Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of The Communication Model Parts of The Communication Model
Parts of The Communication Model Parts of The Communication Model
Uploaded by
Ronhielyn AlbisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Summary of Discourse Analysis by Brian PDocument36 pagesSummary of Discourse Analysis by Brian PIbrahim Badawy50% (4)
- Met 5207 NotesDocument9 pagesMet 5207 NotesIrene makena0% (1)
- Bautista, Bia G. COC-1C Introduction To Communication Media MODULE 1: Assignment 1Document4 pagesBautista, Bia G. COC-1C Introduction To Communication Media MODULE 1: Assignment 1Bia Bautista100% (1)
- Oral Comm. 11 - Quarter 1 - Module 2 - Week 2Document7 pagesOral Comm. 11 - Quarter 1 - Module 2 - Week 2Gerald Palma100% (3)
- Sharing The Planet PYP Planner ScienceDocument4 pagesSharing The Planet PYP Planner ScienceDanielRobertson0% (1)
- Oral Communication in Context First Quarter (Pointers) : 1. Schemata-DrivenDocument13 pagesOral Communication in Context First Quarter (Pointers) : 1. Schemata-DrivenMichael Jan BajenNo ratings yet
- Cont 2 Lesson 3 4Document10 pagesCont 2 Lesson 3 4Raymar BartolomeNo ratings yet
- HBO - Group 3 Written Report (A)Document4 pagesHBO - Group 3 Written Report (A)Cheery Mea CostillasNo ratings yet
- Purposive Module 1Document7 pagesPurposive Module 1merrygraceclabrillazoNo ratings yet
- Communication Derived From The Latin Word Communis-1 PDFDocument37 pagesCommunication Derived From The Latin Word Communis-1 PDFPrecious njeriNo ratings yet
- MCDocument67 pagesMCMayur ZopeNo ratings yet
- Discipline OF CommunicationDocument27 pagesDiscipline OF CommunicationOfelia Managad GrospeNo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument7 pagesOral CommManny Agsunodan ManpatilanNo ratings yet
- Process of CommunicationDocument6 pagesProcess of CommunicationJessie JinlongNo ratings yet
- Communication ModuleDocument46 pagesCommunication ModuleYvonne BascoNo ratings yet
- Oral Com First Sem NotesDocument19 pagesOral Com First Sem NotesnikkidemonyoNo ratings yet
- 505 EB Communicative Skills U 1&2Document20 pages505 EB Communicative Skills U 1&2Preshita MarvaniaNo ratings yet
- Definition of CommunicationDocument3 pagesDefinition of CommunicationSabrina MañulitNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs in OralDocument5 pagesHand Outs in OralArien kaye VallarNo ratings yet
- Nature and Process of CommunicationDocument5 pagesNature and Process of CommunicationBSN2G- SABLA-ON LORRAINE ANNENo ratings yet
- ORAL COMMUNICATION HandoutsDocument23 pagesORAL COMMUNICATION HandoutsNatsumiGraceNo ratings yet
- Communication Process ModelDocument4 pagesCommunication Process ModelcarmenvioNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument8 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerLuis Norbert SantiagoNo ratings yet
- HBO - Group 3 (A)Document46 pagesHBO - Group 3 (A)Cheery Mea CostillasNo ratings yet
- TESDA - Communication (K Caacbay Nootes)Document14 pagesTESDA - Communication (K Caacbay Nootes)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- Communication Studies GuideDocument16 pagesCommunication Studies GuideAkiem JarrettNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles, and EthicsDocument12 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles, and EthicsJack SantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CommunicationDocument19 pagesIntroduction To CommunicationRovin Jae EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Topic1fundamentals of CommunicationDocument23 pagesTopic1fundamentals of Communicationapi-366561602No ratings yet
- GPCOM L1: Communication Processes,: Principles and EthicsDocument10 pagesGPCOM L1: Communication Processes,: Principles and EthicsKate Florenosos100% (1)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument13 pagesPurposive CommunicationCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication ProcessDocument24 pagesEffective Communication ProcessDan JamesNo ratings yet
- Short Opening Prayer Before ClassDocument5 pagesShort Opening Prayer Before ClassjinxNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive CommunicationCrescent AnnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication - NotesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Communication - NotesRamaduguKiranbabu100% (1)
- 1fundamentals of Communication As A Process and SystemDocument18 pages1fundamentals of Communication As A Process and SystemJerwin OliverosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1:the Nature of Language: Karon Is A Word Found Both in HiligaynonDocument17 pagesLesson 1:the Nature of Language: Karon Is A Word Found Both in HiligaynonEilen Joyce BisnarNo ratings yet
- The Process of Communication: Lesson 3Document27 pagesThe Process of Communication: Lesson 3ara de leonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Communication (Autosaved)Document17 pagesLesson 1 - Communication (Autosaved)CATHERINE JUN INCIONo ratings yet
- ORAL COMMUNICATION1112 Q1 LAS 3week 3 1 1Document17 pagesORAL COMMUNICATION1112 Q1 LAS 3week 3 1 1Wesley TampusNo ratings yet
- Villanas - Watch and Buzz Summary - I-BmaDocument2 pagesVillanas - Watch and Buzz Summary - I-BmaNicole VillanasNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 - Language - and - Communication PDFDocument5 pagesTOPIC 1 - Language - and - Communication PDFdevvy anneNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills NotesDocument7 pagesCommunication Skills NotesSarkam AbdiNo ratings yet
- Elements of CommunicationDocument49 pagesElements of CommunicationYska LindsyNo ratings yet
- Communication NotesDocument7 pagesCommunication NotesJacob Clint LipuraNo ratings yet
- CABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMDocument1 pageCABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMKrizahMarieCaballeroNo ratings yet
- CABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMDocument1 pageCABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMKrizahMarieCaballeroNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsDocument5 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles and Ethicsmarygrace carbonelNo ratings yet
- Business Communication NotesDocument14 pagesBusiness Communication NotesAnimesh MayankNo ratings yet
- Communication ProcessDocument85 pagesCommunication Processshamim mohamedNo ratings yet
- English11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedDocument41 pagesEnglish11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Purposive Com ReviewerDocument14 pagesPurposive Com ReviewerAriadna ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive Communicationangelakaye deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesOral CommunicationABM - TOLENTINO, JOANNA MARIE DC.No ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument2 pagesOral CommunicationMario Balao Jr.No ratings yet
- Question1: Describe The Process of Communication in Detail. Answer: The Communication ProcessDocument3 pagesQuestion1: Describe The Process of Communication in Detail. Answer: The Communication ProcessAlam Mohammad Parvez SaifiNo ratings yet
- Simbre (11 - Dewey) 1Document13 pagesSimbre (11 - Dewey) 1Rowilyn Seat IINo ratings yet
- Process of ComunnicationDocument7 pagesProcess of Comunnicationsam AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Aged 409 3. Communication in ExtensionDocument41 pagesAged 409 3. Communication in ExtensionLydia NcubeNo ratings yet
- The Discipline of CommunicationDocument43 pagesThe Discipline of CommunicationJOIEMA ELLANo ratings yet
- Purcomm Module 1Document12 pagesPurcomm Module 1Joross CuadraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 (11) - Media and Information SourcesDocument1 pageLesson 9 (11) - Media and Information SourcesRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 (10) - Media ConvergenceDocument1 pageLesson 8 (10) - Media ConvergenceRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 (9) - Types of MediaDocument1 pageLesson 7 (9) - Types of MediaRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 (7 & 8) - The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument3 pagesLesson 6 (7 & 8) - The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 (5 & 6) - Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument3 pagesLesson 5 (5 & 6) - Responsible Use of Media and InformationRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument74 pagesUntitledRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Information - Defined AsDocument1 pageInformation - Defined AsRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument66 pagesUntitledRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Varivent Seat Valves Catalog 262492Document380 pagesVarivent Seat Valves Catalog 262492Thái Đạo Phạm LêNo ratings yet
- Smart Code FullDocument490 pagesSmart Code FullAnonymous Dm7FwOJXUNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of MotionDocument8 pages1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of MotionRakibul Islam RanaNo ratings yet
- Ceb 1082Document12 pagesCeb 1082oscar horacio floresNo ratings yet
- DD Series Guide Rod Diesel Pile Hammer D Series Diesel Pile HammerDocument7 pagesDD Series Guide Rod Diesel Pile Hammer D Series Diesel Pile HammerMuqorobinNo ratings yet
- Wind LoadDocument13 pagesWind LoadHimani NagarNo ratings yet
- Comments On KING 775 RIG 21 Apr 22Document3 pagesComments On KING 775 RIG 21 Apr 22Shahin ZamanNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: FVR-E11S-7EN FVR-E11S-4ENDocument116 pagesInstruction Manual: FVR-E11S-7EN FVR-E11S-4ENminh đạo nguyễnNo ratings yet
- De Cuong On Tap HK2 Anh 9 Nam 23 24Document6 pagesDe Cuong On Tap HK2 Anh 9 Nam 23 24UserNo ratings yet
- ISB - Mba Handbook 2020-2021 WebDocument27 pagesISB - Mba Handbook 2020-2021 WebTran Nguyet MinhNo ratings yet
- Mcgregor'S Theory X and Theory YDocument11 pagesMcgregor'S Theory X and Theory YMuhammad MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Forum Diskusi 7-1 (Alternating Current)Document5 pagesForum Diskusi 7-1 (Alternating Current)Reyhan Julianto PribadiNo ratings yet
- List of Instrument Available at Wagoora Sub-StationDocument2 pagesList of Instrument Available at Wagoora Sub-StationBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailureDocument27 pagesTheories of FailureBenedict ThomasNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Pts Publications and Standard SpecificationsDocument38 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Pts Publications and Standard SpecificationsadamNo ratings yet
- Clinical GoalsDocument13 pagesClinical GoalsHycient PaulNo ratings yet
- Lecture#8 - Hmis Data QualityDocument24 pagesLecture#8 - Hmis Data Qualitykingwinston ombionNo ratings yet
- Deloitte - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesDeloitte - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediakimmu5100% (1)
- LogDocument6 pagesLognadiafirdiana1973No ratings yet
- S006 - Suicide in An Airpla PDFDocument19 pagesS006 - Suicide in An Airpla PDFruso1900No ratings yet
- 910-911-914-915 Fanuc Ram Parity AlarmDocument2 pages910-911-914-915 Fanuc Ram Parity AlarmShumail JavedNo ratings yet
- E1 T1 TutorialDocument16 pagesE1 T1 Tutorialমোহাম্মাদ নাবিল নূর50% (2)
- MAN - CH - 2 - MCQsDocument6 pagesMAN - CH - 2 - MCQsSaquibh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Dip Lab ReportDocument23 pagesDip Lab Reportfawadnuml1No ratings yet
- AArado - Simplex Method QuizDocument3 pagesAArado - Simplex Method QuizAdelson AradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide: Grade: SubjectDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Guide: Grade: Subjectapi-557528365No ratings yet
- Biblical Narrative and Palestine HistoryDocument25 pagesBiblical Narrative and Palestine HistorydjsNo ratings yet
Parts of The Communication Model Parts of The Communication Model
Parts of The Communication Model Parts of The Communication Model
Uploaded by
Ronhielyn AlbisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of The Communication Model Parts of The Communication Model
Parts of The Communication Model Parts of The Communication Model
Uploaded by
Ronhielyn AlbisCopyright:
Available Formats
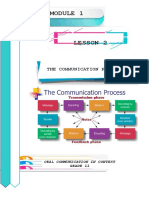
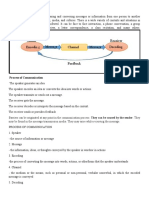
PARTS OF THE PARTS OF THE
COMMUNICATION MODEL COMMUNICATION MODEL
a. Source or Sender – One who sends or delivers a. Source or Sender – One who sends or delivers
a message, and who initiates the communication a message, and who initiates the communication
process. process.
b. Message – The information or the verbal and b. Message – The information or the verbal and
nonverbal message conveyed to another person nonverbal message conveyed to another person
or a group of people. or a group of people.
c. Medium – Media is the plural of “medium”, or c. Medium – Media is the plural of “medium”, or
ways to communicate information. It is also the ways to communicate information. It is also the
channel through which the message is coursed. channel through which the message is coursed.
d. Receiver – This part of the communication d. Receiver – This part of the communication
process receives the message. The process receives the message. The
communication process is considered successful communication process is considered successful
when the receiver responds the way the source when the receiver responds the way the source
intended. However, the communication process intended. However, the communication process
does not end here. The effect of the message and does not end here. The effect of the message and
the feedback of the receiver should also be noted the feedback of the receiver should also be noted
in order to know the result of the communication in order to know the result of the communication
process. process.
e. Effect – Response of the receiver after getting e. Effect – Response of the receiver after getting
the message from the source. the message from the source.
f. Feedback – An important product of the f. Feedback – An important product of the
communication process. It tells the source how communication process. It tells the source how
effective the selected message and channel to the effective the selected message and channel to the
receiver. Feedback confirms whether there is receiver. Feedback confirms whether there is
mutual understanding between the source and mutual understanding between the source and
the receiver. the receiver.
The communication process is not always ideal. The communication process is not always ideal.
Interference can occur when the Interference can occur when the
source sends a message. This is called: source sends a message. This is called:
g. Noise or Barriers – These are the disruptions g. Noise or Barriers – These are the disruptions
in the communication process. In the workplace, in the communication process. In the workplace,
noise can be common especially when people who noise can be common especially when people who
are not familiar with each other communicate. are not familiar with each other communicate.
You might also like
- Summary of Discourse Analysis by Brian PDocument36 pagesSummary of Discourse Analysis by Brian PIbrahim Badawy50% (4)
- Met 5207 NotesDocument9 pagesMet 5207 NotesIrene makena0% (1)
- Bautista, Bia G. COC-1C Introduction To Communication Media MODULE 1: Assignment 1Document4 pagesBautista, Bia G. COC-1C Introduction To Communication Media MODULE 1: Assignment 1Bia Bautista100% (1)
- Oral Comm. 11 - Quarter 1 - Module 2 - Week 2Document7 pagesOral Comm. 11 - Quarter 1 - Module 2 - Week 2Gerald Palma100% (3)
- Sharing The Planet PYP Planner ScienceDocument4 pagesSharing The Planet PYP Planner ScienceDanielRobertson0% (1)
- Oral Communication in Context First Quarter (Pointers) : 1. Schemata-DrivenDocument13 pagesOral Communication in Context First Quarter (Pointers) : 1. Schemata-DrivenMichael Jan BajenNo ratings yet
- Cont 2 Lesson 3 4Document10 pagesCont 2 Lesson 3 4Raymar BartolomeNo ratings yet
- HBO - Group 3 Written Report (A)Document4 pagesHBO - Group 3 Written Report (A)Cheery Mea CostillasNo ratings yet
- Purposive Module 1Document7 pagesPurposive Module 1merrygraceclabrillazoNo ratings yet
- Communication Derived From The Latin Word Communis-1 PDFDocument37 pagesCommunication Derived From The Latin Word Communis-1 PDFPrecious njeriNo ratings yet
- MCDocument67 pagesMCMayur ZopeNo ratings yet
- Discipline OF CommunicationDocument27 pagesDiscipline OF CommunicationOfelia Managad GrospeNo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument7 pagesOral CommManny Agsunodan ManpatilanNo ratings yet
- Process of CommunicationDocument6 pagesProcess of CommunicationJessie JinlongNo ratings yet
- Communication ModuleDocument46 pagesCommunication ModuleYvonne BascoNo ratings yet
- Oral Com First Sem NotesDocument19 pagesOral Com First Sem NotesnikkidemonyoNo ratings yet
- 505 EB Communicative Skills U 1&2Document20 pages505 EB Communicative Skills U 1&2Preshita MarvaniaNo ratings yet
- Definition of CommunicationDocument3 pagesDefinition of CommunicationSabrina MañulitNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs in OralDocument5 pagesHand Outs in OralArien kaye VallarNo ratings yet
- Nature and Process of CommunicationDocument5 pagesNature and Process of CommunicationBSN2G- SABLA-ON LORRAINE ANNENo ratings yet
- ORAL COMMUNICATION HandoutsDocument23 pagesORAL COMMUNICATION HandoutsNatsumiGraceNo ratings yet
- Communication Process ModelDocument4 pagesCommunication Process ModelcarmenvioNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument8 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerLuis Norbert SantiagoNo ratings yet
- HBO - Group 3 (A)Document46 pagesHBO - Group 3 (A)Cheery Mea CostillasNo ratings yet
- TESDA - Communication (K Caacbay Nootes)Document14 pagesTESDA - Communication (K Caacbay Nootes)Tora RaaNo ratings yet
- Communication Studies GuideDocument16 pagesCommunication Studies GuideAkiem JarrettNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles, and EthicsDocument12 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles, and EthicsJack SantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CommunicationDocument19 pagesIntroduction To CommunicationRovin Jae EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Topic1fundamentals of CommunicationDocument23 pagesTopic1fundamentals of Communicationapi-366561602No ratings yet
- GPCOM L1: Communication Processes,: Principles and EthicsDocument10 pagesGPCOM L1: Communication Processes,: Principles and EthicsKate Florenosos100% (1)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument13 pagesPurposive CommunicationCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication ProcessDocument24 pagesEffective Communication ProcessDan JamesNo ratings yet
- Short Opening Prayer Before ClassDocument5 pagesShort Opening Prayer Before ClassjinxNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive CommunicationCrescent AnnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication - NotesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Communication - NotesRamaduguKiranbabu100% (1)
- 1fundamentals of Communication As A Process and SystemDocument18 pages1fundamentals of Communication As A Process and SystemJerwin OliverosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1:the Nature of Language: Karon Is A Word Found Both in HiligaynonDocument17 pagesLesson 1:the Nature of Language: Karon Is A Word Found Both in HiligaynonEilen Joyce BisnarNo ratings yet
- The Process of Communication: Lesson 3Document27 pagesThe Process of Communication: Lesson 3ara de leonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Communication (Autosaved)Document17 pagesLesson 1 - Communication (Autosaved)CATHERINE JUN INCIONo ratings yet
- ORAL COMMUNICATION1112 Q1 LAS 3week 3 1 1Document17 pagesORAL COMMUNICATION1112 Q1 LAS 3week 3 1 1Wesley TampusNo ratings yet
- Villanas - Watch and Buzz Summary - I-BmaDocument2 pagesVillanas - Watch and Buzz Summary - I-BmaNicole VillanasNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 - Language - and - Communication PDFDocument5 pagesTOPIC 1 - Language - and - Communication PDFdevvy anneNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills NotesDocument7 pagesCommunication Skills NotesSarkam AbdiNo ratings yet
- Elements of CommunicationDocument49 pagesElements of CommunicationYska LindsyNo ratings yet
- Communication NotesDocument7 pagesCommunication NotesJacob Clint LipuraNo ratings yet
- CABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMDocument1 pageCABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMKrizahMarieCaballeroNo ratings yet
- CABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMDocument1 pageCABALLERO, KRIZAH MARIE C. BSA 1A - Module 1 Assessment GECCOMKrizahMarieCaballeroNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsDocument5 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles and Ethicsmarygrace carbonelNo ratings yet
- Business Communication NotesDocument14 pagesBusiness Communication NotesAnimesh MayankNo ratings yet
- Communication ProcessDocument85 pagesCommunication Processshamim mohamedNo ratings yet
- English11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedDocument41 pagesEnglish11 q1 Module 1 8 Oral Communication in Context v1 RevisedMarilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Purposive Com ReviewerDocument14 pagesPurposive Com ReviewerAriadna ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive Communicationangelakaye deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesOral CommunicationABM - TOLENTINO, JOANNA MARIE DC.No ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument2 pagesOral CommunicationMario Balao Jr.No ratings yet
- Question1: Describe The Process of Communication in Detail. Answer: The Communication ProcessDocument3 pagesQuestion1: Describe The Process of Communication in Detail. Answer: The Communication ProcessAlam Mohammad Parvez SaifiNo ratings yet
- Simbre (11 - Dewey) 1Document13 pagesSimbre (11 - Dewey) 1Rowilyn Seat IINo ratings yet
- Process of ComunnicationDocument7 pagesProcess of Comunnicationsam AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Aged 409 3. Communication in ExtensionDocument41 pagesAged 409 3. Communication in ExtensionLydia NcubeNo ratings yet
- The Discipline of CommunicationDocument43 pagesThe Discipline of CommunicationJOIEMA ELLANo ratings yet
- Purcomm Module 1Document12 pagesPurcomm Module 1Joross CuadraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 (11) - Media and Information SourcesDocument1 pageLesson 9 (11) - Media and Information SourcesRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 (10) - Media ConvergenceDocument1 pageLesson 8 (10) - Media ConvergenceRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 (9) - Types of MediaDocument1 pageLesson 7 (9) - Types of MediaRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 (7 & 8) - The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument3 pagesLesson 6 (7 & 8) - The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 (5 & 6) - Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument3 pagesLesson 5 (5 & 6) - Responsible Use of Media and InformationRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument74 pagesUntitledRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Information - Defined AsDocument1 pageInformation - Defined AsRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument66 pagesUntitledRonhielyn AlbisNo ratings yet
- Varivent Seat Valves Catalog 262492Document380 pagesVarivent Seat Valves Catalog 262492Thái Đạo Phạm LêNo ratings yet
- Smart Code FullDocument490 pagesSmart Code FullAnonymous Dm7FwOJXUNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of MotionDocument8 pages1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of MotionRakibul Islam RanaNo ratings yet
- Ceb 1082Document12 pagesCeb 1082oscar horacio floresNo ratings yet
- DD Series Guide Rod Diesel Pile Hammer D Series Diesel Pile HammerDocument7 pagesDD Series Guide Rod Diesel Pile Hammer D Series Diesel Pile HammerMuqorobinNo ratings yet
- Wind LoadDocument13 pagesWind LoadHimani NagarNo ratings yet
- Comments On KING 775 RIG 21 Apr 22Document3 pagesComments On KING 775 RIG 21 Apr 22Shahin ZamanNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: FVR-E11S-7EN FVR-E11S-4ENDocument116 pagesInstruction Manual: FVR-E11S-7EN FVR-E11S-4ENminh đạo nguyễnNo ratings yet
- De Cuong On Tap HK2 Anh 9 Nam 23 24Document6 pagesDe Cuong On Tap HK2 Anh 9 Nam 23 24UserNo ratings yet
- ISB - Mba Handbook 2020-2021 WebDocument27 pagesISB - Mba Handbook 2020-2021 WebTran Nguyet MinhNo ratings yet
- Mcgregor'S Theory X and Theory YDocument11 pagesMcgregor'S Theory X and Theory YMuhammad MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Forum Diskusi 7-1 (Alternating Current)Document5 pagesForum Diskusi 7-1 (Alternating Current)Reyhan Julianto PribadiNo ratings yet
- List of Instrument Available at Wagoora Sub-StationDocument2 pagesList of Instrument Available at Wagoora Sub-StationBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailureDocument27 pagesTheories of FailureBenedict ThomasNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Pts Publications and Standard SpecificationsDocument38 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Pts Publications and Standard SpecificationsadamNo ratings yet
- Clinical GoalsDocument13 pagesClinical GoalsHycient PaulNo ratings yet
- Lecture#8 - Hmis Data QualityDocument24 pagesLecture#8 - Hmis Data Qualitykingwinston ombionNo ratings yet
- Deloitte - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesDeloitte - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediakimmu5100% (1)
- LogDocument6 pagesLognadiafirdiana1973No ratings yet
- S006 - Suicide in An Airpla PDFDocument19 pagesS006 - Suicide in An Airpla PDFruso1900No ratings yet
- 910-911-914-915 Fanuc Ram Parity AlarmDocument2 pages910-911-914-915 Fanuc Ram Parity AlarmShumail JavedNo ratings yet
- E1 T1 TutorialDocument16 pagesE1 T1 Tutorialমোহাম্মাদ নাবিল নূর50% (2)
- MAN - CH - 2 - MCQsDocument6 pagesMAN - CH - 2 - MCQsSaquibh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Dip Lab ReportDocument23 pagesDip Lab Reportfawadnuml1No ratings yet
- AArado - Simplex Method QuizDocument3 pagesAArado - Simplex Method QuizAdelson AradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide: Grade: SubjectDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Guide: Grade: Subjectapi-557528365No ratings yet
- Biblical Narrative and Palestine HistoryDocument25 pagesBiblical Narrative and Palestine HistorydjsNo ratings yet