Professional Documents
Culture Documents
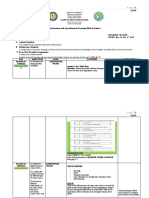
Cfghs-Rmya-Science-8 (Ste)
Cfghs-Rmya-Science-8 (Ste)
Uploaded by
Jelly MendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- OPEN Eoin McCabeDocument219 pagesOPEN Eoin McCabejpmgortagowanNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 8Document3 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 8Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bow Science 8Document3 pagesBow Science 8ARLENE DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Mya - Earth and Life 11-JTSDocument4 pagesMya - Earth and Life 11-JTSJarven SaguinNo ratings yet
- GRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Document2 pagesGRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Rosita CayananNo ratings yet
- Least Most Learned - G8Document1 pageLeast Most Learned - G8Maribel Dizon MangioNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: School Report On The Result of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: School Report On The Result of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentMARK JERALD MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Cfghs-Rmya-Science-9 (Regular)Document4 pagesCfghs-Rmya-Science-9 (Regular)Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Document33 pagesLESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesjimbo09No ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Science 8 Quarter 2Document58 pagesLESSON 1 Science 8 Quarter 2Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- q2 Most and Least LearnedDocument5 pagesq2 Most and Least Learnededmund.guevarraNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Document33 pagesLESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2nd Quarter Learning ActivitiesDocument14 pagesScience 8 2nd Quarter Learning ActivitiesJohn Mark Laurio100% (2)
- Science 10 SyllabusDocument14 pagesScience 10 SyllabusMichelle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Cabangan National High School: Twenty Least Learned CompetenciesDocument2 pagesCabangan National High School: Twenty Least Learned CompetenciesMichaelAbdonDomingoFavo100% (1)
- DLL-Science-8-Q2-Week 2Document8 pagesDLL-Science-8-Q2-Week 2Jun De FontanozaNo ratings yet
- WLP q2 WK 4Document10 pagesWLP q2 WK 4Bing Sepe CulajaoNo ratings yet
- SLM InventoryDocument2 pagesSLM InventoryPETER PAUL NACUANo ratings yet
- Most and Least LearnedDocument20 pagesMost and Least LearnedMariss Joy100% (1)
- TOS Sci 8Document9 pagesTOS Sci 8Bongskie escalonaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 BUDGET OF WORK ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade 10 BUDGET OF WORK ScienceMarshall james G. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Current-Rda Template Most and Least Grade 4Document6 pagesCurrent-Rda Template Most and Least Grade 4Guia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- Current Science 4 Diagnostic Template 1 Most-And-leastDocument2 pagesCurrent Science 4 Diagnostic Template 1 Most-And-leastGuia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- WHLP SCIENCE 8-2nd GradingDocument4 pagesWHLP SCIENCE 8-2nd Gradingmylyn ceraficaNo ratings yet
- Mastered and Least Learned CompetenciesDocument2 pagesMastered and Least Learned CompetenciesGerald LauglaugNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 10Document5 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 10Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Budget of WorkDocument4 pagesSci 10 Budget of WorkAnonymous xagGSIdNo ratings yet
- Week5 ls2 DLL Pathway of TyphoonDocument9 pagesWeek5 ls2 DLL Pathway of Typhoonlowela bagaforoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolNo ratings yet
- TEACHERS-REPORT-ON-THE-RESULTS-OF-THE-REGIONAL-DIAGNOSTIC-ASSESSMENT in Science 8Document3 pagesTEACHERS-REPORT-ON-THE-RESULTS-OF-THE-REGIONAL-DIAGNOSTIC-ASSESSMENT in Science 8Ryan Vincent SugayNo ratings yet
- Tos Grade 10 Not Yet FinishDocument3 pagesTos Grade 10 Not Yet Finishwelfredo yuNo ratings yet
- Q3 Q4 MOST LEARNED Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesQ3 Q4 MOST LEARNED Physical ScienceJoy AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- TOS - 2nd Quarterly-Assessment-2022-23Document2 pagesTOS - 2nd Quarterly-Assessment-2022-23John Alrei MeaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Q4 LEAST LEARNED Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesQ3 Q4 LEAST LEARNED Physical ScienceJoy AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8Document3 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8Rachel MoranteNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 Q2 SUM 2 WITH ANSWER FinalDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 8 Q2 SUM 2 WITH ANSWER Finaldianaliza.banoNo ratings yet
- TOS Sci 8Document9 pagesTOS Sci 8Bongskie escalonaNo ratings yet
- 2nd P TOSSDocument2 pages2nd P TOSSJames Lacuesta TabioloNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKim GenandaNo ratings yet
- Least Learned CompetenciesDocument6 pagesLeast Learned CompetenciesMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Curriculum GuideDocument4 pagesScience 10 Curriculum Guideclay adrian67% (3)
- Q3 Least and Most Science 4Document4 pagesQ3 Least and Most Science 4Ariel PunzalanNo ratings yet
- WLP@2nd Quarter Week 1uploadDocument5 pagesWLP@2nd Quarter Week 1uploadLia FernandezNo ratings yet
- WLP@2nd Quarter Week 1upDocument5 pagesWLP@2nd Quarter Week 1upLia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Q2 Science LASDocument122 pagesGrade 10 Q2 Science LASCln byln80% (15)
- Vp-Green Vale Academy, Inc.: Curriculum Map GRADE: 10 SUBJECT: ScienceDocument5 pagesVp-Green Vale Academy, Inc.: Curriculum Map GRADE: 10 SUBJECT: ScienceRegina Minguez Sabanal100% (1)
- Science 8 Week 1-3Document7 pagesScience 8 Week 1-3Leopoldo Domingo, Jr.No ratings yet
- Science 6 LAS Q4Document50 pagesScience 6 LAS Q4cranchosanchezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Q2 ScienceDocument59 pagesGrade 10 Q2 ScienceShaine Marie Quiñones LuceroNo ratings yet
- TOS 4th-PTDocument1 pageTOS 4th-PTJovel TabiosNo ratings yet
- Science 10 DLL Q1W7 2022 2023Document4 pagesScience 10 DLL Q1W7 2022 2023Anthony Allen Mallari DecenaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Plan in ScienceDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Plan in ScienceAnatasukiNo ratings yet
- Most Mastered Least Learned. SCIENCE8 1ST QUARTER S.Y. 2022 2023Document2 pagesMost Mastered Least Learned. SCIENCE8 1ST QUARTER S.Y. 2022 2023Rosita C.CayananNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Curriculum Map - Unit 2Document4 pagesScience 8 - Curriculum Map - Unit 2Aerone Joshua Magcalayo MoranteNo ratings yet
- Grade Level: 8 Quarter: Second Week: 4 DATES: Dec. 13-Dec. 17, 2021 A. Content Standard: B. Performance Standard: - Focus Most Essential CompetenciesDocument10 pagesGrade Level: 8 Quarter: Second Week: 4 DATES: Dec. 13-Dec. 17, 2021 A. Content Standard: B. Performance Standard: - Focus Most Essential CompetenciesMelanie CoronaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Least Learned Competencies Science 7-9Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Least Learned Competencies Science 7-9Mariss JoyNo ratings yet
- Template Most and Least Learned SkillDocument2 pagesTemplate Most and Least Learned SkillLily RosemaryNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Science 8Document9 pagesBudget of Work Science 8Fernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering by MacromoleculesFrom EverandIntroduction to Dynamic Light Scattering by MacromoleculesNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 10Document5 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 10Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 8Document3 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 8Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 7Document4 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 7Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Intervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-8 (Ste)Document4 pagesIntervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-8 (Ste)Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- English: SectionDocument10 pagesEnglish: SectionJelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Intervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-9 (Ste)Document3 pagesIntervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-9 (Ste)Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- English: SectionDocument10 pagesEnglish: SectionJelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- INTERVENTION PLAN RMYA GRADE 9 Regular ClassDocument4 pagesINTERVENTION PLAN RMYA GRADE 9 Regular ClassJelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Manual: Japan Cricket AssociationDocument32 pagesTeaching Manual: Japan Cricket AssociationYaselaNo ratings yet
- Edited-Hope2 - q2 - MODULE 4-Moderate To Vigorous Physical Actvities - BadmintonDocument24 pagesEdited-Hope2 - q2 - MODULE 4-Moderate To Vigorous Physical Actvities - BadmintonMary Grace Dela Peña100% (15)
- End Sem PresentationDocument4 pagesEnd Sem PresentationShady dtNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Human LanguageDocument4 pagesThe Nature of Human LanguageAlNo ratings yet
- Lab Module 1Document8 pagesLab Module 1Billy Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument1 pageMaslowCik Sri SyarifahNo ratings yet
- Dhruva 11111111Document80 pagesDhruva 11111111Dr Dhruva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mind MapsDocument7 pagesMind MapsnasrullahdharejoNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Educational BackgroundDocument4 pagesWhat Is Your Educational BackgroundDherick RaleighNo ratings yet
- Modified Literacy Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesModified Literacy Lesson Planapi-385014399No ratings yet
- National Power Training Institute: Admission Notice: 2020-21Document3 pagesNational Power Training Institute: Admission Notice: 2020-21a.jainNo ratings yet
- BNMC AdmitCard KKTCPXDocument1 pageBNMC AdmitCard KKTCPXMeherab HossainNo ratings yet
- Master Teacher Monthy Plan 18Document11 pagesMaster Teacher Monthy Plan 18Sonny Matias100% (2)
- Cultural and Religious Factors Affecting The Teaching and Learning of English in Suadi ArabiaDocument10 pagesCultural and Religious Factors Affecting The Teaching and Learning of English in Suadi ArabiasamiraNo ratings yet
- Dejecton EssayDocument8 pagesDejecton Essayrupal aroraNo ratings yet
- Crop PredictionDocument21 pagesCrop Predictionaishwarya kalyanNo ratings yet
- HUMANISTIC TheoryDocument6 pagesHUMANISTIC Theorykalamamark56No ratings yet
- 2022 Pre U Mandarin Chinese Core VocabularyDocument58 pages2022 Pre U Mandarin Chinese Core VocabularyXi WNo ratings yet
- Youth CentreDocument17 pagesYouth CentreShaukat AliNo ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument4 pagesMood Disordersvarsha thakurNo ratings yet
- A Lecture On Syllabus DesignDocument20 pagesA Lecture On Syllabus DesignprettyjeanyNo ratings yet
- GOLDEN PLAZA - 30th OCT - DOUBT COUNTERDocument3 pagesGOLDEN PLAZA - 30th OCT - DOUBT COUNTERz5476259No ratings yet
- Executive MBA Brochure SP Jain School of Global ManagementDocument15 pagesExecutive MBA Brochure SP Jain School of Global ManagementAlex StandoleNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Magazine Vol. 75, No. 1, February 2002Document84 pagesMathematics Magazine Vol. 75, No. 1, February 2002Mohammad ShaikNo ratings yet
- SeatallotDocument1 pageSeatallotPhantom's NetworkNo ratings yet
- The Statement of The Problem: PreparedDocument24 pagesThe Statement of The Problem: PreparedNikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Resume Oct 2023Document1 pageResume Oct 2023api-699842709No ratings yet
- ARTICLE Ex A-CDocument2 pagesARTICLE Ex A-CKádár BiancaNo ratings yet
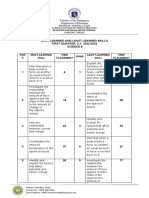
Cfghs-Rmya-Science-8 (Ste)
Cfghs-Rmya-Science-8 (Ste)
Uploaded by
Jelly MendozaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cfghs-Rmya-Science-8 (Ste)
Cfghs-Rmya-Science-8 (Ste)
Uploaded by
Jelly MendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
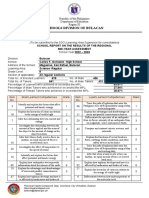
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF BULACAN
Template No. 2
(To be submitted to the SDO (Learning Area Supervisor for consolidation)
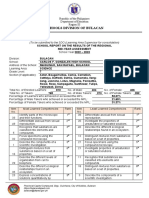
SCHOOL REPORT ON THE RESULTS OF THE REGIONAL
MID-YEAR ASSESSMENT
School Year 2022 – 2023
Division: Bulacan
School: Carlos F. Gonzales High School
Address of the School: Maguinao, San Rafael, Bulacan
Learning Area: Science
Grade Level: 8
Section (if applicable): Mendel (STE)
Total No. of Enrolled Learners: 36 No. of Male: 15 No. of Female: 21
Total No. of Takers: 35 No. of Male Takers: 15 No. of Female Takers: 20
Percentage of Learners who achieved or exceeded the MPL: 94%
Percentage of Male Takers who achieved or exceeded the MPL: 43%
Percentage of Female Takers who achieved or exceeded the MPL: 51%
Item Most Learned Competencies Rank Item Least Learned Competencies Rank
No. No.
Infer that when a body exerts a Infers how typhoon develops and how
15 force on another, an equal amount 1 47 it is affected by landmasses and 1
of force is exerted back on it. bodies of water.
Identify and explain the factors Trace the path of typhoons that enter
16 that affect potential and kinetic 2 42 the Philippine Area of Responsibility 2
energy. using a Map and tracking data.
Investigates the effect of Explain how typhoon develops and
17 temperature to the speed of 3 46 how it is affected by landmasses and 3
sound. bodies of water.
Differentiate the epicenter of an
Explain the hierarchy of colors in
18 4 29 earthquake from its focus: intensity 4
relation to the energy of visible
and magnitude: active and inactive
light.
faults.
Trace the path of typhoons that
enter the Philippine Area of 5 13 Differentiate between heat and 5
33 Responsibility using a Map and temperature at the molecular level.
tracking data.
Identify and explain the factors Describe how typhoon develops and
2 that affect potential and kinetic 6 32 how it is affected by landmasses and 6
energy. bodies of water.
Illustrate how typhoon develops and
Describe the factors that affect
3 7 48 how it is affected by landmasses and 7
potential and kinetic energy.
bodies of water.
Using models or illustrations to
Infer the relationship between
7 8 27 explain the movements along faults 8
current and voltage.
generate earthquakes.
Provincial Capitol Compound, Brgy. Guinhawa, City of Malolos, Bulacan
https://bulacandeped.com
bulacan@deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF BULACAN
9 12 Explains the functions of circuit
Explain the relationship between 9 breakers, fuses, earthing, double 9
current and voltage. insulation, and other safety devices in
the home.
10 Explain the advantages and Explain how earthquake waves
disadvantages of series and 10 50 provide information about the interior 10
parallel connections in homes. of the earth.
Note: *If there is more than one section in a particular grade level, the average percentage of the
learners who achieved or exceeded the MPL shall be reported.
Analysis and Interpretation:
The results of the regional mid-year assessment showed that more than half or 63.61% of grade 8
STE learners who took the test achieved or exceeded the MPL in science 8, while the rest failed to
achieve the MPL.
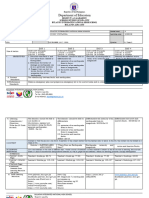
Part B. Cognitive Levels based on Most Learned and Least Learned Competencies
B.1 Most Learned Competencies that Fall under each Cognitive Level
Learning Area: Science 8 (STE)
Bloom’s Taxonomy (Cognitive Level) No.
Low Order Thinking Skills to High Order Thinking Skills of
Grade Level Items
Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating *Creating
Science 8
(STE)
Total 4 2 2 2 0 10
*In case there were items given intended for ‘creating’.
Analysis and Interpretation:
Most of the highest learned competencies fell under lower-order thinking skills (remembering-4,
understanding-3). The results showed that grade 8 regular students found questions involving
lower-order thinking skills easier since they mastered concepts requiring only recall and
comprehension. On the other hand, there were four higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) questions
involving applying and analyzing that students mastered. This showed that those grade 8 regular
students found some HOTS questions easy and thus were able to answer them correctly.
Provincial Capitol Compound, Brgy. Guinhawa, City of Malolos, Bulacan
https://bulacandeped.com
bulacan@deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF BULACAN
B.2 Least Learned Competencies that Fall under each Cognitive Level
Learning Area: SCIENCE 8 (STE)
Bloom’s Taxonomy (Cognitive Level) No.
Low Order Thinking Skills to High Order Thinking Skills of
Grade Level Items
Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating *Creating
Science 8
(STE)
Total 3 2 0 4 1 10
*In case there were items given intended for ‘creating’
Analysis and Interpretation:
Questions involving both lower-order thinking skills (LOTS) and higher-order thinking skills (HOTS)
fell under the least learned competencies. Questions involving higher-order thinking skills like
analyzing and evaluating were found hard by grade 8 STE students and these are understandable
since these require high literacy and numeracy skills. The results also showed that the students
also had poor thinking skills since they failed to master concepts requiring only recall and
comprehension. Perhaps the way the questions were asked or the plausible distractors on those
requiring lower-level thinking skills can be revised so that students can answer them correctly.
Prepared by
RAMIL F. SARMIENTO
School Testing Coordinator
Certified Correct:
CESAR V. VALONDO
School Head
Provincial Capitol Compound, Brgy. Guinhawa, City of Malolos, Bulacan
https://bulacandeped.com
bulacan@deped.gov.ph
You might also like
- OPEN Eoin McCabeDocument219 pagesOPEN Eoin McCabejpmgortagowanNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 8Document3 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 8Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bow Science 8Document3 pagesBow Science 8ARLENE DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Mya - Earth and Life 11-JTSDocument4 pagesMya - Earth and Life 11-JTSJarven SaguinNo ratings yet
- GRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Document2 pagesGRADE-8 Most Essential Learning Competencies Budget of Work School Year 2020-2021Rosita CayananNo ratings yet
- Least Most Learned - G8Document1 pageLeast Most Learned - G8Maribel Dizon MangioNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: School Report On The Result of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: School Report On The Result of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentMARK JERALD MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Cfghs-Rmya-Science-9 (Regular)Document4 pagesCfghs-Rmya-Science-9 (Regular)Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Document33 pagesLESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesjimbo09No ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Science 8 Quarter 2Document58 pagesLESSON 1 Science 8 Quarter 2Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- q2 Most and Least LearnedDocument5 pagesq2 Most and Least Learnededmund.guevarraNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Document33 pagesLESSON 4 Science 8 Quarter 2Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2nd Quarter Learning ActivitiesDocument14 pagesScience 8 2nd Quarter Learning ActivitiesJohn Mark Laurio100% (2)
- Science 10 SyllabusDocument14 pagesScience 10 SyllabusMichelle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Cabangan National High School: Twenty Least Learned CompetenciesDocument2 pagesCabangan National High School: Twenty Least Learned CompetenciesMichaelAbdonDomingoFavo100% (1)
- DLL-Science-8-Q2-Week 2Document8 pagesDLL-Science-8-Q2-Week 2Jun De FontanozaNo ratings yet
- WLP q2 WK 4Document10 pagesWLP q2 WK 4Bing Sepe CulajaoNo ratings yet
- SLM InventoryDocument2 pagesSLM InventoryPETER PAUL NACUANo ratings yet
- Most and Least LearnedDocument20 pagesMost and Least LearnedMariss Joy100% (1)
- TOS Sci 8Document9 pagesTOS Sci 8Bongskie escalonaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 BUDGET OF WORK ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade 10 BUDGET OF WORK ScienceMarshall james G. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Current-Rda Template Most and Least Grade 4Document6 pagesCurrent-Rda Template Most and Least Grade 4Guia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- Current Science 4 Diagnostic Template 1 Most-And-leastDocument2 pagesCurrent Science 4 Diagnostic Template 1 Most-And-leastGuia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- WHLP SCIENCE 8-2nd GradingDocument4 pagesWHLP SCIENCE 8-2nd Gradingmylyn ceraficaNo ratings yet
- Mastered and Least Learned CompetenciesDocument2 pagesMastered and Least Learned CompetenciesGerald LauglaugNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 10Document5 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 10Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Budget of WorkDocument4 pagesSci 10 Budget of WorkAnonymous xagGSIdNo ratings yet
- Week5 ls2 DLL Pathway of TyphoonDocument9 pagesWeek5 ls2 DLL Pathway of Typhoonlowela bagaforoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolNo ratings yet
- TEACHERS-REPORT-ON-THE-RESULTS-OF-THE-REGIONAL-DIAGNOSTIC-ASSESSMENT in Science 8Document3 pagesTEACHERS-REPORT-ON-THE-RESULTS-OF-THE-REGIONAL-DIAGNOSTIC-ASSESSMENT in Science 8Ryan Vincent SugayNo ratings yet
- Tos Grade 10 Not Yet FinishDocument3 pagesTos Grade 10 Not Yet Finishwelfredo yuNo ratings yet
- Q3 Q4 MOST LEARNED Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesQ3 Q4 MOST LEARNED Physical ScienceJoy AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- TOS - 2nd Quarterly-Assessment-2022-23Document2 pagesTOS - 2nd Quarterly-Assessment-2022-23John Alrei MeaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Q4 LEAST LEARNED Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesQ3 Q4 LEAST LEARNED Physical ScienceJoy AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8Document3 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8Rachel MoranteNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 Q2 SUM 2 WITH ANSWER FinalDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 8 Q2 SUM 2 WITH ANSWER Finaldianaliza.banoNo ratings yet
- TOS Sci 8Document9 pagesTOS Sci 8Bongskie escalonaNo ratings yet
- 2nd P TOSSDocument2 pages2nd P TOSSJames Lacuesta TabioloNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKim GenandaNo ratings yet
- Least Learned CompetenciesDocument6 pagesLeast Learned CompetenciesMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Curriculum GuideDocument4 pagesScience 10 Curriculum Guideclay adrian67% (3)
- Q3 Least and Most Science 4Document4 pagesQ3 Least and Most Science 4Ariel PunzalanNo ratings yet
- WLP@2nd Quarter Week 1uploadDocument5 pagesWLP@2nd Quarter Week 1uploadLia FernandezNo ratings yet
- WLP@2nd Quarter Week 1upDocument5 pagesWLP@2nd Quarter Week 1upLia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Q2 Science LASDocument122 pagesGrade 10 Q2 Science LASCln byln80% (15)
- Vp-Green Vale Academy, Inc.: Curriculum Map GRADE: 10 SUBJECT: ScienceDocument5 pagesVp-Green Vale Academy, Inc.: Curriculum Map GRADE: 10 SUBJECT: ScienceRegina Minguez Sabanal100% (1)
- Science 8 Week 1-3Document7 pagesScience 8 Week 1-3Leopoldo Domingo, Jr.No ratings yet
- Science 6 LAS Q4Document50 pagesScience 6 LAS Q4cranchosanchezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Q2 ScienceDocument59 pagesGrade 10 Q2 ScienceShaine Marie Quiñones LuceroNo ratings yet
- TOS 4th-PTDocument1 pageTOS 4th-PTJovel TabiosNo ratings yet
- Science 10 DLL Q1W7 2022 2023Document4 pagesScience 10 DLL Q1W7 2022 2023Anthony Allen Mallari DecenaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Plan in ScienceDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Plan in ScienceAnatasukiNo ratings yet
- Most Mastered Least Learned. SCIENCE8 1ST QUARTER S.Y. 2022 2023Document2 pagesMost Mastered Least Learned. SCIENCE8 1ST QUARTER S.Y. 2022 2023Rosita C.CayananNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Curriculum Map - Unit 2Document4 pagesScience 8 - Curriculum Map - Unit 2Aerone Joshua Magcalayo MoranteNo ratings yet
- Grade Level: 8 Quarter: Second Week: 4 DATES: Dec. 13-Dec. 17, 2021 A. Content Standard: B. Performance Standard: - Focus Most Essential CompetenciesDocument10 pagesGrade Level: 8 Quarter: Second Week: 4 DATES: Dec. 13-Dec. 17, 2021 A. Content Standard: B. Performance Standard: - Focus Most Essential CompetenciesMelanie CoronaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Least Learned Competencies Science 7-9Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Least Learned Competencies Science 7-9Mariss JoyNo ratings yet
- Template Most and Least Learned SkillDocument2 pagesTemplate Most and Least Learned SkillLily RosemaryNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Science 8Document9 pagesBudget of Work Science 8Fernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering by MacromoleculesFrom EverandIntroduction to Dynamic Light Scattering by MacromoleculesNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 10Document5 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 10Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 8Document3 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 8Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- CFGHS Rmya Science 7Document4 pagesCFGHS Rmya Science 7Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Intervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-8 (Ste)Document4 pagesIntervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-8 (Ste)Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- English: SectionDocument10 pagesEnglish: SectionJelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Intervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-9 (Ste)Document3 pagesIntervention-Plan-Rmya-Grade-9 (Ste)Jelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- English: SectionDocument10 pagesEnglish: SectionJelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- INTERVENTION PLAN RMYA GRADE 9 Regular ClassDocument4 pagesINTERVENTION PLAN RMYA GRADE 9 Regular ClassJelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Manual: Japan Cricket AssociationDocument32 pagesTeaching Manual: Japan Cricket AssociationYaselaNo ratings yet
- Edited-Hope2 - q2 - MODULE 4-Moderate To Vigorous Physical Actvities - BadmintonDocument24 pagesEdited-Hope2 - q2 - MODULE 4-Moderate To Vigorous Physical Actvities - BadmintonMary Grace Dela Peña100% (15)
- End Sem PresentationDocument4 pagesEnd Sem PresentationShady dtNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Human LanguageDocument4 pagesThe Nature of Human LanguageAlNo ratings yet
- Lab Module 1Document8 pagesLab Module 1Billy Joe GodoyNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument1 pageMaslowCik Sri SyarifahNo ratings yet
- Dhruva 11111111Document80 pagesDhruva 11111111Dr Dhruva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mind MapsDocument7 pagesMind MapsnasrullahdharejoNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Educational BackgroundDocument4 pagesWhat Is Your Educational BackgroundDherick RaleighNo ratings yet
- Modified Literacy Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesModified Literacy Lesson Planapi-385014399No ratings yet
- National Power Training Institute: Admission Notice: 2020-21Document3 pagesNational Power Training Institute: Admission Notice: 2020-21a.jainNo ratings yet
- BNMC AdmitCard KKTCPXDocument1 pageBNMC AdmitCard KKTCPXMeherab HossainNo ratings yet
- Master Teacher Monthy Plan 18Document11 pagesMaster Teacher Monthy Plan 18Sonny Matias100% (2)
- Cultural and Religious Factors Affecting The Teaching and Learning of English in Suadi ArabiaDocument10 pagesCultural and Religious Factors Affecting The Teaching and Learning of English in Suadi ArabiasamiraNo ratings yet
- Dejecton EssayDocument8 pagesDejecton Essayrupal aroraNo ratings yet
- Crop PredictionDocument21 pagesCrop Predictionaishwarya kalyanNo ratings yet
- HUMANISTIC TheoryDocument6 pagesHUMANISTIC Theorykalamamark56No ratings yet
- 2022 Pre U Mandarin Chinese Core VocabularyDocument58 pages2022 Pre U Mandarin Chinese Core VocabularyXi WNo ratings yet
- Youth CentreDocument17 pagesYouth CentreShaukat AliNo ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument4 pagesMood Disordersvarsha thakurNo ratings yet
- A Lecture On Syllabus DesignDocument20 pagesA Lecture On Syllabus DesignprettyjeanyNo ratings yet
- GOLDEN PLAZA - 30th OCT - DOUBT COUNTERDocument3 pagesGOLDEN PLAZA - 30th OCT - DOUBT COUNTERz5476259No ratings yet
- Executive MBA Brochure SP Jain School of Global ManagementDocument15 pagesExecutive MBA Brochure SP Jain School of Global ManagementAlex StandoleNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Magazine Vol. 75, No. 1, February 2002Document84 pagesMathematics Magazine Vol. 75, No. 1, February 2002Mohammad ShaikNo ratings yet
- SeatallotDocument1 pageSeatallotPhantom's NetworkNo ratings yet
- The Statement of The Problem: PreparedDocument24 pagesThe Statement of The Problem: PreparedNikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Resume Oct 2023Document1 pageResume Oct 2023api-699842709No ratings yet
- ARTICLE Ex A-CDocument2 pagesARTICLE Ex A-CKádár BiancaNo ratings yet