Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antidifferentiation. Definition:: 1.3 Basic Principle of Indefinite Integral
Antidifferentiation. Definition:: 1.3 Basic Principle of Indefinite Integral
Uploaded by
Junelle Amar Bayotas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThis document introduces indefinite integrals and some basic properties:
1) An indefinite integral finds antiderivatives, functions whose derivative is the integrand. It is denoted by the integral sign with no limits.
2) Constants can be moved in and out of integrals. Integrals of sums are the sum of integrals, and integrals of differences are the difference of integrals.
3) The General Power Rule states that the indefinite integral of x^n is (1/n+1)x^(n+1) for any real number n not equal to -1. Several examples of indefinite integrals are given.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document introduces indefinite integrals and some basic properties:
1) An indefinite integral finds antiderivatives, functions whose derivative is the integrand. It is denoted by the integral sign with no limits.
2) Constants can be moved in and out of integrals. Integrals of sums are the sum of integrals, and integrals of differences are the difference of integrals.
3) The General Power Rule states that the indefinite integral of x^n is (1/n+1)x^(n+1) for any real number n not equal to -1. Several examples of indefinite integrals are given.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesAntidifferentiation. Definition:: 1.3 Basic Principle of Indefinite Integral
Antidifferentiation. Definition:: 1.3 Basic Principle of Indefinite Integral
Uploaded by
Junelle Amar BayotasThis document introduces indefinite integrals and some basic properties:
1) An indefinite integral finds antiderivatives, functions whose derivative is the integrand. It is denoted by the integral sign with no limits.
2) Constants can be moved in and out of integrals. Integrals of sums are the sum of integrals, and integrals of differences are the difference of integrals.
3) The General Power Rule states that the indefinite integral of x^n is (1/n+1)x^(n+1) for any real number n not equal to -1. Several examples of indefinite integrals are given.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
MODULE 1 – Lesson 1 1.
3 Basic Principle of Indefinite Integral
INDEFINITE INTEGRAL AND THE GENERAL POWER RULE Our first properties of antiderivatives follow directly from
the simple constant factor, sum, and difference rules for
1.1 Antidifferentiation derivatives.
We have shown the different methods for finding the
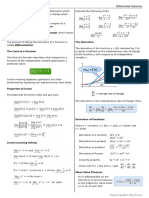
Theorem Suppose that F(x) and G(x) are antiderivatives of f(x)
derivatives of algebraic functions. Now, we will turn our attention
and g(x), respectively, and that c is a constant. Then:
to reversing the operation of differentiation. This process is called (a) If ( ) is equal to a constant; that is,
antidifferentiation.
∫ ∫
Definition: A function F is called an antiderivative of a function
on a given open interval if ( ) ( ) for all x in the interval. (b) A constant factor can be moved through an integral sign; that is,
For example, the function ( ) , its antiderivative is ( )
∫ ∫ ( ) ( )
( ) . Observe that
( ) ( ) ( )
(c) An antiderivative of a sum is the sum of the antiderivatives; that
is,
Consequently, are also antiderivatives of
∫( ( ) ( )) ∫ ( ) ∫ ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) . In fact,
( )
where C is any constant, is an antiderivative of ( ) ; this is (d) An antiderivative of a difference is the difference of the
true because the derivative of a constant is zero. Hence, ( ) antiderivatives; that is,
is the most general antiderivative of ( ) . It is also
called the Indefinite Integral of ( ) ∫( ( ) ( )) ∫ ( ) ∫ ( ) ( ) ( )
1.2 The Indefinite Integral
Let ( ) be an antiderivative of ( ). Then ( ) is (e) If n is any number other than , then
called the indefinite integral of ( ), denoted by:
∫ ( ) ( ) ∫
This process of evaluating ∫ ( ) , that is, finding ( ) is
called integration 1.4 General Power Rule
If ( ) and ( ) exist, then
where: [ ( )]
∫[ ( )] ( )
( ) – is called the integrand of the integral
or by substitution, we get
∫
– constant of integration
( ) – refer to the ( ) is to be integrated with respect to variable ∫
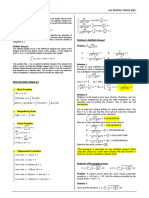
Excercises:
∫( )
∫( )
∫ ( )
∫ ( )
∫( ) ( )
( √ )
∫
√
∫
( )
∫ ( √ )
∫( )( )
You might also like
- Constant of IntegrationDocument9 pagesConstant of IntegrationKathleen V. RamosNo ratings yet
- A Discussion On "Wiener - Khinchin Theorem and Its Applications"Document4 pagesA Discussion On "Wiener - Khinchin Theorem and Its Applications"Harsh Purwar100% (1)
- Integral Calculus PDFDocument32 pagesIntegral Calculus PDFShyam MahendraNo ratings yet
- StewartCalcET7e 04 09Document18 pagesStewartCalcET7e 04 09KLz FluxNo ratings yet
- MIT18 04S18 1802reviewDocument10 pagesMIT18 04S18 1802reviewDanielNo ratings yet
- رياضيات مرحلة 1Document81 pagesرياضيات مرحلة 1سرمد عمرNo ratings yet
- Harmonic OscillatorDocument9 pagesHarmonic OscillatorLinNo ratings yet
- Fourier OpticsDocument15 pagesFourier OpticsWhalsy nNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Part1)Document30 pagesUnit 3 (Part1)Dr. S. Beulah MabelNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Lecture Notes 2023Document2 pagesDifferential Calculus Lecture Notes 2023Romnick IlaganNo ratings yet
- Anti Derivative Chain RuleDocument4 pagesAnti Derivative Chain RulenishagoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntegralDocument42 pagesChapter 1 IntegralAri BagasNo ratings yet
- AEM NotesDocument72 pagesAEM NotesKodali NaniNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument7 pagesUnit VChristal Kaith DuyaNo ratings yet
- General Fourier SeriesDocument18 pagesGeneral Fourier SeriesragujrrNo ratings yet
- Antidifferentiation Up To Power Rule3Document3 pagesAntidifferentiation Up To Power Rule3Mariane BautistaNo ratings yet
- 09 Integral Calculus PrintDocument4 pages09 Integral Calculus PrintJazyl PeralesNo ratings yet
- Anti Derivative of FractionsDocument4 pagesAnti Derivative of FractionsnishagoyalNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesDifferential Calculus Lecture NotesraulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Basic Integration FormulasDocument9 pagesLesson 1 - Basic Integration FormulasCamille ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anti Derivative ListDocument4 pagesAnti Derivative ListnishagoyalNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument35 pagesCalculusClaire Bianca DayananNo ratings yet
- Integration CH 7Document67 pagesIntegration CH 7Shivanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 DifferentiationDocument56 pagesUnit 4 DifferentiationHemanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture NODocument4 pagesLecture NOyashmehrol12No ratings yet
- Mathematical Circle 6Document2 pagesMathematical Circle 6Hameer AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Application and Anti DerivativeDocument4 pagesApplication and Anti DerivativenishagoyalNo ratings yet
- LarCalc11 - 04 - 01 - Antiderivatives and The Indefinite IntegralsDocument25 pagesLarCalc11 - 04 - 01 - Antiderivatives and The Indefinite IntegralsAlexandra RoderoNo ratings yet
- LarCalc10 ch04 Sec1Document26 pagesLarCalc10 ch04 Sec1Bela RilloNo ratings yet
- (Math - Maths 12 (02) ) Various - Mathematics 12 Part II. 2-National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), India (2021)Document336 pages(Math - Maths 12 (02) ) Various - Mathematics 12 Part II. 2-National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), India (2021)うずまきクシナNo ratings yet
- 11 ApplsDivThm 22C W15Document24 pages11 ApplsDivThm 22C W15Venkatesan SwamyNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument72 pagesIntegralSachin5586No ratings yet
- Finite Volume Method For Diffusion ProblemsDocument7 pagesFinite Volume Method For Diffusion ProblemsIkhmal HisyamNo ratings yet
- DIFFCAL FormulaDocument7 pagesDIFFCAL FormulaRocelle Andrea BelandresNo ratings yet
- 13 Expected Values - ContinuousDocument3 pages13 Expected Values - ContinuousKavi SanjaiNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Differentiation Techniques Power and Sum Difference RulesDocument4 pages1.5 Differentiation Techniques Power and Sum Difference RulesVhigherlearning100% (1)
- 3 Function, Limit of FunctionDocument27 pages3 Function, Limit of FunctionMd FaizanNo ratings yet
- Math2 Final RevisionDocument23 pagesMath2 Final RevisionAhmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Math CircuitsDocument30 pagesMath CircuitsBaibhaw Kumar Singh 21BEC2152No ratings yet
- Path IntegralsAnomaliesDocument6 pagesPath IntegralsAnomaliesJosé JiménezNo ratings yet
- Example Problem With SolutionsDocument5 pagesExample Problem With SolutionsEunice Jane DoctorNo ratings yet
- IntegralsDocument1 pageIntegralsryanclark104No ratings yet
- 20 Indefinite IntegrationDocument107 pages20 Indefinite Integrationtusharfiitjee80No ratings yet
- Fundamental Differentiation Formula PDFDocument5 pagesFundamental Differentiation Formula PDFPrincess Shyne PeñaNo ratings yet
- The Dirac Sea: J. Dimock Dept. of Mathematics SUNY at Buffalo Buffalo, NY 14260 November 26, 2010Document7 pagesThe Dirac Sea: J. Dimock Dept. of Mathematics SUNY at Buffalo Buffalo, NY 14260 November 26, 2010Haider ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1, DerivativesDocument11 pagesChapter 3.1, DerivativesaungminsfuNo ratings yet
- Antidifferentiation Up To Power RuleDocument3 pagesAntidifferentiation Up To Power Rulekirsmeds13No ratings yet
- A Continuous Normal Approximation To The Binomial DistributionDocument25 pagesA Continuous Normal Approximation To The Binomial DistributionHugo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Anti Derivative of ArctanDocument4 pagesAnti Derivative of Arctanapi-143521979No ratings yet
- Probability Transforms - Expected Value of FunctionsDocument27 pagesProbability Transforms - Expected Value of FunctionsHugo HernandezNo ratings yet
- AntiderivativesDocument2 pagesAntiderivativesapi-327768386No ratings yet
- Stem 003: Basic Calculus: I. Utcomes of LearningDocument11 pagesStem 003: Basic Calculus: I. Utcomes of Learningreyziel barganNo ratings yet
- Lectures 1 and 2Document5 pagesLectures 1 and 2Mario CacasennoNo ratings yet
- Week 006 Calculus I - Differentiation FormulasDocument4 pagesWeek 006 Calculus I - Differentiation Formulasvit.chinnajiginisaNo ratings yet
- Ehrenfest PDFDocument5 pagesEhrenfest PDFRajiv RajputNo ratings yet
- DSP NotesDocument14 pagesDSP NotesSuman RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Math2Document32 pagesLecture 1 Math2yazan alNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Discrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81From EverandDiscrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81No ratings yet
- Group-A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Document3 pagesGroup-A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Anikendu MaitraNo ratings yet
- First Order Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument20 pagesFirst Order Ordinary Differential EquationsMJ BeatzNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - 5.2 Magnetic Flux - Induced EmfDocument4 pages5.1 - 5.2 Magnetic Flux - Induced EmfAFIQ HAFIZ NAJMI BIN KHUSAIRIE MUAZAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Indefinite IntegrationDocument29 pagesIndefinite IntegrationBharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- Ma201 Linear Algebra &complex Analysis (For All Branches) : Question BankDocument39 pagesMa201 Linear Algebra &complex Analysis (For All Branches) : Question BankChinnumol FrancisNo ratings yet
- Adams 2020 Adams Vibration User GuideDocument164 pagesAdams 2020 Adams Vibration User GuideDanish HassanNo ratings yet
- Sample Q & ADocument11 pagesSample Q & AwanjabaNo ratings yet
- Series DPG-3 Specification SheetDocument2 pagesSeries DPG-3 Specification SheetWattsNo ratings yet
- Radio Propagation Models Comparison and Tuning For LTE Based On Experimental Data in Tripoli-LibyaDocument4 pagesRadio Propagation Models Comparison and Tuning For LTE Based On Experimental Data in Tripoli-LibyaTaha AlmoktarNo ratings yet
- Radians and DegreesDocument19 pagesRadians and DegreesBassem KhalidNo ratings yet
- Z Transform 2 of 3Document18 pagesZ Transform 2 of 3Gilbert SigalaNo ratings yet
- Cold-Source Measurements For Noise Figure CalculationDocument6 pagesCold-Source Measurements For Noise Figure CalculationVedran IbrahimovicNo ratings yet
- Course Policy MA108!22!23Document20 pagesCourse Policy MA108!22!23Aditya DwivediNo ratings yet
- Addition and Subtraction of Fractions With Common DenominatorsDocument2 pagesAddition and Subtraction of Fractions With Common DenominatorsAlNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1938-14 Standard Test Method For Tear PropagationDocument4 pagesASTM D1938-14 Standard Test Method For Tear PropagationLicitacion04 msNo ratings yet
- The Blanchard (1985) Model of Perpetual Youth: August 28, 2019Document13 pagesThe Blanchard (1985) Model of Perpetual Youth: August 28, 2019utsoreeNo ratings yet
- Haskell FunctionalDocument22 pagesHaskell FunctionaldfjhNo ratings yet
- Pore Pressure Prediction From Well Logs (Methods)Document16 pagesPore Pressure Prediction From Well Logs (Methods)Muhamad S BraimNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Foundations of Computational Linguistics: Manfred Klenner and Jannis VamvasDocument32 pagesMathematical Foundations of Computational Linguistics: Manfred Klenner and Jannis VamvasRichard SalnikovNo ratings yet
- Gattus 2020 Eur. J. Phys. 41 065407Document24 pagesGattus 2020 Eur. J. Phys. 41 065407jeetgetsdigitalNo ratings yet
- Ellipstat User's ManualDocument7 pagesEllipstat User's ManualalfonsxxxNo ratings yet
- 2 - The LineDocument18 pages2 - The LineRoxanne Chan OzoaNo ratings yet
- Variables Worksheet PDFDocument6 pagesVariables Worksheet PDFshasagailNo ratings yet
- M2-Exam 2Document13 pagesM2-Exam 2youngturtlevibesNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 Class: T.E. Computer Subject: Theory of ComputationDocument6 pagesAssignment No. 1 Class: T.E. Computer Subject: Theory of ComputationVinit TribhuvanNo ratings yet
- ABS-G-Guidance On Spectral-Based Fatigue Analysis For Vessels-Jan-2012Document38 pagesABS-G-Guidance On Spectral-Based Fatigue Analysis For Vessels-Jan-2012Alicia JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Bombers and SeagullsDocument8 pagesBombers and SeagullshpgeraldNo ratings yet
- D.E. DPP 5Document3 pagesD.E. DPP 5Priyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Computing Project: Numerical Solver For The 2D-Channel-Flow in Vorticity-Streamfunction FormulationDocument18 pagesComputing Project: Numerical Solver For The 2D-Channel-Flow in Vorticity-Streamfunction FormulationHappy SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - QWADocument58 pagesChapter 10 - QWADr.K E Reby RoyNo ratings yet