Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsKyobu XP
Kyobu XP
Uploaded by
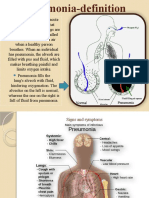
censorship bitesThis document provides descriptions and interpretations of various findings that may appear on a chest x-ray. It explains conditions like pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung nodules, and enlarged heart that require follow-up actions like interviews, tests, or treatment. Other findings like pleural thickening or old surgery scars may not need further action but should be monitored. The chest x-ray reveals important information about respiratory and cardiac health that physicians evaluate to diagnose issues and determine next steps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsDocument1 pagePneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsJoshua Villarba80% (5)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Burned PatientDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plans For Burned PatientJunah Marie Rubinos Palarca85% (26)
- Bombas HidraulicasDocument158 pagesBombas HidraulicasESAVE100% (1)
- Rotation 5 - SicDocument5 pagesRotation 5 - SicColeen PequitNo ratings yet
- SGL6 - CoughDocument63 pagesSGL6 - CoughDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: SecretionsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: SecretionsMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- Partial Lobar Collapse of Lung in Young Adult: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesPartial Lobar Collapse of Lung in Young Adult: A Case ReportGusti Ngurah PNo ratings yet
- PEDIA-Emphysema and Atelectasis, Overinflation Diseases of The Pleura, Pleural Effusion, Tumors (Dr. Talatala)Document2 pagesPEDIA-Emphysema and Atelectasis, Overinflation Diseases of The Pleura, Pleural Effusion, Tumors (Dr. Talatala)Monique BorresNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument15 pagesCOPDMary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- ICD Pulmo Session 3Document4 pagesICD Pulmo Session 3Mary Christine IlangaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal EmergenciesDocument21 pagesNeonatal EmergenciesRNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Pneumonia and SepsisDocument9 pagesLecture 5 Pneumonia and Sepsishenlo hiNo ratings yet
- Poster Traumatic Lung Cyst FinalDocument1 pagePoster Traumatic Lung Cyst FinaladilNo ratings yet
- Surgery For Bullous DiseaseDocument22 pagesSurgery For Bullous DiseaseAlan SeikkaNo ratings yet
- (PULMO) - ABG Interpretation PDFDocument7 pages(PULMO) - ABG Interpretation PDFKeith LajotNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia EnglezaDocument7 pagesPneumonia EnglezaMihai StefanaruNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatiDocument42 pagesGambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatisabariaNo ratings yet
- Mikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakDocument19 pagesMikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakVania TobingNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Step 2 CK NoteDocument41 pagesRespiratory Step 2 CK NoteXboyx MahdiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests: Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument23 pagesDiagnostic Tests: Community-Acquired PneumoniaJim Christian EllaserNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Radiological Evaluation of Emphysematous Chest - A Prospective StudyDocument5 pagesClinical and Radiological Evaluation of Emphysematous Chest - A Prospective StudyTony AndersonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of PneumothoraxDocument3 pagesClinical Aspects of PneumothoraxelisabethNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: Welcome!Document119 pagesRespiratory: Welcome!Majo ParagasNo ratings yet
- (Materi Dr. Heny) PneumoniaDocument86 pages(Materi Dr. Heny) PneumoniaFathiyah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument23 pagesPleural EffusionYousra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuDocument41 pagesDr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuYuni SaviraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument55 pagesRespiratory SystemEndla SriniNo ratings yet
- Asthma DX Article 1Document16 pagesAsthma DX Article 1Pat Caz SarNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument43 pagesPneumothoraxSravani KanchiNo ratings yet
- Emphysema Notes DownloadDocument6 pagesEmphysema Notes DownloadJubitta JobyNo ratings yet
- IPPA SampleDocument28 pagesIPPA Samplekimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pagi RonaDocument28 pagesLaporan Pagi Ronaronakartika1No ratings yet
- Breathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaDocument16 pagesBreathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaLory cNo ratings yet
- Bullous Lung DiseaseDocument6 pagesBullous Lung DiseaseSrujanaNo ratings yet
- Flexible BronchosDocument2 pagesFlexible BronchosBhanu PratapNo ratings yet
- Breathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaDocument16 pagesBreathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaVlad ZecaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Diagnosis and Treatment of A Pleural Effusion in A 24-Year-Old ManDocument4 pagesRapid Diagnosis and Treatment of A Pleural Effusion in A 24-Year-Old ManJonathan EdbertNo ratings yet
- MEDSRUG Respiratory System NotesDocument6 pagesMEDSRUG Respiratory System NotesMichaela Katrice MacabangunNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument95 pagesPneumothoraxYan Sheng HoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsDocument7 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- resp د. وفاءDocument22 pagesresp د. وفاءProf. Wafaa Mohammed Al-AttarNo ratings yet
- Progressive Dyspnea and A Persistentwheeze A Subtle Presentation of Pulmonary Embolism in A 64 Year 6856Document3 pagesProgressive Dyspnea and A Persistentwheeze A Subtle Presentation of Pulmonary Embolism in A 64 Year 6856Sophia RoseNo ratings yet
- TB Treatment 2Document6 pagesTB Treatment 2Mary BarbacionNo ratings yet
- Pe 2ns Year-1Document15 pagesPe 2ns Year-1aarti sahuNo ratings yet
- A 24-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Hemoptysis: Physical Examination FindingsDocument5 pagesA 24-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Hemoptysis: Physical Examination FindingsRaihanun Nisa DinurNo ratings yet
- Breathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaDocument16 pagesBreathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaFelipe Paulo de AssisNo ratings yet
- Kardiorespirasi 5Document83 pagesKardiorespirasi 5Naufal MubarakNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics - Must Know' Classical Signs in Thoracic RadiologyDocument30 pagesBack To Basics - Must Know' Classical Signs in Thoracic Radiologyvalencia suwardiNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax: Xie Can Mao 1st Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen UniverstyDocument95 pagesPneumothorax: Xie Can Mao 1st Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen UniverstySalman HabeebNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesRespiratory SystemYasser AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Lung Pathology Lab Encoded PDFDocument85 pagesThe Lung Pathology Lab Encoded PDFJustinNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray ReviewDocument145 pagesChest X-Ray ReviewHamid ShaalanNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesDiseases of Respiratory SystemMarchelle Fae EsmallaNo ratings yet
- K26 - PneumothoraxDocument39 pagesK26 - PneumothoraxSupriyadiNo ratings yet
- Piercing Wound of The Thorax: Dr. Jason Rahmadi RuslieDocument34 pagesPiercing Wound of The Thorax: Dr. Jason Rahmadi Rusliearryandres11No ratings yet
- Pneumothorax and AsthmaDocument8 pagesPneumothorax and AsthmaKyle FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cherian2019 PDFDocument23 pagesCherian2019 PDFnugra raturandangNo ratings yet
- CRJ2016 1460480Document4 pagesCRJ2016 1460480Jhonnatan Cahuapas BallartaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Kekkanomikata EDocument1 pageKekkanomikata Ecensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- GIH e 09Document159 pagesGIH e 09censorship bitesNo ratings yet
- General Information General Information General Information General Information General InformationDocument4 pagesGeneral Information General Information General Information General Information General Informationcensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- Deadbeats: Justice ForDocument3 pagesDeadbeats: Justice Forcensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- 06 Feature 4 Feb 05Document2 pages06 Feature 4 Feb 05censorship bitesNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Japan'S Patent System: Office of Technology PolicyDocument69 pagesA Guide To Japan'S Patent System: Office of Technology Policycensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- Msds Feso4.7h2o EnglishDocument6 pagesMsds Feso4.7h2o EnglishAlivia Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- Procedure 48-4: Suctioning A Tracheostomy or Endotracheal TubeDocument4 pagesProcedure 48-4: Suctioning A Tracheostomy or Endotracheal Tubeamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Device TherapyDocument21 pagesAerosol Device TherapyRey Jane PaguioNo ratings yet
- Safety AssignmentDocument2 pagesSafety AssignmentShafril HakimiNo ratings yet
- Fructose - MSDSDocument3 pagesFructose - MSDSDoly DoolNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchiectasis PathophysiologyRayne Dunstan Pascual VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Indications For Mechanical VentilationDocument57 pagesChapter 4. Indications For Mechanical VentilationNeurofisiología INCMNSZNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario StemiDocument2 pagesCase Scenario StemiWILJOHN DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Mum LatecityDocument14 pagesMum LatecityGkiniNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Suctioning ChildDocument3 pagesTracheostomy Suctioning ChildKeila RosalesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Educators Guide 2010Document20 pagesClinical Educators Guide 2010PPINo ratings yet
- AED Program Policies and ProceduresDocument22 pagesAED Program Policies and ProceduresBudi Darmawan DiswanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet - Version 5.0: Toronto Research ChemicalsDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet - Version 5.0: Toronto Research Chemicalsjuan marinNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Pulse Rate and Inspiration RatesDocument1 pageTemperature, Pulse Rate and Inspiration RatesmvladysemaNo ratings yet
- Government of Jharkhand: Labour, Employment, Training and Skill Development DepartmentDocument31 pagesGovernment of Jharkhand: Labour, Employment, Training and Skill Development DepartmentNitesh kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: G96, Multi-Purpose Cleaner (24-165A) : G9624Document10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: G96, Multi-Purpose Cleaner (24-165A) : G9624JUAN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hygiene Company ProfileDocument12 pagesDr. Hygiene Company ProfileShubhodeep DasNo ratings yet
- Self Declaration Form Details For International Arriving PassengersDocument2 pagesSelf Declaration Form Details For International Arriving PassengersKoteswar MandavaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Product InformationDocument2 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Product Informationmohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support: Siska Christianingsih, S.Kep.,Ns.M.KepDocument31 pagesAdvanced Life Support: Siska Christianingsih, S.Kep.,Ns.M.KepFlorenciaNo ratings yet
- Dum SpiroDocument2 pagesDum SpiroSundaresan MNo ratings yet
- Funda PostDocument10 pagesFunda PostChaina MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical TransesDocument144 pagesMedical Surgical Transesmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- 3 Care of Respiratory and CirculatoryDocument63 pages3 Care of Respiratory and Circulatoryfrancoise b.No ratings yet
- MAPPING PALEM 1 (TB) - 03 Mei 2021: Prof - Dr.dr.H.Muh - Amin, SP.P (K)Document5 pagesMAPPING PALEM 1 (TB) - 03 Mei 2021: Prof - Dr.dr.H.Muh - Amin, SP.P (K)Yudi ApriyantoNo ratings yet
- Sf6 Gas - MsdsDocument11 pagesSf6 Gas - Msdsvinil radhakrishnaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0300289621001745 mmc2Document2 pages1 s2.0 S0300289621001745 mmc2aris dwiprasetyaNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinnitis-DoneDocument11 pagesAllergic Rhinnitis-Donecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
Kyobu XP
Kyobu XP
Uploaded by
censorship bites0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThis document provides descriptions and interpretations of various findings that may appear on a chest x-ray. It explains conditions like pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung nodules, and enlarged heart that require follow-up actions like interviews, tests, or treatment. Other findings like pleural thickening or old surgery scars may not need further action but should be monitored. The chest x-ray reveals important information about respiratory and cardiac health that physicians evaluate to diagnose issues and determine next steps.
Original Description:
Interpretation of Chest X-ray Findings
Original Title
kyobuXP.Epdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides descriptions and interpretations of various findings that may appear on a chest x-ray. It explains conditions like pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung nodules, and enlarged heart that require follow-up actions like interviews, tests, or treatment. Other findings like pleural thickening or old surgery scars may not need further action but should be monitored. The chest x-ray reveals important information about respiratory and cardiac health that physicians evaluate to diagnose issues and determine next steps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageKyobu XP
Kyobu XP
Uploaded by
censorship bitesThis document provides descriptions and interpretations of various findings that may appear on a chest x-ray. It explains conditions like pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung nodules, and enlarged heart that require follow-up actions like interviews, tests, or treatment. Other findings like pleural thickening or old surgery scars may not need further action but should be monitored. The chest x-ray reveals important information about respiratory and cardiac health that physicians evaluate to diagnose issues and determine next steps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
as aging and inflammation.
Interpretation of Chest X-ray Findings Increased Lung Markings 肺紋理増強
Condition in which the shadow of the pulmonary artery and vein is expanded. If a diagnosis has not
been made, its cause must be determined.
A You have no abnormal chest X-ray findings. Lung Cyst 肺嚢胞
B You have abnormal chest X-ray findings as described in your report, but you do not need an interview with Condition in which there is an abnormal sac (bullae, blebs) in the lung, which may rupture
medical staff, further tests or treatment to attend or work in school.
C You have abnormal chest X-ray findings as described in your report, and you need an interview with medical spontaneously or by sudden pressure changes. Divers should consult a physician specializing in the
staff, further tests or treatment to attend or work in school. respiratory system before diving.
Lung Cavity 空洞
If your result is “A” or “B”, you have no problem attending or working in school. You will be required to undergo the next Lung cavity is formed by necrosis of the lung tissue, caused by congenital diseases or inflammation.
periodic health examination and if you have symptoms such as persistent cough and low fever, please seek medical advice Activity of the causative disease must be determined.
as soon as possible.
If you are under the care of a physician, please report the test results to your physician. Atelectasis 無気肺
Loss of air in the alveoli caused by a blockage of the bronchus or a space-occupying intrathoracic
Lung Apex
process. The presence of an underlying disease must be determined.
Clavicle Pulmonary Edema 肺水腫
What Does a Chest X-ray Reveal? Aorta An abnormal build up of fluid in the lungs, primarily caused by heart failure or renal failure. Treatment
Bronchi Upper Lung is required.
Bronchodilation 気管支拡張
A chest X-ray is performed to detect active An expansion of the air passages through the bronchi of the lungs, primarily caused by congenital
Mid-lung
pulmonary tuberculosis. Other diseases of abnormalities and inflammation. Treatment is required for repeated infection or hemorrhage.
Lung Hilum Heart
the lungs and heart might also be found by Enlarged Lymph Node リンパ節腫大
the chest X-ray. Lower Lung
Condition in which the lymph node(s) is swollen. Underlying disease and its activity must be determined.
Diaphragm Nodular Shadow, Neoplastic Shadow, Emphysematous Changes, Interstitial Shadow, Ground Glass Opacity,
*Pleura: The pleura is the serous membrane enveloping the lungs and lining the walls of the pulmonary cavities. Infiltrative Shadow / Patchy Shadow, Linear Shadow / Band-like Shadow, Reticular Shadow, Granular
*Mediastinum: The mediastinum is the median partition of the thoracic cavity, containing all of the thoracic viscera and structures Shadow
except the lungs. 結節性陰影,腫瘍性陰影,気腫性変化,間質性陰影,スリガラス状陰影,浸潤影・斑状影,線状影・索
Active and Inactive Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Primary Complex 状影,網状影,粒状影
肺結核(活動性),肺結核(不活動性) ,初期変化群 The above are all shadows which may indicate a variety of lung diseases. Causes and activities should
The symptoms of tuberculosis infection (cough, sputum, low fever, night sweats, fatigue) typically be considered.
develop slowly and such individuals are likely to infect others. The cases of inactive tuberculosis must Angiectopia 血管走行等の異常
be regularly monitored for signs of recurrence. The cases of active tuberculosis require immediate An abnormal position or course of a vessel, which may be caused by congenital disease or aging.
treatment and preventive care.
Aortic Calcification 大動脈石灰化
Nontuberculous mycobacterial disease 非結核性抗酸菌症
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are mycobacteria which do not cause tuberculosis or Hansen's Condition in which large calcium deposits form on the aorta, which is an indication of atherosclerosis.
disease. Infection occurs rarely through contact with soil, dust or water. NTM infections are usually Protrusion of the Left Second, Third, Fourth and Right Second Aortic Arches
not contagious, but in advanced cases, treatment is required. 左第二弓突出,左第三弓突出,左第四弓突出,右第二弓突出
Thoracoplasty, Postoperative Changes 胸郭形成,術後変化 This is indicative that part of the heart is enlarged due to a heart disease. Further tests are
Reveals the postoperative changes in the pleura and the lungs. recommended. There may be findings related to obesity, thoracic deformity or poor inspiration, even if
no heart abnormalities are present.
Pleural Thickening, Adhesion 胸膜肥厚・癒着
Post-cardiac Operative Changes 心臓術後変化
Condition mainly brought on by past inflammation, surgery or structural changes in the subpleural lung
tissue. It requires follow-up care, but conditions that accompany respiratory symptoms require Reveals the presence of a cardiac surgical scar (including pacemaker implantation).
treatment. Divers should consult a physician specializing in the respiratory system before diving. Dexiocardia 右胸心
Pneumothorax 気胸 Condition in which the heart is displaced to the right side of the chest. Treatment is not necessary if
Condition in which air leaks into the pleural space, creating pressure against the lung that causes the there is no associated malformation.
lung to collapse. Treatment is required. Spinal Curvature 脊柱弯曲
Pleural Effusion 胸水 An abnormal change in the position of the backbone or spine, which is often associated with a twist in
Condition that results from the accumulation of fluid between the pleura lining the lung and the wall of the spine itself.
the chest cavity. Possible underlying causes include pleural and lung disease, cardiovascular disease Abnormal Bone Shadows 骨陰影の異常
and intra-abdominal disease. Findings in the bones indicative of bone fracture or an abnormality in the formation of bones.
Thoracic Deformity, Dysplasia / Azygos Lobe 胸郭変形,形成異常・奇静脈葉等 Postoperative Changes in the Bone 骨術後変化
Indicative of abnormalities in the formation of a bodily structure, such as the lungs, blood vessels and Postoperative conditions may show the presence of medical apparatus such as reinforcement metals.
the ribs. Medical Apparatus, etc. 医療器具等
Diaphragm Elevation 横隔膜挙上
The presence of medical apparatus such as needles and magnets.
An abnormally high position of the diaphragm which may be caused by obesity, pleural thickening and
digestive system disease. CTR(cardiothoracic ratio) 心胸郭比
Hernia ヘルニア The cardiothoracic ratio is obtained by dividing the transverse cardiac diameter by the transverse
A hernia is an abnormal weakness or hole in the muscular wall which allows abdominal contents to thoracic diameter. The ratio is an indicator of cardiac enlargement.
protrude into the chest cavity through the esophageal opening in the diaphragm. Any serious chest Upon recognition of the above referenced findings and in the event of the necessity of further tests, monitoring or
pain and nausea should receive prompt medical attention. referrals to medical institutions, the Health Center will contact you to visit the Center. If no abnormal findings were
Post-inflammatory Changes 炎症後変化 found or if findings identified do not require treatment to attend or work in school, you will be required to undergo the
Destruction or deterioration of normal lung structure and function caused by the inflammation of the next periodic health examination and to seek treatment upon the onset of symptoms. Please seek prompt medical
treatment for persistent coughing and low fever. If you are under the care of a physician, please report the test results
lungs and the bronchus. If the underlying cause is treated, the patient should be put on observation. to your physician. Students should report the test results to their parents.
Calcification 石灰化
Calcification is a process characterized by the formation of calcium deposits, caused by factors such http://www.hcc.keio.ac.jp/ Keio University Health Center Ver. 1.04
You might also like
- Pneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsDocument1 pagePneumothorax Concept Map: Diagnostic TestsJoshua Villarba80% (5)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Burned PatientDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plans For Burned PatientJunah Marie Rubinos Palarca85% (26)
- Bombas HidraulicasDocument158 pagesBombas HidraulicasESAVE100% (1)
- Rotation 5 - SicDocument5 pagesRotation 5 - SicColeen PequitNo ratings yet
- SGL6 - CoughDocument63 pagesSGL6 - CoughDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: SecretionsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: SecretionsMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- Partial Lobar Collapse of Lung in Young Adult: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesPartial Lobar Collapse of Lung in Young Adult: A Case ReportGusti Ngurah PNo ratings yet
- PEDIA-Emphysema and Atelectasis, Overinflation Diseases of The Pleura, Pleural Effusion, Tumors (Dr. Talatala)Document2 pagesPEDIA-Emphysema and Atelectasis, Overinflation Diseases of The Pleura, Pleural Effusion, Tumors (Dr. Talatala)Monique BorresNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument15 pagesCOPDMary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- ICD Pulmo Session 3Document4 pagesICD Pulmo Session 3Mary Christine IlangaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal EmergenciesDocument21 pagesNeonatal EmergenciesRNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Pneumonia and SepsisDocument9 pagesLecture 5 Pneumonia and Sepsishenlo hiNo ratings yet
- Poster Traumatic Lung Cyst FinalDocument1 pagePoster Traumatic Lung Cyst FinaladilNo ratings yet
- Surgery For Bullous DiseaseDocument22 pagesSurgery For Bullous DiseaseAlan SeikkaNo ratings yet
- (PULMO) - ABG Interpretation PDFDocument7 pages(PULMO) - ABG Interpretation PDFKeith LajotNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia EnglezaDocument7 pagesPneumonia EnglezaMihai StefanaruNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatiDocument42 pagesGambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatisabariaNo ratings yet
- Mikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakDocument19 pagesMikroorganisme Penyebab ISPA Pada AnakVania TobingNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Step 2 CK NoteDocument41 pagesRespiratory Step 2 CK NoteXboyx MahdiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests: Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument23 pagesDiagnostic Tests: Community-Acquired PneumoniaJim Christian EllaserNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Radiological Evaluation of Emphysematous Chest - A Prospective StudyDocument5 pagesClinical and Radiological Evaluation of Emphysematous Chest - A Prospective StudyTony AndersonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of PneumothoraxDocument3 pagesClinical Aspects of PneumothoraxelisabethNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: Welcome!Document119 pagesRespiratory: Welcome!Majo ParagasNo ratings yet
- (Materi Dr. Heny) PneumoniaDocument86 pages(Materi Dr. Heny) PneumoniaFathiyah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument23 pagesPleural EffusionYousra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuDocument41 pagesDr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuYuni SaviraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument55 pagesRespiratory SystemEndla SriniNo ratings yet
- Asthma DX Article 1Document16 pagesAsthma DX Article 1Pat Caz SarNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument43 pagesPneumothoraxSravani KanchiNo ratings yet
- Emphysema Notes DownloadDocument6 pagesEmphysema Notes DownloadJubitta JobyNo ratings yet
- IPPA SampleDocument28 pagesIPPA Samplekimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pagi RonaDocument28 pagesLaporan Pagi Ronaronakartika1No ratings yet
- Breathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaDocument16 pagesBreathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaLory cNo ratings yet
- Bullous Lung DiseaseDocument6 pagesBullous Lung DiseaseSrujanaNo ratings yet
- Flexible BronchosDocument2 pagesFlexible BronchosBhanu PratapNo ratings yet
- Breathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaDocument16 pagesBreathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaVlad ZecaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Diagnosis and Treatment of A Pleural Effusion in A 24-Year-Old ManDocument4 pagesRapid Diagnosis and Treatment of A Pleural Effusion in A 24-Year-Old ManJonathan EdbertNo ratings yet
- MEDSRUG Respiratory System NotesDocument6 pagesMEDSRUG Respiratory System NotesMichaela Katrice MacabangunNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument95 pagesPneumothoraxYan Sheng HoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsDocument7 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- resp د. وفاءDocument22 pagesresp د. وفاءProf. Wafaa Mohammed Al-AttarNo ratings yet
- Progressive Dyspnea and A Persistentwheeze A Subtle Presentation of Pulmonary Embolism in A 64 Year 6856Document3 pagesProgressive Dyspnea and A Persistentwheeze A Subtle Presentation of Pulmonary Embolism in A 64 Year 6856Sophia RoseNo ratings yet
- TB Treatment 2Document6 pagesTB Treatment 2Mary BarbacionNo ratings yet
- Pe 2ns Year-1Document15 pagesPe 2ns Year-1aarti sahuNo ratings yet
- A 24-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Hemoptysis: Physical Examination FindingsDocument5 pagesA 24-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Hemoptysis: Physical Examination FindingsRaihanun Nisa DinurNo ratings yet
- Breathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaDocument16 pagesBreathing Problems and Thoracic TraumaFelipe Paulo de AssisNo ratings yet
- Kardiorespirasi 5Document83 pagesKardiorespirasi 5Naufal MubarakNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics - Must Know' Classical Signs in Thoracic RadiologyDocument30 pagesBack To Basics - Must Know' Classical Signs in Thoracic Radiologyvalencia suwardiNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax: Xie Can Mao 1st Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen UniverstyDocument95 pagesPneumothorax: Xie Can Mao 1st Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen UniverstySalman HabeebNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesRespiratory SystemYasser AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Lung Pathology Lab Encoded PDFDocument85 pagesThe Lung Pathology Lab Encoded PDFJustinNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray ReviewDocument145 pagesChest X-Ray ReviewHamid ShaalanNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesDiseases of Respiratory SystemMarchelle Fae EsmallaNo ratings yet
- K26 - PneumothoraxDocument39 pagesK26 - PneumothoraxSupriyadiNo ratings yet
- Piercing Wound of The Thorax: Dr. Jason Rahmadi RuslieDocument34 pagesPiercing Wound of The Thorax: Dr. Jason Rahmadi Rusliearryandres11No ratings yet
- Pneumothorax and AsthmaDocument8 pagesPneumothorax and AsthmaKyle FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cherian2019 PDFDocument23 pagesCherian2019 PDFnugra raturandangNo ratings yet
- CRJ2016 1460480Document4 pagesCRJ2016 1460480Jhonnatan Cahuapas BallartaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Kekkanomikata EDocument1 pageKekkanomikata Ecensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- GIH e 09Document159 pagesGIH e 09censorship bitesNo ratings yet
- General Information General Information General Information General Information General InformationDocument4 pagesGeneral Information General Information General Information General Information General Informationcensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- Deadbeats: Justice ForDocument3 pagesDeadbeats: Justice Forcensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- 06 Feature 4 Feb 05Document2 pages06 Feature 4 Feb 05censorship bitesNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Japan'S Patent System: Office of Technology PolicyDocument69 pagesA Guide To Japan'S Patent System: Office of Technology Policycensorship bitesNo ratings yet
- Msds Feso4.7h2o EnglishDocument6 pagesMsds Feso4.7h2o EnglishAlivia Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- Procedure 48-4: Suctioning A Tracheostomy or Endotracheal TubeDocument4 pagesProcedure 48-4: Suctioning A Tracheostomy or Endotracheal Tubeamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Device TherapyDocument21 pagesAerosol Device TherapyRey Jane PaguioNo ratings yet
- Safety AssignmentDocument2 pagesSafety AssignmentShafril HakimiNo ratings yet
- Fructose - MSDSDocument3 pagesFructose - MSDSDoly DoolNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchiectasis PathophysiologyRayne Dunstan Pascual VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Indications For Mechanical VentilationDocument57 pagesChapter 4. Indications For Mechanical VentilationNeurofisiología INCMNSZNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario StemiDocument2 pagesCase Scenario StemiWILJOHN DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Mum LatecityDocument14 pagesMum LatecityGkiniNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Suctioning ChildDocument3 pagesTracheostomy Suctioning ChildKeila RosalesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Educators Guide 2010Document20 pagesClinical Educators Guide 2010PPINo ratings yet
- AED Program Policies and ProceduresDocument22 pagesAED Program Policies and ProceduresBudi Darmawan DiswanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet - Version 5.0: Toronto Research ChemicalsDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet - Version 5.0: Toronto Research Chemicalsjuan marinNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Pulse Rate and Inspiration RatesDocument1 pageTemperature, Pulse Rate and Inspiration RatesmvladysemaNo ratings yet
- Government of Jharkhand: Labour, Employment, Training and Skill Development DepartmentDocument31 pagesGovernment of Jharkhand: Labour, Employment, Training and Skill Development DepartmentNitesh kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: G96, Multi-Purpose Cleaner (24-165A) : G9624Document10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: G96, Multi-Purpose Cleaner (24-165A) : G9624JUAN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hygiene Company ProfileDocument12 pagesDr. Hygiene Company ProfileShubhodeep DasNo ratings yet
- Self Declaration Form Details For International Arriving PassengersDocument2 pagesSelf Declaration Form Details For International Arriving PassengersKoteswar MandavaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Product InformationDocument2 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Product Informationmohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support: Siska Christianingsih, S.Kep.,Ns.M.KepDocument31 pagesAdvanced Life Support: Siska Christianingsih, S.Kep.,Ns.M.KepFlorenciaNo ratings yet
- Dum SpiroDocument2 pagesDum SpiroSundaresan MNo ratings yet
- Funda PostDocument10 pagesFunda PostChaina MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical TransesDocument144 pagesMedical Surgical Transesmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- 3 Care of Respiratory and CirculatoryDocument63 pages3 Care of Respiratory and Circulatoryfrancoise b.No ratings yet
- MAPPING PALEM 1 (TB) - 03 Mei 2021: Prof - Dr.dr.H.Muh - Amin, SP.P (K)Document5 pagesMAPPING PALEM 1 (TB) - 03 Mei 2021: Prof - Dr.dr.H.Muh - Amin, SP.P (K)Yudi ApriyantoNo ratings yet
- Sf6 Gas - MsdsDocument11 pagesSf6 Gas - Msdsvinil radhakrishnaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0300289621001745 mmc2Document2 pages1 s2.0 S0300289621001745 mmc2aris dwiprasetyaNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinnitis-DoneDocument11 pagesAllergic Rhinnitis-Donecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet