essential-NewbornDocument22 pagesLesson Plan On - Essential-NewbornSwati Sharma100% (2)
- Intercostal DrainDocument44 pagesIntercostal Drainvamshidh100% (1)
- Water Seal DrainageDocument6 pagesWater Seal DrainageAmit MartinNo ratings yet
- Advice Sheet A12 - Infection Control in Dentistry - Identist - 2 PDFDocument31 pagesAdvice Sheet A12 - Infection Control in Dentistry - Identist - 2 PDFizeldien5870No ratings yet
- Management of LBW BabiesDocument67 pagesManagement of LBW BabiesEllen Angel100% (4)
- V V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageDocument1 pageV V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageCyndiNo ratings yet
- Chest TubeDocument21 pagesChest TubeClaudio Nicolas Retamal YevenesNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Rose & Sadava - Chest Tube InsertionDocument19 pagesGroup 2 - Rose & Sadava - Chest Tube InsertionRay Anthony RoseNo ratings yet
- Care of Chest Tube Drainage & Nursing Manangement SHDocument82 pagesCare of Chest Tube Drainage & Nursing Manangement SHJoanna RemollinoNo ratings yet
- CSL Lumbar Puncture, Central line & Chest tube insertionDocument38 pagesCSL Lumbar Puncture, Central line & Chest tube insertionbm19110053No ratings yet
- SPH CT ProtocolDocument13 pagesSPH CT ProtocolRahel GrunderNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy SsDocument56 pagesIV Therapy Sssaeed_chohan100% (8)
- Advance Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Document47 pagesAdvance Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Ben Man Jun100% (2)
- Care of Clients With Chest TubeDocument55 pagesCare of Clients With Chest TubeMarc Andreo MalalaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Placement (Adult)Document8 pagesChest Tube Placement (Adult)Ariane Joyce SalibioNo ratings yet
- CVPDocument23 pagesCVPShalini KaluraNo ratings yet
- Vats and Post Op CareDocument18 pagesVats and Post Op CareVenz100% (1)
- Physiological Adaptation Handout6132024Document27 pagesPhysiological Adaptation Handout6132024harinder singhNo ratings yet
- Respi Modalities 2Document6 pagesRespi Modalities 2Karlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Intro To Specialized Nursing ProceduresDocument156 pagesIntro To Specialized Nursing ProceduresJimmy MainaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Procedures: - Defibrillation in CPRDocument20 pagesEmergency Procedures: - Defibrillation in CPRDuy Phương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument39 pagesIV TherapyChannelGNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument15 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringvineeta.ashoknagarNo ratings yet
- Procedures ThoracentesisDocument4 pagesProcedures ThoracentesisPatty MArivel ReinosoNo ratings yet
- Water Sael DrainageDocument36 pagesWater Sael DrainageerlinaNo ratings yet
- Invasive Blood Pressure Monitoring: Group MembersDocument88 pagesInvasive Blood Pressure Monitoring: Group Membersallenshanique1999No ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument4 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringgurneet kourNo ratings yet
- Go With The Flow of Chest Tube Therapy: by Arlene M. Coughlin, RN, MSN, and Carolyn Parchinsky, RN, MADocument14 pagesGo With The Flow of Chest Tube Therapy: by Arlene M. Coughlin, RN, MSN, and Carolyn Parchinsky, RN, MAhady920100% (1)
- Checklists MergedDocument10 pagesChecklists MergedEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Laparoscopic SurgeriesDocument40 pagesComplications of Laparoscopic Surgeriesrajan kumar100% (10)
- Tracheostomy SlidesDocument24 pagesTracheostomy SlidesMohammed AdamNo ratings yet
- Safe SuctioningDocument31 pagesSafe SuctioningKatrina Ponce100% (2)
- Nursing Care of ThoracentesisDocument15 pagesNursing Care of ThoracentesisNora AlnaimNo ratings yet
- NasopharyngealairwayDocument16 pagesNasopharyngealairwayChyndi dami 1216No ratings yet
- Assisting in Patients Undergoing A ThoracentesisDocument7 pagesAssisting in Patients Undergoing A Thoracentesiscoosa liquors0% (1)
- CH 2 SuctioningDocument90 pagesCH 2 SuctioningMaherNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument11 pagesLumbar PunctureBavi ThraNo ratings yet
- CVP Final 2021Document11 pagesCVP Final 2021Ahmed AshrafNo ratings yet
- IR Lctr 10 part 2Document33 pagesIR Lctr 10 part 2seemabfarwauaeNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)Document12 pagesComputed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)jgcriste100% (9)
- Tracheostomy: ENT Department DMC & Hospital Ludhiana PunjabDocument46 pagesTracheostomy: ENT Department DMC & Hospital Ludhiana PunjabVikrant MittalNo ratings yet
- Dvanced Nursing ProceduresDocument125 pagesDvanced Nursing Procedurestum chrisNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Thoracostomy Tube InsertionDocument54 pagesAssisting in Thoracostomy Tube Insertioncoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Central Venous CathetersDocument12 pagesCentral Venous CathetersarisastraNo ratings yet
- Thoracentesis PPT - ExpoDocument22 pagesThoracentesis PPT - ExpoScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Atls 1Document44 pagesAtls 1zekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Chest Drain ManagementDocument7 pagesChest Drain ManagementanuzNo ratings yet
- Suctioning Trache Care NebuDocument11 pagesSuctioning Trache Care NebuROLAND LAURENCE BARGO JARDIOLINNo ratings yet
- Airway Management: by Paul Edmer CorcueraDocument40 pagesAirway Management: by Paul Edmer CorcueraJeco ValdezNo ratings yet
- Emergency Durante ChatgptDocument55 pagesEmergency Durante Chatgptshayansehat8No ratings yet
- Thoracocentasis: INTRODUCTION:-Thoracentasis Also Known As The Thoracocentasis or Plural Tap Is AnDocument7 pagesThoracocentasis: INTRODUCTION:-Thoracentasis Also Known As The Thoracocentasis or Plural Tap Is AnaparnaNo ratings yet
- CTT SpiroDocument10 pagesCTT SpiroKryzl Anne LigsayNo ratings yet
- Care of The Clients With Respiratory DisordersDocument10 pagesCare of The Clients With Respiratory Disordersdexter100% (3)
- Management For CTD - MsDocument63 pagesManagement For CTD - MsNarz CupahanNo ratings yet
- ATLS TemplateDocument6 pagesATLS Templatesyasya100% (1)
- Critical Care SuctioningDocument5 pagesCritical Care SuctioningChinta Nabila 조롱 수없는No ratings yet
- 3730 Monitoring Hemodinamik-2019Document52 pages3730 Monitoring Hemodinamik-2019ojika olandaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube DrainageDocument7 pagesChest Tube Drainagekim reyes100% (1)
- IV Therapy IV Incorporation NEWDocument74 pagesIV Therapy IV Incorporation NEWSteffi AubreyNo ratings yet
- Oncology - Presentation EditedDocument71 pagesOncology - Presentation EditedSarah Racheal AkelloNo ratings yet
- Nusing Skills Output (Nso)Document3 pagesNusing Skills Output (Nso)leroux2890No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- SubluxationDocument5 pagesSubluxationJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- TriageDocument1 pageTriageJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument1 pageCopdJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- BANTAY - Meniere's DiseaseDocument4 pagesBANTAY - Meniere's DiseaseJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- OPD Topics CAP UTI and DewormingDocument24 pagesOPD Topics CAP UTI and DewormingJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Copd 7Document1 pageCopd 7JAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Asthma 1Document9 pagesAsthma 1JAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan Fromat 1Document14 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Fromat 1JAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocument4 pagesQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Multivitamins + B ComplexDocument12 pagesMultivitamins + B ComplexJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Report Dust Mite212Document5 pagesReport Dust Mite212Rowell MarianoNo ratings yet
- Heartbeat HomeostasisDocument1 pageHeartbeat Homeostasisapi-296692561No ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Novel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudyDocument9 pagesNovel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudymarcelodentNo ratings yet
- Maternity Benefits Requirements DocsDocument2 pagesMaternity Benefits Requirements DocsGladys April CatarojaNo ratings yet
- OCA Circular No. 51-2021Document2 pagesOCA Circular No. 51-2021MaricrisNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Guide - Emergency General Surgery Acute Abdominal PainDocument32 pagesCommissioning Guide - Emergency General Surgery Acute Abdominal PainAnisNabillahMohdAzliNo ratings yet
- WHO Mediterranean Zoonosis Control Centre - Information Circular - No. 51 February 2001 - ISSN 1020-1378Document16 pagesWHO Mediterranean Zoonosis Control Centre - Information Circular - No. 51 February 2001 - ISSN 1020-1378christiankoederNo ratings yet
- Survival Guide 2014 2015Document107 pagesSurvival Guide 2014 2015Manpreet BajwaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and RX of CovidDocument11 pagesPathogenesis and RX of CovidYawer Yousuf100% (4)
- Ophthalmic PDFDocument48 pagesOphthalmic PDFMichael Andre CorosNo ratings yet
- 2023 EDITED EP-Lian-C3-Socio-Part-3Document35 pages2023 EDITED EP-Lian-C3-Socio-Part-3Mark Andrei GubacNo ratings yet
- Netherlands Vitamin B12 Deficiency and The Lack of Its Consequences in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Using MetforminDocument5 pagesNetherlands Vitamin B12 Deficiency and The Lack of Its Consequences in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Using Metforminmachoka.peninaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal KebidananDocument12 pagesJurnal KebidananhanaNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 5003 Assessment 1 Identifying Community Health NeedsDocument5 pagesNURS FPX 5003 Assessment 1 Identifying Community Health Needsfarwaamjad771No ratings yet
- OIA Milky Fish Appendix 1Document3 pagesOIA Milky Fish Appendix 1NewshubNo ratings yet
- Case 3 Embryology and Microanatomy of The Kidneys (Lecture Slides)Document45 pagesCase 3 Embryology and Microanatomy of The Kidneys (Lecture Slides)pqp7mpk7v6No ratings yet
- Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument7 pagesChlamydia TrachomatisDewi SetiawatiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Deficits in Long Covid-19Document3 pagesCognitive Deficits in Long Covid-19Nazly ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Spelling Mistakes Corrections of Jahangir's Pool of FCPS Part 1 DentistryDocument16 pagesSpelling Mistakes Corrections of Jahangir's Pool of FCPS Part 1 DentistryAisha BanoNo ratings yet
- Vapcotrim: Injectable SolutionDocument1 pageVapcotrim: Injectable Solutionandi AlyaNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLE Is The First of A New Class of Drugs That Inhibit Gastric Secretion by Altering The Activity of HDocument39 pagesOMEPRAZOLE Is The First of A New Class of Drugs That Inhibit Gastric Secretion by Altering The Activity of HRinNo ratings yet
- Language of Teeth DCDocument6 pagesLanguage of Teeth DCapi-273181309No ratings yet
- Brolucizumab in Neovascular Age Related Macular Degeneration and Diabetic Macular EdemaDocument17 pagesBrolucizumab in Neovascular Age Related Macular Degeneration and Diabetic Macular EdemaKang LimbaNo ratings yet
- Beauty HolidaysDocument3 pagesBeauty HolidaysKristen Anne Camotes SolonNo ratings yet
Respi Chest Drainage
Respi Chest Drainage
Uploaded by
JAN FEDERICK BANTAY0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views15 pagesChest drainage systems are used to drain air or fluid from the pleural cavity through strategically positioned chest tubes. Chest tubes are connected to drainage systems to continuously drain fluid, blood, or air from the pleural cavity or to allow medication instillation. This restores normal intrapleural pressure and facilitates lung expansion. Proper maintenance of the closed drainage system and chest tube is important to prevent infection and maintain appropriate drainage and pressure in the pleural cavity.
Original Description:
Original Title
RESPI-CHEST-DRAINAGE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChest drainage systems are used to drain air or fluid from the pleural cavity through strategically positioned chest tubes. Chest tubes are connected to drainage systems to continuously drain fluid, blood, or air from the pleural cavity or to allow medication instillation. This restores normal intrapleural pressure and facilitates lung expansion. Proper maintenance of the closed drainage system and chest tube is important to prevent infection and maintain appropriate drainage and pressure in the pleural cavity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views15 pagesRespi Chest Drainage
Respi Chest Drainage
Uploaded by
JAN FEDERICK BANTAYChest drainage systems are used to drain air or fluid from the pleural cavity through strategically positioned chest tubes. Chest tubes are connected to drainage systems to continuously drain fluid, blood, or air from the pleural cavity or to allow medication instillation. This restores normal intrapleural pressure and facilitates lung expansion. Proper maintenance of the closed drainage system and chest tube is important to prevent infection and maintain appropriate drainage and pressure in the pleural cavity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 15
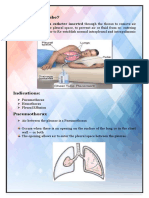
■Chest Drainage
– Is a closed system designed to drain air or fluid from the
pleural cavity while restoring or maintaining negative
intrapleural pressure needed to keep the lungs properly
expanded.
Chest Tubes
- Are positioned strategically in the pleural space, sutured
to the skin and connected to remove the residual air and fluid
from the pleural or mediastinal space
1. TO CONTINUOUSLY DRAIN FLUID, BLOOD OR AIR FROM THE
PLEURAL CAVITY
2. FOR MEDICATION INSTILLATION
3. TO RESTORE NORMAL INTRAPLEURAL PRESSURE AND
FACILITATE EXPANSION OF LUNG
EQUIPMENT
■STERILE TUBE THORACOSTOMY TRAY INCLUDES:
– DRAPES
– GAUZE SPONES
– 25 GAUGE NEEDLE
– 10 ML SYRINGE
– 22 GAUGE NEEDLE
– #11 BLADE SCALPEL
– FORCEPS
EQUIPMENT
■TWO LARGE CLAMPS
■SUTURE MATERIAL
■LOCAL ANESTHETIC
■CHEST TUBE (APPROPRIATE SIZE) TROCAR,
CONNECTOR
■PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
■CHEST DRAINAGE SYSTEM
EQUIPMENT
■STERILE WATER OR SALINE
■SKIN CLEANING SOLUTION
■EXTRA 4X4 GAUZE OT OTHER OCCLUSIVE
DRESSING MATERIAL
■PETROLEUM GAUZE (OPTIONAL)
ACTION RATIONALE
1. IDENTIFY PATIENT ■ To ensure correct patient
-Perform a complete respiratory ■ Baseline assessment and vital
assessment, baseline vital signs signs are essential for any invasive
and pulse oximetry. procedure. Other tube insertion
often causes respiratory distress.
■ To evaluate extent of lung collapse
2. Obtain a chest XRAY. Other
of amount of bleeding in pleural
means of localization of pleural
space.
fluid include ultrasound or
fluoroscopic localization.
ACTION RATIONALE
3. Obtain informed consent
4. Pre-medicate the client for pain ■ To reduce pain
if needed
5. Obtain V/S including oxygen
saturation for baseline data and
then monitor every 4 hours
■ To prevent microorganism from
6. Set up the drainage system entering the system and
( Follow strict surgical technique) subsequently entering the
client’s pleural cavity
WATER SEAL CHAMBER
■ THE TIP OF THE TUBE 2-5CM UNDERWATER
■ IF LESS THAN 2 CM, ADD STERILE WATER
■ NORMAL: INTERMITTENT, GENTLE BUBBLING, OSCILLATION
■ INCREASED CONTINUOUS BUBBLING: AIR LEAK
■ NO MOVEMENT: OBSTRUCTION OR REEXPANSION OF THE LUNGS
NURSING INTERVENTION
■ KEEP THE SYSTEM CLOSED AND BELOW THE CHEST LEVEL
■ REPORT ANY DRAINAGE THAT’S EXCESSIVE, CLOUDY OR BLOODY
■ AN OCCLUSIVE DRESSING IS MAINTAINED AT THE INSERTION SITE
■ DO NOT STRIP OR MILK THE CHEST TUBE UNLESS SPECIFICALLY
DIRECTED BY THE HCP AND IF THE HOSPITAL ALLOWS IT
■ KEEP A CLAMP; MAY BE NEEDED IF THE SYSTEM NEEDS TO BE
CHANGED AND A STERILE OCCLUSIVE DRESSING AT BEDSIDE AT ALL
TIMES
■ NEVER CLAMP THE CHEST TUBE WITHOUT A WRITTEN ORDER FROM
THE HCP; ALSO DETERMINE HOSPITAL POLICY FOR CLAMPING A CHEST
TUBE
■ ENCOURAGE PATIENT TO PERFORM DEEP BREATHING, COUGHING
EXERCISE
■ WHEN THE CHEST TUBE IS REMOVED, IMMEDIATELY APPLY STERILE
OCCLUSIVE PETROLEUM GAUZE DRESSING OVER THE SITE TO
1. The chest drainage system did not pose a hazard for infection
or loss of air seal to the client
2. The chest tube and drainage system are maintained in a safe
manner
3. The amount of drainage from the chest drainage system was
accurately determined and recorded
DOCUMENTATION
1. Indicate the type of chest drainage system used.
2. Note presence or absence of leak
3. Record chest tube drainage amount and color.
You might also like
- DR Lal Path LabDocument2 pagesDR Lal Path LabRockey Singh0% (1)
- Lesson Plan On - Essential-NewbornDocument22 pagesLesson Plan On - Essential-NewbornSwati Sharma100% (2)
- Intercostal DrainDocument44 pagesIntercostal Drainvamshidh100% (1)
- Water Seal DrainageDocument6 pagesWater Seal DrainageAmit MartinNo ratings yet
- Advice Sheet A12 - Infection Control in Dentistry - Identist - 2 PDFDocument31 pagesAdvice Sheet A12 - Infection Control in Dentistry - Identist - 2 PDFizeldien5870No ratings yet
- Management of LBW BabiesDocument67 pagesManagement of LBW BabiesEllen Angel100% (4)
- V V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageDocument1 pageV V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageCyndiNo ratings yet
- Chest TubeDocument21 pagesChest TubeClaudio Nicolas Retamal YevenesNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Rose & Sadava - Chest Tube InsertionDocument19 pagesGroup 2 - Rose & Sadava - Chest Tube InsertionRay Anthony RoseNo ratings yet
- Care of Chest Tube Drainage & Nursing Manangement SHDocument82 pagesCare of Chest Tube Drainage & Nursing Manangement SHJoanna RemollinoNo ratings yet
- CSL Lumbar Puncture, Central line & Chest tube insertionDocument38 pagesCSL Lumbar Puncture, Central line & Chest tube insertionbm19110053No ratings yet
- SPH CT ProtocolDocument13 pagesSPH CT ProtocolRahel GrunderNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy SsDocument56 pagesIV Therapy Sssaeed_chohan100% (8)
- Advance Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Document47 pagesAdvance Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Ben Man Jun100% (2)
- Care of Clients With Chest TubeDocument55 pagesCare of Clients With Chest TubeMarc Andreo MalalaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Placement (Adult)Document8 pagesChest Tube Placement (Adult)Ariane Joyce SalibioNo ratings yet
- CVPDocument23 pagesCVPShalini KaluraNo ratings yet
- Vats and Post Op CareDocument18 pagesVats and Post Op CareVenz100% (1)
- Physiological Adaptation Handout6132024Document27 pagesPhysiological Adaptation Handout6132024harinder singhNo ratings yet
- Respi Modalities 2Document6 pagesRespi Modalities 2Karlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Intro To Specialized Nursing ProceduresDocument156 pagesIntro To Specialized Nursing ProceduresJimmy MainaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Procedures: - Defibrillation in CPRDocument20 pagesEmergency Procedures: - Defibrillation in CPRDuy Phương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IV TherapyDocument39 pagesIV TherapyChannelGNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument15 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringvineeta.ashoknagarNo ratings yet
- Procedures ThoracentesisDocument4 pagesProcedures ThoracentesisPatty MArivel ReinosoNo ratings yet
- Water Sael DrainageDocument36 pagesWater Sael DrainageerlinaNo ratings yet
- Invasive Blood Pressure Monitoring: Group MembersDocument88 pagesInvasive Blood Pressure Monitoring: Group Membersallenshanique1999No ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument4 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringgurneet kourNo ratings yet
- Go With The Flow of Chest Tube Therapy: by Arlene M. Coughlin, RN, MSN, and Carolyn Parchinsky, RN, MADocument14 pagesGo With The Flow of Chest Tube Therapy: by Arlene M. Coughlin, RN, MSN, and Carolyn Parchinsky, RN, MAhady920100% (1)
- Checklists MergedDocument10 pagesChecklists MergedEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Laparoscopic SurgeriesDocument40 pagesComplications of Laparoscopic Surgeriesrajan kumar100% (10)
- Tracheostomy SlidesDocument24 pagesTracheostomy SlidesMohammed AdamNo ratings yet
- Safe SuctioningDocument31 pagesSafe SuctioningKatrina Ponce100% (2)
- Nursing Care of ThoracentesisDocument15 pagesNursing Care of ThoracentesisNora AlnaimNo ratings yet
- NasopharyngealairwayDocument16 pagesNasopharyngealairwayChyndi dami 1216No ratings yet
- Assisting in Patients Undergoing A ThoracentesisDocument7 pagesAssisting in Patients Undergoing A Thoracentesiscoosa liquors0% (1)
- CH 2 SuctioningDocument90 pagesCH 2 SuctioningMaherNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument11 pagesLumbar PunctureBavi ThraNo ratings yet
- CVP Final 2021Document11 pagesCVP Final 2021Ahmed AshrafNo ratings yet
- IR Lctr 10 part 2Document33 pagesIR Lctr 10 part 2seemabfarwauaeNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)Document12 pagesComputed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)jgcriste100% (9)
- Tracheostomy: ENT Department DMC & Hospital Ludhiana PunjabDocument46 pagesTracheostomy: ENT Department DMC & Hospital Ludhiana PunjabVikrant MittalNo ratings yet
- Dvanced Nursing ProceduresDocument125 pagesDvanced Nursing Procedurestum chrisNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Thoracostomy Tube InsertionDocument54 pagesAssisting in Thoracostomy Tube Insertioncoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Central Venous CathetersDocument12 pagesCentral Venous CathetersarisastraNo ratings yet
- Thoracentesis PPT - ExpoDocument22 pagesThoracentesis PPT - ExpoScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Atls 1Document44 pagesAtls 1zekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Chest Drain ManagementDocument7 pagesChest Drain ManagementanuzNo ratings yet
- Suctioning Trache Care NebuDocument11 pagesSuctioning Trache Care NebuROLAND LAURENCE BARGO JARDIOLINNo ratings yet
- Airway Management: by Paul Edmer CorcueraDocument40 pagesAirway Management: by Paul Edmer CorcueraJeco ValdezNo ratings yet
- Emergency Durante ChatgptDocument55 pagesEmergency Durante Chatgptshayansehat8No ratings yet
- Thoracocentasis: INTRODUCTION:-Thoracentasis Also Known As The Thoracocentasis or Plural Tap Is AnDocument7 pagesThoracocentasis: INTRODUCTION:-Thoracentasis Also Known As The Thoracocentasis or Plural Tap Is AnaparnaNo ratings yet
- CTT SpiroDocument10 pagesCTT SpiroKryzl Anne LigsayNo ratings yet
- Care of The Clients With Respiratory DisordersDocument10 pagesCare of The Clients With Respiratory Disordersdexter100% (3)
- Management For CTD - MsDocument63 pagesManagement For CTD - MsNarz CupahanNo ratings yet
- ATLS TemplateDocument6 pagesATLS Templatesyasya100% (1)
- Critical Care SuctioningDocument5 pagesCritical Care SuctioningChinta Nabila 조롱 수없는No ratings yet
- 3730 Monitoring Hemodinamik-2019Document52 pages3730 Monitoring Hemodinamik-2019ojika olandaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube DrainageDocument7 pagesChest Tube Drainagekim reyes100% (1)
- IV Therapy IV Incorporation NEWDocument74 pagesIV Therapy IV Incorporation NEWSteffi AubreyNo ratings yet
- Oncology - Presentation EditedDocument71 pagesOncology - Presentation EditedSarah Racheal AkelloNo ratings yet
- Nusing Skills Output (Nso)Document3 pagesNusing Skills Output (Nso)leroux2890No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- SubluxationDocument5 pagesSubluxationJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- TriageDocument1 pageTriageJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument1 pageCopdJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- BANTAY - Meniere's DiseaseDocument4 pagesBANTAY - Meniere's DiseaseJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- OPD Topics CAP UTI and DewormingDocument24 pagesOPD Topics CAP UTI and DewormingJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Copd 7Document1 pageCopd 7JAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Asthma 1Document9 pagesAsthma 1JAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan Fromat 1Document14 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Fromat 1JAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocument4 pagesQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Multivitamins + B ComplexDocument12 pagesMultivitamins + B ComplexJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Report Dust Mite212Document5 pagesReport Dust Mite212Rowell MarianoNo ratings yet
- Heartbeat HomeostasisDocument1 pageHeartbeat Homeostasisapi-296692561No ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Novel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudyDocument9 pagesNovel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudymarcelodentNo ratings yet
- Maternity Benefits Requirements DocsDocument2 pagesMaternity Benefits Requirements DocsGladys April CatarojaNo ratings yet
- OCA Circular No. 51-2021Document2 pagesOCA Circular No. 51-2021MaricrisNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Guide - Emergency General Surgery Acute Abdominal PainDocument32 pagesCommissioning Guide - Emergency General Surgery Acute Abdominal PainAnisNabillahMohdAzliNo ratings yet
- WHO Mediterranean Zoonosis Control Centre - Information Circular - No. 51 February 2001 - ISSN 1020-1378Document16 pagesWHO Mediterranean Zoonosis Control Centre - Information Circular - No. 51 February 2001 - ISSN 1020-1378christiankoederNo ratings yet
- Survival Guide 2014 2015Document107 pagesSurvival Guide 2014 2015Manpreet BajwaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and RX of CovidDocument11 pagesPathogenesis and RX of CovidYawer Yousuf100% (4)
- Ophthalmic PDFDocument48 pagesOphthalmic PDFMichael Andre CorosNo ratings yet
- 2023 EDITED EP-Lian-C3-Socio-Part-3Document35 pages2023 EDITED EP-Lian-C3-Socio-Part-3Mark Andrei GubacNo ratings yet
- Netherlands Vitamin B12 Deficiency and The Lack of Its Consequences in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Using MetforminDocument5 pagesNetherlands Vitamin B12 Deficiency and The Lack of Its Consequences in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Using Metforminmachoka.peninaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal KebidananDocument12 pagesJurnal KebidananhanaNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 5003 Assessment 1 Identifying Community Health NeedsDocument5 pagesNURS FPX 5003 Assessment 1 Identifying Community Health Needsfarwaamjad771No ratings yet
- OIA Milky Fish Appendix 1Document3 pagesOIA Milky Fish Appendix 1NewshubNo ratings yet
- Case 3 Embryology and Microanatomy of The Kidneys (Lecture Slides)Document45 pagesCase 3 Embryology and Microanatomy of The Kidneys (Lecture Slides)pqp7mpk7v6No ratings yet
- Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument7 pagesChlamydia TrachomatisDewi SetiawatiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Deficits in Long Covid-19Document3 pagesCognitive Deficits in Long Covid-19Nazly ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Spelling Mistakes Corrections of Jahangir's Pool of FCPS Part 1 DentistryDocument16 pagesSpelling Mistakes Corrections of Jahangir's Pool of FCPS Part 1 DentistryAisha BanoNo ratings yet
- Vapcotrim: Injectable SolutionDocument1 pageVapcotrim: Injectable Solutionandi AlyaNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLE Is The First of A New Class of Drugs That Inhibit Gastric Secretion by Altering The Activity of HDocument39 pagesOMEPRAZOLE Is The First of A New Class of Drugs That Inhibit Gastric Secretion by Altering The Activity of HRinNo ratings yet
- Language of Teeth DCDocument6 pagesLanguage of Teeth DCapi-273181309No ratings yet
- Brolucizumab in Neovascular Age Related Macular Degeneration and Diabetic Macular EdemaDocument17 pagesBrolucizumab in Neovascular Age Related Macular Degeneration and Diabetic Macular EdemaKang LimbaNo ratings yet
- Beauty HolidaysDocument3 pagesBeauty HolidaysKristen Anne Camotes SolonNo ratings yet