Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pain Management Algorithm
Pain Management Algorithm
Uploaded by
api-662596662Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Arthritis NCPDocument2 pagesArthritis NCPTri Sha100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- NCP Post Op PainDocument2 pagesNCP Post Op PainLiz Liwag0% (1)
- Assessment and Management of Chronic Pain Guideline SummaryDocument8 pagesAssessment and Management of Chronic Pain Guideline SummaryBiby AnneNo ratings yet
- Pain and Fever in The PharmacyDocument11 pagesPain and Fever in The PharmacyP D SpencerNo ratings yet
- Pain Algorithim 2Document1 pagePain Algorithim 2api-662601291No ratings yet
- Dr. Erwin A.D. Nanulaitta, SPKFR - Physical Rehabilitation in Pain ManagementDocument29 pagesDr. Erwin A.D. Nanulaitta, SPKFR - Physical Rehabilitation in Pain ManagementFreade AkbarNo ratings yet
- Pain Dr. HenryDocument36 pagesPain Dr. Henryreagan setiawanNo ratings yet
- Advance Pain ManagementDocument50 pagesAdvance Pain ManagementAkmal ZaibNo ratings yet
- Manajemen NyeriDocument27 pagesManajemen Nyerivera100% (1)
- Reumatology DR Mai KadryDocument19 pagesReumatology DR Mai KadryIbrahim SabraNo ratings yet
- Mixed Pain Jainuri Erik Pratama-1Document37 pagesMixed Pain Jainuri Erik Pratama-1Trie WulandariNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument11 pagesAnalgesicsNafisa TasnimNo ratings yet
- Bahan SharingDocument40 pagesBahan SharingkfcrajanyaayamNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing:: (BTP) - or Endure Acute Pain FromDocument6 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing:: (BTP) - or Endure Acute Pain FromELAGNE MEDINANo ratings yet
- Manajemen Nyeri Motik RS BhinaDocument36 pagesManajemen Nyeri Motik RS Bhinayn_faisalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pain Pathways and Its Modulation: DR HassanDocument79 pagesPhysiology of Pain Pathways and Its Modulation: DR HassanvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- PAIN IN ORTHOPAEDIC DR - ASP EditDocument50 pagesPAIN IN ORTHOPAEDIC DR - ASP EditElisabeth Permatasari SidabutarNo ratings yet
- Anes 8 Introduction To Pain ManagementDocument4 pagesAnes 8 Introduction To Pain ManagementJanica Marie RagsacNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJoselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Electrotherapy 28822Document8 pagesElectrotherapy 28822Cornel BazeliucNo ratings yet
- Pad Bundle Ce Final - Presentation ViewDocument60 pagesPad Bundle Ce Final - Presentation ViewJeremy WalleyNo ratings yet
- 3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018Document58 pages3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018Ika IrawatiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Pain: Pathophysiology and ManagementDocument43 pagesMixed Pain: Pathophysiology and ManagementAndreas AdiwinataNo ratings yet
- Mixed Pain DR Novi Irawan SPSDocument25 pagesMixed Pain DR Novi Irawan SPSnovi irawanNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi NyeriDocument99 pagesPatofisiologi NyeriWandi WDNo ratings yet
- Pain AssessmentDocument5 pagesPain AssessmentLyssa KateNo ratings yet
- K3. Penatalaksanaan Kasus Neurologi Di FKTP - Dr. Achmad Faqih, SP.SDocument30 pagesK3. Penatalaksanaan Kasus Neurologi Di FKTP - Dr. Achmad Faqih, SP.SLia pramitaNo ratings yet
- Gastrits PDFDocument47 pagesGastrits PDFAnas kareemNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- PAINDocument16 pagesPAINBlueyNo ratings yet
- 3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018Document58 pages3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018SATIYO SATIYONo ratings yet
- Slide PGB - Management of Neuropathic Pain 22022020ADocument36 pagesSlide PGB - Management of Neuropathic Pain 22022020AMohamad NasrullohNo ratings yet
- Nyeri Pada Pasien KritisDocument35 pagesNyeri Pada Pasien KritisICU DewasaNo ratings yet
- M2 PPT Treating PainDocument44 pagesM2 PPT Treating PainMeena CtNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument29 pagesPain ManagementCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- TVP-2020 Pain-Management EbookDocument44 pagesTVP-2020 Pain-Management Ebookizabelle.pereiraNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument7 pagesPain ManagementHazel ZullaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Dr. Darwin Amir Sp. S (K) - Neurogenic Inflammation in Chronic Pain SyndromesDocument16 pagesProf. Dr. Dr. Darwin Amir Sp. S (K) - Neurogenic Inflammation in Chronic Pain SyndromesRizki Muhammad RanandaNo ratings yet
- Scanned With CamscannerDocument18 pagesScanned With CamscannerMiliza MayangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisGaming BoyNo ratings yet
- The Brain On Opioids.5Document7 pagesThe Brain On Opioids.5Jonathan ZapataNo ratings yet
- 2021 Update Management Pain (Dokter & Medical)Document30 pages2021 Update Management Pain (Dokter & Medical)Andri MuliaNo ratings yet
- Trans-Viva-Anes-Lec 11-Pain ManagementDocument4 pagesTrans-Viva-Anes-Lec 11-Pain ManagementJeno Luis J. ACUBNo ratings yet
- Pain Assessment and O2 SaturationDocument62 pagesPain Assessment and O2 SaturationVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- Ncm116 Lesson2 Rle Pain ManagementDocument4 pagesNcm116 Lesson2 Rle Pain ManagementMilcah NuylesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For InfluenzaDocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For InfluenzaJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- E PaediatricsfordoctorsDocument53 pagesE PaediatricsfordoctorsJimmy RahuNo ratings yet
- AAHAAAFP Pain Management GuidelinesDocument15 pagesAAHAAAFP Pain Management GuidelinesMr. questionNo ratings yet
- Management NyeriDocument49 pagesManagement NyeriYuke ArmikaNo ratings yet
- Management Acute PainDocument110 pagesManagement Acute PainjohannesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions For Acute PainDocument5 pagesNursing Interventions For Acute Painrosita d. ramosNo ratings yet
- Marquina Chronic Neuro PainDocument63 pagesMarquina Chronic Neuro PainLukasNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain Post Op CSDocument3 pagesNCP Pain Post Op CSKersey Adricula Ricalde100% (1)
- MOD014 Nyeri KankerDocument23 pagesMOD014 Nyeri KankerMien Dwi CahyaniNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of MeditationDocument3 pagesThe Benefits of Meditationسيتي اميرةNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For PharyngitisDocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For PharyngitisJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Agung HidayatullahDocument58 pagesAgung HidayatullahIta Aprilia SaktiNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainMimi Nacor100% (3)
- Soap NoteDocument7 pagesSoap Noteapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Controlled Substances RequirementsDocument5 pagesControlled Substances Requirementsapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Cover Letter For PortfolioDocument1 pageCover Letter For Portfolioapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Green Modern Minimal This or That Instagram PostDocument1 pageGreen Modern Minimal This or That Instagram Postapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Emily Seelys Testimony ld1151 - SignedDocument1 pageEmily Seelys Testimony ld1151 - Signedapi-662596662No ratings yet
- CV Feb 2023Document3 pagesCV Feb 2023api-662596662No ratings yet
- Soap NoteDocument6 pagesSoap Noteapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Medical Fitness FormDocument1 pageMedical Fitness FormvickyreddyNo ratings yet
- Keto Diet Benefits 0 DrawbacksDocument3 pagesKeto Diet Benefits 0 DrawbacksAysha AnamNo ratings yet
- Primary Empty Sella 2005Document7 pagesPrimary Empty Sella 2005Paúl Otañez MolinaNo ratings yet
- VVIR Vs DDDRDocument2 pagesVVIR Vs DDDRNITACORDEIRONo ratings yet
- Honey Bees and Also Untamed Pollinators Vary Within Their Desire Regarding and Employ of Presented Flower Sourceshlwhg PDFDocument1 pageHoney Bees and Also Untamed Pollinators Vary Within Their Desire Regarding and Employ of Presented Flower Sourceshlwhg PDFlowtimer98No ratings yet
- Yashwanth - IHD HFrEfDocument16 pagesYashwanth - IHD HFrEfYashwanth N BNo ratings yet
- Linagliptin - DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageLinagliptin - DRUG STUDYAcads useNo ratings yet
- Tissue NematodesDocument60 pagesTissue NematodesAmanuel Eshetu Amanuel EshetuNo ratings yet
- OET Case Notes 2.0 Downloadable v2Document6 pagesOET Case Notes 2.0 Downloadable v2Оля ЧуднаяNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument2 pagesVaginitisFilip JovanovskiNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Observational Multi Centre Study On The Use of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument7 pagesA Prospective Observational Multi Centre Study On The Use of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Diabetic Foot UlcerHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Somatoform DisorderDocument30 pagesSomatoform DisorderRujuta BaramateNo ratings yet
- 20-Year History of Diarrhea With Intermittent ConstipationDocument2 pages20-Year History of Diarrhea With Intermittent Constipationhossein kasiriNo ratings yet
- Photovoice Paper HLTH 102Document7 pagesPhotovoice Paper HLTH 102api-625678417No ratings yet
- uk-pl-casodex-excipients-guideline-ONC 20 0015Document5 pagesuk-pl-casodex-excipients-guideline-ONC 20 0015Deisy ClerkeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Dimension of Development Health AwarenessDocument43 pagesChapter 6 Dimension of Development Health AwarenessRechienvhel OccianoNo ratings yet
- Maam Jean OR SCHED 10112022Document2 pagesMaam Jean OR SCHED 10112022Jean Camille Lazo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer DissertationDocument6 pagesDiabetic Foot Ulcer DissertationPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperForMeSingapore100% (1)
- DNB Questions Year WiseDocument120 pagesDNB Questions Year WisesalyouhaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Kel 6Document7 pagesBahasa Inggris Kel 6Akun NyampahNo ratings yet
- Taylor Medication EffectivenessDocument3 pagesTaylor Medication EffectivenessJudy SissonsNo ratings yet
- Qafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalDocument11 pagesQafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalPrem MathewNo ratings yet
- Edited Essay On MalariaDocument2 pagesEdited Essay On MalariaVincentius KrigeNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder and Difference Between Genders: Dzevad Sabic, Adela Sabic, Amila Bacic-BecirovicDocument4 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder and Difference Between Genders: Dzevad Sabic, Adela Sabic, Amila Bacic-BecirovicDzevad SabicNo ratings yet
- 为什么你总在吃,还一直饿?Document5 pages为什么你总在吃,还一直饿?Victoria TangNo ratings yet
- SHN Form 5-BlankDocument5 pagesSHN Form 5-BlankLiza BacudoNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Disorder: Schizophrenia & It's Case StudyDocument26 pagesBehavioral Disorder: Schizophrenia & It's Case StudySaba Parvin Haque100% (1)
- RN Targeted Medical Surgical Immune Online Practice 2019Document6 pagesRN Targeted Medical Surgical Immune Online Practice 2019Adriana RemedioNo ratings yet
- Building Your Peripheral Artery Disease Toolkit MDocument11 pagesBuilding Your Peripheral Artery Disease Toolkit MehaffejeeNo ratings yet
- Post Liver Transplant Patient CareDocument15 pagesPost Liver Transplant Patient Carechan kimNo ratings yet
Pain Management Algorithm
Pain Management Algorithm
Uploaded by
api-662596662Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pain Management Algorithm
Pain Management Algorithm
Uploaded by
api-662596662Copyright:
Available Formats
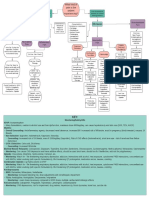
Pain Management
Peripheral
sensitization: proinflammatory and
1 st line treatment for pain:
immune mediators sensitize the
Always non-pharmacologic
nociceptors
Is the pain self limiting (Diet, Behavioural therapy,
Central sensitization: prolonged
and the result of a recent Integrative therapy,
activation causes a change in the
injury? Electroanalgesia, Physical
CNS pain pathways that allows
[e.g. exercise, physical
pain to occur with no presence of a Yes No therapy])
peripheral processes
Acute pain
Acute Pain/ protects from Chronic Pain/
Adaptive further injury Maladaptive
and encourages
healing
Tissue damage Stimuli causing a Chronic pain Pain in the bones,
Nerve
leading to sharp, shock-like, Perioperative Pain often persists
damage/injury? joints, tendons,
inflammation? tingling pain? past the normal ligaments and muscle?
healing process
Pre-op: 1 – 2 hours Neuropathic
Inflammatory Musculoskeletal
Nociceptive Pain before surgery, Prevent
Pain Pain
peripheral sensitization Pain
Intra-op: During 1 st line - Non-
operation, Prevent Trigeminal Postherpetic Diabetic pharm treatment:
1 st line - Pharm
Fibromyalgia Exercise and
treatment: central sensitization due Neuralgia Neuralgia peripheral
to incisional injury neuropathy Multidisciplinary
Acetaminophen and
management
NSAIDS
1 st line - Pharm 1 st line – Non-
Post-op: Reduce acute Prevention: 1 st line - Pharm
treatment: pharm treatment:
pain and prevent Shingles vaccine 2 nd line - Pharm
2 nd
line - Pharm Carbamazepine treatment:
chronic pain, ~1 week Physical activity, treatment:
treatment: Opioids and Pregabalin,
post-op, Oral preferred Education, and Acetaminophen
Combination opioids Duloxetine
2 nd line - Pharm 1 st line - Pharm Psychological and NSAIDS
treatment: treatment: support
rd Acetaminophen,
3 line - Pharm Oxcarbazepine Lidocaine patch 2 nd line - Pharm
treatment: Full opioid NSAIDs, Gabapentin, treatment: 3 rd line - Pharm
agonists Pregabalin, Local 2 nd
line - Pharm Gabapentin, treatment: Muscle
anesthetics, and 3 rd line - Pharm 2 ndline - Pharm relaxants, Weak
treatment: TCAs,
Opioids are preferred treatment: Combo treatment: opioids,
Amitriptyline, Venlafaxine
for perioperative pain therapy Gabapentin, Antidepressants
Duloxetine,
Pregabalin, Milnacipran,
Key: TCAs, Topical 3 rd line - Pharm
NSAIDS = Selective: Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Indomethacin; Non-selective: Celecoxib, Diclofenac Pregabalin, treatment: Combo
capsaicin Last line - Pharm
• Monitoring: Decreased renal clearance, increased blood pressure, increased risk of MI/stroke, avoid in pregnancy third trimester, Cyclobenzaprine, therapy
Tramadol treatment: Strong
nausea, GI bleed
• Non-selective: Antiplatelet activity, increased risk of GI bleed, risk of CNS effects, short term use only due to risk of renal and liver 3 rd line - Pharm opioids,
treatment: Last line - Pharm Anticonvulsants
failure
Tramadol 3 rd line - Pharm treatment:
• Selective: Increased risk of MI/stroke
treatment: Opioids
Acetaminophen
Gabapentin,
• Monitoring: Caution in alcohol use and liver dysfunction; Can cause hepatotoxicity and rarely severe skin reactions (SJS, TEN,
AGEP). Venlafaxine,
SSRIs,
Combination opioids = Hydrocodone & Acetaminophen
Cannabinoids
• Monitoring: Life-threatening respiratory depression, addiction, abuse, and misuse, life-threatening QT prolongation, and neonatal
opioid withdrawal syndrome
Opioids (Full opioid agonists) = Morphine, Hydromorphone, Codeine, Oxycodone, etc.
• Monitoring: Life-threatening respiratory depression, addiction, abuse, and misuse, life-threatening QT prolongation, and neonatal
opioid withdrawal syndrome
Muscle relaxants = Baclofen, Cyclobenzaprine, Methocarbamol, Carisoprodol
• Monitoring: Cause CNS depression and can have additive effects, should be used short term, should be discontinued if ineffective, add
risk for polypharmacy
Antidepressants = Duloxetine, Venlafaxine (TCA), Amitriptyline
• Monitoring: SSRIs - Increased risk for bleeding, avoid CrCl<30mL/min, avoid/caution in liver disease, dose adjustments with
renal/hepatic impairment. TCAs - Lower doses necessary for analgesia compared to MDD doses, multiple cardiac and anticholinergic
adverse effects
Anticonvulsants = Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Topiramate, Lamotrigine, Carbamazepine
• Monitoring: CNS depression, increased risk for impairment, drug rashes and hepatotoxicity, blood dyscrasias, bone loss, suicide risk
You might also like
- Arthritis NCPDocument2 pagesArthritis NCPTri Sha100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- NCP Post Op PainDocument2 pagesNCP Post Op PainLiz Liwag0% (1)
- Assessment and Management of Chronic Pain Guideline SummaryDocument8 pagesAssessment and Management of Chronic Pain Guideline SummaryBiby AnneNo ratings yet
- Pain and Fever in The PharmacyDocument11 pagesPain and Fever in The PharmacyP D SpencerNo ratings yet
- Pain Algorithim 2Document1 pagePain Algorithim 2api-662601291No ratings yet
- Dr. Erwin A.D. Nanulaitta, SPKFR - Physical Rehabilitation in Pain ManagementDocument29 pagesDr. Erwin A.D. Nanulaitta, SPKFR - Physical Rehabilitation in Pain ManagementFreade AkbarNo ratings yet
- Pain Dr. HenryDocument36 pagesPain Dr. Henryreagan setiawanNo ratings yet
- Advance Pain ManagementDocument50 pagesAdvance Pain ManagementAkmal ZaibNo ratings yet
- Manajemen NyeriDocument27 pagesManajemen Nyerivera100% (1)
- Reumatology DR Mai KadryDocument19 pagesReumatology DR Mai KadryIbrahim SabraNo ratings yet
- Mixed Pain Jainuri Erik Pratama-1Document37 pagesMixed Pain Jainuri Erik Pratama-1Trie WulandariNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument11 pagesAnalgesicsNafisa TasnimNo ratings yet
- Bahan SharingDocument40 pagesBahan SharingkfcrajanyaayamNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing:: (BTP) - or Endure Acute Pain FromDocument6 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing:: (BTP) - or Endure Acute Pain FromELAGNE MEDINANo ratings yet
- Manajemen Nyeri Motik RS BhinaDocument36 pagesManajemen Nyeri Motik RS Bhinayn_faisalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pain Pathways and Its Modulation: DR HassanDocument79 pagesPhysiology of Pain Pathways and Its Modulation: DR HassanvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- PAIN IN ORTHOPAEDIC DR - ASP EditDocument50 pagesPAIN IN ORTHOPAEDIC DR - ASP EditElisabeth Permatasari SidabutarNo ratings yet
- Anes 8 Introduction To Pain ManagementDocument4 pagesAnes 8 Introduction To Pain ManagementJanica Marie RagsacNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJoselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Electrotherapy 28822Document8 pagesElectrotherapy 28822Cornel BazeliucNo ratings yet
- Pad Bundle Ce Final - Presentation ViewDocument60 pagesPad Bundle Ce Final - Presentation ViewJeremy WalleyNo ratings yet
- 3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018Document58 pages3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018Ika IrawatiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Pain: Pathophysiology and ManagementDocument43 pagesMixed Pain: Pathophysiology and ManagementAndreas AdiwinataNo ratings yet
- Mixed Pain DR Novi Irawan SPSDocument25 pagesMixed Pain DR Novi Irawan SPSnovi irawanNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi NyeriDocument99 pagesPatofisiologi NyeriWandi WDNo ratings yet
- Pain AssessmentDocument5 pagesPain AssessmentLyssa KateNo ratings yet
- K3. Penatalaksanaan Kasus Neurologi Di FKTP - Dr. Achmad Faqih, SP.SDocument30 pagesK3. Penatalaksanaan Kasus Neurologi Di FKTP - Dr. Achmad Faqih, SP.SLia pramitaNo ratings yet
- Gastrits PDFDocument47 pagesGastrits PDFAnas kareemNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- PAINDocument16 pagesPAINBlueyNo ratings yet
- 3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018Document58 pages3 DR Hery - Pain Management 2018SATIYO SATIYONo ratings yet
- Slide PGB - Management of Neuropathic Pain 22022020ADocument36 pagesSlide PGB - Management of Neuropathic Pain 22022020AMohamad NasrullohNo ratings yet
- Nyeri Pada Pasien KritisDocument35 pagesNyeri Pada Pasien KritisICU DewasaNo ratings yet
- M2 PPT Treating PainDocument44 pagesM2 PPT Treating PainMeena CtNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument29 pagesPain ManagementCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- TVP-2020 Pain-Management EbookDocument44 pagesTVP-2020 Pain-Management Ebookizabelle.pereiraNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument7 pagesPain ManagementHazel ZullaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Dr. Darwin Amir Sp. S (K) - Neurogenic Inflammation in Chronic Pain SyndromesDocument16 pagesProf. Dr. Dr. Darwin Amir Sp. S (K) - Neurogenic Inflammation in Chronic Pain SyndromesRizki Muhammad RanandaNo ratings yet
- Scanned With CamscannerDocument18 pagesScanned With CamscannerMiliza MayangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Patient Name: James Japitana AGE:28 Sex:Male DiagnosisGaming BoyNo ratings yet
- The Brain On Opioids.5Document7 pagesThe Brain On Opioids.5Jonathan ZapataNo ratings yet
- 2021 Update Management Pain (Dokter & Medical)Document30 pages2021 Update Management Pain (Dokter & Medical)Andri MuliaNo ratings yet
- Trans-Viva-Anes-Lec 11-Pain ManagementDocument4 pagesTrans-Viva-Anes-Lec 11-Pain ManagementJeno Luis J. ACUBNo ratings yet
- Pain Assessment and O2 SaturationDocument62 pagesPain Assessment and O2 SaturationVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- Ncm116 Lesson2 Rle Pain ManagementDocument4 pagesNcm116 Lesson2 Rle Pain ManagementMilcah NuylesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For InfluenzaDocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For InfluenzaJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- E PaediatricsfordoctorsDocument53 pagesE PaediatricsfordoctorsJimmy RahuNo ratings yet
- AAHAAAFP Pain Management GuidelinesDocument15 pagesAAHAAAFP Pain Management GuidelinesMr. questionNo ratings yet
- Management NyeriDocument49 pagesManagement NyeriYuke ArmikaNo ratings yet
- Management Acute PainDocument110 pagesManagement Acute PainjohannesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions For Acute PainDocument5 pagesNursing Interventions For Acute Painrosita d. ramosNo ratings yet
- Marquina Chronic Neuro PainDocument63 pagesMarquina Chronic Neuro PainLukasNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain Post Op CSDocument3 pagesNCP Pain Post Op CSKersey Adricula Ricalde100% (1)
- MOD014 Nyeri KankerDocument23 pagesMOD014 Nyeri KankerMien Dwi CahyaniNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of MeditationDocument3 pagesThe Benefits of Meditationسيتي اميرةNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For PharyngitisDocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For PharyngitisJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Agung HidayatullahDocument58 pagesAgung HidayatullahIta Aprilia SaktiNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainMimi Nacor100% (3)
- Soap NoteDocument7 pagesSoap Noteapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Controlled Substances RequirementsDocument5 pagesControlled Substances Requirementsapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Cover Letter For PortfolioDocument1 pageCover Letter For Portfolioapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Green Modern Minimal This or That Instagram PostDocument1 pageGreen Modern Minimal This or That Instagram Postapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Emily Seelys Testimony ld1151 - SignedDocument1 pageEmily Seelys Testimony ld1151 - Signedapi-662596662No ratings yet
- CV Feb 2023Document3 pagesCV Feb 2023api-662596662No ratings yet
- Soap NoteDocument6 pagesSoap Noteapi-662596662No ratings yet
- Medical Fitness FormDocument1 pageMedical Fitness FormvickyreddyNo ratings yet
- Keto Diet Benefits 0 DrawbacksDocument3 pagesKeto Diet Benefits 0 DrawbacksAysha AnamNo ratings yet
- Primary Empty Sella 2005Document7 pagesPrimary Empty Sella 2005Paúl Otañez MolinaNo ratings yet
- VVIR Vs DDDRDocument2 pagesVVIR Vs DDDRNITACORDEIRONo ratings yet
- Honey Bees and Also Untamed Pollinators Vary Within Their Desire Regarding and Employ of Presented Flower Sourceshlwhg PDFDocument1 pageHoney Bees and Also Untamed Pollinators Vary Within Their Desire Regarding and Employ of Presented Flower Sourceshlwhg PDFlowtimer98No ratings yet
- Yashwanth - IHD HFrEfDocument16 pagesYashwanth - IHD HFrEfYashwanth N BNo ratings yet
- Linagliptin - DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageLinagliptin - DRUG STUDYAcads useNo ratings yet
- Tissue NematodesDocument60 pagesTissue NematodesAmanuel Eshetu Amanuel EshetuNo ratings yet
- OET Case Notes 2.0 Downloadable v2Document6 pagesOET Case Notes 2.0 Downloadable v2Оля ЧуднаяNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument2 pagesVaginitisFilip JovanovskiNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Observational Multi Centre Study On The Use of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument7 pagesA Prospective Observational Multi Centre Study On The Use of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Diabetic Foot UlcerHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Somatoform DisorderDocument30 pagesSomatoform DisorderRujuta BaramateNo ratings yet
- 20-Year History of Diarrhea With Intermittent ConstipationDocument2 pages20-Year History of Diarrhea With Intermittent Constipationhossein kasiriNo ratings yet
- Photovoice Paper HLTH 102Document7 pagesPhotovoice Paper HLTH 102api-625678417No ratings yet
- uk-pl-casodex-excipients-guideline-ONC 20 0015Document5 pagesuk-pl-casodex-excipients-guideline-ONC 20 0015Deisy ClerkeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Dimension of Development Health AwarenessDocument43 pagesChapter 6 Dimension of Development Health AwarenessRechienvhel OccianoNo ratings yet
- Maam Jean OR SCHED 10112022Document2 pagesMaam Jean OR SCHED 10112022Jean Camille Lazo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer DissertationDocument6 pagesDiabetic Foot Ulcer DissertationPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperForMeSingapore100% (1)
- DNB Questions Year WiseDocument120 pagesDNB Questions Year WisesalyouhaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Kel 6Document7 pagesBahasa Inggris Kel 6Akun NyampahNo ratings yet
- Taylor Medication EffectivenessDocument3 pagesTaylor Medication EffectivenessJudy SissonsNo ratings yet
- Qafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalDocument11 pagesQafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalPrem MathewNo ratings yet
- Edited Essay On MalariaDocument2 pagesEdited Essay On MalariaVincentius KrigeNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder and Difference Between Genders: Dzevad Sabic, Adela Sabic, Amila Bacic-BecirovicDocument4 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder and Difference Between Genders: Dzevad Sabic, Adela Sabic, Amila Bacic-BecirovicDzevad SabicNo ratings yet
- 为什么你总在吃,还一直饿?Document5 pages为什么你总在吃,还一直饿?Victoria TangNo ratings yet
- SHN Form 5-BlankDocument5 pagesSHN Form 5-BlankLiza BacudoNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Disorder: Schizophrenia & It's Case StudyDocument26 pagesBehavioral Disorder: Schizophrenia & It's Case StudySaba Parvin Haque100% (1)
- RN Targeted Medical Surgical Immune Online Practice 2019Document6 pagesRN Targeted Medical Surgical Immune Online Practice 2019Adriana RemedioNo ratings yet
- Building Your Peripheral Artery Disease Toolkit MDocument11 pagesBuilding Your Peripheral Artery Disease Toolkit MehaffejeeNo ratings yet
- Post Liver Transplant Patient CareDocument15 pagesPost Liver Transplant Patient Carechan kimNo ratings yet